Abstract
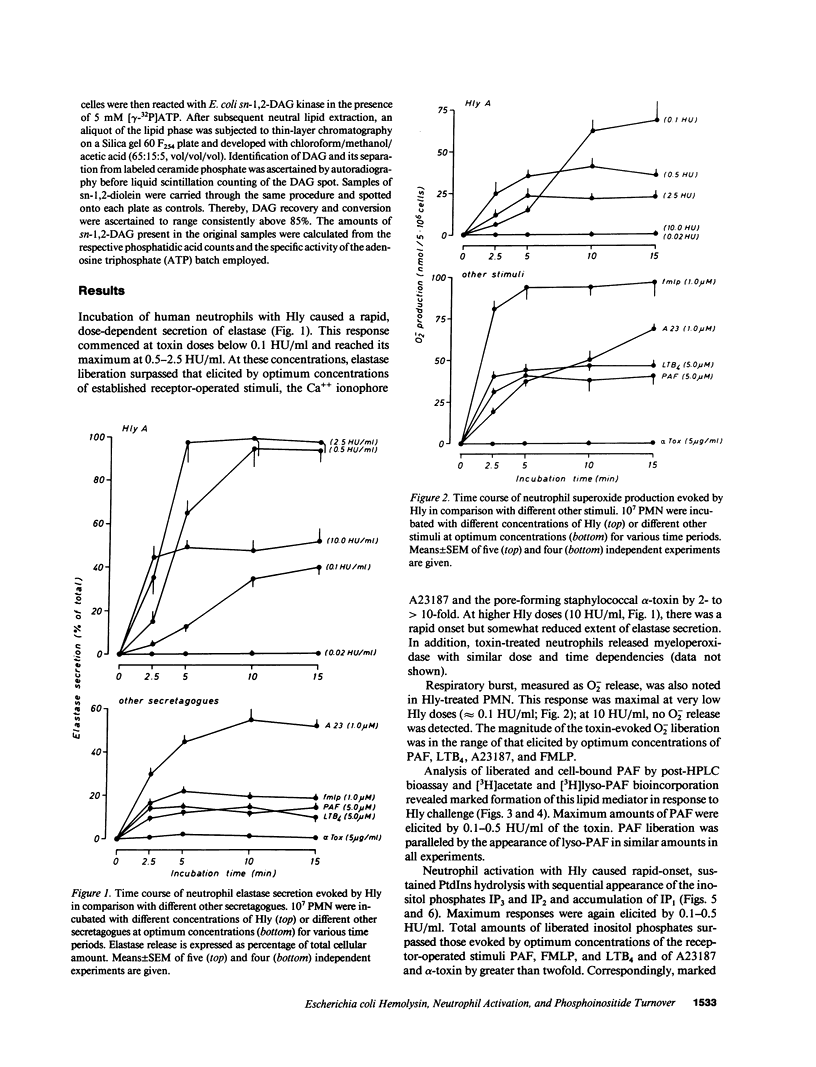
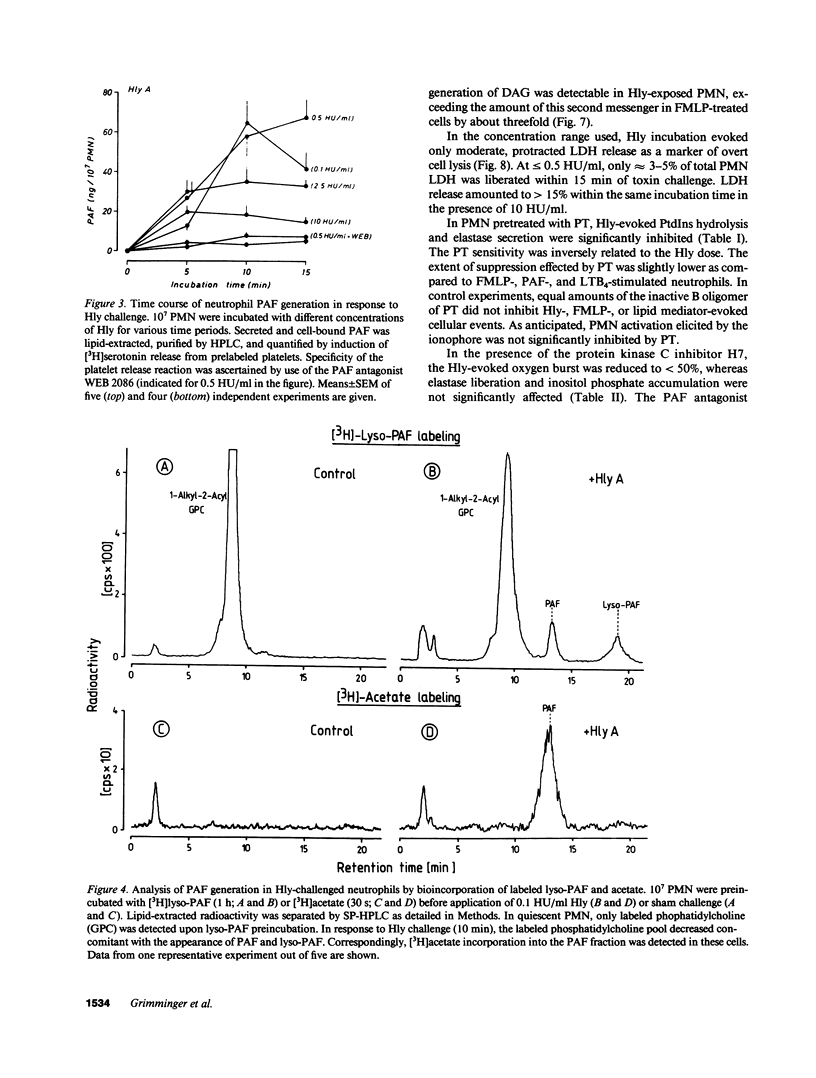
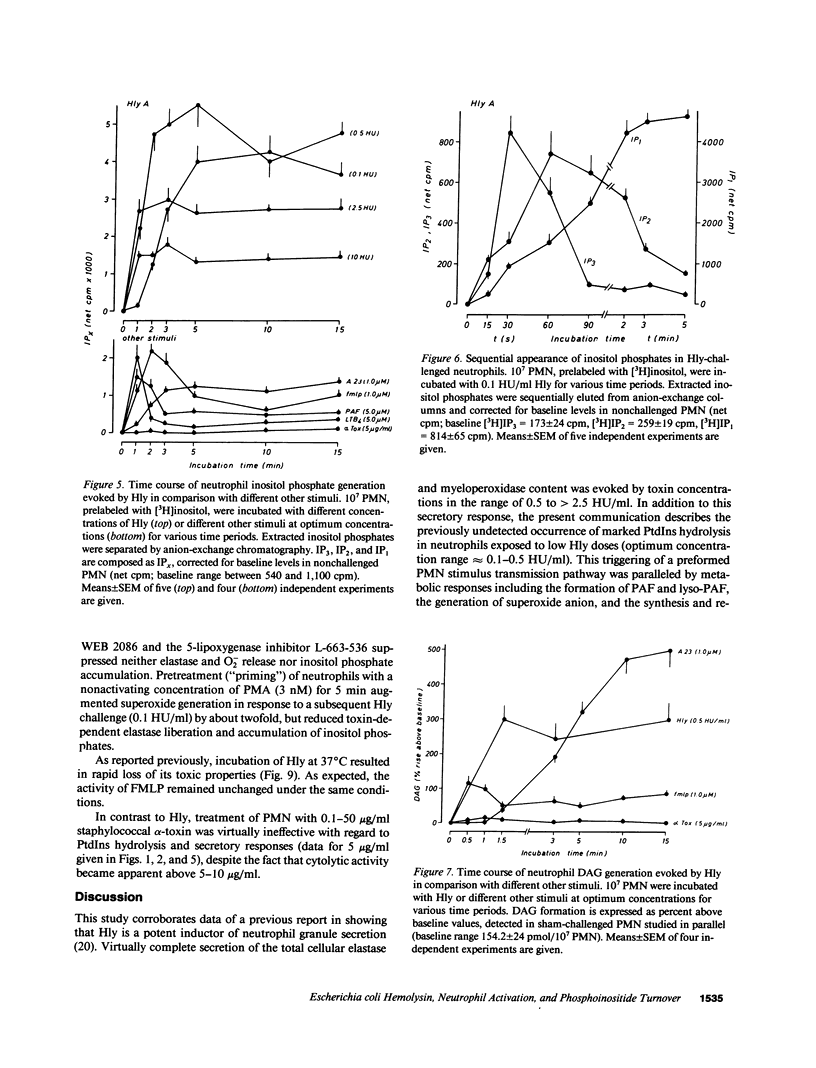
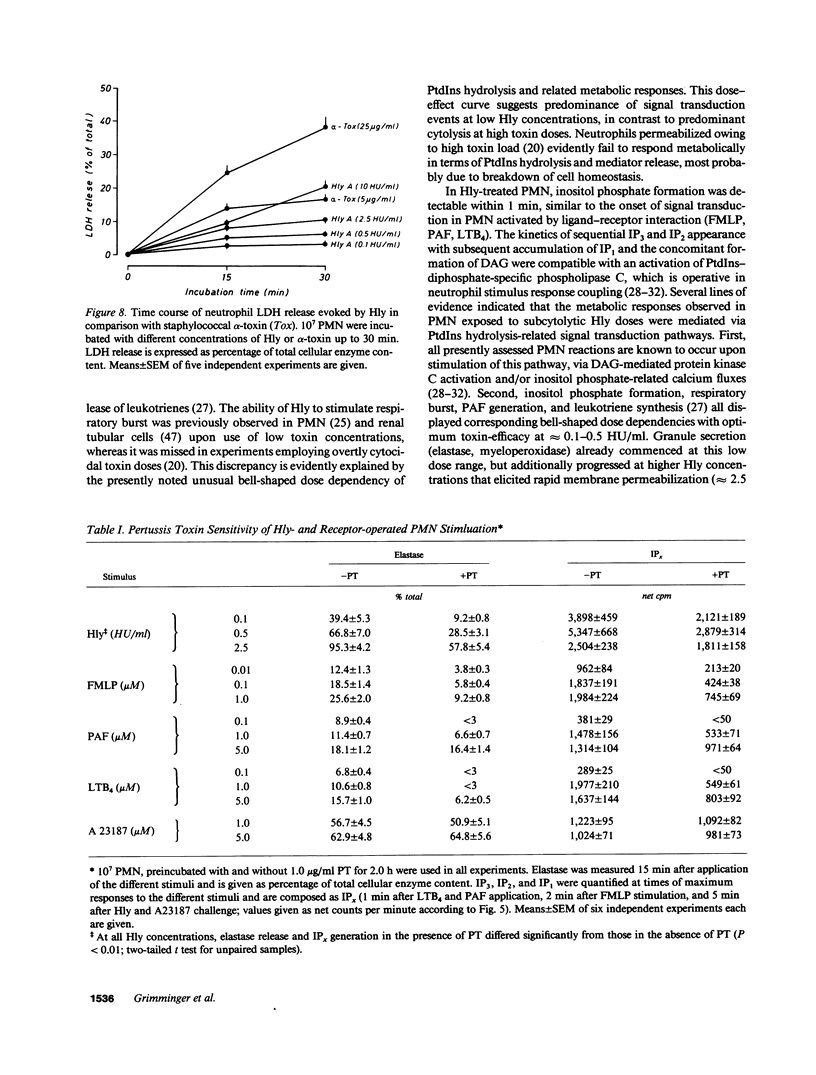
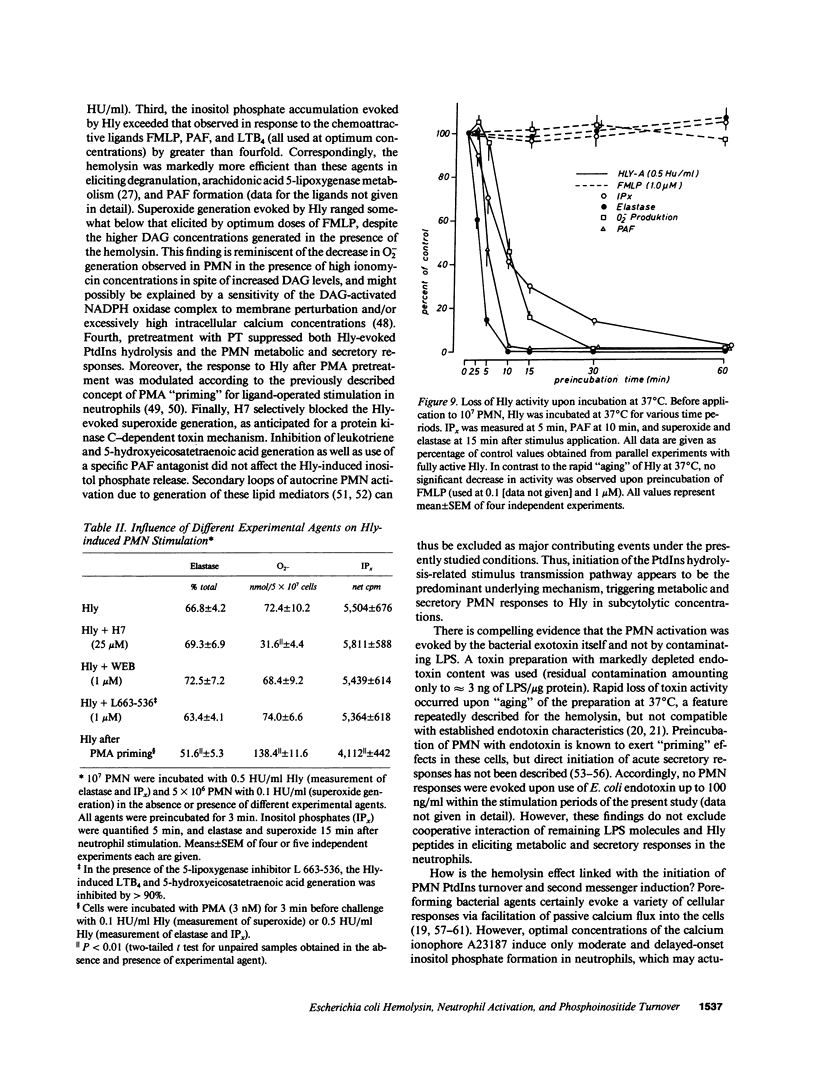
Escherichia coli hemolysin (Hly) is a proteinaceous pore-forming exotoxin that probably represents a significant virulence factor in E. coli infections. We investigated its influence on human polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN), previously identified as highly susceptible targets. Hly provoked rapid secretion of elastase and myeloperoxidase, generation of superoxide, and synthesis of platelet-activating factor (PAF) and lyso-PAF. Concomitantly, marked phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns) hydrolysis with sequential appearance of the inositol-phosphates, inositol-phosphates, inositol triphosphate, diphosphate, and monophosphate, respectively, and formation of diacylglycerol, occurred. The metabolic responses displayed distinct bell-shaped dose dependencies, with maximum events noted at low toxin concentrations of 0.1-0.5 hemolytic units per milliliter. PtdIns hydrolysis and metabolic responses elicited by Hly exceeded those evoked by optimal concentrations of formylmethionyl-leucyl phenylalanine, PAF, leukotriene B4, A23187, or staphylococcal alpha-toxin. The toxin-induced effects were sensitive toward modulators of PMN stimulus transmission pathways (pertussis toxin, the kinase C inhibitor H7, and phorbol myristate acetate "priming"). We conclude that the marked capacity of low doses of Hly to elicit degranulation, respiratory burst, and lipid mediator generation in human PMN probably envolves signal transduction via PtdIns hydrolysis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aderem A. A., Cohen D. S., Wright S. D., Cohn Z. A. Bacterial lipopolysaccharides prime macrophages for enhanced release of arachidonic acid metabolites. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):165–179. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkon D. L., Rasmussen H. A spatial-temporal model of cell activation. Science. 1988 Feb 26;239(4843):998–1005. doi: 10.1126/science.2830669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Greulich S., Muhly M., Eberspächer B., Becker H., Thiele A., Hugo F. Potent leukocidal action of Escherichia coli hemolysin mediated by permeabilization of target cell membranes. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):737–754. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Mackman N., Nicaud J. M., Holland I. B. Escherichia coli hemolysin may damage target cell membranes by generating transmembrane pores. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):63–69. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.63-69.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Muhly M., Mannhardt U., Hugo F., Klapettek K., Mueller-Eckhardt C., Roka L. Staphylococcal alpha toxin promotes blood coagulation via attack on human platelets. J Exp Med. 1988 Aug 1;168(2):527–542. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.2.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Damage to cell membranes by pore-forming bacterial cytolysins. Prog Allergy. 1988;40:1–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Damage to mammalian cells by proteins that form transmembrane pores. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1987;107:147–223. doi: 10.1007/BFb0027646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehm D. F., Welch R. A., Snyder I. S. Calcium is required for binding of Escherichia coli hemolysin (HlyA) to erythrocyte membranes. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1951–1958. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1951-1958.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehm D. F., Welch R. A., Snyder I. S. Domains of Escherichia coli hemolysin (HlyA) involved in binding of calcium and erythrocyte membranes. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1959–1964. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1959-1964.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. A., Rittenhouse S. E., Powers C. W., Ekstein L. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Alexander R. W. Phorbol ester and 1-oleoyl-2-acetylglycerol inhibit angiotensin activation of phospholipase C in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14158–14162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalieri S. J., Bohach G. A., Snyder I. S. Escherichia coli alpha-hemolysin: characteristics and probable role in pathogenicity. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Dec;48(4):326–343. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.4.326-343.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalieri S. J., Snyder I. S. Effect of Escherichia coli alpha-hemolysin on human peripheral leukocyte function in vitro. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):966–974. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.966-974.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilton F. H., Ellis J. M., Olson S. C., Wykle R. L. 1-O-alkyl-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine. A common source of platelet-activating factor and arachidonate in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12014–12019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen H. J., Chovaniec M. E. Superoxide generation by digitonin-stimulated guinea pig granulocytes. A basis for a continuous assay for monitoring superoxide production and for the study of the activation of the generating system. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):1081–1087. doi: 10.1172/JCI109007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danner R. L., Joiner K. A., Parrillo J. E. Inhibition of endotoxin-induced priming of human neutrophils by lipid X and 3-Aza-lipid X. J Clin Invest. 1987 Sep;80(3):605–612. doi: 10.1172/JCI113112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Virgilio F., Vicentini L. M., Treves S., Riz G., Pozzan T. Inositol phosphate formation in fMet-Leu-Phe-stimulated human neutrophils does not require an increase in the cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 15;229(2):361–367. doi: 10.1042/bj2290361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler M. E., Danner R. L., Shelhamer J. H., Parrillo J. E. Bacterial lipopolysaccharides prime human neutrophils for enhanced production of leukotriene B4. J Clin Invest. 1989 Mar;83(3):970–977. doi: 10.1172/JCI113983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty R. W., Godfrey P. P., Hoyle P. C., Putney J. W., Jr, Freer R. J. Secretagogue-induced phosphoinositide metabolism in human leucocytes. Biochem J. 1984 Sep 1;222(2):307–314. doi: 10.1042/bj2220307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberspächer B., Hugo F., Pohl M., Bhakdi S. Functional similarity between the haemolysins of Escherichia coli and Morganella morganii. J Med Microbiol. 1990 Nov;33(3):165–170. doi: 10.1099/00222615-33-3-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felmlee T., Pellett S., Welch R. A. Nucleotide sequence of an Escherichia coli chromosomal hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):94–105. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.94-105.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forehand J. R., Pabst M. J., Phillips W. A., Johnston R. B., Jr Lipopolysaccharide priming of human neutrophils for an enhanced respiratory burst. Role of intracellular free calcium. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jan;83(1):74–83. doi: 10.1172/JCI113887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freissmuth M., Casey P. J., Gilman A. G. G proteins control diverse pathways of transmembrane signaling. FASEB J. 1989 Aug;3(10):2125–2131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friberger P., Knös M., Mellstam L. A quantitative endotoxin assay utilizing LAL and a chromogenic substrate. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1982;93:195–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fünfstück R., Tschäpe H., Stein G., Kunath H., Bergner M., Wessel G. Virulence properties of Escherichia coli strains in patients with chronic pyelonephritis. Infection. 