Abstract
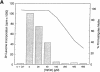
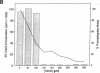
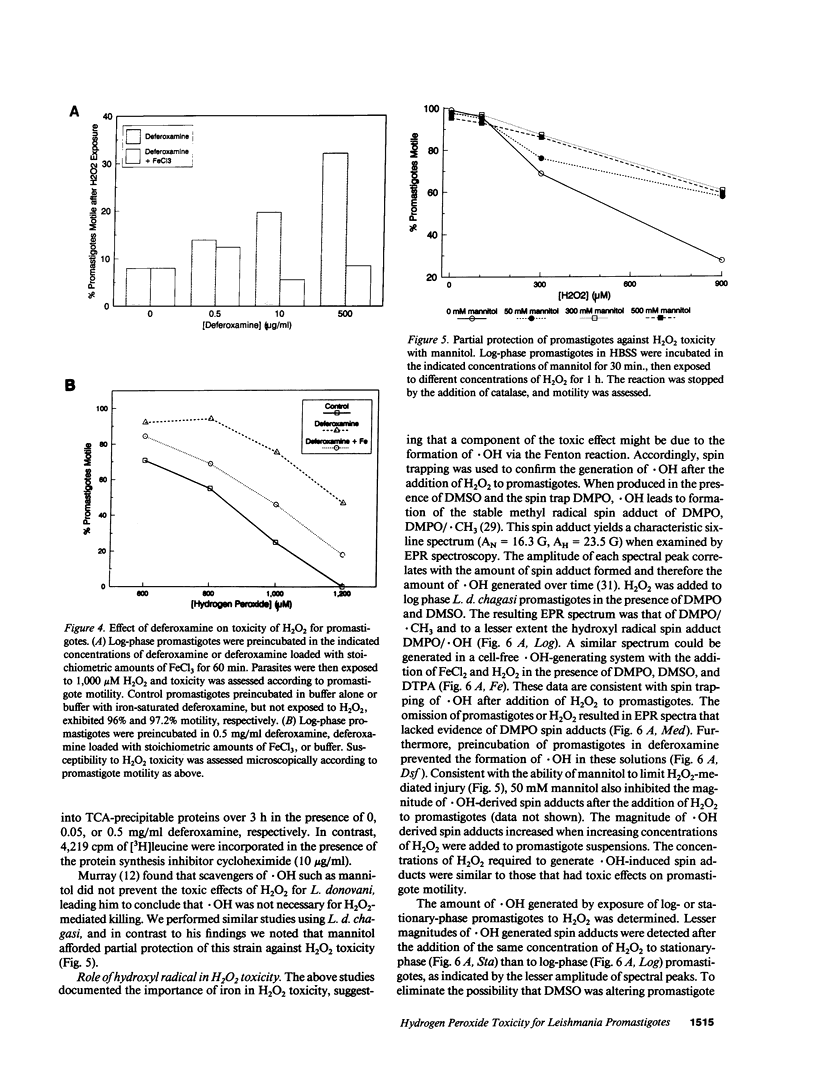
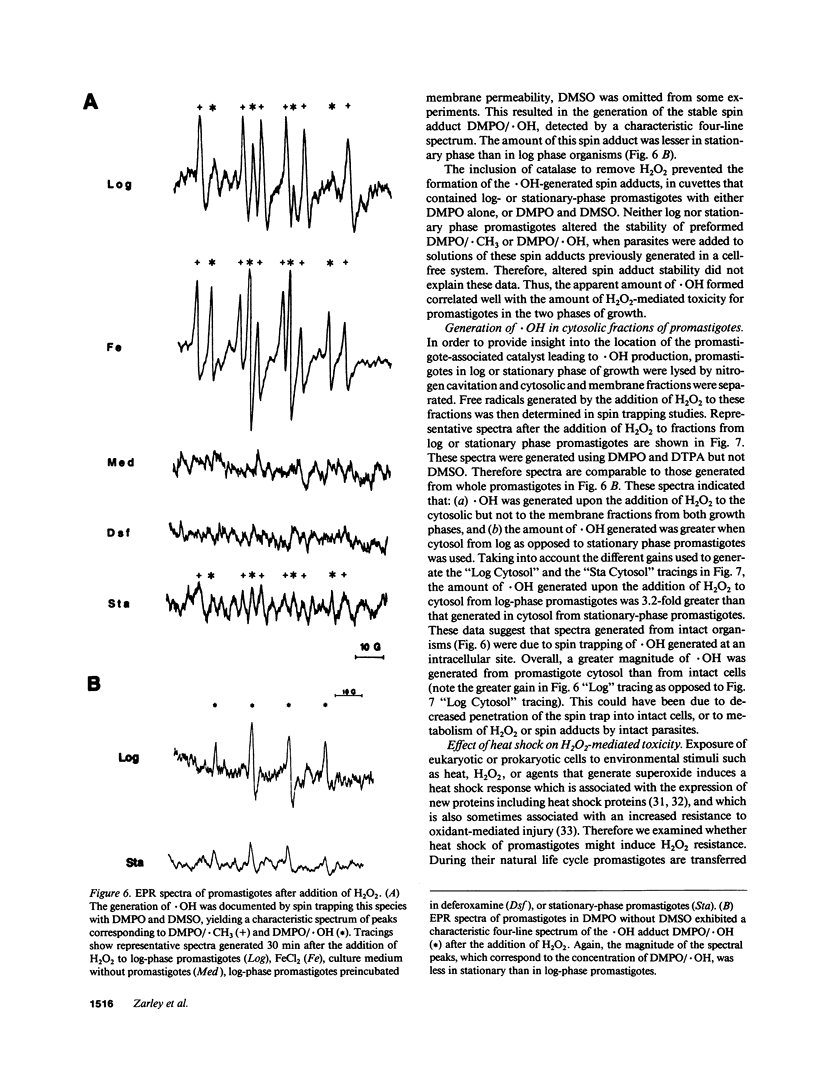
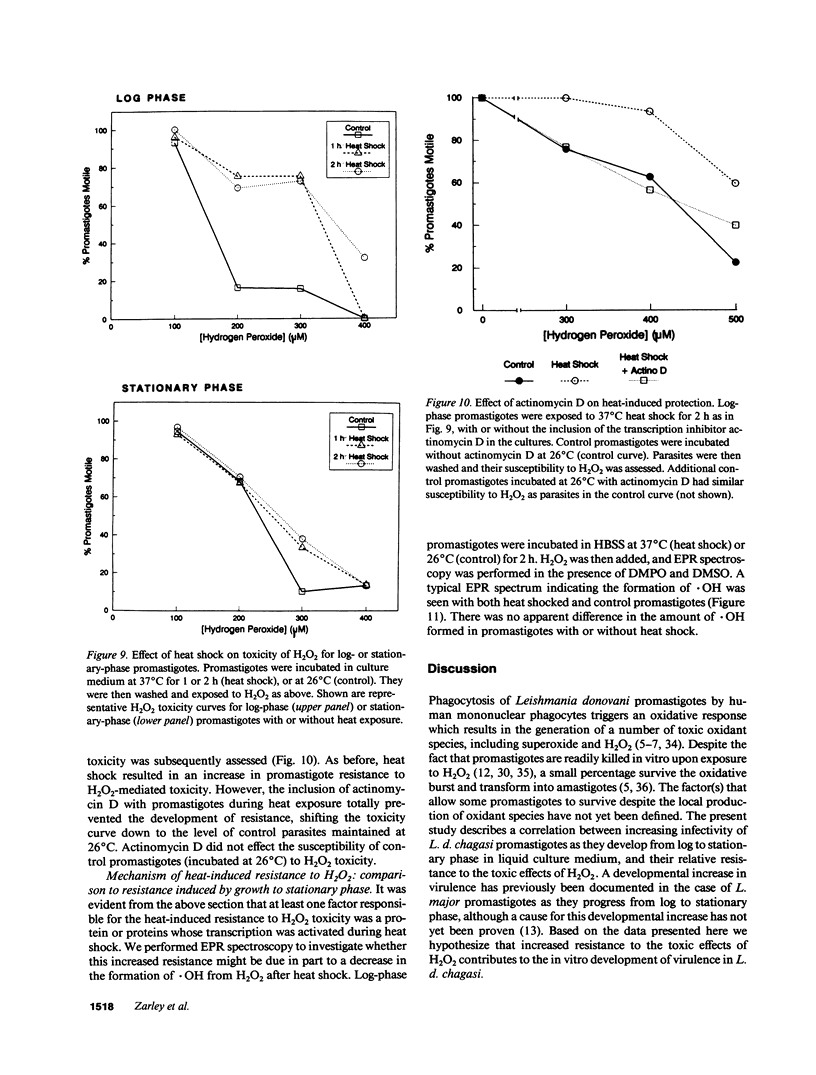
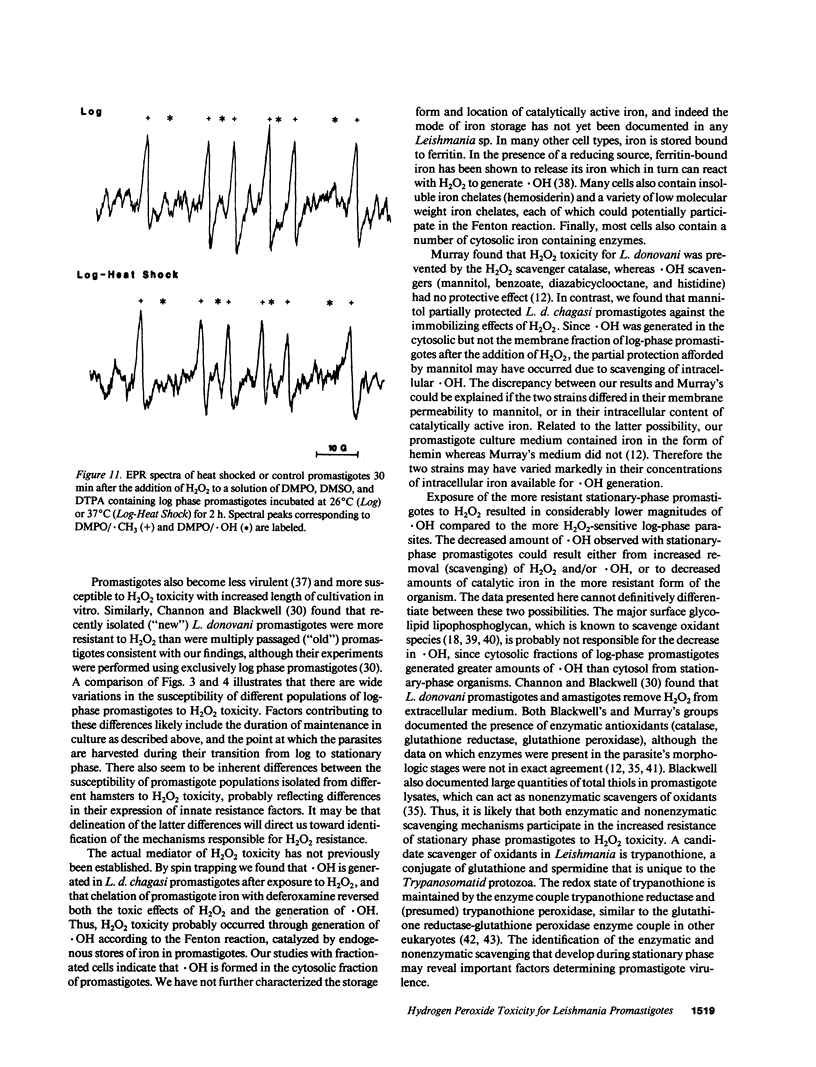
Leishmania must survive despite exposure to the toxic oxidant hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) during phagocytosis by macrophages. We investigated the mechanism of H2O2 toxicity for L. donovani chagasi promastigotes, and factors responsible for their relative H2O2 resistance. There was a dose-dependent toxic effect of H2O2 for promastigotes isolated during logarithmic phase of growth. In contrast, stationary phase promastigotes were less susceptible to H2O2 toxicity, and more infectious for BALB/c mice. By spin trapping we found that hydroxyl radical (.OH) was generated after exposure of promastigotes to H2O2, and the amount of .OH was greater with log-phase than with stationary-phase promastigotes. .OH was generated after the addition of H2O2 to the cytosol but not the membranes of fractionated promastigotes, and the magnitude of .OH was greater in log than in stationary promastigote cytosol. Deferoxamine inhibition suggested that intracellular promastigote iron catalyzes .OH formation via the Fenton reaction. Furthermore, exposure of log-phase promastigotes to heat shock induced a relative H2O2-resistant state, which was not associated with a decrease in .OH formation but which required ongoing transcription. Thus, growth to stationary phase and heat shock both induce a state of relative H2O2 resistance, but these are probably due to different resistance mechanisms.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackwell J. M., Ezekowitz R. A., Roberts M. B., Channon J. Y., Sim R. B., Gordon S. Macrophage complement and lectin-like receptors bind Leishmania in the absence of serum. J Exp Med. 1985 Jul 1;162(1):324–331. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britigan B. E., Rosen G. M., Chai Y., Cohen M. S. Do human neutrophils make hydroxyl radical? Determination of free radicals generated by human neutrophils activated with a soluble or particulate stimulus using electron paramagnetic resonance spectrometry. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4426–4431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier N. A., Heffron F. Induction of Salmonella stress proteins upon infection of macrophages. Science. 1990 May 11;248(4956):730–732. doi: 10.1126/science.1970672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmüller-Rouiller Y., Mauël J. Impairment of the oxidative metabolism of mouse peritoneal macrophages by intracellular Leishmania spp. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):587–593. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.587-593.