Abstract
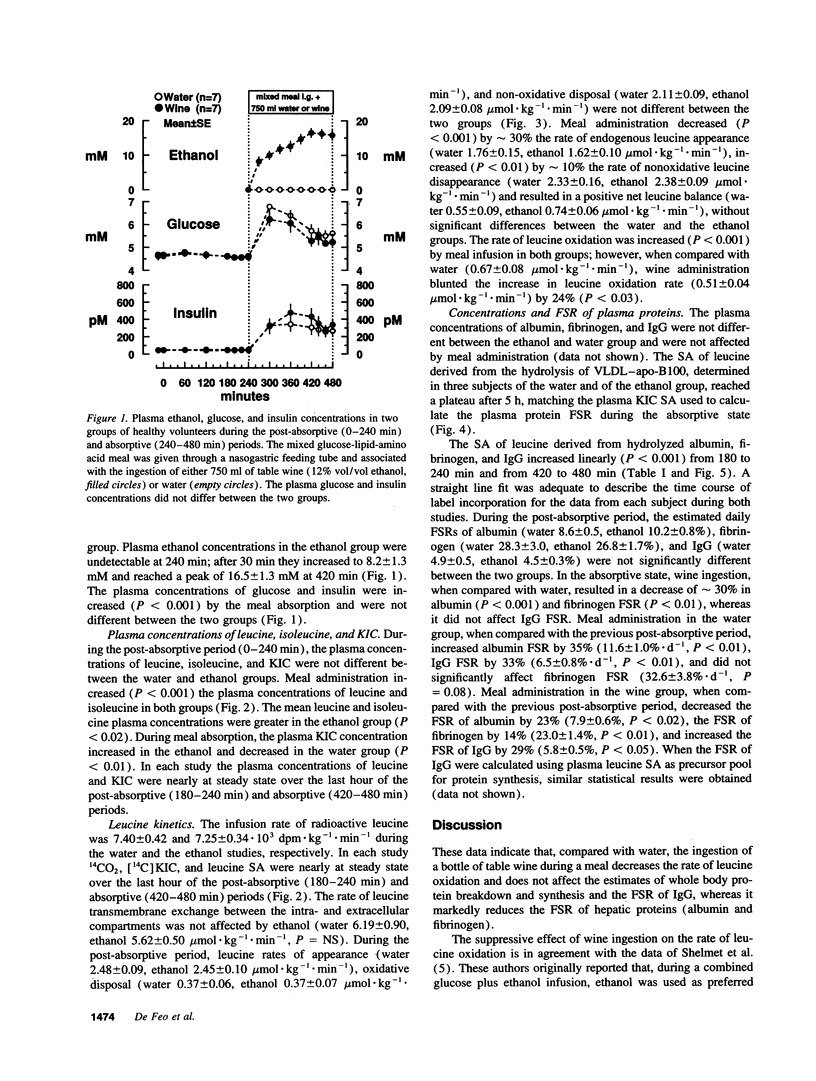
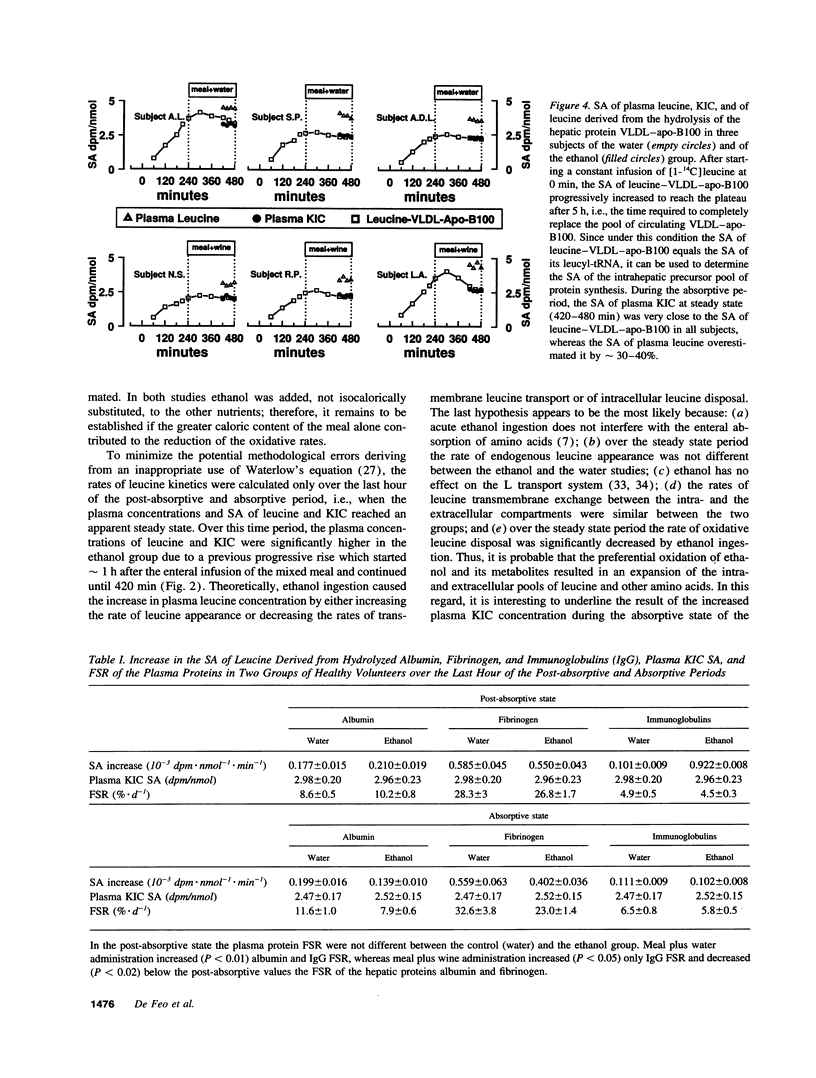
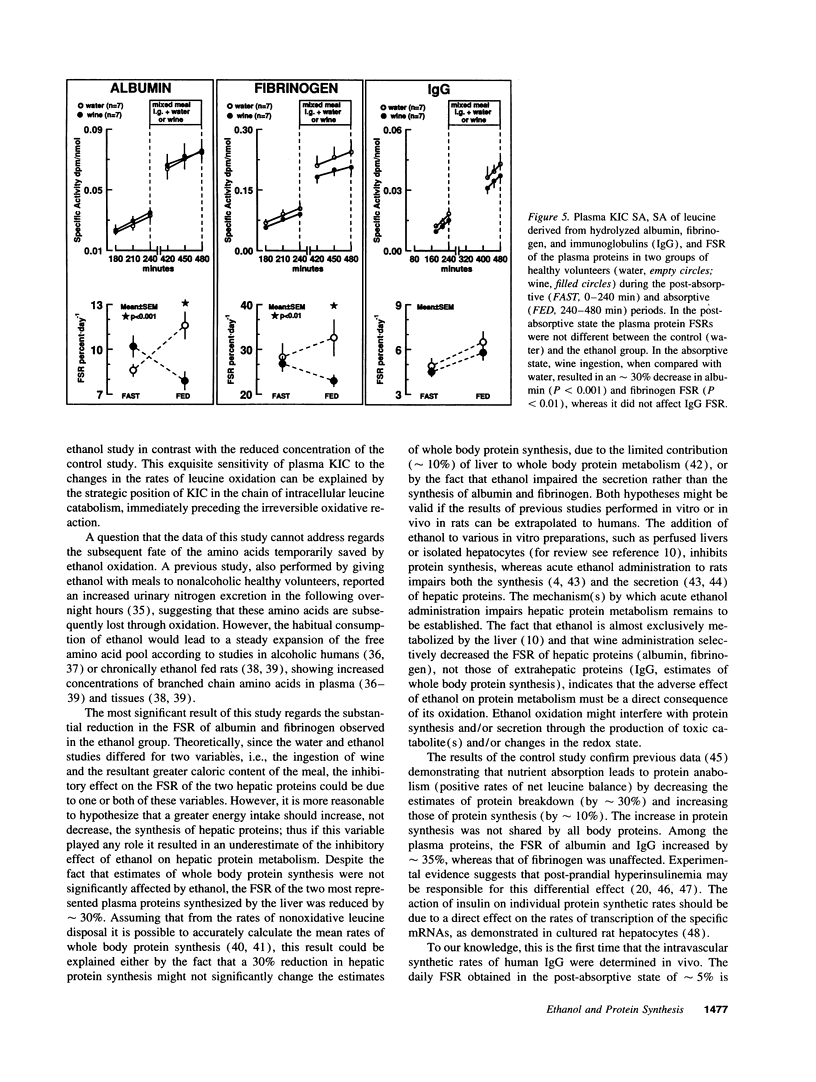
The effects of acute ethanol ingestion on whole body and hepatic protein metabolism in humans are not known. To simulate social drinking, we compared the effects of the association of a mixed meal (632 kcal, 17% amino acids, 50% glucose, 33% lipids) with a bottle of either table wine (ethanol content 71 g) or water on the estimates ([1-14C]-leucine infusion) of whole body protein breakdown, oxidation, and synthesis, and on the intravascular fractional secretory rates (FSR) of hepatically (albumin, fibrinogen) and extrahepatically (IgG) synthesized plasma proteins in two randomized groups (ethanol n = 7, water n = 7) of healthy nonalcoholic volunteers. Each study was carried out for 8 h. Protein kinetics were measured in the overnight post-absorptive state, over the first 4 h, and during a meal infusion (via a nasogastric feeding tube at constant rate) combined with the oral ingestion of wine or water, over the last 4 h. When compared with water, wine ingestion during the meal reduced (P < 0.03) by 24% the rate of leucine oxidation, did not modify the estimates of whole body protein breakdown and synthesis, reduced (P < 0.01) by approximately 30% the FSR of albumin and fibrinogen, but did not affect IgG FSR. In conclusion, 70 g of ethanol, an amount usual among social drinkers, impairs hepatic protein metabolism. The habitual consumption of such amounts by reducing the synthesis and/or secretion of hepatic proteins might lead to the progressive development of liver injury and to hypoalbuminemia also in the absence of protein malnutrition.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aref G. H., el-Din M. K., Hassan A. I., Araby I. I. Immunoglobulins in kwashiorkor. J Trop Med Hyg. 1970 Aug;73(8):186–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avogaro A., Cibin M., Croatto T., Rizzo A., Gallimberti L., Tiengo A. Alcohol intake and withdrawal: effects on branched chain amino acids and alanine. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1986 Jun;10(3):300–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1986.tb05094.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baraona E., Pikkarainen P., Salaspuro M., Finkelman F., Lieber C. S. Acute effects of ethanol on hepatic protein synthesis and secretion in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1980 Jul;79(1):104–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernal C. A., Vazquez J. A., Adibi S. A. Leucine metabolism during chronic ethanol consumption. Metabolism. 1993 Sep;42(9):1084–1086. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(93)90262-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunout D., Petermann M., Ugarte G., Barrera G., Iturriaga H. Nitrogen economy in alcoholic patients without liver disease. Metabolism. 1987 Jul;36(7):651–653. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(87)90148-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S., FREEMAN T. Metabolic heterogeneity of human gamma-globulin. Biochem J. 1960 Sep;76:475–487. doi: 10.1042/bj0760475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox A. M., Turner R., Cooper E. H. Separation and characterisation of glycoproteins from normal, pregnancy, and acute inflammatory sera. J Chromatogr. 1987 Jun 26;397:213–222. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)85004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Feo P., Gaisano M. G., Haymond M. W. Differential effects of insulin deficiency on albumin and fibrinogen synthesis in humans. J Clin Invest. 1991 Sep;88(3):833–840. doi: 10.1172/JCI115384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Feo P., Horber F. F., Haymond M. W. Meal stimulation of albumin synthesis: a significant contributor to whole body protein synthesis in humans. Am J Physiol. 1992 Oct;263(4 Pt 1):E794–E799. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1992.263.4.E794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Feo P., Volpi E., Lucidi P., Cruciani G., Reboldi G., Siepi D., Mannarino E., Santeusanio F., Brunetti P., Bolli G. B. Physiological increments in plasma insulin concentrations have selective and different effects on synthesis of hepatic proteins in normal humans. Diabetes. 1993 Jul;42(7):995–1002. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.7.995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionigi R., Ariszonta, Dominioni L., Gnes F., Ballabio A. The effects of total parenteral nutrition on immunodepression due to malnutrition. Ann Surg. 1977 Apr;185(4):467–474. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197704000-00017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorio R. J., Hoek J. B., Rubin E. Ethanol treatment selectively decreases neutral amino acid transport in cultured hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11430–11435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doumas B. T., Watson W. A., Biggs H. G. Albumin standards and the measurement of serum albumin with bromcresol green. Clin Chim Acta. 1971 Jan;31(1):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(71)90365-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elwyn D. H., Parikh H. C., Shoemaker W. C. Amino acid movements between gut, liver, and periphery in unanesthetized dogs. Am J Physiol. 1968 Nov;215(5):1260–1275. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.5.1260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facchini F., Chen Y. D., Reaven G. M. Light-to-moderate alcohol intake is associated with enhanced insulin sensitivity. Diabetes Care. 1994 Feb;17(2):115–119. doi: 10.2337/diacare.17.2.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman G. D., Klatsky A. L. Is alcohol good for your health? N Engl J Med. 1993 Dec 16;329(25):1882–1883. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199312163292510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaziano J. M., Buring J. E., Breslow J. L., Goldhaber S. Z., Rosner B., VanDenburgh M., Willett W., Hennekens C. H. Moderate alcohol intake, increased levels of high-density lipoprotein and its subfractions, and decreased risk of myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1993 Dec 16;329(25):1829–1834. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199312163292501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg H. N. Lipoprotein physiology and its relationship to atherogenesis. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 1990 Jun;19(2):211–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoerr R. A., Yu Y. M., Wagner D. A., Burke J. F., Young V. R. Recovery of 13C in breath from NaH13CO3 infused by gut and vein: effect of feeding. Am J Physiol. 1989 Sep;257(3 Pt 1):E426–E438. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1989.257.3.E426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horber F. F., Haymond M. W. Human growth hormone prevents the protein catabolic side effects of prednisone in humans. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jul;86(1):265–272. doi: 10.1172/JCI114694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horber F. F., Kahl J., Lecavalier L., Krom B., Haymond M. W. Determination of leucine and alpha-ketoisocaproic acid concentrations and specific activity in plasma and leucine specific activities in proteins using high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1989 Oct 27;495:81–94. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)82611-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeejeebhoy K. N., Phillips M. J., Bruce-Robertson A., Ho J., Sodtke U. The acute effect of ethanol on albumin, fibrinogen and transferrin synthesis in the rat. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;126(5):1111–1124. doi: 10.1042/bj1261111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsten M. A., Lieber C. S. Nutrition in the alcoholic. Med Clin North Am. 1979 Sep;63(5):963–972. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31653-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecavalier L., De Feo P., Haymond M. W. Isolated hypoisoleucinemia impairs whole body but not hepatic protein synthesis in humans. Am J Physiol. 1991 Nov;261(5 Pt 1):E578–E586. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1991.261.5.E578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber C. S. Alcohol, protein metabolism, and liver injury. Gastroenterology. 1980 Aug;79(2):373–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindholm J., Steiniche T., Rasmussen E., Thamsborg G., Nielsen I. O., Brockstedt-Rasmussen H., Storm T., Hyldstrup L., Schou C. Bone disorder in men with chronic alcoholism: a reversible disease? J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 Jul;73(1):118–124. doi: 10.1210/jcem-73-1-118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manil L., Motté P., Pernas P., Troalen F., Bohuon C., Bellet D. Evaluation of protocols for purification of mouse monoclonal antibodies. Yield and purity in two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Jun 10;90(1):25–37. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90379-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews D. E. Stable isotope methodologies in studying human amino acid and protein metabolism. Ital J Gastroenterol. 1993 Feb-Mar;25(2):72–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. T., Margen S. Wine versus ethanol in human nutrition. I. Nitrogen and calorie balance. Am J Clin Nutr. 1976 Oct;29(10):1093–1103. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/29.10.1093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire E. A., Helderman J. H., Tobin J. D., Andres R., Berman M. Effects of arterial versus venous sampling on analysis of glucose kinetics in man. J Appl Physiol. 1976 Oct;41(4):565–573. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1976.41.4.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meguid M. M., Matthews D. E., Bier D. M., Meredith C. N., Soeldner J. S., Young V. R. Leucine kinetics at graded leucine intakes in young men. Am J Clin Nutr. 1986 May;43(5):770–780. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/43.5.770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meguid M. M., Matthews D. E., Bier D. M., Meredith C. N., Young V. R. Valine kinetics at graded valine intakes in young men. Am J Clin Nutr. 1986 May;43(5):781–786. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/43.5.781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meredith C. N., Wen Z. M., Bier D. M., Matthews D. E., Young V. R. Lysine kinetics at graded lysine intakes in young men. Am J Clin Nutr. 1986 May;43(5):787–794. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/43.5.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell M. C., Herlong H. F. Alcohol and nutrition: caloric value, bioenergetics, and relationship to liver damage. Annu Rev Nutr. 1986;6:457–474. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.06.070186.002325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley R. H., Murphy S. M. Effects of ethanol on amino acid transport in basolateral liver plasma membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1989 Mar;256(3 Pt 1):G458–G465. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.256.3.G458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mørland J., Bessesen A., Svendsen L. Incorporation of labelled amino acids into proteins of isolated parenchymal and nonparenchymal rat liver cells in the absence and presence of ethanol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 27;561(2):464–474. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90154-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair K. S., Halliday D., Griggs R. C. Leucine incorporation into mixed skeletal muscle protein in humans. Am J Physiol. 1988 Feb;254(2 Pt 1):E208–E213. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.254.2.E208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REDDY V., SRIKANTIA S. G. ANTIBODY RESPONSE IN KWASHIORKOR. Indian J Med Res. 1964 Nov;52:1154–1158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinus J. F., Heymsfield S. B., Wiskind R., Casper K., Galambos J. T. Ethanol: relative fuel value and metabolic effects in vivo. Metabolism. 