1986 May-Jun;14(3):145–150. doi: 10.1007/BF01643482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadeberg O. V., Orskov I., Rhodes J. M. Cytotoxic effect of an alpha-hemolytic Escherichia coli strain on human blood monocytes and granulocytes in vitro. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):358–364. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.358-364.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimminger F., Becker G., Seeger W. High yield enzymatic conversion of intravascular leukotriene A4 in blood-free perfused lungs. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2431–2436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimminger F., Kreusler B., Schneider U., Becker G., Seeger W. Influence of microvascular adherence on neutrophil leukotriene generation. Evidence for cooperative eicosanoid synthesis. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1866–1872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hacker J., Hughes C., Hof H., Goebel W. Cloned hemolysin genes from Escherichia coli that cause urinary tract infection determine different levels of toxicity in mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):57–63. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.57-63.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M. The immunologic release of constituents from neutrophil leukocytes. II. Mechanisms of release during phagocytosis, and adherence to nonphagocytosable surfaces. J Immunol. 1971 Dec;107(6):1547–1557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keane W. F., Welch R., Gekker G., Peterson P. K. Mechanism of Escherichia coli alpha-hemolysin-induced injury to isolated renal tubular cells. Am J Pathol. 1987 Feb;126(2):350–357. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koronakis V., Cross M., Senior B., Koronakis E., Hughes C. The secreted hemolysins of Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, and Morganella morganii are genetically related to each other and to the alpha-hemolysin of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1509–1515. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1509-1515.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramps J. A., van Twisk C., van der Linden A. C. L-Pyroglutamyl-L-prolyl-L-valine-p-nitroanilide, a highly specific substrate for granulocyte elastase. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1983 Sep;43(5):427–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo R. Y., Strathdee C. A., Shewen P. E. Nucleotide sequence of the leukotoxin genes of Pasteurella haemolytica A1. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):1987–1996. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.1987-1996.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig A., Jarchau T., Benz R., Goebel W. The repeat domain of Escherichia coli haemolysin (HlyA) is responsible for its Ca2+-dependent binding to erythrocytes. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Nov;214(3):553–561. doi: 10.1007/BF00330494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackman N., Holland I. B. Secretion of a 107 K dalton polypeptide into the medium from a haemolytic E. coli K12 strain. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;193(2):312–315. doi: 10.1007/BF00330686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Connolly T. M., Bansal V. S., Inhorn R. C., Ross T. S., Lips D. L. Inositol phosphates: synthesis and degradation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3051–3054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menestrina G., Mackman N., Holland I. B., Bhakdi S. Escherichia coli haemolysin forms voltage-dependent ion channels in lipid membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Nov 27;905(1):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta H., Okajima F., Ui M. Inhibition by islet-activating protein of a chemotactic peptide-induced early breakdown of inositol phospholipids and Ca2+ mobilization in guinea pig neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15771–15780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omann G. M., Allen R. A., Bokoch G. M., Painter R. G., Traynor A. E., Sklar L. A. Signal transduction and cytoskeletal activation in the neutrophil. Physiol Rev. 1987 Jan;67(1):285–322. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.1.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinckard R. N., Farr R. S., Hanahan D. J. Physicochemical and functional identity of rabbit platelet-activating factor (PAF) released in vivo during IgE anaphylaxis with PAF released in vitro from IgE sensitized basophils. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1847–1857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss J., Loomis C. R., Bishop W. R., Stein R., Niedel J. E., Bell R. M. Quantitative measurement of sn-1,2-diacylglycerols present in platelets, hepatocytes, and ras- and sis-transformed normal rat kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8597–8600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisine T. Pertussis toxin in the analysis of receptor mechanisms. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 May 15;39(10):1499–1504. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90513-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. G., Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Lee S. Y. Studies of inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):546–550. doi: 10.1126/science.2541501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rider L. G., Niedel J. E. Diacylglycerol accumulation and superoxide anion production in stimulated human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5603–5608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandborg R. R., Smolen J. E. Early biochemical events in leukocyte activation. Lab Invest. 1988 Sep;59(3):300–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger W., Bauer M., Bhakdi S. Staphylococcal alpha-toxin elicits hypertension in isolated rabbit lungs. Evidence for thromboxane formation and the role of extracellular calcium. J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):849–858. doi: 10.1172/JCI111502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger W., Suttorp N., Hellwig A., Bhakdi S. Noncytolytic terminal complement complexes may serve as calcium gates to elicit leukotriene B4 generation in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 15;137(4):1286–1293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger W., Walter H., Suttorp N., Muhly M., Bhakdi S. Thromboxane-mediated hypertension and vascular leakage evoked by low doses of Escherichia coli hemolysin in rabbit lungs. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):220–227. doi: 10.1172/JCI114144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. G., Dubbin P. N., Harris T., Dusting G. J. Platelet-activating factor may act as a second messenger in the release of icosanoids and superoxide anions from leukocytes and endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3215–3219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathdee C. A., Lo R. Y. Extensive homology between the leukotoxin of Pasteurella haemolytica A1 and the alpha-hemolysin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3233–3236. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3233-3236.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Flöer B., Schnittler H., Seeger W., Bhakdi S. Effects of Escherichia coli hemolysin on endothelial cell function. Infect Immun. 1990 Nov;58(11):3796–3801. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3796-3801.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Seeger W., Dewein E., Bhakdi S., Roka L. Staphylococcal alpha-toxin-induced PGI2 production in endothelial cells: role of calcium. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jan;248(1 Pt 1):C127–C134. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.248.1.C127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Seeger W., Uhl J., Lutz F., Roka L. Pseudomonas aeruginosa cytotoxin stimulates prostacyclin production in cultured pulmonary artery endothelial cells: membrane attack and calcium influx. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Apr;123(1):64–72. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041230111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Seeger W., Zucker-Reimann J., Roka L., Bhakdi S. Mechanism of leukotriene generation in polymorphonuclear leukocytes by staphylococcal alpha-toxin. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):104–110. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.104-110.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessner T. G., O'Flaherty J. T., Wykle R. L. Stimulation of platelet-activating factor synthesis by a nonmetabolizable bioactive analog of platelet-activating factor and influence of arachidonic acid metabolites. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):4794–4799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi S. R., Tamura M., Burnham D. N., Lambeth J. D. Phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) augments chemoattractant-induced diglyceride generation in human neutrophils but inhibits phosphoinositide hydrolysis. Implications for the mechanism of PMA priming of the respiratory burst. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13191–13198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verghese M. W., Charles L., Jakoi L., Dillon S. B., Snyderman R. Role of a guanine nucleotide regulatory protein in the activation of phospholipase C by different chemoattractants. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4374–4380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. A., Dellinger E. P., Minshew B., Falkow S. Haemolysin contributes to virulence of extra-intestinal E. coli infections. Nature. 1981 Dec 17;294(5842):665–667. doi: 10.1038/294665a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. A., Falkow S. Characterization of Escherichia coli hemolysins conferring quantitative differences in virulence. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):156–160. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.156-160.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. A. Identification of two different hemolysin determinants in uropathogenic Proteus isolates. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2183–2190. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2183-2190.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. A., Pellett S. Transcriptional organization of the Escherichia coli hemolysin genes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1622–1630. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1622-1630.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