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmüller Y., Mauel J. Studies on the mechanisms of macrophage activation: possible involvement of oxygen metabolites in killing of Leishmania enrietti by activated mouse macrophages. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1981 Mar;29(3):181–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron M. L., Granger D. L., Weinberg J. B., Kozumbo W. J., Koren H. S. Human alveolar and peritoneal macrophages mediate fungistasis independently of L-arginine oxidation to nitrite or nitrate. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Dec;142(6 Pt 1):1313–1319. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.6_Pt_1.1313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan J., Fujiwara T., Brennan P., McNeil M., Turco S. J., Sibille J. C., Snapper M., Aisen P., Bloom B. R. Microbial glycolipids: possible virulence factors that scavenge oxygen radicals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2453–2457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Channon J. Y., Blackwell J. M. A study of the sensitivity of Leishmania donovani promastigotes and amastigotes to hydrogen peroxide. I. Differences in sensitivity correlate with parasite-mediated removal of hydrogen peroxide. Parasitology. 1985 Oct;91(Pt 2):197–206. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000057309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Channon J. Y., Blackwell J. M. A study of the sensitivity of Leishmania donovani promastigotes and amastigotes to hydrogen peroxide. II. Possible mechanisms involved in protective H2O2 scavenging. Parasitology. 1985 Oct;91(Pt 2):207–217. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000057310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descoteaux A., Turco S. J., Sacks D. L., Matlashewski G. Leishmania donovani lipophosphoglycan selectively inhibits signal transduction in macrophages. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 15;146(8):2747–2753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixit V. M., Green S., Sarma V., Holzman L. B., Wolf F. W., O'Rourke K., Ward P. A., Prochownik E. V., Marks R. M. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induction of novel gene products in human endothelial cells including a macrophage-specific chemotaxin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2973–2978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairlamb A. H., Henderson G. B., Cerami A. Trypanothione is the primary target for arsenical drugs against African trypanosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2607–2611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. J., Meltzer M. S., Hibbs J. B., Jr, Nacy C. A. Activated macrophages destroy intracellular Leishmania major amastigotes by an L-arginine-dependent killing mechanism. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):278–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. T., Demple B. A global response induced in Escherichia coli by redox-cycling agents overlaps with that induced by peroxide stress. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3933–3939. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3933-3939.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell B., Gutteridge J. M. Oxygen free radicals and iron in relation to biology and medicine: some problems and concepts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 May 1;246(2):501–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90305-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imlay J. A., Linn S. DNA damage and oxygen radical toxicity. Science. 1988 Jun 3;240(4857):1302–1309. doi: 10.1126/science.3287616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins D. E., Schultz J. E., Matin A. Starvation-induced cross protection against heat or H2O2 challenge in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):3910–3914. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.3910-3914.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jockers-Scherübl M. C., Schirmer R. H., Krauth-Siegel R. L. Trypanothione reductase from Trypanosoma cruzi. Catalytic properties of the enzyme and inhibition studies with trypanocidal compounds. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Mar 15;180(2):267–272. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14643.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. D., Jr, Mei B., Cohn Z. A. The separation, long-term cultivation, and maturation of the human monocyte. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1613–1626. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz S., Rossi J., Petko L., Lindquist S. An ancient developmental induction: heat-shock proteins induced in sporulation and oogenesis. Science. 1986 Mar 7;231(4742):1154–1157. doi: 10.1126/science.3511530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kweider M., Lemesre J. L., Darcy F., Kusnierz J. P., Capron A., Santoro F. Infectivity of Leishmania braziliensis promastigotes is dependent on the increasing expression of a 65,000-dalton surface antigen. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 1;138(1):299–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathigra R. B., Butcher P. D., Garbe T. R., Young D. B. Heat shock proteins as virulence factors of pathogens. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991;167:125–143. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75875-1_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence F., Robert-Gero M. Induction of heat shock and stress proteins in promastigotes of three Leishmania species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4414–4417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Atkinson B. L., Giannini S. H., Van der Ploeg L. H. Structure and expression of the hsp 70 gene family of Leishmania major. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9567–9585. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y., Millott S., Parkinson C., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Macrophage killing of Leishmania parasite in vivo is mediated by nitric oxide from L-arginine. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4794–4797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. The heat-shock response. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1151–1191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauël J., Buchmüller-Rouiller Y. Effect of lipopolysaccharide on intracellular killing of Leishmania enriettii and correlation with macrophage oxidative metabolism. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Feb;17(2):203–208. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeely T. B., Turco S. J. Inhibition of protein kinase C activity by the Leishmania donovani lipophosphoglycan. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Oct 29;148(2):653–657. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90926-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Cartelli D. M. Killing of intracellular Leishmania donovani by human mononuclear phagocytes. Evidence for oxygen-dependent and -independent leishmanicidal activity. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):32–44. doi: 10.1172/JCI110972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W. Cell-mediated immune response in experimental visceral leishmaniasis. II. Oxygen-dependent killing of intracellular Leishmania donovani amastigotes. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W. Cellular resistance to protozoal infection. Annu Rev Med. 1986;37:61–69. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.37.020186.000425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W. Interaction of Leishmania with a macrophage cell line. Correlation between intracellular killing and the generation of oxygen intermediates. J Exp Med. 1981 Jun 1;153(6):1690–1695. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.6.1690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W. Susceptibility of Leishmania to oxygen intermediates and killing by normal macrophages. J Exp Med. 1981 May 1;153(5):1302–1315. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.5.1302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. D., Harcus J. L., Roberts D., Donowitz G. R. Differential survival of Leishmania donovani amastigotes in human monocytes. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1994–1999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. D., Harcus J. L., Symes P. H., Romito R., Donowitz G. R. Failure of the phagocytic oxidative response to protect human monocyte-derived macrophages from infection by Leishmania donovani. J Immunol. 1982 Sep;129(3):1282–1286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. D., Steigbigel R. T. Mechanism of lethal effect of human serum upon Leishmania donovani. J Immunol. 1980 Nov;125(5):2195–2201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. D., Wheeler D. A., Harrison L. H., Kay H. D. The immunobiology of leishmaniasis. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5(5):907–927. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.5.907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Speculations on the functions of the major heat shock and glucose-regulated proteins. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):959–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90693-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polla B. S. A role for heat shock proteins in inflammation? Immunol Today. 1988 May;9(5):134–137. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91199-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remaley A. T., Kuhns D. B., Basford R. E., Glew R. H., Kaplan S. S. Leishmanial phosphatase blocks neutrophil O-2 production. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11173–11175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repine J. E., Fox R. B., Berger E. M. Hydrogen peroxide kills Staphylococcus aureus by reacting with staphylococcal iron to form hydroxyl radical. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7094–7096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. G., Talamas-Rohana P. Leishmania and the macrophage: a marriage of inconvenience. Immunol Today. 1989 Oct;10(10):328–333. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90188-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks D. L., Brodin T. N., Turco S. J. Developmental modification of the lipophosphoglycan from Leishmania major promastigotes during metacyclogenesis. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 Sep-Oct;42(2):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90165-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks D. L., Perkins P. V. Identification of an infective stage of Leishmania promastigotes. Science. 1984 Mar 30;223(4643):1417–1419. doi: 10.1126/science.6701528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks D. L., da Silva R. P. The generation of infective stage Leishmania major promastigotes is associated with the cell-surface expression and release of a developmentally regulated glycolipid. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 1;139(9):3099–3106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle S., Campos A. J., Coulson R. M., Spithill T. W., Smith D. F. A family of heat shock protein 70-related genes are expressed in the promastigotes of Leishmania major. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):5081–5095. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.5081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira M., McEwen J. G., Jaffe C. L. Temperature effects on molecular processes which lead to stage differentiation in Leishmania. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2895–2901. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03147.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smejkal R. M., Wolff R., Olenick J. G. Leishmania braziliensis panamensis: increased infectivity resulting from heat shock. Exp Parasitol. 1988 Feb;65(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(88)90101-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ploeg L. H., Giannini S. H., Cantor C. R. Heat shock genes: regulatory role for differentiation in parasitic protozoa. Science. 1985 Jun 21;228(4706):1443–1446. doi: 10.1126/science.4012301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J. Oxygen, ischemia and inflammation. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1986;548:9–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. E., Hardin K. K., Donelson J. E. Expression of the major surface glycoprotein of Leishmania donovani chagasi in virulent and attenuated promastigotes. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 15;143(2):678–684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. E., Hardin K. K. The major concanavalin A-binding surface glycoprotein of Leishmania donovani chagasi promastigotes is involved in attachment to human macrophages. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):265–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. E., Pearson R. D. Evidence that Leishmania donovani utilizes a mannose receptor on human mononuclear phagocytes to establish intracellular parasitism. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4681–4688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. E., Pearson R. D. Roles of CR3 and mannose receptors in the attachment and ingestion of Leishmania donovani by human mononuclear phagocytes. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):363–369. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.363-369.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Silva R., Sacks D. L. Metacyclogenesis is a major determinant of Leishmania promastigote virulence and attenuation. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2802–2806. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2802-2806.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]