Abstract
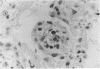
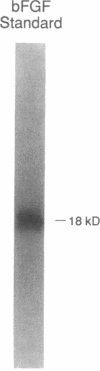
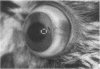
Survival after acute lung injury (ALI) depends on prompt alveolar repair, a process frequently subverted by the development of granulation tissue within the alveolar airspace. Immunohistochemical examination of the intraalveolar granulation tissue confirmed that capillaries as well as myofibroblasts were the principal cellular constituents. We therefore hypothesized that angiogenesis factors would be present on the air-lung interface after ALI. To evaluate this hypothesis, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from patients with ALI (n = 25) and patient controls (n = 8) was examined for angiogenesis bioactivity by its ability of induce endothelial cell migration. While lavage fluid from controls had no bioactivity, lavage fluid from 72% of patients with ALI promoted endothelial cell migration. Heparin affinity, ion exchange, and gel filtration chromatography resolved the bioactivity into at least two moieties. One appeared identical to the well characterized endothelial cell growth factor, basic fibroblast growth factor. The other was a 150-kD non-heparin binding protein that mediated endothelial cell migration and attachment in vitro, and the growth of new vessels in vivo. These data are consistent with the hypothesis that the growth of capillaries into the alveolar airspace results from angiogenesis factors present on the alveolar surface of the lung after ALI.
Full text
PDF


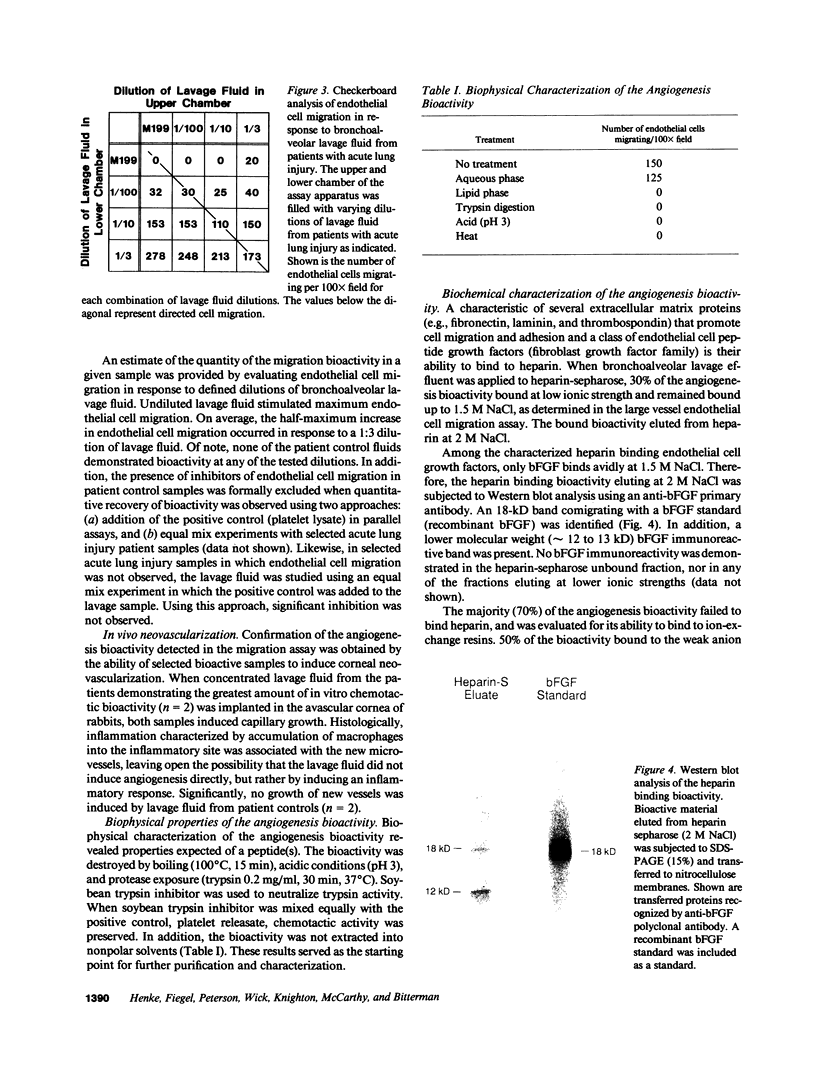
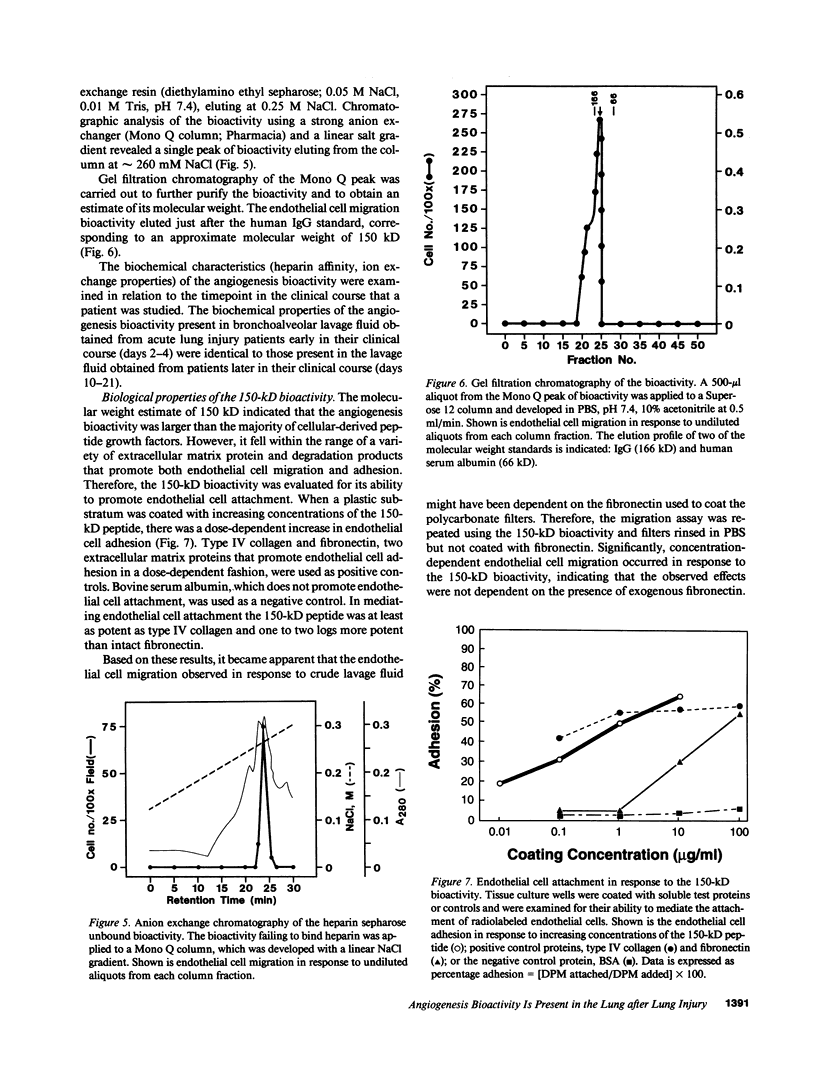




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ausprunk D. H., Folkman J. Migration and proliferation of endothelial cells in preformed and newly formed blood vessels during tumor angiogenesis. Microvasc Res. 1977 Jul;14(1):53–65. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(77)90141-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachofen M., Weibel E. R. Alterations of the gas exchange apparatus in adult respiratory insufficiency associated with septicemia. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Oct;116(4):589–615. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.116.4.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banda M. J., Knighton D. R., Hunt T. K., Werb Z. Isolation of a nonmitogenic angiogenesis factor from wound fluid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7773–7777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang R. L., Levin W., Wood A. W., Lehr R. E., Kumar S., Yagi H., Jerina D. M., Conney A. H. Tumorigenicity of bay-region diol-epoxides and other benzo-ring derivatives of dibenzo(a,h)pyrene and dibenzo(a,i)pyrene on mouse skin and in newborn mice. Cancer Res. 1982 Jan;42(1):25–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., DellaPelle P., Manseau E., Lanigan J. M., Dvorak H. F., Colvin R. B. Blood vessel fibronectin increases in conjunction with endothelial cell proliferation and capillary ingrowth during wound healing. J Invest Dermatol. 1982 Nov;79(5):269–276. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12500076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson J. M., Klagsbrun M., Hill K. E., Buckley A., Sullivan R., Brewer P. S., Woodward S. C. Accelerated wound repair, cell proliferation, and collagen accumulation are produced by a cartilage-derived growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;100(4):1219–1227. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.4.1219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. B., Rennard S. I., Bitterman P. B., Crystal R. G. Pulmonary oxygen toxicity. Early reversible changes in human alveolar structures induced by hyperoxia. N Engl J Med. 1983 Oct 13;309(15):878–883. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198310133091502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenic factors. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):442–447. doi: 10.1126/science.2432664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M., Sasse J., Wadzinski M., Ingber D., Vlodavsky I. A heparin-binding angiogenic protein--basic fibroblast growth factor--is stored within basement membrane. Am J Pathol. 1988 Feb;130(2):393–400. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredj-Reygrobellet D., Plouet J., Delayre T., Baudouin C., Bourret F., Lapalus P. Effects of aFGF and bFGF on wound healing in rabbit corneas. Curr Eye Res. 1987 Oct;6(10):1205–1209. doi: 10.3109/02713688709025230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda Y., Ishizaki M., Masuda Y., Kimura G., Kawanami O., Masugi Y. The role of intraalveolar fibrosis in the process of pulmonary structural remodeling in patients with diffuse alveolar damage. Am J Pathol. 1987 Jan;126(1):171–182. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cotran R. S., Leapman S. B., Folkman J. Tumor growth and neovascularization: an experimental model using the rabbit cornea. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Feb;52(2):413–427. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.2.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Cheng J., Lui G. M., Baird A., Böhlent P. Isolation of brain fibroblast growth factor by heparin-Sepharose affinity chromatography: identity with pituitary fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6963–6967. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasleton P. S. Adult respiratory distress syndrome--a review. Histopathology. 1983 May;7(3):307–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1983.tb02247.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayek A., Culler F. L., Beattie G. M., Lopez A. D., Cuevas P., Baird A. An in vivo model for study of the angiogenic effects of basic fibroblast growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Sep 15;147(2):876–880. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst T. J., McCarthy J. B., Tsilibary E. C., Furcht L. T. Differential effects of laminin, intact type IV collagen, and specific domains of type IV collagen on endothelial cell adhesion and migration. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1365–1373. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holter J. F., Weiland J. E., Pacht E. R., Gadek J. E., Davis W. B. Protein permeability in the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Loss of size selectivity of the alveolar epithelium. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1513–1522. doi: 10.1172/JCI112743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. K., Knighton D. R., Thakral K. K., Goodson W. H., 3rd, Andrews W. S. Studies on inflammation and wound healing: angiogenesis and collagen synthesis stimulated in vivo by resident and activated wound macrophages. Surgery. 1984 Jul;96(1):48–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa F., Miyazono K., Hellman U., Drexler H., Wernstedt C., Hagiwara K., Usuki K., Takaku F., Risau W., Heldin C. H. Identification of angiogenic activity and the cloning and expression of platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor. Nature. 1989 Apr 13;338(6216):557–562. doi: 10.1038/338557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph-Silverstein J., Rifkin D. B. Endothelial cell growth factors and the vessel wall. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1987 Oct;13(4):504–513. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1003526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., Vlodavsky I. Biosynthesis and storage of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) by endothelial cells: implication for the mechanism of action of angiogenesis. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1988;266:55–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Ciresi K. F., Fiegel V. D., Austin L. L., Butler E. L. Classification and treatment of chronic nonhealing wounds. Successful treatment with autologous platelet-derived wound healing factors (PDWHF). Ann Surg. 1986 Sep;204(3):322–330. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198609000-00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Fiegel V. D. Macrophage-derived growth factors in wound healing: regulation of growth factor production by the oxygen microenvironment. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Oct;140(4):1108–1111. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.4.1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Phillips G. D., Fiegel V. D. Wound healing angiogenesis: indirect stimulation by basic fibroblast growth factor. J Trauma. 1990 Dec;30(12 Suppl):S134–S144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn C., 3rd, Boldt J., King T. E., Jr, Crouch E., Vartio T., McDonald J. A. An immunohistochemical study of architectural remodeling and connective tissue synthesis in pulmonary fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Dec;140(6):1693–1703. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.6.1693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawler J., Weinstein R., Hynes R. O. Cell attachment to thrombospondin: the role of ARG-GLY-ASP, calcium, and integrin receptors. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2351–2361. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibovich S. J., Ross R. The role of the macrophage in wound repair. A study with hydrocortisone and antimacrophage serum. Am J Pathol. 1975 Jan;78(1):71–100. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibovich S. J., Wiseman D. M. Macrophages, wound repair and angiogenesis. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1988;266:131–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maciag T., Mehlman T., Friesel R., Schreiber A. B. Heparin binds endothelial cell growth factor, the principal endothelial cell mitogen in bovine brain. Science. 1984 Aug 31;225(4665):932–935. doi: 10.1126/science.6382607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy J. B., Hagen S. T., Furcht L. T. Human fibronectin contains distinct adhesion- and motility-promoting domains for metastatic melanoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;102(1):179–188. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazono K., Heldin C. H. High-yield purification of platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor: structural characterization and establishment of a specific antiserum. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 21;28(4):1704–1710. doi: 10.1021/bi00430a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazono K., Okabe T., Urabe A., Takaku F., Heldin C. H. Purification and properties of an endothelial cell growth factor from human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4098–4103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F., Doyle M. J., Jaffe E. A. Synthesis and secretion of thrombospondin by cultured human endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 May;93(2):343–348. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.2.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F. Physiology of thrombospondin. Annu Rev Med. 1990;41:85–97. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.41.020190.000505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy-Ullrich J. E., Hök M. Thrombospondin modulates focal adhesions in endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1309–1319. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepe P. E., Potkin R. T., Reus D. H., Hudson L. D., Carrico C. J. Clinical predictors of the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Surg. 1982 Jul;144(1):124–130. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(82)90612-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty T. L. Adult respiratory distress syndrome: definition and historical perspective. Clin Chest Med. 1982 Jan;3(1):3–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postlethwaite A. E., Snyderman R., Kang A. H. The chemotactic attraction of human fibroblasts to a lymphocyte-derived factor. J Exp Med. 1976 Nov 2;144(5):1188–1203. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.5.1188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presta M., Rifkin D. B. New aspects of blood vessel growth: tumor and tissue-derived angiogenesis factors. Haemostasis. 1988;18(1):6–17. doi: 10.1159/000215778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappolee D. A., Mark D., Banda M. J., Werb Z. Wound macrophages express TGF-alpha and other growth factors in vivo: analysis by mRNA phenotyping. Science. 1988 Aug 5;241(4866):708–712. doi: 10.1126/science.3041594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raugi G. J., Olerud J. E., Gown A. M. Thrombospondin in early human wound tissue. J Invest Dermatol. 1987 Dec;89(6):551–554. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12461198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldo J. E., Rogers R. M. Adult respiratory-distress syndrome: changing concepts of lung injury and repair. N Engl J Med. 1982 Apr 15;306(15):900–909. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198204153061504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The fibroblast and wound repair. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1968 Feb;43(1):51–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1968.tb01109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E. Fibronectin and its receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:375–413. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOEFL G. I. STUDIES ON INFLAMMATION. III. GROWING CAPILLARIES: THEIR STRUCTURE AND PERMEABILITY. Virchows Arch Pathol Anat Physiol Klin Med. 1963 Nov 8;337:97–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela O., Rifkin D. B. Release of basic fibroblast growth factor-heparan sulfate complexes from endothelial cells by plasminogen activator-mediated proteolytic activity. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):767–775. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltini C., Hance A. J., Ferrans V. J., Basset F., Bitterman P. B., Crystal R. G. Accurate quantification of cells recovered by bronchoalveolar lavage. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Oct;130(4):650–658. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.4.650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. B., Winkler M. E., Derynck R. Transforming growth factor-alpha: a more potent angiogenic mediator than epidermal growth factor. Science. 1986 Jun 6;232(4755):1250–1253. doi: 10.1126/science.2422759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz U., Schuppan D., Oberbäumer I., Glanville R. W., Deutzmann R., Timpl R., Kühn K. Structure of mouse type IV collagen. Amino-acid sequence of the C-terminal 511-residue-long triple-helical segment of the alpha 2(IV) chain and its comparison with the alpha 1(IV) chain. Eur J Biochem. 1986 May 15;157(1):49–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09636.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shing Y., Folkman J., Haudenschild C., Lund D., Crum R., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenesis is stimulated by a tumor-derived endothelial cell growth factor. J Cell Biochem. 1985;29(4):275–287. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240290402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shing Y., Folkman J., Sullivan R., Butterfield C., Murray J., Klagsbrun M. Heparin affinity: purification of a tumor-derived capillary endothelial cell growth factor. Science. 1984 Mar 23;223(4642):1296–1299. doi: 10.1126/science.6199844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sholley M. M., Ferguson G. P., Seibel H. R., Montour J. L., Wilson J. D. Mechanisms of neovascularization. Vascular sprouting can occur without proliferation of endothelial cells. Lab Invest. 1984 Dec;51(6):624–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer A., Rifkin D. B. Interaction of heparin with human basic fibroblast growth factor: protection of the angiogenic protein from proteolytic degradation by a glycosaminoglycan. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Jan;138(1):215–220. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041380129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein O., Stein Y. Bovine aortic endothelial cells display macrophage-like properties towards acetylated 125I-labelled low density lipoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec 5;620(3):631–635. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(80)90155-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomashefski J. F., Jr, Davies P., Boggis C., Greene R., Zapol W. M., Reid L. M. The pulmonary vascular lesions of the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Pathol. 1983 Jul;112(1):112–126. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I., Folkman J., Sullivan R., Fridman R., Ishai-Michaeli R., Sasse J., Klagsbrun M. Endothelial cell-derived basic fibroblast growth factor: synthesis and deposition into subendothelial extracellular matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2292–2296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadzinski M. G., Folkman J., Sasse J., Devey K., Ingber D., Klagsbrun M. Heparin-binding angiogenesis factors: detection by immunological methods. Clin Physiol Biochem. 1987;5(3-4):200–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiland J. E., Davis W. B., Holter J. F., Mohammed J. R., Dorinsky P. M., Gadek J. E. Lung neutrophils in the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Clinical and pathophysiologic significance. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Feb;133(2):218–225. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.2.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]