Abstract
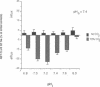
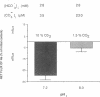
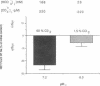
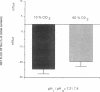
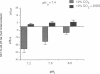
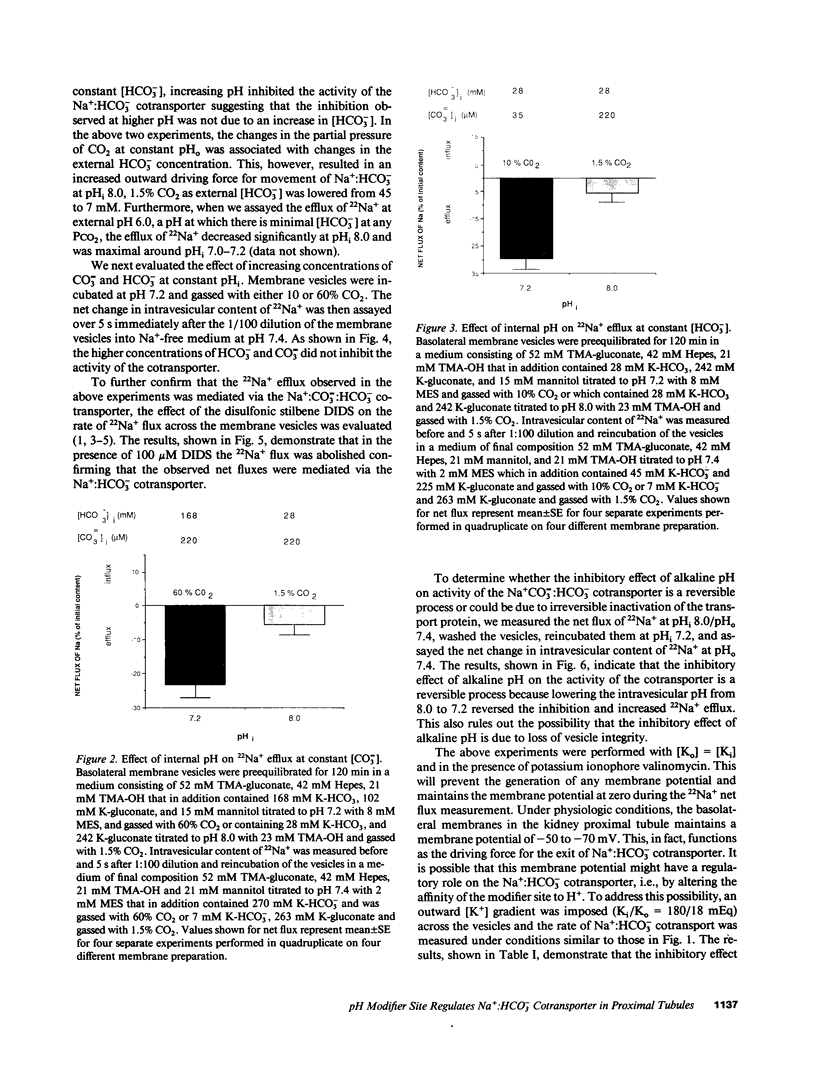
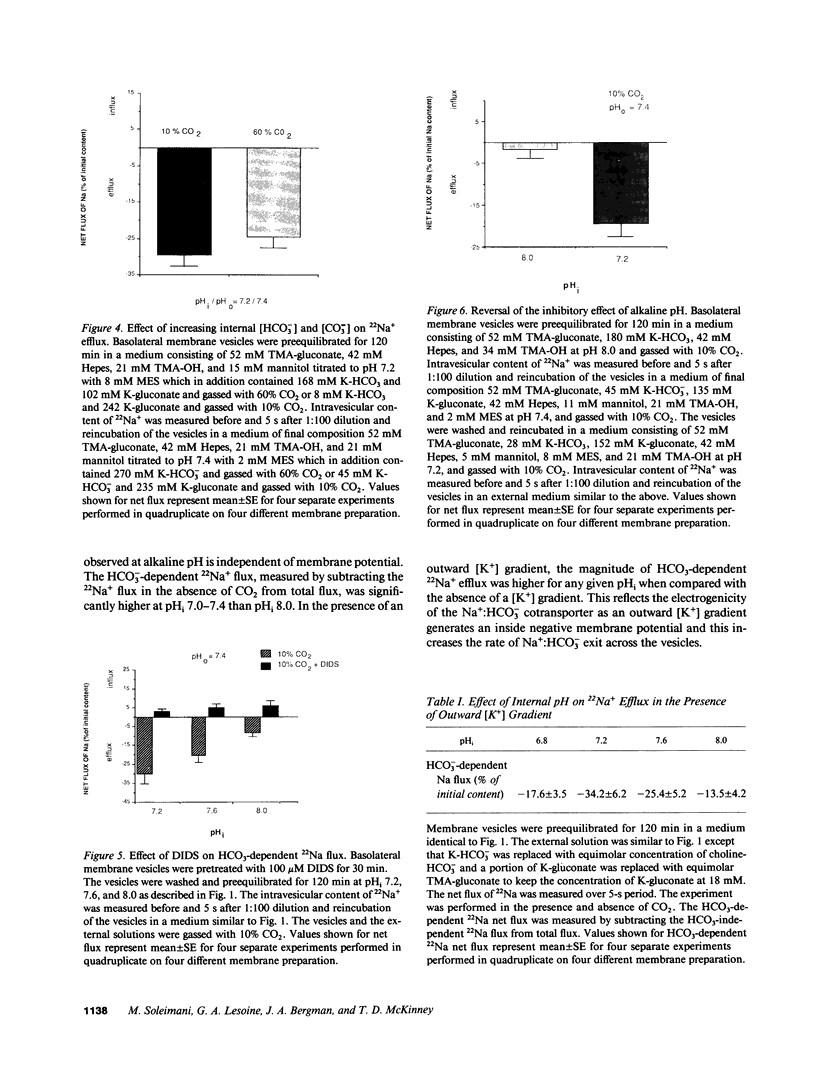
HCO3- exit across the basolateral membrane of the kidney proximal tubule cell is mediated via an electrogenic Na+:HCO3- cotransporter. In these experiments, we have studied the effect of internal pH on the activity of the Na+:HCO3- cotransport system in basolateral membrane vesicles isolated from rabbit renal cortex. Equilibrium thermodynamics predicts that in the presence of constant intravesicular concentration of Na+, an increasing concentration of HCO3- will be associated with an increasing driving force for Na+:HCO3- cotransport across the vesicles. Our experimental approach was to preequilibrate the membrane vesicles with 1 mM 22Na+ at pHi 6.8-8.0 and known concentrations of HCO3-. The vesicles were diluted 1:100 into Na(+)-free solution at pH 7.4 and the net flux of 22Na+ was assayed over 5 s. The results demonstrate that the net flux of Na+ was significantly higher at pHi 7.2 than pHi 8.0 despite much higher [HCO3-] at pHi 8.0. This suggests that an internal pH-sensitive site regulates the activity of the Na+:HCO3- cotransporter. This modifier site inhibits the cotransporter at alkaline pH despite significant base concentration and is maximally functional around physiologic pH. The combination of modifier sites on the luminal Na+/H+ exchanger and the basolateral Na+:HCO3- cotransporter should help maintain intracellular pH in a narrow range with changes in extracellular pH.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiba T., Alpern R. J., Eveloff J., Calamina J., Warnock D. G. Electrogenic sodium/bicarbonate cotransport in rabbit renal cortical basolateral membrane vesicles. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1472–1478. doi: 10.1172/JCI112738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpern R. J. Cell mechanisms of proximal tubule acidification. Physiol Rev. 1990 Jan;70(1):79–114. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson P. S. Mechanisms of active H+ secretion in the proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1983 Dec;245(6):F647–F659. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.245.6.F647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson P. S., Nee J., Suhm M. A. Modifier role of internal H+ in activating the Na+-H+ exchanger in renal microvillus membrane vesicles. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):161–163. doi: 10.1038/299161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson P. S., Soleimani M., Grassl S. M. Properties of the renal Na(+)-HCO3- cotransporter. Semin Nephrol. 1991 Jan;11(1):28–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astion M. L., Obaid A. L., Orkand R. K. Effects of barium and bicarbonate on glial cells of Necturus optic nerve. Studies with microelectrodes and voltage-sensitive dyes. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Apr;93(4):731–744. doi: 10.1085/jgp.93.4.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boron W. F., Boulpaep E. L. Intracellular pH regulation in the renal proximal tubule of the salamander. Basolateral HCO3- transport. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Jan;81(1):53–94. doi: 10.1085/jgp.81.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curci S., Debellis L., Frömter E. Evidence for rheogenic sodium bicarbonate cotransport in the basolateral membrane of oxyntic cells of frog gastric fundus. Pflugers Arch. 1987 May;408(5):497–504. doi: 10.1007/BF00585075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitz J. G., Persico M., Scharschmidt B. F. Electrophysiological evidence for Na+-coupled bicarbonate transport in cultured rat hepatocytes. Am J Physiol. 1989 Mar;256(3 Pt 1):G491–G500. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.256.3.G491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassl S. M., Aronson P. S. Na+/HCO3-co-transport in basolateral membrane vesicles isolated from rabbit renal cortex. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8778–8783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch T. J., Stahlknecht T. R., Hollwede H., Fischer D. G., Keller S. K., Wiederholt M. A bicarbonate-dependent process inhibitable by disulfonic stilbenes and a Na+/H+ exchange mediate 22Na+ uptake into cultured bovine corneal endothelium. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):795–801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krapf R. Basolateral membrane H/OH/HCO3 transport in the rat cortical thick ascending limb. Evidence for an electrogenic Na/HCO3 cotransporter in parallel with a Na/H antiporter. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jul;82(1):234–241. doi: 10.1172/JCI113576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krapf R., Berry C. A., Alpern R. J., Rector F. C., Jr Regulation of cell pH by ambient bicarbonate, carbon dioxide tension, and pH in the rabbit proximal convoluted tubule. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):381–389. doi: 10.1172/JCI113330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason M. J., Smith J. D., Garcia-Soto J. J., Grinstein S. Internal pH-sensitive site couples Cl-(-)HCO3- exchange to Na+-H+ antiport in lymphocytes. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 1):C428–C433. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.2.C428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mugharbil A., Knickelbein R. G., Aronson P. S., Dobbins J. W. Rabbit ileal brush-border membrane Cl-HCO3 exchanger is activated by an internal pH-sensitive modifier site. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 1):G666–G670. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.259.4.G666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preisig P. A., Alpern R. J. Basolateral membrane H-OH-HCO3 transport in the proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1989 May;256(5 Pt 2):F751–F765. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.5.F751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soleimani M., Aronson P. S. Effects of acetazolamide on Na+-HCO-3 cotransport in basolateral membrane vesicles isolated from rabbit renal cortex. J Clin Invest. 1989 Mar;83(3):945–951. doi: 10.1172/JCI113980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soleimani M., Aronson P. S. Ionic mechanism of Na+-HCO3- cotransport in rabbit renal basolateral membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18302–18308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soleimani M., Bergman J. A., Hosford M. A., McKinney T. D. Potassium depletion increases luminal Na+/H+ exchange and basolateral Na+:CO3=:HCO3- cotransport in rat renal cortex. J Clin Invest. 1990 Oct;86(4):1076–1083. doi: 10.1172/JCI114810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soleimani M., Grassi S. M., Aronson P. S. Stoichiometry of Na+-HCO-3 cotransport in basolateral membrane vesicles isolated from rabbit renal cortex. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1172/JCI112948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshitomi K., Burckhardt B. C., Frömter E. Rheogenic sodium-bicarbonate cotransport in the peritubular cell membrane of rat renal proximal tubule. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Dec;405(4):360–366. doi: 10.1007/BF00595689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]