Abstract
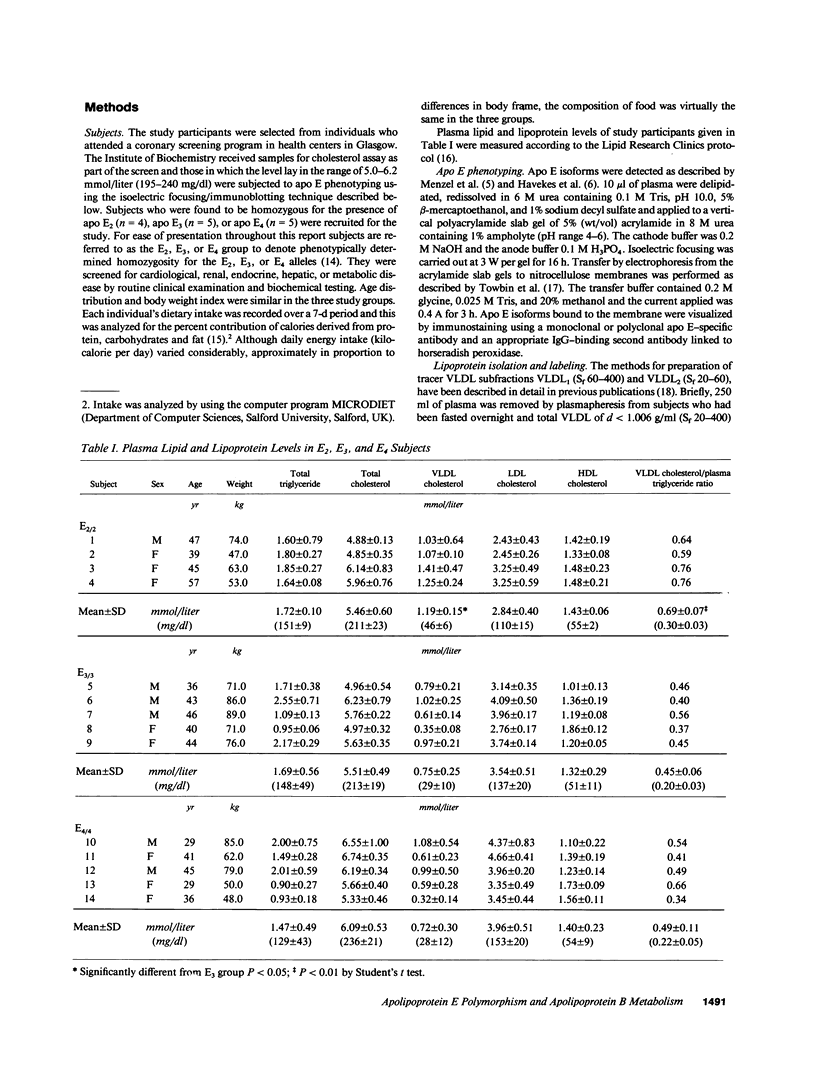
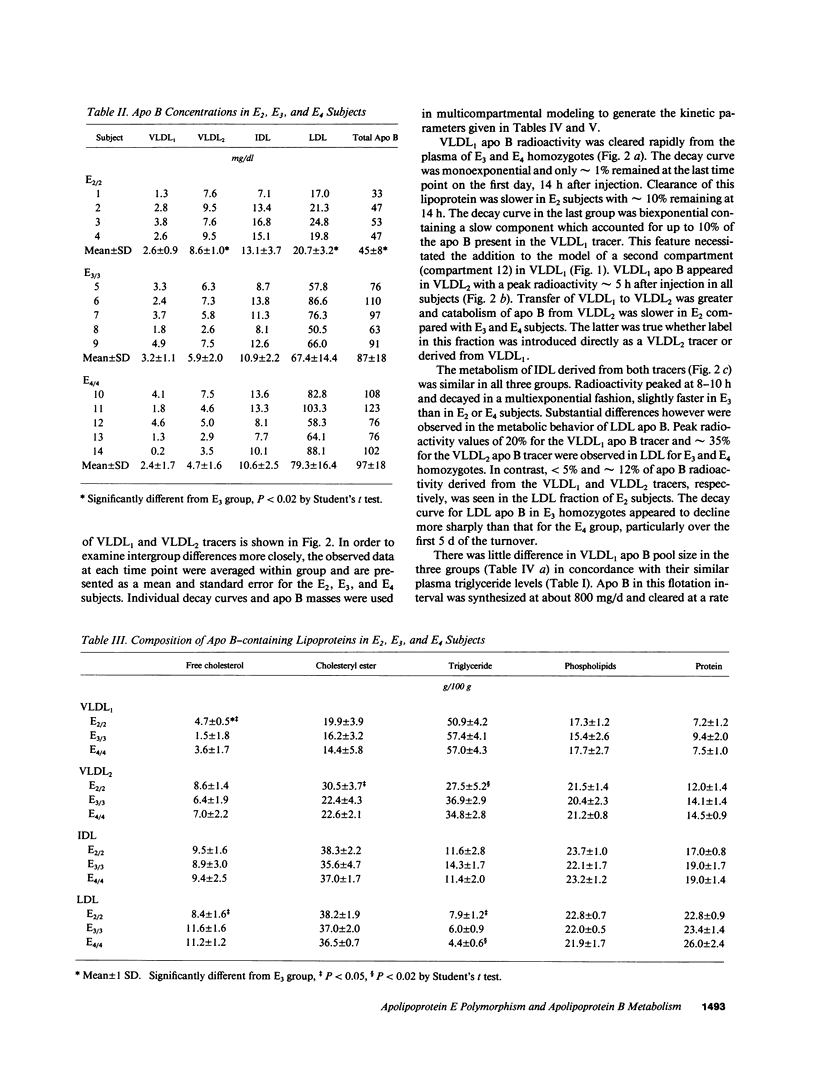
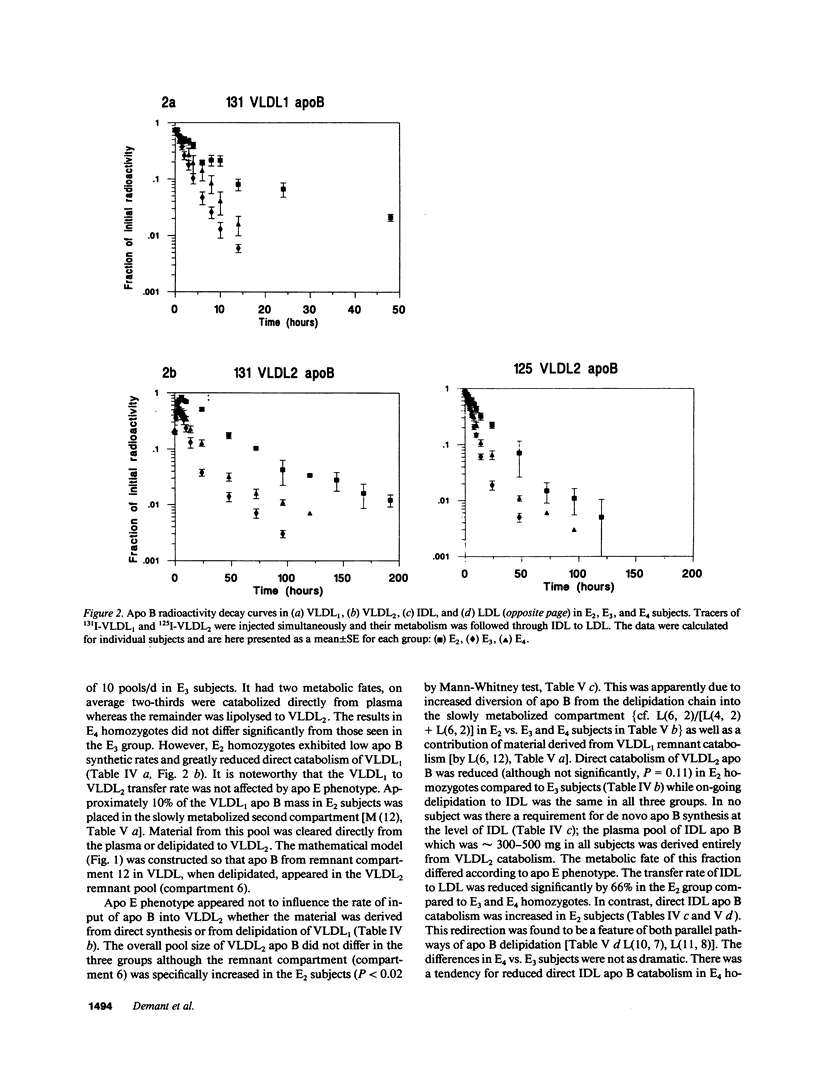
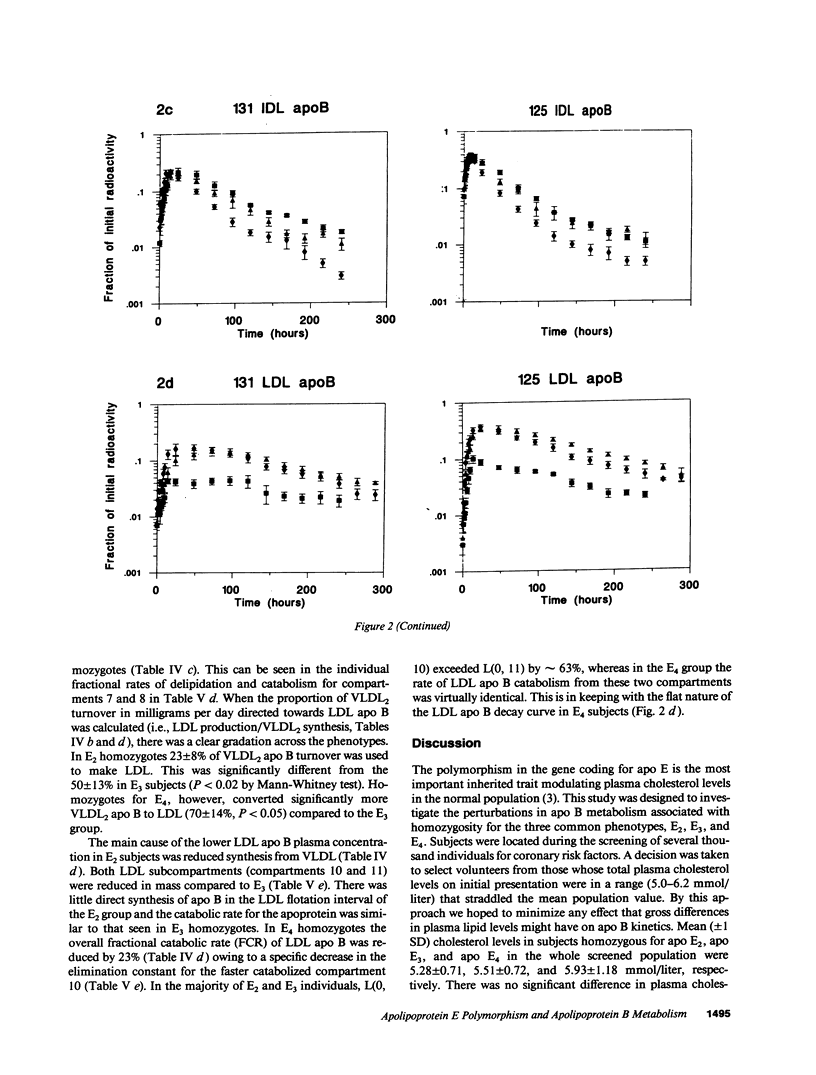
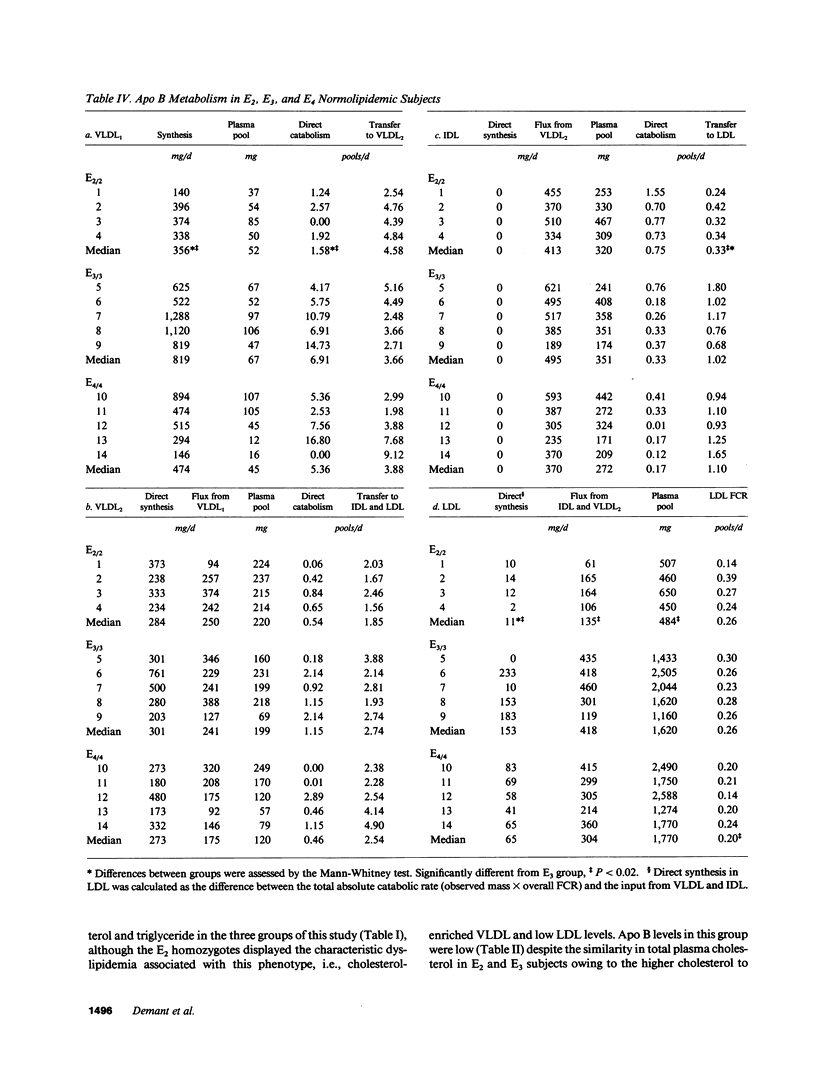
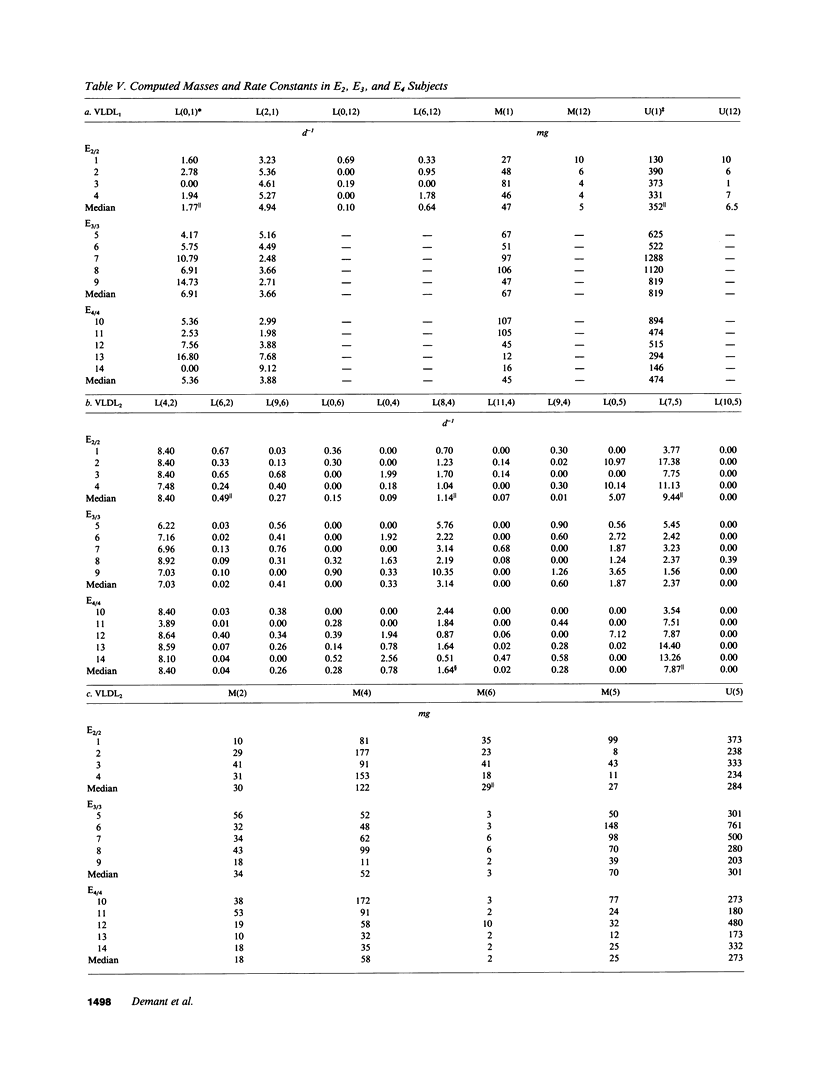
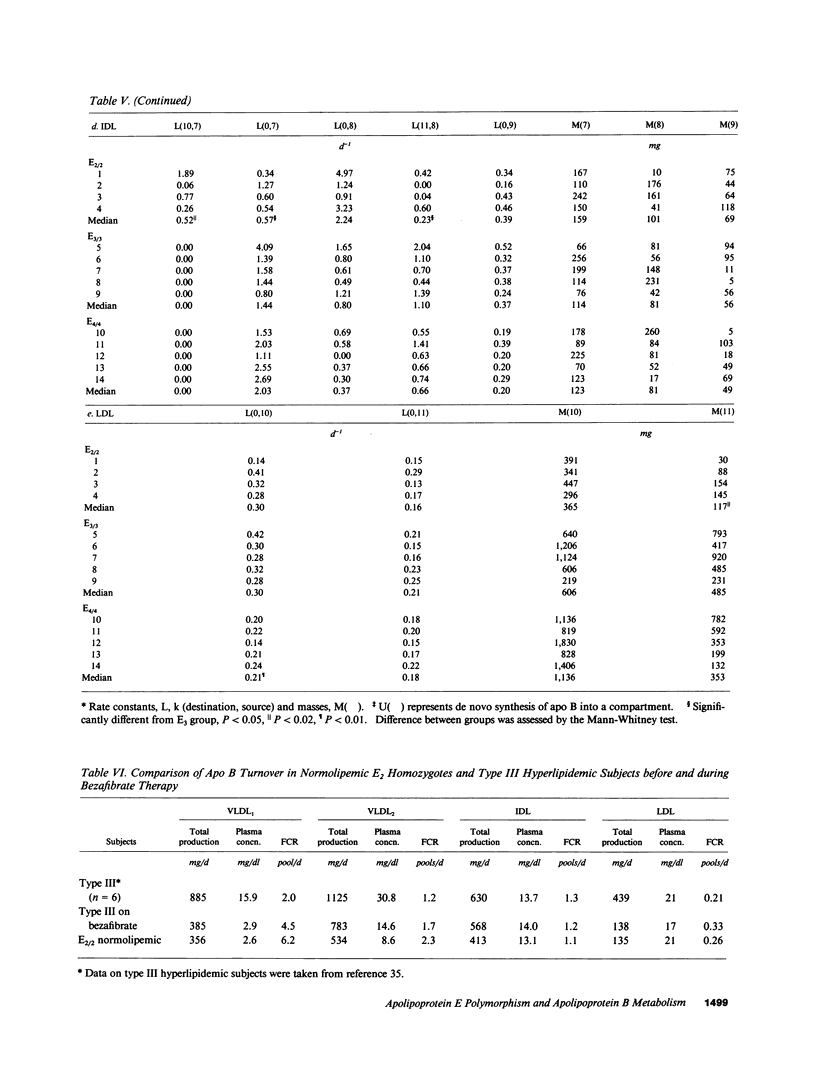
This study examined apolipoprotein (apo) B metabolism in normolipemic subjects homozygous for the apo E2 (n = 4), apo E3 (n = 5), or apo E4 (n = 5) phenotype. Radioiodinated very low density lipoprotein (VLDL1) (ultracentrifuge flotation rate [Sf] 60-400) and VLDL2 (Sf 20-60) were injected into volunteers and the conversion of apo B was followed through intermediate density lipoprotein (IDL) to low density lipoprotein (LDL). Subjects homozygous for E3 converted approximately 50% of LVDL2 to LDL, the remainder being lost by direct catabolism. Those with the E2 phenotype produced less VLDL1, but converted more of it to VLDL2 (compared to E3 subjects). They displayed a characteristic dyslipidemia with the presence of slowly catabolized VLDL1 and VLDL2 remnants. LDL levels were low owing to increased direct catabolism of VLDL2 and IDL and a reduced efficiency of delipidation; only 25% of VLDL2 apo B was directed to LDL production. In contrast, E4 subjects converted more VLDL2 apo B to LDL than E3 subjects. About 70% of VLDL2 apo B was found in LDL; direct catabolism of VLDL and IDL was reduced as was the fractional catabolic rate of LDL (0.2 vs. 0.26 in E3 subjects). These changes in the VLDL----IDL----LDL metabolic cascade can in part be explained by alterations in hepatic LDL receptors with E2 subjects having higher and E4 subjects lower activities than those in E3 homozygotes.