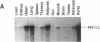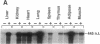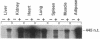Abstract
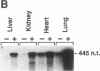
The regulation of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1) gene expression was studied in vivo employing a murine model system. Nuclease protection analysis revealed relatively high concentrations of PAI-1 mRNA in the aorta, adipose tissue, heart, and lungs of untreated CB6 (BalbC X C57B16) mice. Treatment of CB6 mice with LPS, TNF-alpha, or transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) increased the steady-state levels of PAI-1 mRNA within 3 h in all tissues examined. However, the greatest responses to TGF-beta were observed in adipose tissue and the kidney, while LPS and TNF-alpha strongly stimulated PAI-1 gene expression in the liver, kidney, lung, and adrenals. In C3H/HeJ mice, which exhibit defective TNF-alpha release in response to LPS, the response of the PAI-1 gene to LPS was severely attenuated. However, injection of these mice with TNF-alpha increased PAI-1 mRNA in a tissue-specific pattern strikingly similar to that observed in LPS-treated CB6 mice. These results demonstrate that the PAI-1 gene is regulated in a complex and tissue-specific manner in vivo, and suggest a role for TNF-alpha in the response of the PAI-1 gene to sepsis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aillaud M. F., Juhan-Vague I., Alessi M. C., Marecal M., Vinson M. F., Arnaud C., Vague P., Collen D. Increased PA-inhibitor levels in the postoperative period--no cause-effect relation with increased cortisol. Thromb Haemost. 1985 Aug 30;54(2):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almér L. O., Ohlin H. Elevated levels of the rapid inhibitor of plasminogen activator (t-PAI) in acute myocardial infarction. Thromb Res. 1987 Aug 1;47(3):335–339. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(87)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assoian R. K., Fleurdelys B. E., Stevenson H. C., Miller P. J., Madtes D. K., Raines E. W., Ross R., Sporn M. B. Expression and secretion of type beta transforming growth factor by activated human macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6020–6024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auwerx J., Bouillon R., Collen D., Geboers J. Tissue-type plasminogen activator antigen and plasminogen activator inhibitor in diabetes mellitus. Arteriosclerosis. 1988 Jan-Feb;8(1):68–72. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.8.1.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin: more than a tumor necrosis factor. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 12;316(7):379–385. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702123160705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Krochin N., Milsark I. W., Luedke C., Cerami A. Control of cachectin (tumor necrosis factor) synthesis: mechanisms of endotoxin resistance. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):977–980. doi: 10.1126/science.3754653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björntorp P. "Portal" adipose tissue as a generator of risk factors for cardiovascular disease and diabetes. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 Jul-Aug;10(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castelli W. P. The triglyceride issue: a view from Framingham. Am Heart J. 1986 Aug;112(2):432–437. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(86)90296-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colucci M., Paramo J. A., Collen D. Generation in plasma of a fast-acting inhibitor of plasminogen activator in response to endotoxin stimulation. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):818–824. doi: 10.1172/JCI111777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diéval J., Nguyen G., Gross S., Delobel J., Kruithof E. K. A lifelong bleeding disorder associated with a deficiency of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1. Blood. 1991 Feb 1;77(3):528–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eeckhout Y., Vaes G. Further studies on the activation of procollagenase, the latent precursor of bone collagenase. Effects of lysosomal cathepsin B, plasmin and kallikrein, and spontaneous activation. Biochem J. 1977 Jul 15;166(1):21–31. doi: 10.1042/bj1660021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emeis J. J., Kooistra T. Interleukin 1 and lipopolysaccharide induce an inhibitor of tissue-type plasminogen activator in vivo and in cultured endothelial cells. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1260–1266. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii S., Sobel B. E. Induction of plasminogen activator inhibitor by products released from platelets. Circulation. 1990 Oct;82(4):1485–1493. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.82.4.1485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamsten A., Wiman B., de Faire U., Blombäck M. Increased plasma levels of a rapid inhibitor of tissue plasminogen activator in young survivors of myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 19;313(25):1557–1563. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512193132501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamsten A., de Faire U., Walldius G., Dahlén G., Szamosi A., Landou C., Blombäck M., Wiman B. Plasminogen activator inhibitor in plasma: risk factor for recurrent myocardial infarction. Lancet. 1987 Jul 4;2(8549):3–9. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)93050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hekman C. M., Loskutoff D. J. Kinetic analysis of the interactions between plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 and both urokinase and tissue plasminogen activator. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Apr;262(1):199–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90182-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubert H. B., Feinleib M., McNamara P. M., Castelli W. P. Obesity as an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease: a 26-year follow-up of participants in the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 1983 May;67(5):968–977. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.67.5.968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juhan-Vague I., Vague P., Alessi M. C., Badier C., Valadier J., Aillaud M. F., Atlan C. Relationships between plasma insulin triglyceride, body mass index, and plasminogen activator inhibitor 1. Diabete Metab. 1987 Jul;13(3 Pt 2):331–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juhan-Vague I., Valadier J., Alessi M. C., Aillaud M. F., Ansaldi J., Philip-Joet C., Holvoet P., Serradimigni A., Collen D. Deficient t-PA release and elevated PA inhibitor levels in patients with spontaneous or recurrent deep venous thrombosis. Thromb Haemost. 1987 Feb 3;57(1):67–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluft C., Verheijen J. H., Jie A. F., Rijken D. C., Preston F. E., Sue-Ling H. M., Jespersen J., Aasen A. O. The postoperative fibrinolytic shutdown: a rapidly reverting acute phase pattern for the fast-acting inhibitor of tissue-type plasminogen activator after trauma. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1985 Nov;45(7):605–610. doi: 10.3109/00365518509155267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen B. S., Harpel P. C., Nachman R. L. Plasminogen activator inhibitor is associated with the extracellular matrix of cultured bovine smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;80(4):1082–1089. doi: 10.1172/JCI113164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kooistra T., Bosma P. J., Töns H. A., van den Berg A. P., Meyer P., Princen H. M. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1: biosynthesis and mRNA level are increased by insulin in cultured human hepatocytes. Thromb Haemost. 1989 Sep 29;62(2):723–728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruithof E. K., Tran-Thang C., Gudinchet A., Hauert J., Nicoloso G., Genton C., Welti H., Bachmann F. Fibrinolysis in pregnancy: a study of plasminogen activator inhibitors. Blood. 1987 Feb;69(2):460–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiho M., Saksela O., Keski-Oja J. Transforming growth factor-beta induction of type-1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. Pericellular deposition and sensitivity to exogenous urokinase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17467–17474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laug W. E. Vascular smooth muscle cells inhibit the plasminogen activators secreted by endothelial cells. Thromb Haemost. 1985 Apr 22;53(2):165–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J., Sawdey M., Mimuro J. Type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1989;9:87–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J., van Mourik J. A., Erickson L. A., Lawrence D. Detection of an unusually stable fibrinolytic inhibitor produced by bovine endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2956–2960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucore C. L., Fujii S., Wun T. C., Sobel B. E., Billadello J. J. Regulation of the expression of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor in Hep G2 cells by epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):15845–15848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund L. R., Riccio A., Andreasen P. A., Nielsen L. S., Kristensen P., Laiho M., Saksela O., Blasi F., Danø K. Transforming growth factor-beta is a strong and fast acting positive regulator of the level of type-1 plasminogen activator inhibitor mRNA in WI-38 human lung fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1281–1286. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02365.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathison J. C., Ulevitch R. J. The clearance, tissue distribution, and cellular localization of intravenously injected lipopolysaccharide in rabbits. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):2133–2143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimuro J., Schleef R. R., Loskutoff D. J. Extracellular matrix of cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells contains functionally active type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. Blood. 1987 Sep;70(3):721–728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mroczka D. L., Cassidy B., Busch H., Rothblum L. I. Characterization of rat ribosomal DNA. The highly repetitive sequences that flank the ribosomal RNA transcription unit are homologous and contain RNA polymerase III transcription initiation sites. J Mol Biol. 1984 Mar 25;174(1):141–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90369-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musson R. A., Morrison D. C., Ulevitch R. J. Distribution of endotoxin (lipopolysaccharide) in the tissues of lipopolysaccharide-responsive and -unresponsive mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):448–457. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.448-457.