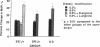Abstract
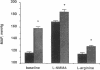
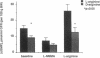
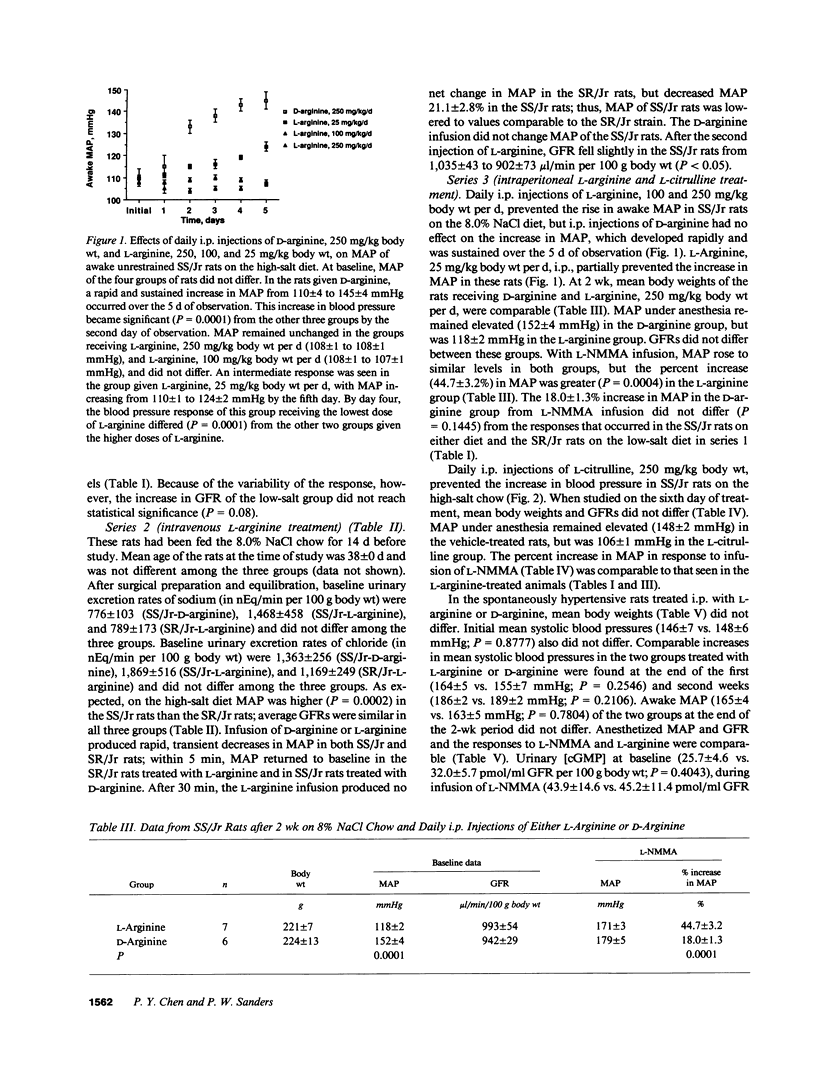
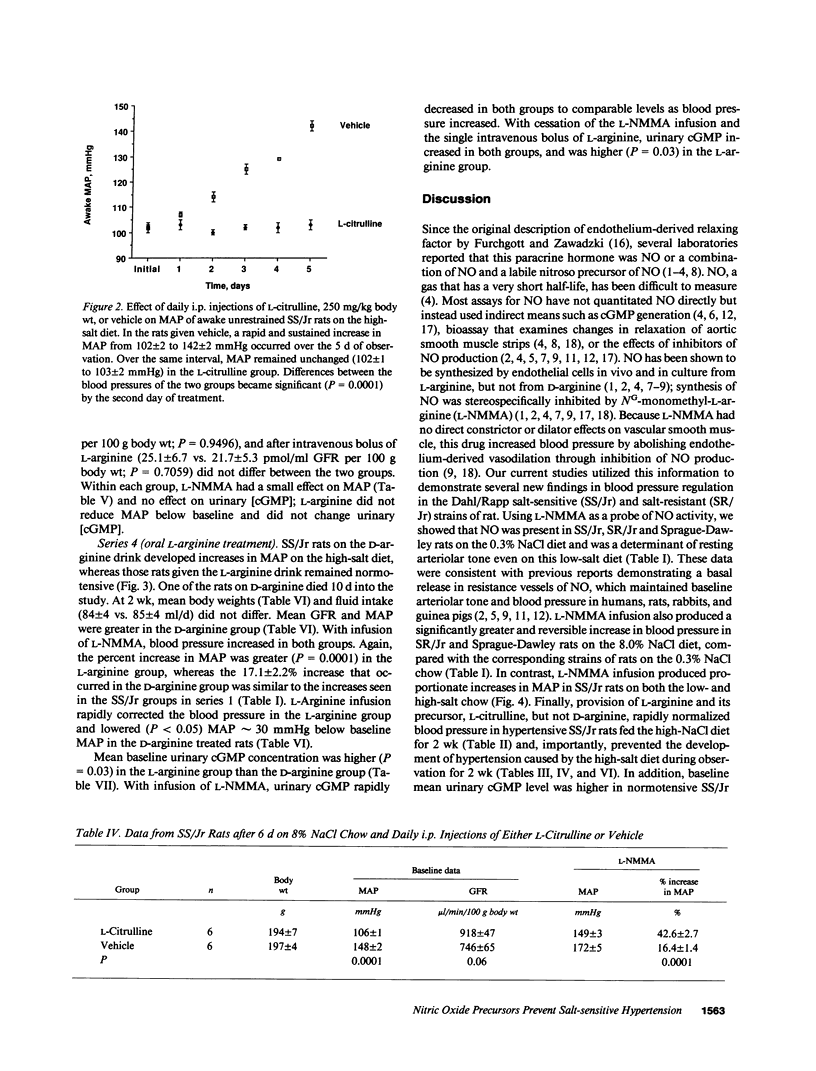
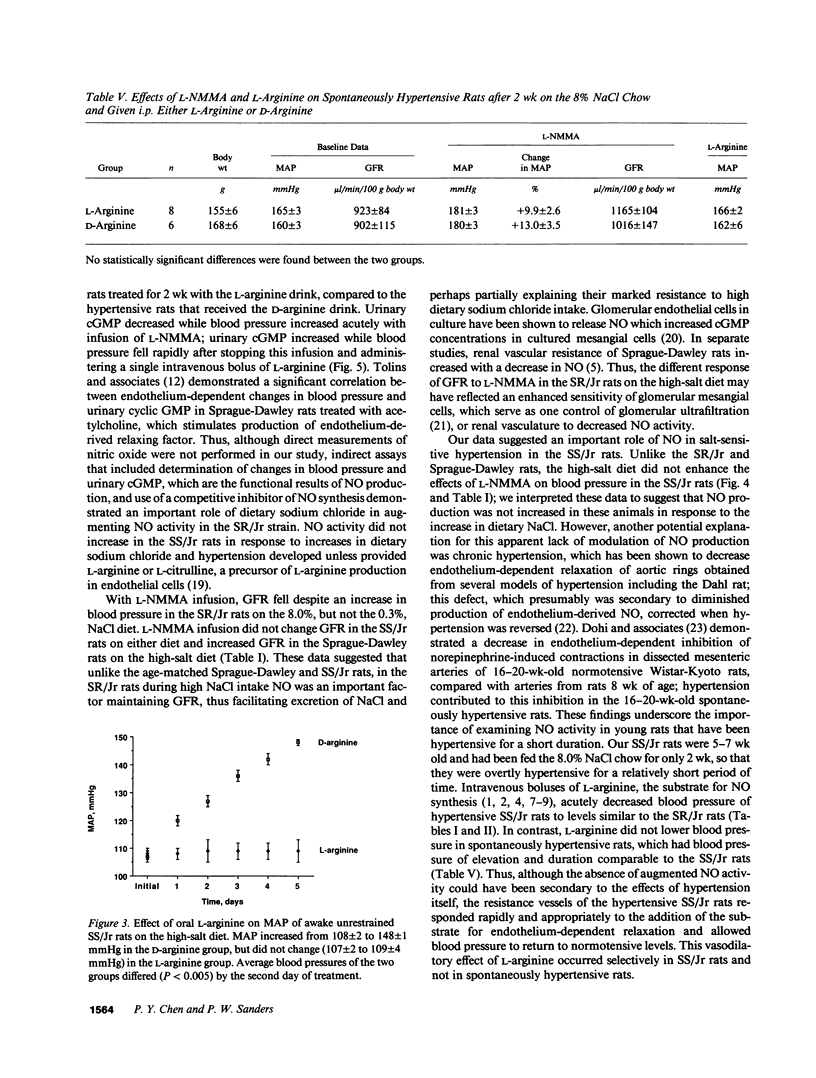
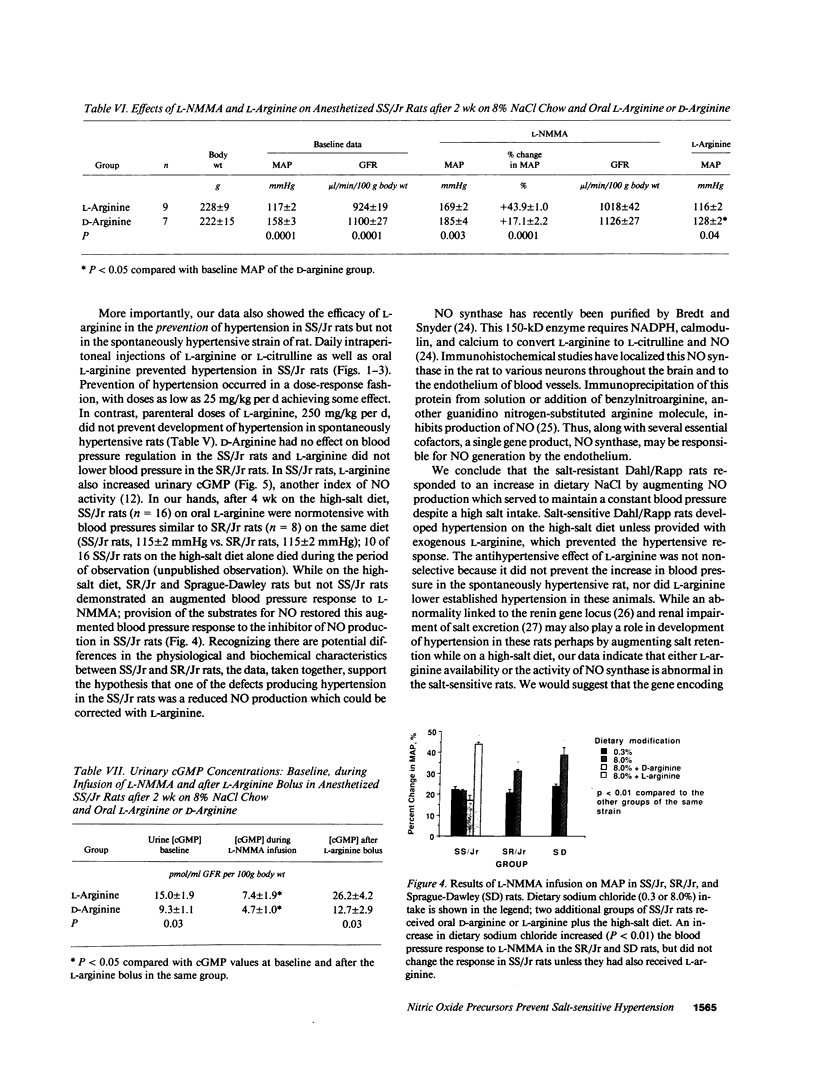
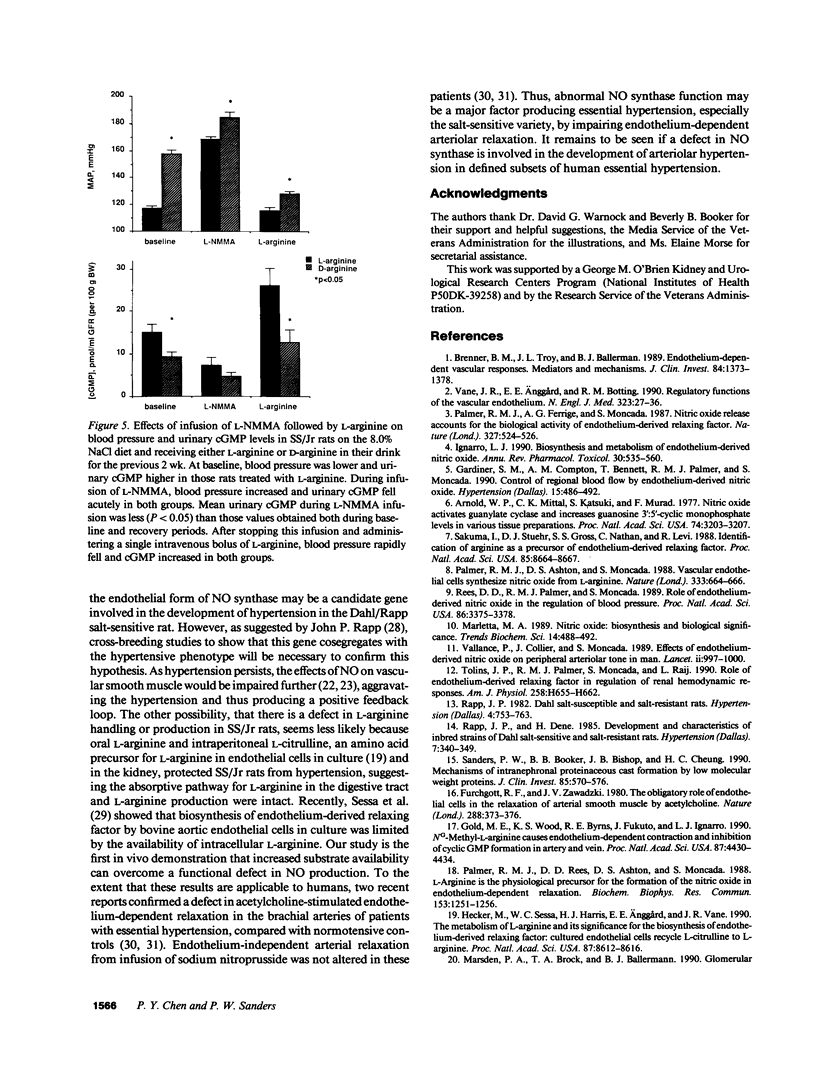
This study examined the contribution of nitric oxide (NO) to the susceptibility or resistance to the hypertensive effects of high sodium chloride (8.0% NaCl) intake in young Dahl/Rapp salt-sensitive (SS/Jr) and salt-resistant (SR/Jr) rats. Using NG-monomethyl-L-arginine (L-NMMA) as a probe for NO production in vivo, we found that increasing dietary sodium chloride increased NO activity in salt-resistant rats, but not in salt-sensitive rats. Exogenous L-arginine, the substrate for NO synthesis, decreased blood pressure to normotensive levels in salt-sensitive rats made hypertensive for 2 wk from 8.0% NaCl chow. D-arginine had no effect on blood pressure of these rats and L-arginine did not change blood pressure of salt-resistant rats. Intraperitoneal injections of L-arginine and its precursor, L-citrulline, and oral L-arginine, but not D-arginine, prevented the increase in blood pressure in salt-sensitive rats on the high salt chow over 2 wk of observation. In contrast, L-arginine did not alter the development of hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Mean urinary cGMP levels were higher in salt-sensitive rats on oral L-arginine than salt-sensitive rats on D-arginine. Infusion of L-NMMA acutely decreased, whereas intravenous L-arginine rapidly increased, urinary cGMP in both groups. L-arginine and L-citrulline increased production of NO and prevented salt-sensitive hypertension in Dahl/Rapp rats.