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angelin B., Holmquist L., Leijd B., Einarsson K. Bile acid metabolism in familial dysbetalipoproteinaemia: studies in subjects with the apolipoprotein E-2/2 phenotype. Eur J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;20(2):143–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1990.tb02261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman M., Hall M., 3rd, Levy R. I., Eisenberg S., Bilheimer D. W., Phair R. D., Goebel R. H. Metabolsim of apoB and apoC lipoproteins in man: kinetic studies in normal and hyperlipoproteininemic subjects. J Lipid Res. 1978 Jan;19(1):38–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilheimer D. W., Eisenberg S., Levy R. I. The metabolism of very low density lipoprotein proteins. I. Preliminary in vitro and in vivo observations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 21;260(2):212–221. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley W. A., Hwang S. L., Karlin J. B., Lin A. H., Prasad S. C., Gotto A. M., Jr, Gianturco S. H. Low-density lipoprotein receptor binding determinants switch from apolipoprotein E to apolipoprotein B during conversion of hypertriglyceridemic very-low-density lipoprotein to low-density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14728–14735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenninkmeijer B. J., Stuyt P. M., Demacker P. N., Stalenhoef A. F., van 't Laar A. Catabolism of chylomicron remnants in normolipidemic subjects in relation to the apoprotein E phenotype. J Lipid Res. 1987 Apr;28(4):361–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davignon J., Gregg R. E., Sing C. F. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis. 1988 Jan-Feb;8(1):1–21. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.8.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demant T., Carlson L. A., Holmquist L., Karpe F., Nilsson-Ehle P., Packard C. J., Shepherd J. Lipoprotein metabolism in hepatic lipase deficiency: studies on the turnover of apolipoprotein B and on the effect of hepatic lipase on high density lipoprotein. J Lipid Res. 1988 Dec;29(12):1603–1611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehnholm C., Mahley R. W., Chappell D. A., Weisgraber K. H., Ludwig E., Witztum J. L. Role of apolipoprotein E in the lipolytic conversion of beta-very low density lipoproteins to low density lipoproteins in type III hyperlipoproteinemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5566–5570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eto M., Sato T., Watanabe K., Iwashima Y., Makino I. Effects of probucol on plasma lipids and lipoproteins in familial hypercholesterolemic patients with and without apolipoprotein E4. Atherosclerosis. 1990 Sep;84(1):49–53. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(90)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabelli C., Gregg R. E., Zech L. A., Manzato E., Brewer H. B., Jr Abnormal low density lipoprotein metabolism in apolipoprotein E deficiency. J Lipid Res. 1986 Mar;27(3):326–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg I. J., Le N. A., Ginsberg H. N., Krauss R. M., Lindgren F. T. Lipoprotein metabolism during acute inhibition of lipoprotein lipase in the cynomolgus monkey. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):561–568. doi: 10.1172/JCI113354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havekes L. M., de Knijff P., Beisiegel U., Havinga J., Smit M., Klasen E. A rapid micromethod for apolipoprotein E phenotyping directly in serum. J Lipid Res. 1987 Apr;28(4):455–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz J., Hamann U., Rogne S., Myklebost O., Gausepohl H., Stanley K. K. Surface location and high affinity for calcium of a 500-kd liver membrane protein closely related to the LDL-receptor suggest a physiological role as lipoprotein receptor. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4119–4127. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03306.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James R. W., Martin B., Pometta D., Fruchart J. C., Duriez P., Puchois P., Farriaux J. P., Tacquet A., Demant T., Clegg R. J. Apolipoprotein B metabolism in homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. J Lipid Res. 1989 Feb;30(2):159–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. P., Sata T., Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J. Apoprotein composition of very low density lipoproteins of human serum. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1622–1634. doi: 10.1172/JCI108245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kesäniemi Y. A., Ehnholm C., Miettinen T. A. Intestinal cholesterol absorption efficiency in man is related to apoprotein E phenotype. J Clin Invest. 1987 Aug;80(2):578–581. doi: 10.1172/JCI113107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowal R. C., Herz J., Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Opposing effects of apolipoproteins E and C on lipoprotein binding to low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10771–10779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krul E. S., Tikkanen M. J., Cole T. G., Davie J. M., Schonfeld G. Roles of apolipoproteins B and E in the cellular binding of very low density lipoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1985 Feb;75(2):361–369. doi: 10.1172/JCI111708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Innerarity T. L., Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H. Plasma lipoproteins: apolipoprotein structure and function. J Lipid Res. 1984 Dec 1;25(12):1277–1294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packard C. J., Boag D. E., Clegg R., Bedford D., Shepherd J. Effects of 1,2-cyclohexanedione modification on the metabolism of very low density lipoprotein apolipoprotein B: potential role of receptors in intermediate density lipoprotein catabolism. J Lipid Res. 1985 Sep;26(9):1058–1067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packard C. J., Clegg R. J., Dominiczak M. H., Lorimer A. R., Shepherd J. Effects of bezafibrate on apolipoprotein B metabolism in type III hyperlipoproteinemic subjects. J Lipid Res. 1986 Sep;27(9):930–938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packard C. J., Munro A., Lorimer A. R., Gotto A. M., Shepherd J. Metabolism of apolipoprotein B in large triglyceride-rich very low density lipoproteins of normal and hypertriglyceridemic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1984 