Abstract
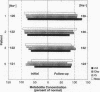
The pathogenesis of morbidity associated with hyponatremia is postulated to be determined by the state of intracellular cerebral osmolytes. Previously inaccessible, these metabolites can now be quantitated by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. An in vivo quantitative assay of osmolytes was performed in 12 chronic hyponatremic patients (mean serum sodium 120 meq/liter) and 10 normal controls. Short echo time proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of occipital gray and parietal white matter locations revealed dramatic reduction in the concentrations of several metabolites. In gray matter, myo-inositol was most profoundly reduced at 49% of control value. Choline containing compounds were reduced 36%, creatine/phosphocreatine 19%, and N-acetylaspartate 11% from controls. Similar changes were found in white matter. Recovery of osmolyte concentrations was demonstrated in four patients studied 8-14 wk later. These results are consistent with a reversible osmolyte reduction under hypoosmolar stress in the intact human brain and offer novel suggestions for treatment and monitoring of this common clinical event.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson D. J., Laing R. B., Nathwani D. Alcoholism, hyponatraemia and central neurological damage: more than pontine myelinolysis? Scott Med J. 1992 Jun;37(3):83–84. doi: 10.1177/003693309203700307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arieff A. I. Hyponatremia, convulsions, respiratory arrest, and permanent brain damage after elective surgery in healthy women. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jun 12;314(24):1529–1535. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198606123142401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayus J. C., Krothapalli R. K., Arieff A. I. Treatment of symptomatic hyponatremia and its relation to brain damage. A prospective study. N Engl J Med. 1987 Nov 5;317(19):1190–1195. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198711053171905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berl T. Treating hyponatremia: what is all the controversy about? Ann Intern Med. 1990 Sep 15;113(6):417–419. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-113-6-417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burcar P. J., Norenberg M. D., Yarnell P. R. Hyponatremia and central pontine myelinolysis. Neurology. 1977 Mar;27(3):223–226. doi: 10.1212/wnl.27.3.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dila C. J., Pappius H. M. Cerebral water and electrolytes. An experimental model of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone. Arch Neurol. 1972 Jan;26(1):85–90. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1972.00490070103013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreis R., Farrow N., Ross B. D. Diagnosis of hepatic encephalopathy by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Lancet. 1990 Sep 8;336(8715):635–636. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)93439-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreis R., Farrow N., Ross B. D. Diagnosis of hepatic encephalopathy by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Lancet. 1990 Sep 8;336(8715):635–636. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)93439-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreis R., Farrow N., Ross B. D. Localized 1H NMR spectroscopy in patients with chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Analysis of changes in cerebral glutamine, choline and inositols. NMR Biomed. 1991 Apr;4(2):109–116. doi: 10.1002/nbm.1940040214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreis R., Ross B. D. Cerebral metabolic disturbances in patients with subacute and chronic diabetes mellitus: detection with proton MR spectroscopy. Radiology. 1992 Jul;184(1):123–130. doi: 10.1148/radiology.184.1.1319074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. H., Arcinue E., Ross B. D. Brief report: organic osmolytes in the brain of an infant with hypernatremia. N Engl J Med. 1994 Aug 18;331(7):439–442. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199408183310704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lien Y. H., Shapiro J. I., Chan L. Effects of hypernatremia on organic brain osmoles. J Clin Invest. 1990 May;85(5):1427–1435. doi: 10.1172/JCI114587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lien Y. H., Shapiro J. I., Chan L. Study of brain electrolytes and organic osmolytes during correction of chronic hyponatremia. Implications for the pathogenesis of central pontine myelinolysis. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jul;88(1):303–309. doi: 10.1172/JCI115292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton J. E., Nattie E. E. Brain and CSF water and ions during dilutional and isosmotic hyponatremia in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1983 May;244(5):R724–R732. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1983.244.5.R724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messert B., Orrison W. W., Hawkins M. J., Quaglieri C. E. Central pontine myelinolysis. Considerations on etiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Neurology. 1979 Feb;29(2):147–160. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.2.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis T., Merboldt K. D., Hänicke W., Gyngell M. L., Bruhn H., Frahm J. On the identification of cerebral metabolites in localized 1H NMR spectra of human brain in vivo. NMR Biomed. 