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold W. P., Mittal C. K., Katsuki S., Murad F. Nitric oxide activates guanylate cyclase and increases guanosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate levels in various tissue preparations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3203–3207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Hwang P. M., Snyder S. H. Localization of nitric oxide synthase indicating a neural role for nitric oxide. Nature. 1990 Oct 25;347(6295):768–770. doi: 10.1038/347768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Isolation of nitric oxide synthetase, a calmodulin-requiring enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):682–685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Troy J. L., Ballermann B. J. Endothelium-dependent vascular responses. Mediators and mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1373–1378. doi: 10.1172/JCI114309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohi Y., Thiel M. A., Bühler F. R., Lüscher T. F. Activation of endothelial L-arginine pathway in resistance arteries. Effect of age and hypertension. Hypertension. 1990 Aug;16(2):170–179. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.16.2.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F., Zawadzki J. V. The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):373–376. doi: 10.1038/288373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner S. M., Compton A. M., Bennett T., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Control of regional blood flow by endothelium-derived nitric oxide. Hypertension. 1990 May;15(5):486–492. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.15.5.486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. E., Wood K. S., Byrns R. E., Fukuto J., Ignarro L. J. NG-methyl-L-arginine causes endothelium-dependent contraction and inhibition of cyclic GMP formation in artery and