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oseroff A., Krishnamurti C., Hassett A., Tang D., Alving B. Plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor activities in men with coronary artery disease. J Lab Clin Med. 1989 Jan;113(1):88–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paramo J. A., Colucci M., Collen D., van de Werf F. Plasminogen activator inhibitor in the blood of patients with coronary artery disease. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Aug 31;291(6495):573–574. doi: 10.1136/bmj.291.6495.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Diamond L. E., Dahl D., Cole M. D. The c-myc-regulated gene mrl encodes plasminogen activator inhibitor 1. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1265–1269. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax P. H., van den Hoogen C. M., Verheijen J. H., Padro T., Zeheb R., Gelehrter T. D., van Berkel T. J., Kuiper J., Emeis J. J. Endotoxin induction of plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 mRNA in rat tissues in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15560–15563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly C. F., McFall R. C. Platelet-derived growth factor and transforming growth factor-beta regulate plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 synthesis in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9419–9427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remick D. G., Strieter R. M., Lynch J. P., 3rd, Nguyen D., Eskandari M., Kunkel S. L. In vivo dynamics of murine tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene expression. Kinetics of dexamethasone-induced suppression. Lab Invest. 1989 Jun;60(6):766–771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawdey M., Podor T. J., Loskutoff D. J. Regulation of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor gene expression in cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. Induction by transforming growth factor-beta, lipopolysaccharide, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10396–10401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleef R. R., Bevilacqua M. P., Sawdey M., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Loskutoff D. J. Cytokine activation of vascular endothelium. Effects on tissue-type plasminogen activator and type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5797–5803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleef R. R., Higgins D. L., Pillemer E., Levitt L. J. Bleeding diathesis due to decreased functional activity of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. J Clin Invest. 1989 May;83(5):1747–1752. doi: 10.1172/JCI114076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B., Wakefield L. M., de Crombrugghe B. Some recent advances in the chemistry and biology of transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1039–1045. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengers E. D., Kluft C. Plasminogen activator inhibitors. Blood. 1987 Feb;69(2):381–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suffredini A. F., Harpel P. C., Parrillo J. E. Promotion and subsequent inhibition of plasminogen activation after administration of intravenous endotoxin to normal subjects. N Engl J Med. 1989 May 4;320(18):1165–1172. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198905043201802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thalacker F. W., Nilsen-Hamilton M. Specific induction of secreted proteins by transforming growth factor-beta and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. Relationship with an inhibitor of plasminogen activator. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2283–2290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vague P., Juhan-Vague I., Aillaud M. F., Badier C., Viard R., Alessi M. C., Collen D. Correlation between blood fibrinolytic activity, plasminogen activator inhibitor level, plasma insulin level, and relative body weight in normal and obese subjects. Metabolism. 1986 Mar;35(3):250–253. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(86)90209-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerhausen D. R., Jr, Hopkins W. E., Billadello J. J. Multiple transforming growth factor-beta-inducible elements regulate expression of the plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 gene in Hep G2 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1092–1100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Chmielewska J. A novel fast inhibitor to tissue plasminogen activator in plasma, which may be of great pathophysiological significance. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1985;177:43–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Deventer S. J., Büller H. R., ten Cate J. W., Aarden L. A., Hack C. E., Sturk A. Experimental endotoxemia in humans: analysis of cytokine release and coagulation, fibrinolytic, and complement pathways. Blood. 1990 Dec 15;76(12):2520–2526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hinsbergh V. W., Bauer K. A., Kooistra T., Kluft C., Dooijewaard G., Sherman M. L., Nieuwenhuizen W. Progress of fibrinolysis during tumor necrosis factor infusions in humans. Concomitant increase in tissue-type plasminogen activator, plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1, and fibrin(ogen) degradation products. Blood. 1990 Dec 1;76(11):2284–2289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hinsbergh V. W., Kooistra T., van den Berg E. A., Princen H. M., Fiers W., Emeis J. J. Tumor necrosis factor increases the production of plasminogen activator inhibitor in human endothelial cells in vitro and in rats in vivo. Blood. 1988 Nov;72(5):1467–1473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]