1991 Apr;4(2):90–98. doi: 10.1002/nbm.1940040211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller B. L. A review of chemical issues in 1H NMR spectroscopy: N-acetyl-L-aspartate, creatine and choline. NMR Biomed. 1991 Apr;4(2):47–52. doi: 10.1002/nbm.1940040203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller B. L., Moats R. A., Shonk T., Ernst T., Woolley S., Ross B. D. Alzheimer disease: depiction of increased cerebral myo-inositol with proton MR spectroscopy. Radiology. 1993 May;187(2):433–437. doi: 10.1148/radiology.187.2.8475286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narins R. G. Therapy of hyponatremia: does haste make waste? N Engl J Med. 1986 Jun 12;314(24):1573–1575. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198606123142409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitsch R. M., Blusztajn J. K., Pittas A. G., Slack B. E., Growdon J. H., Wurtman R. J. Evidence for a membrane defect in Alzheimer disease brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1671–1675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norenberg M. D., Leslie K. O., Robertson A. S. Association between rise in serum sodium and central pontine myelinolysis. Ann Neurol. 1982 Feb;11(2):128–135. doi: 10.1002/ana.410110204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh M. S., Choi K. C., Uribarri J., Sher J., Rao C., Carroll H. J. Prevention of myelinolysis in rats by dexamethasone or colchicine. Am J Nephrol. 1990;10(2):158–161. doi: 10.1159/000168071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross B. D., Jacobson S., Villamil F., Korula J., Kreis R., Ernst T., Shonk T., Moats R. A. Subclinical hepatic encephalopathy: proton MR spectroscopic abnormalities. Radiology. 1994 Nov;193(2):457–463. doi: 10.1148/radiology.193.2.7972763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rymer M. M., Fishman R. A. Protective adaptation of brain to water intoxication. Arch Neurol. 1973 Jan;28(1):49–54. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490190067009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soupart A., Penninckx R., Stenuit A., Perier O., Decaux G. Treatment of chronic hyponatremia in rats by intravenous saline: comparison of rate versus magnitude of correction. Kidney Int. 1992 Jun;41(6):1662–1667. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soupart A., Stenuit A., Perier O., Decaux G. Limits of brain tolerance to daily increments in serum sodium in chronically hyponatraemic rats treated with hypertonic saline or urea: advantages of urea. Clin Sci (Lond) 1991 Jan;80(1):77–84. doi: 10.1042/cs0800077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterns R. H., Baer J., Ebersol S., Thomas D., Lohr J. W., Kamm D. E. Organic osmolytes in acute hyponatremia. Am J Physiol. 1993 May;264(5 Pt 2):F833–F836. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.264.5.F833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterns R. H., Riggs J. E., Schochet S. S., Jr Osmotic demyelination syndrome following correction of hyponatremia. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jun 12;314(24):1535–1542. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198606123142402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterns R. H. Severe symptomatic hyponatremia: treatment and outcome. A study of 64 cases. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Nov;107(5):656–664. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-5-656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterns R. H., Thomas D. J., Herndon R. M. Brain dehydration and neurologic deterioration after rapid correction of hyponatremia. Kidney Int. 1989 Jan;35(1):69–75. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurston J. H., Hauhart R. E. Brain amino acids decrease in chronic hyponatremia and rapid correction causes brain dehydration: possible clinical significance. Life Sci. 1987 Jun 29;40(26):2539–2542. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90076-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurston J. H., Hauhart R. E., Nelson J. S. Adaptive decreases in amino acids (taurine in particular), creatine, and electrolytes prevent cerebral edema in chronically hyponatremic mice: rapid correction (experimental model of central pontine myelinolysis) causes dehydration and shrinkage of brain. Metab Brain Dis. 1987 Dec;2(4):223–241. doi: 10.1007/BF00999694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tien R., Arieff A. I., Kucharczyk W., Wasik A., Kucharczyk J. Hyponatremic encephalopathy: is central pontine myelinolysis a component? Am J Med. 1992 May;92(5):513–522. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(92)90748-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Reeth O., Decaux G. Rapid correction of hyponatraemia with urea may protect against brain damage in rats. Clin Sci (Lond) 1989 Sep;77(3):351–355. doi: 10.1042/cs0770351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbalis J. G., Gullans S. R. Rapid correction of hyponatremia produces differential effects on brain osmolyte and electrolyte reaccumulation in rats. Brain Res. 1993 Mar 19;606(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91564-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancey P. H., Clark M. E., Hand S. C., Bowlus R. D., Somero G. N. Living with water stress: evolution of osmolyte systems. Science. 1982 Sep 24;217(4566):1214–1222. doi: 10.1126/science.7112124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]