Abstract
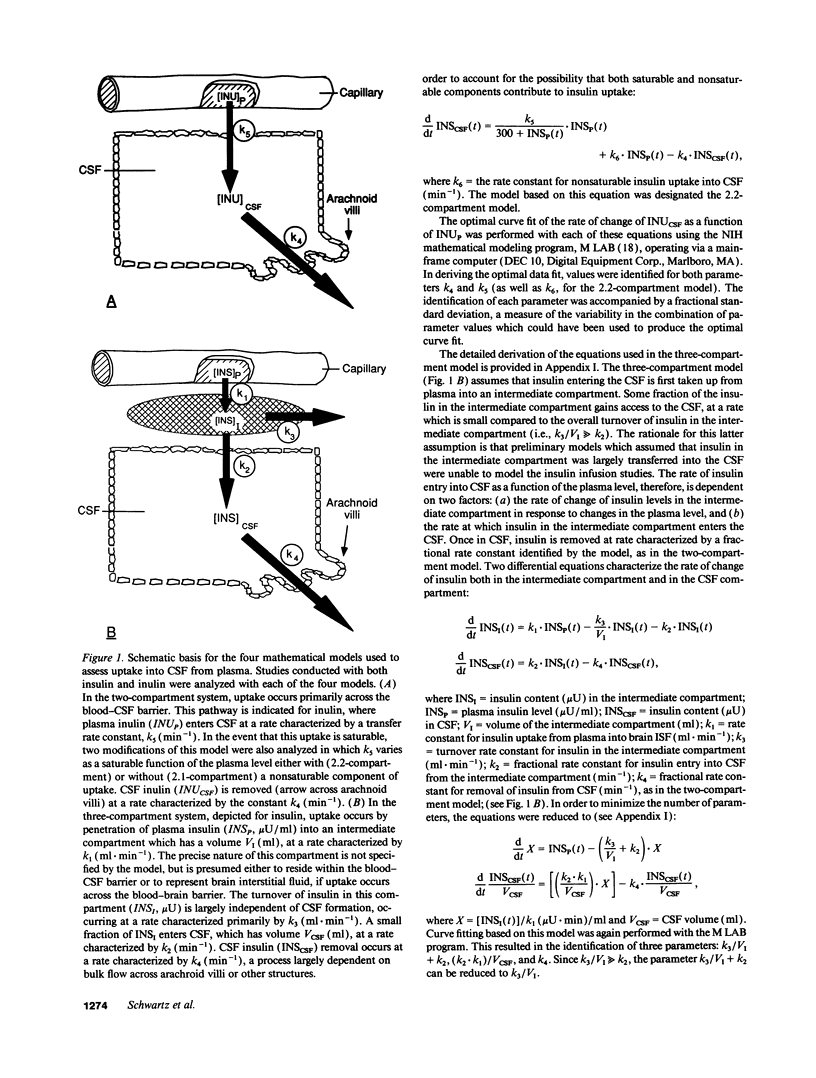
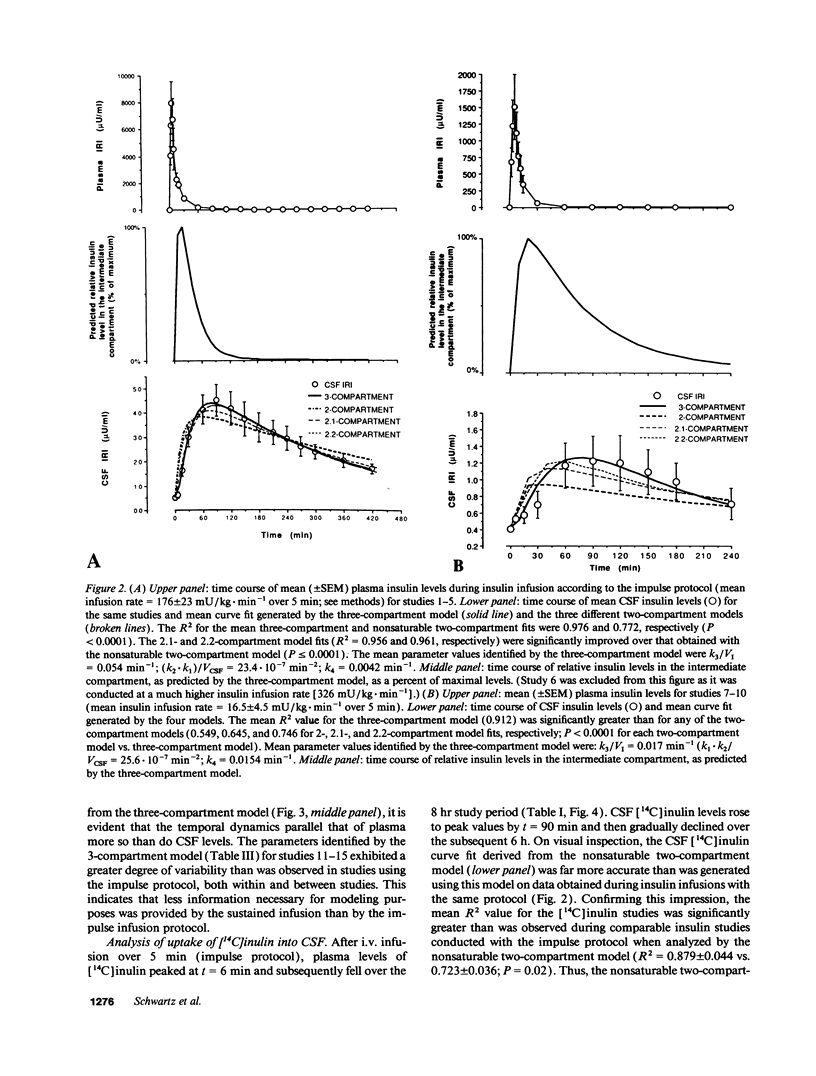
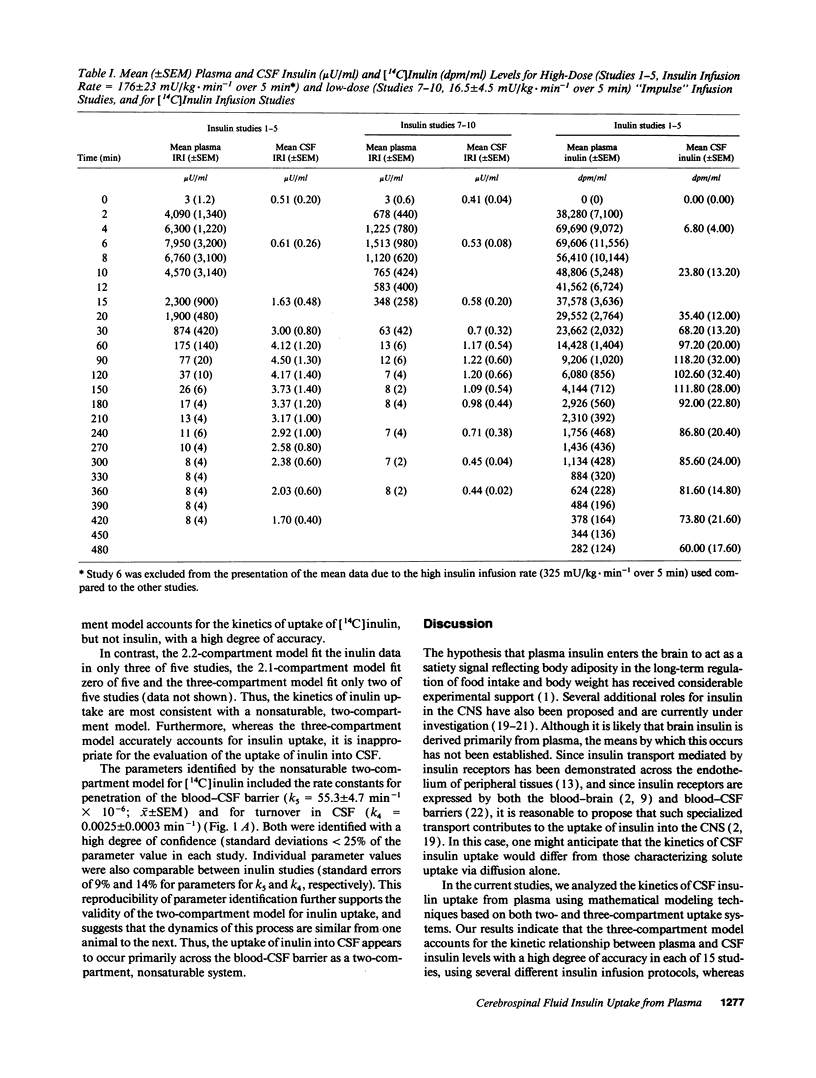
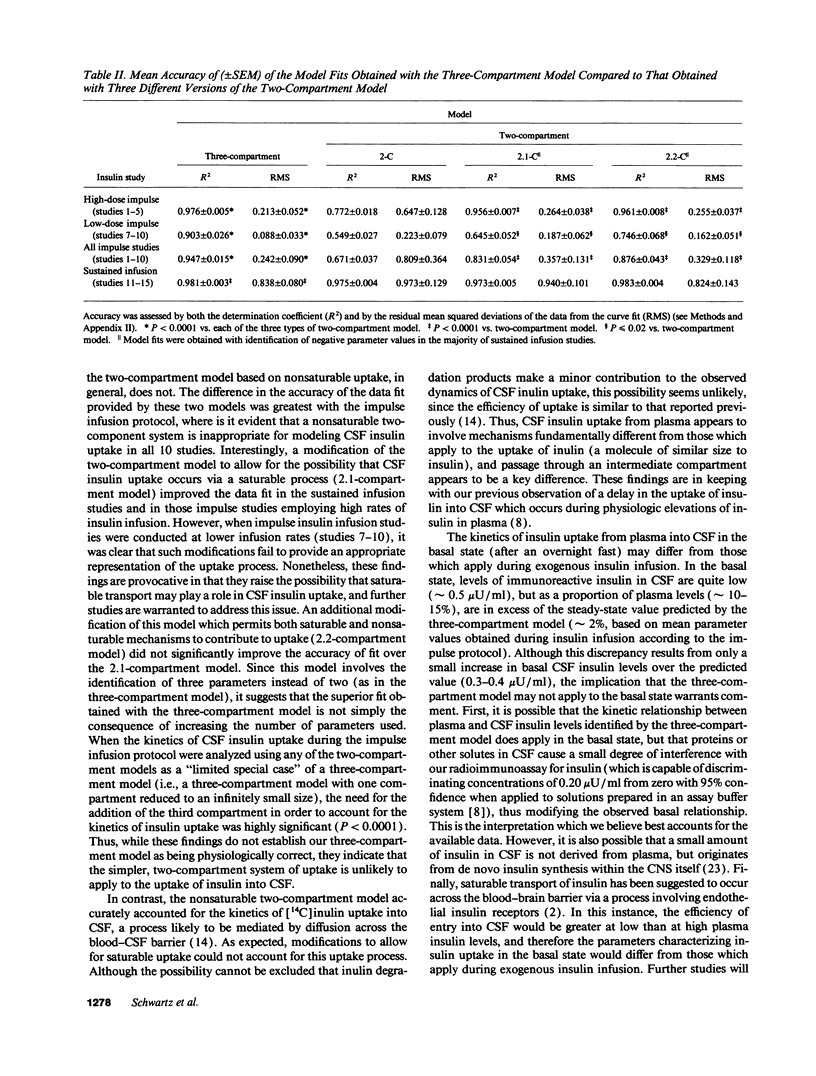
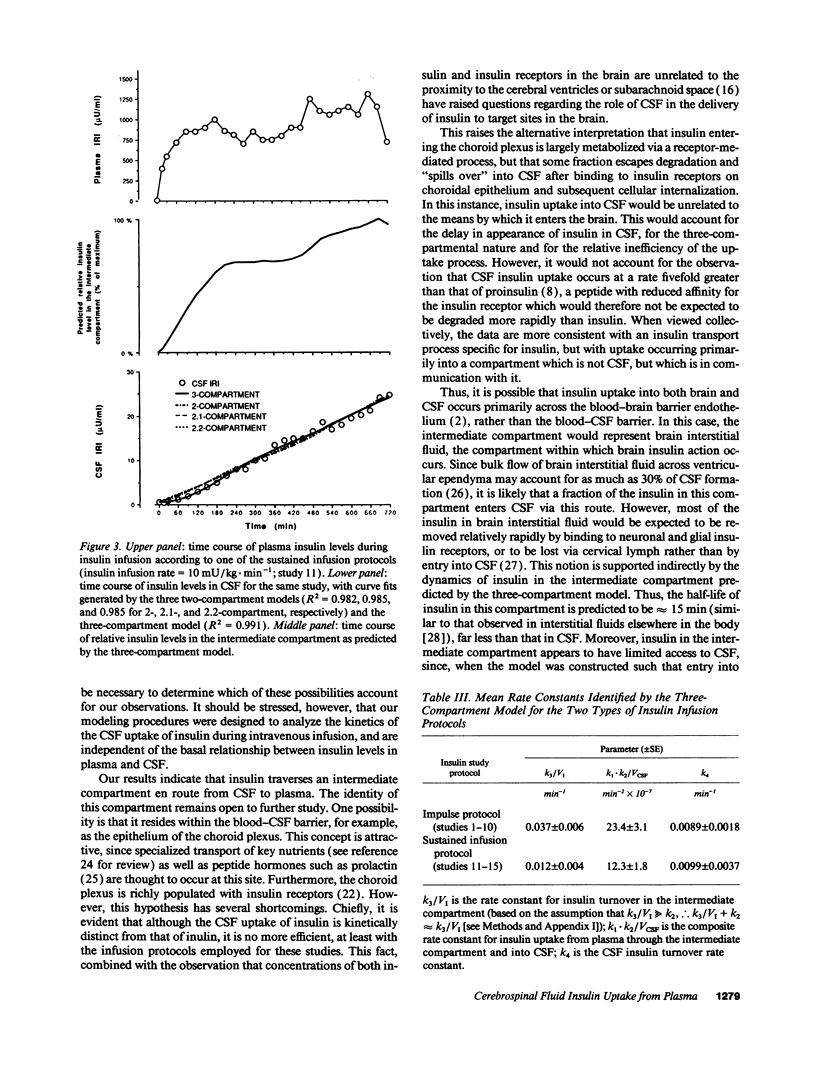
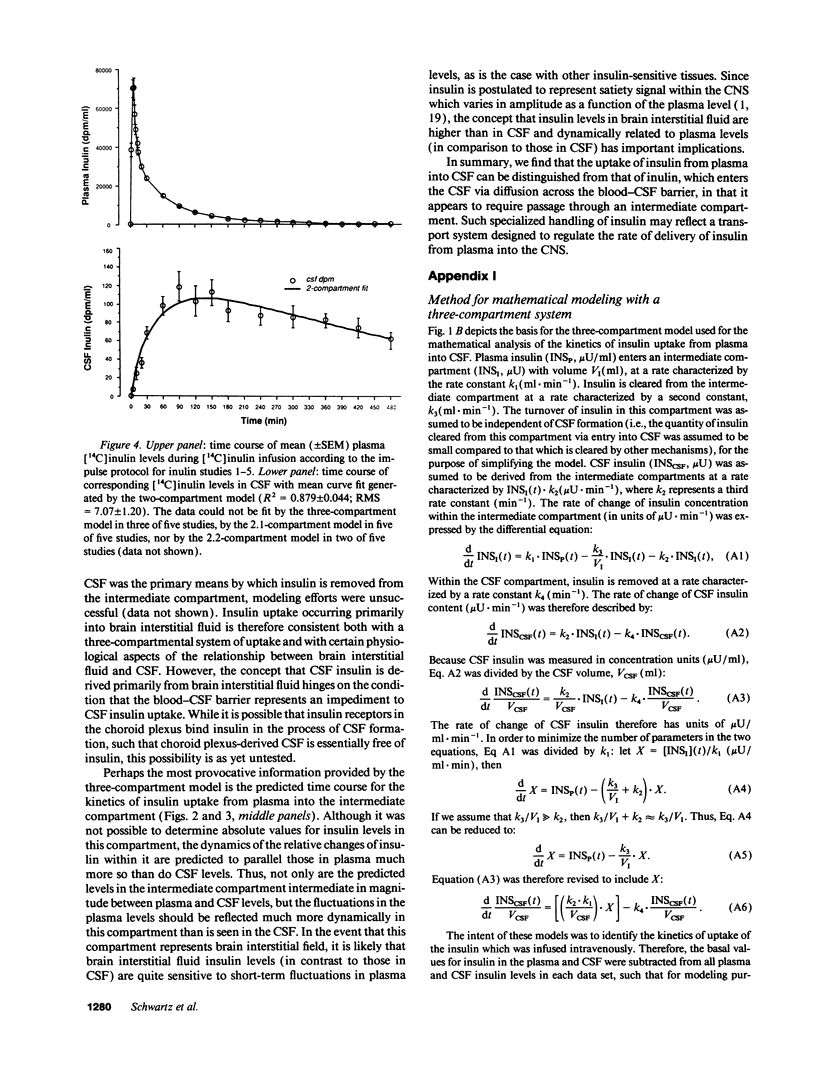
To study the route by which plasma insulin enters cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), the kinetics of uptake from plasma into cisternal CSF of both insulin and [14C]inulin were analyzed during intravenous infusion in anesthetized dogs. Four different mathematical models were used: three based on a two-compartment system (transport directly across the blood-CSF barrier by nonsaturable, saturable, or a combination of both mechanisms) and a fourth based on three compartments (uptake via an intermediate compartment). The kinetics of CSF uptake of [14C]inulin infused according to an "impulse" protocol were accurately accounted for only by the nonsaturable two-compartment model (determination coefficient [R2] = 0.879 +/- 0.044; mean +/- SEM; n = 5), consistent with uptake via diffusion across the blood-CSF barrier. When the same infusion protocol and model were used to analyze the kinetics of insulin uptake, the data fit (R2 = 0.671 +/- 0.037; n = 10) was significantly worse than that obtained with [14C]inulin (P = 0.02). Addition of a saturable component of uptake to the two-compartment model improved this