Abstract
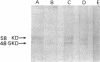
The autoantigen(s) that we have previously described in human glomeruli, recognized in IgA nephropathy, has (have) been identified as mesangial cell in origin. Cultured mesangial cells expressed 48- and 55-kD components binding IgG isotype autoantibodies (IgG-MESCA) present in sera of patients with both IgA nephropathy and Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP). IgG-MESCA were not detected in sera of normals, or patients with other autoimmune-mediated glomerulonephritides: anti-glomerular basement membrane disease, Wegener's granulomatosis, or in IgM-mesangial proliferative disease. Binding specificity was proven by F(ab')2 studies in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and Western blotting, and there was no significant affinity of IgA or IgM immunoglobulins. Fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated IgG from ELISA-positive sera localized to the mesangium and peripheral capillary loops of glomeruli, supporting the belief that the antigen is expressed in normal human renal tissue. However, only about one third of mesangial cells in culture showed affinity for IgG from ELISA-positive sera, suggesting variable expression of the antigen(s) in vitro. The only autoantigen(s) present in glomeruli, and extractable from whole normal glomeruli by the techniques employed, localized on the mesangial cell. In both IgA nephropathy and HSP, autoimmunity was intermittently present, with fluctuating levels of IgG-MESCA detectable in sera. There were positive correlations with the degree of glomerular injury assessed by erythrocyturia and proteinuria in IgA nephropathy, but significance was reached with only the degree of hematuria in HSP. These findings suggest a contributing role in the pathogenesis of the mesangial proliferative lesions and demonstrate autoimmunity common to both IgA nephropathy and HSP.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballardie F. W., Brenchley P. E., Williams S., O'Donoghue D. J. Autoimmunity in IgA nephropathy. Lancet. 1988 Sep 10;2(8611):588–592. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90637-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger J., Hinglais N. Les ddpôts intercapillaires d'IgA-IgG. J Urol Nephrol (Paris) 1968 Sep;74(9):694–695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Border W. A. Distinguishing minimal-change disease from mesangial disorders. Kidney Int. 1988 Sep;34(3):419–434. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brentjens J. R., Andres G. Interaction of antibodies with renal cell surface antigens. Kidney Int. 1989 Apr;35(4):954–968. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cederholm B., Wieslander J., Bygren P., Heinegård D. Circulating complexes containing IgA and fibronectin in patients with primary IgA nephropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4865–4868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cederholm B., Wieslander J., Bygren P., Heinegård D. Patients with IgA nephropathy have circulating anti-basement membrane antibodies reacting with structures common to collagen I, II, and IV. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6151–6155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colten H. R., Bienenstock J. Lack of C3 activation through classical or alternate pathways by human secretory IgA anti blood group A antibody. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1974;45(0):305–308. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-4550-3_36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E., Cooper M. D., Michael A. F. Selective deposition of immunoglobulin A1 in immunoglobulin A nephropathy, anaphylactoid purpura nephritis, and systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;66(6):1432–1436. doi: 10.1172/JCI109998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czerkinsky C., Koopman W. J., Jackson S., Collins J. E., Crago S. S., Schrohenloher R. E., Julian B. A., Galla J. H., Mestecky J. Circulating immune complexes and immunoglobulin A rheumatoid factor in patients with mesangial immunoglobulin A nephropathies. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1931–1938. doi: 10.1172/JCI112522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amico G., Imbasciati E., Barbiano Di Belgioioso G., Bertoli S., Fogazzi G., Ferrario F., Fellin G., Ragni A., Colasanti G., Minetti L. Idiopathic IgA mesangial nephropathy. Clinical and histological study of 374 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 1985 Jan;64(1):49–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amico G., Minetti L., Ponticelli C., Fellin G., Ferrario F., Barbiano di Belgioioso G., Imbasciati E., Ragni A., Bertoli S., Fogazzi G. Prognostic indicators in idiopathic IgA mesangial nephropathy. Q J Med. 1986 Apr;59(228):363–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amico G. The commonest glomerulonephritis in the world: IgA nephropathy. Q J Med. 1987 Sep;64(245):709–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Druet P., Bariety J., Bernard D., Lagrue G. Les glomérulopathies primitives a dépots mésangiaux d'IgA et D'IgG. Etude clinique et morphologiaue de 52 cas. Presse Med. 1970 Mar 14;78(13):583–587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emancipator S. N., Gallo G. R., Lamm M. E. IgA nephropathy: perspectives on pathogenesis and classification. Clin Nephrol. 1985 Oct;24(4):161–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emancipator S. N., Lamm M. E. IgA nephropathy: pathogenesis of the most common form of glomerulonephritis. Lab Invest. 1989 Feb;60(2):168–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emancipator S. N., Ovary Z., Lamm M. E. The role of mesangial complement in the hematuria of experimental IgA nephropathy. Lab Invest. 1987 Sep;57(3):269–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feehally J. Immune mechanisms in glomerular IgA deposition. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1988;3(4):361–378. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.ndt.a091683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiss J. M., Goroff D. K. IgA blocks IgM and IgG-initiated immune lysis by separate molecular mechanisms. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2882–2885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guesdon J. L., Ternynck T., Avrameas S. The use of avidin-biotin interaction in immunoenzymatic techniques. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979 Aug;27(8):1131–1139. doi: 10.1177/27.8.90074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiemstra P. S., Biewenga J., Gorter A., Stuurman M. E., Faber A., van Es L. A., Daha M. R. Activation of complement by human serum IgA, secretory IgA and IgA1 fragments. Mol Immunol. 1988 Jun;25(6):527–533. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(88)90074-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai H., Chen A., Wyatt R. J., Rifai A. Lack of complement activation by human IgA immune complexes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Sep;73(3):479–483. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M., Mestecky J., Russell M. W. Defense mechanisms involving Fc-dependent functions of immunoglobulin A and their subversion by bacterial immunoglobulin A proteases. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jun;52(2):296–303. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.2.296-303.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi Y., Tateno S., Hiki Y., Shigematsu H. IgA nephropathy: prognostic significance of proteinuria and histological alterations. Nephron. 1983;34(3):146–153. doi: 10.1159/000183000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meadow S. R., Scott D. G. Berger disease: Henoch-Schönlein syndrome without the rash. J Pediatr. 1985 Jan;106(1):27–32. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80459-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls K. M., Fairley K. F., Dowling J. P., Kincaid-Smith P. The clinical course of mesangial IgA associated nephropathy in adults. Q J Med. 1984 Spring;53(210):227–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto Y., Suga T., Miura M., Nomoto H., Tomino Y., Sakai H. Characterization of an acidic nuclear protein recognized by autoantibodies in sera from patients with IgA nephropathy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Sep;65(3):513–519. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack A., Collin P., Mustonen J., Reunala T., Rantala I., Laurila K., Teppo A. M. Glomerular IgA deposits in patients with celiac disease. Clin Nephrol. 1990 Aug;34(2):56–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffenbach G., Lamm M. E., Gigli I. Activation of the guinea pig alternative complement pathway by mouse IgA immune complexes. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):231–247. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnoff W. D., Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. The role of antibody in the activation of the alternative complement pathway. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1983;6(4):361–371. doi: 10.1007/BF02116280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauterberg E. W., Lieberknecht H. M., Wingen A. M., Ritz E. Complement membrane attack (MAC) in idiopathic IgA-glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1987 Mar;31(3):820–829. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifai A., Chen A., Imai H. Complement activation in experimental IgA nephropathy: an antigen-mediated process. Kidney Int. 1987 Dec;32(6):838–844. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. A., Wilz D. R., Theil G. B. Schönlein-Henoch syndrome in adults. Q J Med. 1985 May;55(217):145–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. W., Mansa B. Complement-fixing properties of human IgA antibodies. Alternative pathway complement activation by plastic-bound, but not specific antigen-bound, IgA. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Aug;30(2):175–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb01199.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santiago A., Satriano J., DeCandido S., Holthofer H., Schreiber R., Unkeless J., Schlondorff D. A specific Fc gamma receptor on cultured rat mesangial cells. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 15;143(8):2575–2582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinico R. A., Fornasieri A., Oreni N., Benuzzi S., D'Amico G. Polymeric IgA rheumatoid factor in idiopathic IgA mesangial nephropathy (Berger's disease). J Immunol. 1986 Jul 15;137(2):536–541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Striker G. E., Killen P. D., Farin F. M. Human glomerular cells in vitro: isolation and characterization. Transplant Proc. 1980 Sep;12(3 Suppl 1):88–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Striker G. E., Striker L. J. Glomerular cell culture. Lab Invest. 1985 Aug;53(2):122–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syré G. IGA mesangial glomerulonephritis; significance and pathogenesis of segmental-focal glomerular lesions. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1983;402(1):11–24. doi: 10.1007/BF00695045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomino Y., Sakai H., Endoh M., Suga T., Miura M., Kaneshige H., Nomoto Y. Cross-reactivity of IgA antibodies between renal mesangial areas and nuclei of tonsillar cells in patients with IgA nephropathy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Mar;51(3):605–610. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. C., Giangiacomo J., Zuckner J. Letter: Dermal IgA deposits in Henoch-Schönlein purpura and Berger's nephritis. Lancet. 1975 Feb 8;1(7902):342–343. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91260-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilches A. R., Turner D. R., Cameron J. S., Ogg C. S., Chantler C., Williams D. G. Significance of mesangial IgM deposition in "minimal change" nephrotic syndrome. Lab Invest. 1982 Jan;46(1):10–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodroffe A. J., Gormly A. A., McKenzie P. E., Wootton A. M., Thompson A. J., Seymour A. E., Clarkson A. R. Immunologic studies in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 1980 Sep;18(3):366–374. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yap H. K., Sakai R. S., Bahn L., Rappaport V., Woo K. T., Ananthurman V., Lim C. H., Chiang G. S., Jordan S. C. Anti-vascular endothelial cell antibodies in patients with IgA nephropathy: frequency and clinical significance. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Dec;49(3):450–462. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(88)90132-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman S. W., Burkholder P. M. Immunoglobulin A nephropathy. Arch Intern Med. 1975 Sep;135(9):1217–1223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]