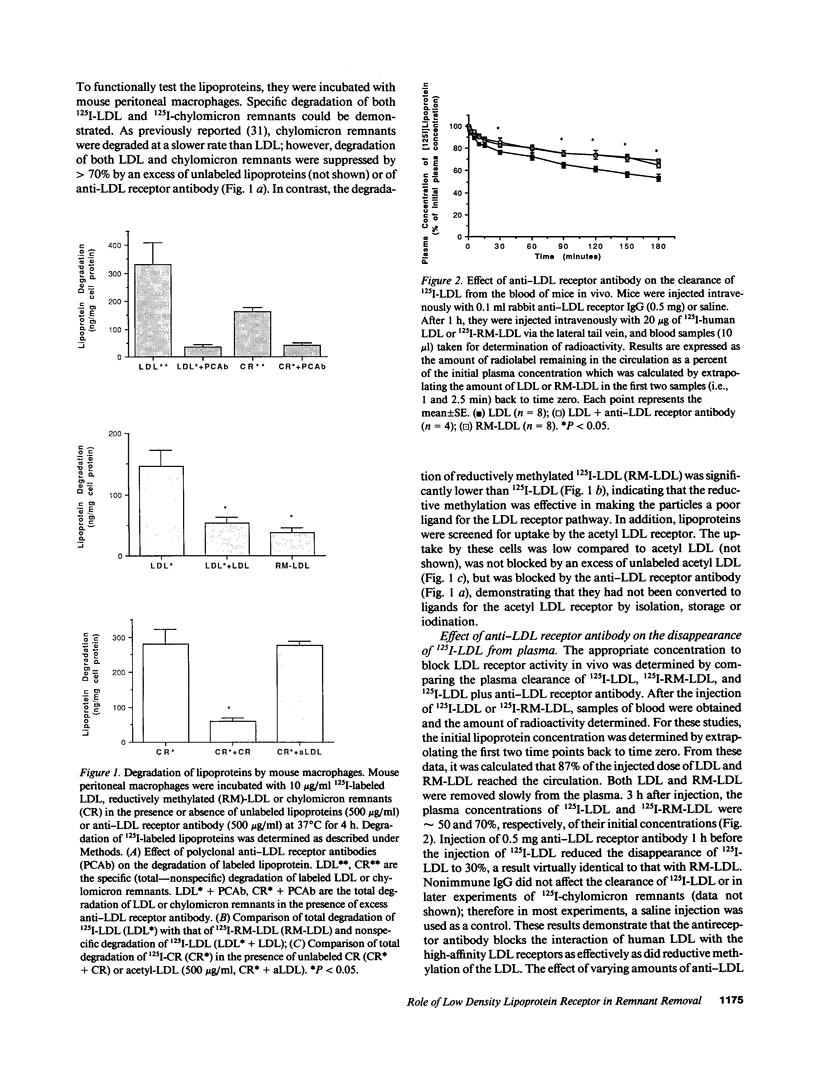
Abstract
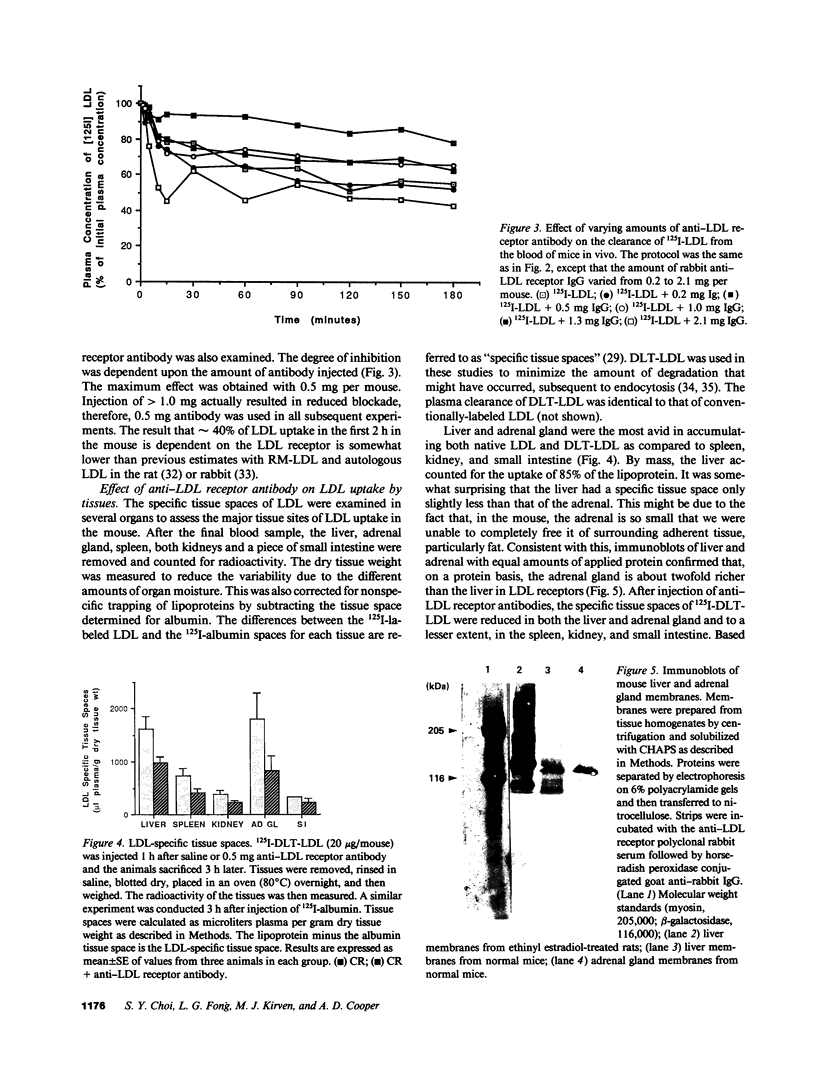
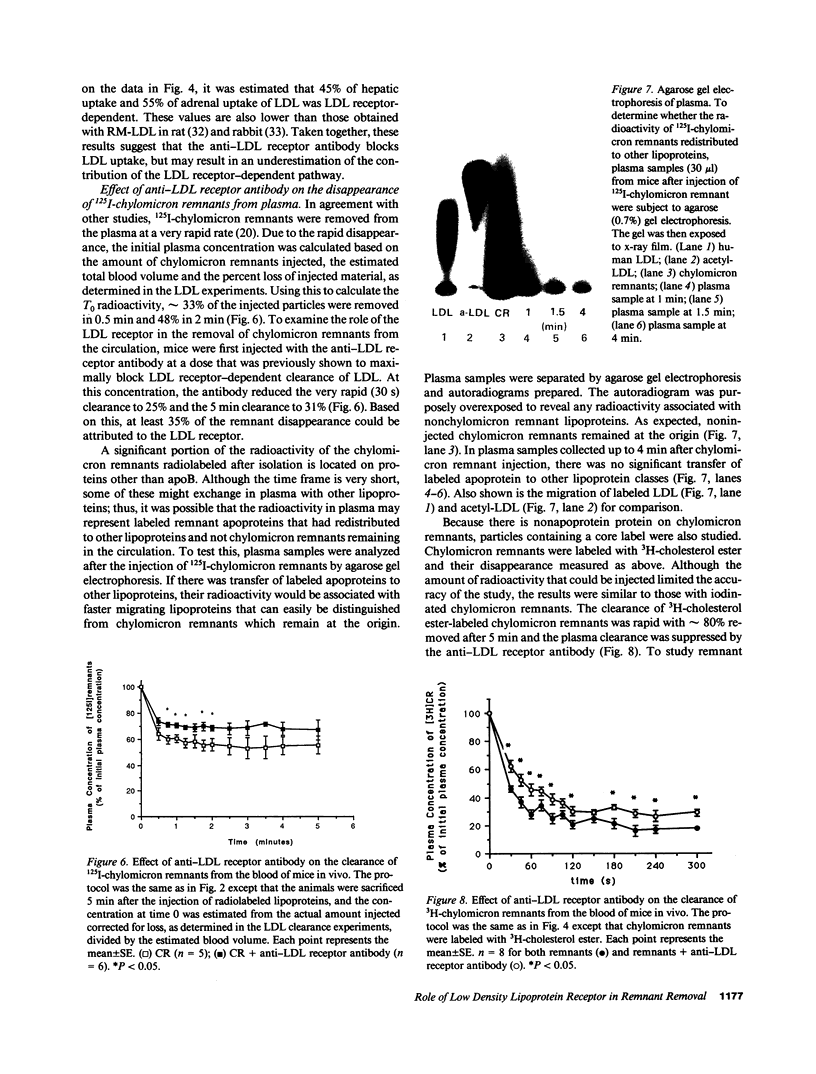
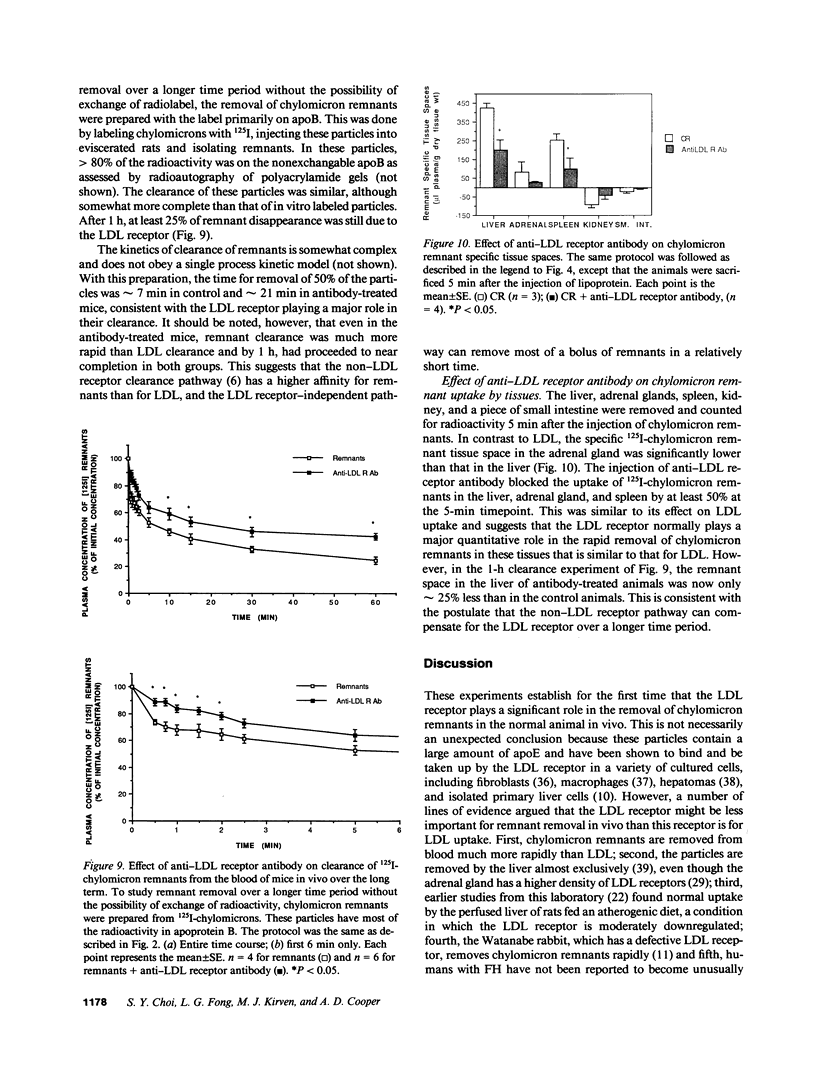
Lipoproteins are removed from the plasma by LDL receptor-dependent and -independent pathways. The relative contribution of these has been established for LDL by using modified lipoproteins, but this has not been possible for apoE-rich lipoproteins, such as chylomicron remnants. To do this, we used a monospecific antibody to the rat LDL receptor. The antibody was injected intravenously into mice followed by 125I-lipoproteins. Blood samples were obtained sequentially and radioactivity measured to determine the plasma clearance of the lipoproteins. The animals were then sacrificed and the tissues removed, dried, and the radioactivity measured to determine tissue uptake. An albumin space was also measured to correct for blood trapping. With 125I-human LDL, approximately 50% of the injected dose was cleared in 180 min. This was reduced to 30% by the antibody and this was identical to the disappearance of reductively methylated LDL. This is a lower estimate of LDL-mediated uptake (40%) than in other species. LDL uptake per gram tissue was similar for the liver and the adrenal gland and was approximately 50% LDL receptor-dependent in both tissues. With 125I-chylomicron remnants, clearance was much more rapid with approximately 50% cleared in 5 min. By agarose gel electrophoresis, radioactivity was not transferred from chylomicron remnants to other lipoprotein classes. Chylomicron remnants with label on only apoB or in 3H-cholesterol esters showed a similar pattern. Combining the estimates of the three labeling procedures, approximately 35% of the 30 s and 25% of the 5 min chylomicron remnant disappearance was LDL receptor dependent. The liver, per gram tissue, took up five times as much radioactivity as the adrenal gland. At 5 min, at least 50% of this was LDL receptor-dependent in liver and 65% in adrenal gland. We conclude that the LDL receptor plays a major, and somewhat similar quantitative role in the clearance of both LDL and chylomicron remnants in the mouse. However, at least in the mouse, non-LDL receptor-mediated lipoprotein clearance is quantitatively important and is also very rapid for chylomicron remnants. Thus, for chylomicron remnants, it can easily compensate for LDL receptors if they are blocked or absent. Further, the tissue distribution of lipoprotein uptake may be directed by factors other than LDL receptor density.