vein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4430–4434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecker M., Sessa W. C., Harris H. J., Anggård E. E., Vane J. R. The metabolism of L-arginine and its significance for the biosynthesis of endothelium-derived relaxing factor: cultured endothelial cells recycle L-citrulline to L-arginine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8612–8616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J. Biosynthesis and metabolism of endothelium-derived nitric oxide. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;30:535–560. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.30.040190.002535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchner K. A. Greater loop chloride uptake contributes to blunted pressure natriuresis in Dahl salt sensitive rats. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1990 Aug;1(2):180–186. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V12180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder L., Kiowski W., Bühler F. R., Lüscher T. F. Indirect evidence for release of endothelium-derived relaxing factor in human forearm circulation in vivo. Blunted response in essential hypertension. Circulation. 1990 Jun;81(6):1762–1767. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.81.6.1762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marletta M. A. Nitric oxide: biosynthesis and biological significance. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Dec;14(12):488–492. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90181-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden P. A., Brock T. A., Ballermann B. J. Glomerular endothelial cells respond to calcium-mobilizing agonists with release of EDRF. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 2):F1295–F1303. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.5.F1295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mené P., Simonson M. S., Dunn M. J. Physiology of the mesangial cell. Physiol Rev. 1989 Oct;69(4):1347–1424. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.4.1347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ashton D. S., Moncada S. Vascular endothelial cells synthesize nitric oxide from L-arginine. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):664–666. doi: 10.1038/333664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ferrige A. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):524–526. doi: 10.1038/327524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Rees D. D., Ashton D. S., Moncada S. L-arginine is the physiological precursor for the formation of nitric oxide in endothelium-dependent relaxation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jun 30;153(3):1251–1256. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81362-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panza J. A., Quyyumi A. A., Brush J. E., Jr, Epstein S. E. Abnormal endothelium-dependent vascular relaxation in patients with essential hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jul 5;323(1):22–27. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199007053230105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp J. P. Dahl salt-susceptible and salt-resistant rats. A review. Hypertension. 1982 Nov-Dec;4(6):753–763. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.4.6.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp J. P., Dene H. Development and characteristics of inbred strains of Dahl salt-sensitive and salt-resistant rats. Hypertension. 1985 May-Jun;7(3 Pt 1):340–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp J. P., Wang S. M., Dene H. A genetic polymorphism in the renin gene of Dahl rats cosegregates with blood pressure. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):542–544. doi: 10.1126/science.2563177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Role of endothelium-derived nitric oxide in the regulation of blood pressure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3375–3378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakuma I., Stuehr D. J., Gross S. S., Nathan C., Levi R. Identification of arginine as a precursor of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8664–8667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders P. W., Booker B. B., Bishop J. B., Cheung H. C. Mechanisms of intranephronal proteinaceous cast formation by low molecular weight proteins. J Clin Invest. 1990 Feb;85(2):570–576. doi: 10.1172/JCI114474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sessa W. C., Hecker M., Mitchell J. A., Vane J. R. The metabolism of L-arginine and its significance for the biosynthesis of endothelium-derived relaxing factor: L-glutamine inhibits the generation of L-arginine by cultured endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8607–8611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolins J. P., Palmer R. M., Moncada S., Raij L. Role of endothelium-derived relaxing factor in regulation of renal hemodynamic responses. Am J Physiol. 1990 Mar;258(3 Pt 2):H655–H662. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.258.3.H655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallance P., Collier J., Moncada S. Effects of endothelium-derived nitric oxide on peripheral arteriolar tone in man. Lancet. 1989 Oct 28;2(8670):997–1000. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R., Anggård E. E., Botting R. M. Regulatory functions of the vascular endothelium. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jul 5;323(1):27–36. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199007053230106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]