fit, but was clearly inadequate for a subset of insulin infusion studies. In contrast, the three-compartment model accurately accounted for CSF insulin uptake in each study, regardless of infusion protocol (impulse infusion R2 = 0.947 +/- 0.026; n = 10; P less than 0.0001 vs. each two-compartment model; sustained infusion R2 = 0.981 +/- 0.003; n = 5). Thus, a model in which insulin passes through an intermediate compartment en route from plasma to CSF, as a part of a specialized transport system for the delivery of insulin to the brain, best accounts for the dynamics of this uptake process. This intermediate compartment could reside within the blood-CSF barrier or it may represent brain interstitial fluid, if CNS insulin uptake occurs preferentially across the blood-brain barrier.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assies J., Schellekens A. P., Touber J. L. Protein hormones in cerebrospinal fluid: evidence for retrograde transport of prolactin from the pituitary to the brain in man. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1978 Jun;8(6):487–491. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1978.tb02186.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar R. S., Boes M., Sandra A. Vascular transport of insulin to rat cardiac muscle. Central role of the capillary endothelium. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1225–1233. doi: 10.1172/JCI113439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskin D. G., Brewitt B., Davidson D. A., Corp E., Paquette T., Figlewicz D. P., Lewellen T. K., Graham M. K., Woods S. G., Dorsa D. M. Quantitative autoradiographic evidence for insulin receptors in the choroid plexus of the rat brain. Diabetes. 1986 Feb;35(2):246–249. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.2.246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskin D. G., Figlewicz D. P., Woods S. C., Porte D., Jr, Dorsa D. M. Insulin in the brain. Annu Rev Physiol. 1987;49:335–347. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.49.030187.002003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskin D. G., Woods S. C., West D. B., van Houten M., Posner B. I., Dorsa D. M., Porte D., Jr Immunocytochemical detection of insulin in rat hypothalamus and its possible uptake from cerebrospinal fluid. Endocrinology. 1983 Nov;113(5):1818–1825. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-5-1818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury M. W., Cserr H. F., Westrop R. J. Drainage of cerebral interstitial fluid into deep cervical lymph of the rabbit. Am J Physiol. 1981 Apr;240(4):F329–F336. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.240.4.F329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy K. R., Pardridge W. M. Blood-brain barrier transcytosis of insulin in developing rabbits. Brain Res. 1987 Sep 8;420(1):32–38. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank H. J., Jankovic-Vokes T., Pardridge W. M., Morris W. L. Enhanced insulin binding to blood-brain barrier in vivo and to brain microvessels in vitro in newborn rabbits. Diabetes. 1985 Aug;34(8):728–733. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.8.728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. L., Johnson S. M. Receptor-mediated transport of insulin across endothelial cells. Science. 1985 Mar 29;227(4694):1583–1586. doi: 10.1126/science.3883490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knott G. D. Mlab--a mathematical modeling tool. Comput Programs Biomed. 1979 Dec;10(3):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(79)90075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardridge W. M. Receptor-mediated peptide transport through the blood-brain barrier. Endocr Rev. 1986 Aug;7(3):314–330. doi: 10.1210/edrv-7-3-314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puro D. G., Agardh E. Insulin-mediated regulation of neuronal maturation. Science. 1984 Sep 14;225(4667):1170–1172. doi: 10.1126/science.6089343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi T., Takahashi M., Bray G. A. Diurnal changes in sympathetic activity. Relation to food intake and to insulin injected into the ventromedial or suprachiasmatic nucleus. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jul;82(1):282–286. doi: 10.1172/JCI113584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. W., Sipols A., Kahn S. E., Lattemann D. F., Taborsky G. J., Jr, Bergman R. N., Woods S. C., Porte D., Jr Kinetics and specificity of insulin uptake from plasma into cerebrospinal fluid. Am J Physiol. 1990 Sep;259(3 Pt 1):E378–E383. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1990.259.3.E378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector R., Eells J. Deoxynucleoside and vitamin transport into the central nervous system. Fed Proc. 1984 Feb;43(2):196–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein L. J., Dorsa D. M., Baskin D. G., Figlewicz D. P., Porte D., Jr, Woods S. C. Reduced effect of experimental peripheral hyperinsulinemia to elevate cerebrospinal fluid insulin concentrations of obese Zucker rats. Endocrinology. 1987 Nov;121(5):1611–1615. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-5-1611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallum B. J., Taborsky G. J., Jr, Porte D., Jr, Figlewicz D. P., Jacobson L., Beard J. C., Ward W. K., Dorsa D. Cerebrospinal fluid insulin levels increase during intravenous insulin infusions in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Jan;64(1):190–194. doi: 10.1210/jcem-64-1-190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch K., Sadler K. Permeability of the choroid plexus of the rabbit to several solutes. Am J Physiol. 1966 Mar;210(3):652–660. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.3.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods S. C., Porte D., Jr, Bobbioni E., Ionescu E., Sauter J. F., Rohner-Jeanrenaud F., Jeanrenaud B. Insulin: its relationship to the central nervous system and to the control of food intake and body weight. Am J Clin Nutr. 1985 Nov;42(5 Suppl):1063–1071. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/42.5.1063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods S. C., Porte D., Jr Relationship between plasma and cerebrospinal fluid insulin levels of dogs. Am J Physiol. 1977 Oct;233(4):E331–E334. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1977.233.4.E331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. J., Hope I. D., Ader M., Bergman R. N. Insulin transport across capillaries is rate limiting for insulin action in dogs. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1620–1628. doi: 10.1172/JCI114339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. J., Youn J. H., Bergman R. N. Modified protocols improve insulin sensitivity estimation using the minimal model. Am J Physiol. 1987 Dec;253(6 Pt 1):E595–E602. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.253.6.E595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



