Abstract
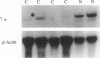
We investigated the effect of cholesterol feeding on plasma cholesterol concentrations, hepatic activities and mRNA levels of HMG-CoA reductase and cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase and hepatic LDL receptor function and mRNA levels in 23 New Zealand White (NZW) and 17 Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic (WHHL) rabbits. Plasma cholesterol concentrations were 9.9 times greater in WHHL than NZW rabbits and rose significantly in both groups when cholesterol was fed. Baseline liver cholesterol levels were 50% higher but rose only 26% in WHHL as compared with 3.6-fold increase with the cholesterol diet in NZW rabbits. In both rabbit groups, hepatic total HMG-CoA reductase activity was similar and declined > 60% without changing enzyme mRNA levels after cholesterol was fed. In NZW rabbits, cholesterol feeding inhibited LDL receptor function but not mRNA levels. As expected, receptor-mediated LDL binding was reduced in WHHL rabbits. Hepatic cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase activity and mRNA levels were 2.8 and 10.4 times greater in NZW than WHHL rabbits. Unexpectedly, cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase activity was reduced 53% and mRNA levels were reduced 79% in NZW rabbits with 2% cholesterol feeding. These results demonstrate that WHHL as compared with NZW rabbits have markedly elevated plasma and higher liver cholesterol concentrations, less hepatic LDL receptor function, and very low hepatic cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase activity and mRNA levels. Feeding cholesterol to NZW rabbits increased plasma and hepatic concentrations greatly, inhibited LDL receptor-mediated binding, and unexpectedly suppressed cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase activity and mRNA to minimum levels similar to WHHL rabbits. Dietary cholesterol accumulates in the plasma of NZW rabbits, and WHHL rabbits are hypercholesterolemic because reduced LDL receptor function is combined with decreased catabolism of cholesterol to bile acids.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beynen A. C., Katan M. B., Van Zutphen L. F. Hypo- and hyperresponders: individual differences in the response of serum cholesterol concentration to changes in diet. Adv Lipid Res. 1987;22:115–171. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-024922-0.50008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkhem I., Eggertsen G., Andersson U. On the mechanism of stimulation of cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase by dietary cholesterol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Oct 1;1085(3):329–335. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(91)90137-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Lipoprotein receptors in the liver. Control signals for plasma cholesterol traffic. J Clin Invest. 1983 Sep;72(3):743–747. doi: 10.1172/JCI111044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M., Kita T., Suckling K. E., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Cholesterol synthesis in vivo and in vitro in the WHHL rabbit, an animal with defective low density lipoprotein receptors. J Lipid Res. 1983 Apr;24(4):469–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly T. M., Kelsey S. F., Levine D. M., Parker T. S. Control of variance in experimental studies of hyperlipidemia using the WHHL rabbit. J Lipid Res. 1991 Jul;32(7):1089–1098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George R., Davis P. J., Luong L., Poznansky M. J. Cholesterol-mediated regulation of HMG-CoA reductase in microsomes from human skin fibroblasts and rat liver. Biochem Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;68(3):674–679. doi: 10.1139/o90-097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Basu S. K., Brown M. S. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of low-density lipoprotein in cultured cells. Methods Enzymol. 1983;98:241–260. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)98152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Progress in understanding the LDL receptor and HMG-CoA reductase, two membrane proteins that regulate the plasma cholesterol. J Lipid Res. 1984 Dec 15;25(13):1450–1461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELLSTROEM K. ON THE BILE ACID AND NEUTRAL FECAL STEROID EXCRETION IN MAN AND RABBITS FOLLOWING CHOLESTEROL FEEDING. BILE ACIDS AND STEROIDS 150. Acta Physiol Scand. 1965 Jan-Feb;63:21–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1965.tb04038.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton J. D., Cuthbert J. A., Spady D. K. Dietary fatty acids regulate hepatic low density lipoprotein (LDL) transport by altering LDL receptor protein and mRNA levels. J Clin Invest. 1993 Aug;92(2):743–749. doi: 10.1172/JCI116645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek D. F., Andersson S., Slaughter C. A., Russell D. W. Cloning and regulation of cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase, the rate-limiting enzyme in bile acid biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8190–8197. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koelz H. R., Sherrill B. C., Turley S. D., Dietschy J. M. Correlation of low and high density lipoprotein binding in vivo with rates of lipoprotein degradation in the rat. A comparison of lipoproteins of rat and human origin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8061–8072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo T., Watanabe Y. A heritable hyperlipemic rabbit. Jikken Dobutsu. 