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attie A. D., Pittman R. C., Watanabe Y., Steinberg D. Low density lipoprotein receptor deficiency in cultured hepatocytes of the WHHL rabbit. Further evidence of two pathways for catabolism of exogenous proteins. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):9789–9792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnard G. F., Erickson S. K., Cooper A. D. Lipoprotein metabolism by rat hepatomas. Studies on the etiology of defective dietary feedback inhibition of cholesterol synthesis. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jul;74(1):173–184. doi: 10.1172/JCI111399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu S. K., Goldstein J. L., Anderson G. W., Brown M. S. Degradation of cationized low density lipoprotein and regulation of cholesterol metabolism in homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3178–3182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Receptor-mediated endocytosis: insights from the lipoprotein receptor system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3330–3337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camus M. C., Chapman M. J., Forgez P., Laplaud P. M. Distribution and characterization of the serum lipoproteins and apoproteins in the mouse, Mus musculus. J Lipid Res. 1983 Sep;24(9):1210–1228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. D., Nutik R., Chen J. Characterization of the estrogen-induced lipoprotein receptor of rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1987 Jan;28(1):59–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. D. The metabolism of chylomicron remnants by isolated perfused rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 28;488(3):464–474. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90204-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellsworth J. L., Fong L. G., Kraemer F. B., Cooper A. D. Differences in the processing of chylomicron remnants and beta-VLDL by macrophages. J Lipid Res. 1990 Aug;31(8):1399–1411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellsworth J. L., Kraemer F. B., Cooper A. D. Transport of beta-very low density lipoproteins and chylomicron remnants by macrophages is mediated by the low density lipoprotein receptor pathway. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2316–2325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everson G. T., McKinley C., Kern F., Jr Mechanisms of gallstone formation in women. Effects of exogenous estrogen (Premarin) and dietary cholesterol on hepatic lipid metabolism. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jan;87(1):237–246. doi: 10.1172/JCI114977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florén C. H., Albers J. J., Kudchodkar B. J., Bierman E. L. Receptor-dependent uptake of human chylomicron remnants by cultured skin fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):425–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forgez P., Chapman M. J., Rall S. C., Jr, Camus M. C. The lipid transport system in the mouse, Mus musculus: isolation and characterization of apolipoproteins B, A-I, A-II, and C-III. J Lipid Res. 1984 Sep;25(9):954–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN D. S. The metabolism of chylomicron cholesterol ester in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1962 Oct;41:1886–1896. doi: 10.1172/JCI104645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. The low-density lipoprotein pathway and its relation to atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz J., Hamann U., Rogne S., Myklebost O., Gausepohl H., Stanley K. K. Surface location and high affinity for calcium of a 500-kd liver membrane protein closely related to the LDL-receptor suggest a physiological role as lipoprotein receptor. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4119–4127. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03306.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz J., Kowal R. C., Ho Y. K., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein mediates endocytosis of monoclonal antibodies in cultured cells and rabbit liver. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21355–21362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kesaniemi Y. A., Witztum J. L., Steinbrecher U. P. Receptor-mediated catabolism of low density lipoprotein in man. Quantitation using glucosylated low density lipoprotein. J Clin Invest. 1983 Apr;71(4):950–959. doi: 10.1172/JCI110849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita T., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Watanabe Y., Hornick C. A., Havel R. J. Hepatic uptake of chylomicron remnants in WHHL rabbits: a mechanism genetically distinct from the low density lipoprotein receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3623–3627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koelz H. R., Sherrill B. C., Turley S. D., Dietschy J. M. Correlation of low and high density lipoprotein binding in vivo with rates of lipoprotein degradation in the rat. A comparison of lipoproteins of rat and human origin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8061–8072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowal R. C., Herz J., Goldstein J. L., Esser V., Brown M. S. Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein mediates uptake of cholesteryl esters derived from apoprotein E-enriched lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5810–5814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowal R. C., Herz J., Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Opposing effects of apolipoproteins E and C on lipoprotein binding to low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10771–10779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kris-Etherton P. M., Cooper A. D. Studies on the etiology of the hyperlipemia in rats fed an atherogenic diet. J Lipid Res. 1980 May;21(4):435–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Innerarity T. L. Interaction of canine and swine lipoproteins with the low density lipoprotein receptor of fibroblasts as correlated with heparin/manganese precipitability. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3980–3986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May K., Kraemer F. B., Chen J., Cooper A. D. ELISA measurement of LDL receptors. J Lipid Res. 1990 Sep;31(9):1683–1691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata Y., Chen J., Cooper A. D. Role of low density lipoprotein receptor-dependent and -independent sites in binding and uptake of chylomicron remnants in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):15151–15158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman R. C., Attie A. D., Carew T. E., Steinberg D. Tissue sites of degradation of low density lipoprotein: application of a method for determining the fate of plasma proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5345–5349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman R. C., Carew T. E., Attie A. D., Witztum J. L., Watanabe Y., Steinberg D. Receptor-dependent and receptor-independent degradation of low density lipoprotein in normal rabbits and in receptor-deficient mutant rabbits. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):7994–8000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman R. C., Carew T. E., Glass C. K., Green S. R., Taylor C. A., Jr, Attie A. D. A radioiodinated, intracellularly trapped ligand for determining the sites of plasma protein degradation in vivo. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):791–800. doi: 10.1042/bj2120791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redgrave T. G., Martin G. Effects of chronic ethanol consumption on the catabolism of chylomicron triacylglycerol and cholesteryl ester in the rat. Atherosclerosis. 1977 Sep;28(1):69–80. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(77)90200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinsztein D. C., Cohen J. C., Berger G. M., van der Westhuyzen D. R., Coetzee G. A., Gevers W. Chylomicron remnant clearance from the plasma is normal in familial hypercholesterolemic homozygotes with defined receptor defects. J Clin Invest. 1990 Oct;86(4):1306–1312. doi: 10.1172/JCI114839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd J., Bicker S., Lorimer A. R., Packard C. J. Receptor-mediated low density lipoprotein catabolism in man. J Lipid Res. 1979 Nov;20(8):999–1006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spady D. K., Bilheimer D. W., Dietschy J. M. Rates of receptor-dependent and -independent low density lipoprotein uptake in the hamster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3499–3503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spady D. K., Huettinger M., Bilheimer D. W., Dietschy J. M. Role of receptor-independent low density lipoprotein transport in the maintenance of tissue cholesterol balance in the normal and WHHL rabbit. J Lipid Res. 1987 Jan;28(1):32–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spady D. K., Meddings J. B., Dietschy J. M. Kinetic constants for receptor-dependent and receptor-independent low density lipoprotein transport in the tissues of the rat and hamster. J Clin Invest. 1986 May;77(5):1474–1481. doi: 10.1172/JCI112460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel J. L., Baynes J. W., Thorpe S. R. 125I-glycoconjugate labels for identifying sites of protein catabolism in vivo: effect of structure and chemistry of coupling to protein on label entrapment in cells after protein degradation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Aug 1;240(2):635–645. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Zuiden P. E., Erickson S. K., Cooper A. D. Effect of removal of lipoproteins of different composition on hepatic 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase activity and hepatic very low density lipoprotein secretion. J Lipid Res. 1983 Apr;24(4):418–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Role of lysine residues of plasma lipoproteins in high affinity binding to cell surface receptors on human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):9053–9062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W., Kowal R. C., Herz J., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Apolipoprotein C-I modulates the interaction of apolipoprotein E with beta-migrating very low density lipoproteins (beta-VLDL) and inhibits binding of beta-VLDL to low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22453–22459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]