Dec;74(6):2178–2192. doi: 10.1172/JCI111644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer E. J., Gregg R. E., Ghiselli G., Forte T. M., Ordovas J. M., Zech L. A., Brewer H. B., Jr Familial apolipoprotein E deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1206–1219. doi: 10.1172/JCI112704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd J., Packard C. J., Grundy S. M., Yeshurun D., Gotto A. M., Jr, Taunton O. D. Effects of saturated and polyunsaturated fat diets on the chemical composition and metabolism of low density lipoproteins in man. J Lipid Res. 1980 Jan;21(1):91–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalenhoef A. F., Malloy M. J., Kane J. P., Havel R. J. Metabolism of apolipoproteins B-48 and B-100 of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins in normal and lipoprotein lipase-deficient humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1839–1843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tikkanen M. J., Huttunen J. K., Ehnholm C., Pietinen P. Apolipoprotein E4 homozygosity predisposes to serum cholesterol elevation during high fat diet. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 Mar-Apr;10(2):285–288. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.2.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner P. R., Cortese C., Wootton R., Marenah C., Miller N. E., Lewis B. Plasma apolipoprotein B metabolism in familial type III dysbetalipoproteinaemia. Eur J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;15(2):100–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1985.tb00152.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Hees M., Steinmetz A. Polymorphism of apolipoprotein E and occurrence of dysbetalipoproteinaemia in man. Nature. 1977 Oct 13;269(5629):604–607. doi: 10.1038/269604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G. Isolation and partial characterization of an arginine-rich apolipoprotein from human plasma very-low-density lipoproteins: apolipoprotein E. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1975 Jul;356(7):1113–1121. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1975.356.2.1113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub M. S., Eisenberg S., Breslow J. L. Dietary fat clearance in normal subjects is regulated by genetic variation in apolipoprotein E. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1571–1577. doi: 10.1172/JCI113243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Abnormal lipoprotein receptor-binding activity of the human E apoprotein due to cysteine-arginine interchange at a single site. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2518–2521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L. Human very low density lipoprotein apolipoprotein E isoprotein polymorphism is explained by genetic variation and posttranslational modification. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):1033–1041. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L., Utermann G., Mahley R. W., Weisgraber K. H., Havel R. J., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Schonfeld G., Hazzard W. R. Proposed nomenclature of apoE isoproteins, apoE genotypes, and phenotypes. J Lipid Res. 1982 Aug;23(6):911–914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