1975 Jul;24(3):89–94. doi: 10.1538/expanim1957.24.3_89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovanen P. T., Brown M. S., Basu S. K., Bilheimer D. W., Goldstein J. L. Saturation and suppression of hepatic lipoprotein receptors: a mechanism for the hypercholesterolemia of cholesterol-fed rabbits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1396–1400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovanen P. T., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Increased binding of low density lipoprotein to liver membranes from rats treated with 17 alpha-ethinyl estradiol. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11367–11373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause B. R., Pape M. E., Kieft K., Auerbach B., Bisgaier C. L., Homan R., Newton R. S. ACAT inhibition decreases LDL cholesterol in rabbits fed a cholesterol-free diet. Marked changes in LDL cholesterol without changes in LDL receptor mRNA abundance. Arterioscler Thromb. 1994 Apr;14(4):598–604. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.14.4.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ness G. C., Keller R. K., Pendleton L. C. Feedback regulation of hepatic 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase activity by dietary cholesterol is not due to altered mRNA levels. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):14854–14857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen L. B., Shefer S., Salen G., Horak I., Tint G. S., McNamara D. J. The effect of abnormal plasma and cellular sterol content and composition on low density lipoprotein uptake and degradation by monocytes and lymphocytes in sitosterolemia with xanthomatosis. Metabolism. 1988 Apr;37(4):346–351. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(88)90134-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen L. B., Shefer S., Salen G., Ness G. C., Tint G. S., Zaki F. G., Rani I. A molecular defect in hepatic cholesterol biosynthesis in sitosterolemia with xanthomatosis. J Clin Invest. 1990 Sep;86(3):923–931. doi: 10.1172/JCI114794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandak W. M., Li Y. C., Chiang J. Y., Studer E. J., Gurley E. C., Heuman D. M., Vlahcevic Z. R., Hylemon P. B. Regulation of cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase mRNA and transcriptional activity by taurocholate and cholesterol in the chronic biliary diverted rat. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3416–3421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poorman J. A., Buck R. A., Smith S. A., Overturf M. L., Loose-Mitchell D. S. Bile acid excretion and cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase expression in hypercholesterolemia-resistant rabbits. J Lipid Res. 1993 Oct;34(10):1675–1685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross A. C., Zilversmit D. B. Chylomicron remnant cholesteryl esters as the major constituent of very low density lipoproteins in plasma of cholesterol-fed rabbits. J Lipid Res. 1977 Mar;18(2):169–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudel L., Deckelman C., Wilson M., Scobey M., Anderson R. Dietary cholesterol and downregulation of cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase and cholesterol absorption in African green monkeys. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jun;93(6):2463–2472. doi: 10.1172/JCI117255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salen G., Ahrens E. H., Jr, Grundy S. M. Metabolism of beta-sitosterol in man. J Clin Invest. 1970 May;49(5):952–967. doi: 10.1172/JCI106315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shefer S., Hauser S., Bekersky I., Mosbach E. H. Biochemical site of regulation of bile acid biosynthesis in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1970 Sep;11(5):404–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shefer S., Nguyen L. B., Salen G., Ness G. C., Chowdhary I. R., Lerner S., Batta A. K., Tint G. S. Differing effects of cholesterol and taurocholate on steady state hepatic HMG-CoA reductase and cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase activities and mRNA levels in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1992 Aug;33(8):1193–1200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spady D. K., Cuthbert J. A. Regulation of hepatic sterol metabolism in the rat. Parallel regulation of activity and mRNA for 7 alpha-hydroxylase but not 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase or low density lipoprotein receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5584–5591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spady D. K., Dietschy J. M. Sterol synthesis in vivo in 18 tissues of the squirrel monkey, guinea pig, rabbit, hamster, and rat. J Lipid Res. 1983 Mar;24(3):303–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y. Serial inbreeding of rabbits with hereditary hyperlipidemia (WHHL-rabbit). Atherosclerosis. 1980 Jun;36(2):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(80)90234-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu G., Salen G., Shefer S., Batta A. K., Ness G. C., Nguyen L. B., Zhao Z., Chen T. S., Niemann W., Tint G. S. Different feedback regulation of hepatic cholesterol and bile acid synthesis by glycodeoxycholic acid in rabbits. Gastroenterology. 1993 Oct;105(4):1192–1199. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90967-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]