1989 Feb;38(2):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(89)90251-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild M. A., Oratz M., Schreiber S. S. Alcohol, amino acids, and albumin synthesis. Gastroenterology. 1974 Dec;67(6):1200–1213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwenk W. F., Beaufrere B., Haymond M. W. Use of reciprocal pool specific activities to model leucine metabolism in humans. Am J Physiol. 1985 Dec;249(6 Pt 1):E646–E650. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.249.6.E646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwenk W. F., Rubanyi E., Haymond M. W. Effect of a protein synthetic inhibitor on in vivo estimates of protein synthesis in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1987 May;252(5 Pt 1):E595–E598. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.252.5.E595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw S., Lieber C. S. Plasma amino acid abnormalities in the alcoholic: respective role of alcohol, nutrition, and liver injury. Gastroenterology. 1978 Apr;74(4):677–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelmet J. J., Reichard G. A., Skutches C. L., Hoeldtke R. D., Owen O. E., Boden G. Ethanol causes acute inhibition of carbohydrate, fat, and protein oxidation and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1137–1145. doi: 10.1172/JCI113428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorrell M. F., Nauss J. M., Donohue T. M., Jr, Tuma D. J. Effects of chronic ethanol administration on hepatic glycoprotein secretion in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1983 Mar;84(3):580–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanko R. T., Morse E. L., Adibi S. A. Prevention of effects of ethanol on amino acid concentrations in plasma and tissues by hepatic lipotropic factors in rats. Gastroenterology. 1979 Jan;76(1):132–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suter P. M., Schutz Y., Jequier E. The effect of ethanol on fat storage in healthy subjects. N Engl J Med. 1992 Apr 9;326(15):983–987. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199204093261503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan S., Pacy P. J., Wenham D., Halliday D. Very-low-density lipoprotein-apolipoprotein B turnover studies in normal subjects: a stable isotope study. Biochem Soc Trans. 1990 Dec;18(6):1192–1193. doi: 10.1042/bst0181192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whicher J. T., Warren C., Chambers R. E. Immunochemical assays for immunoglobulins. Ann Clin Biochem. 1984 Mar;21(Pt 2):78–91. doi: 10.1177/000456328402100202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao X. H., Wen Z. M., Meredith C. N., Matthews D. E., Bier D. M., Young V. R. Threonine kinetics at graded threonine intakes in young men. Am J Clin Nutr. 1986 May;43(5):795–802. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/43.5.795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



