Abstract
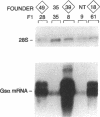
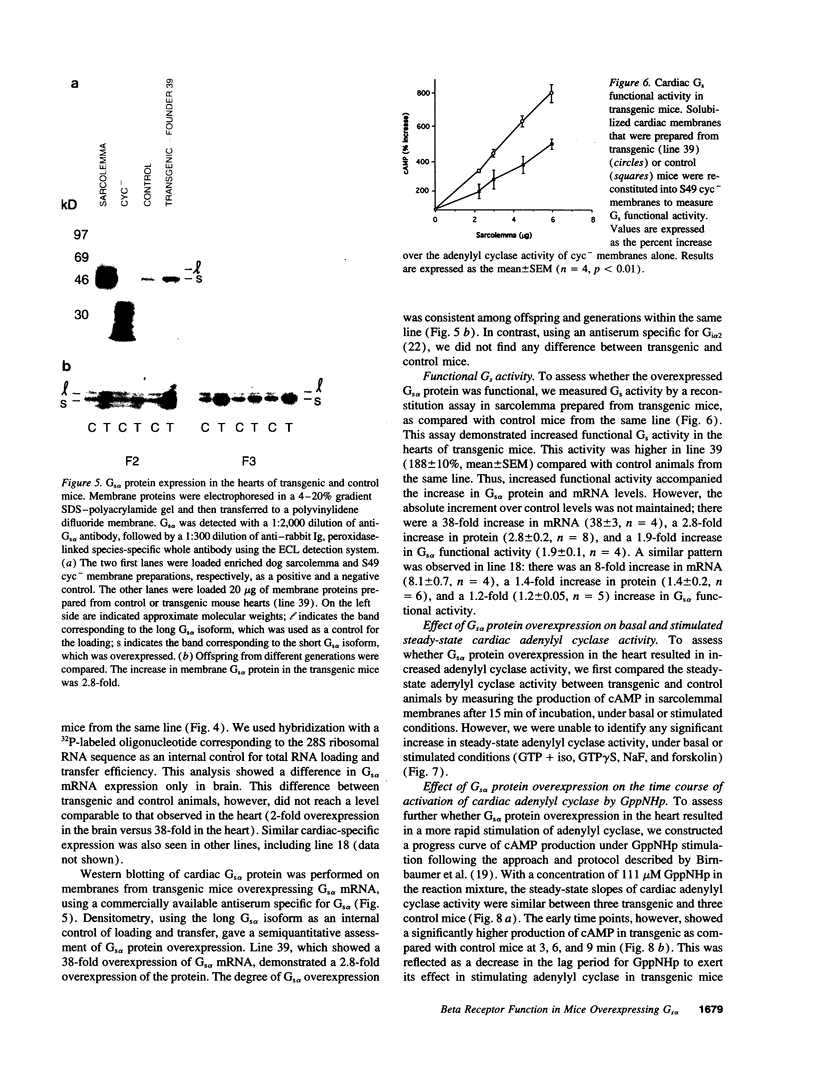
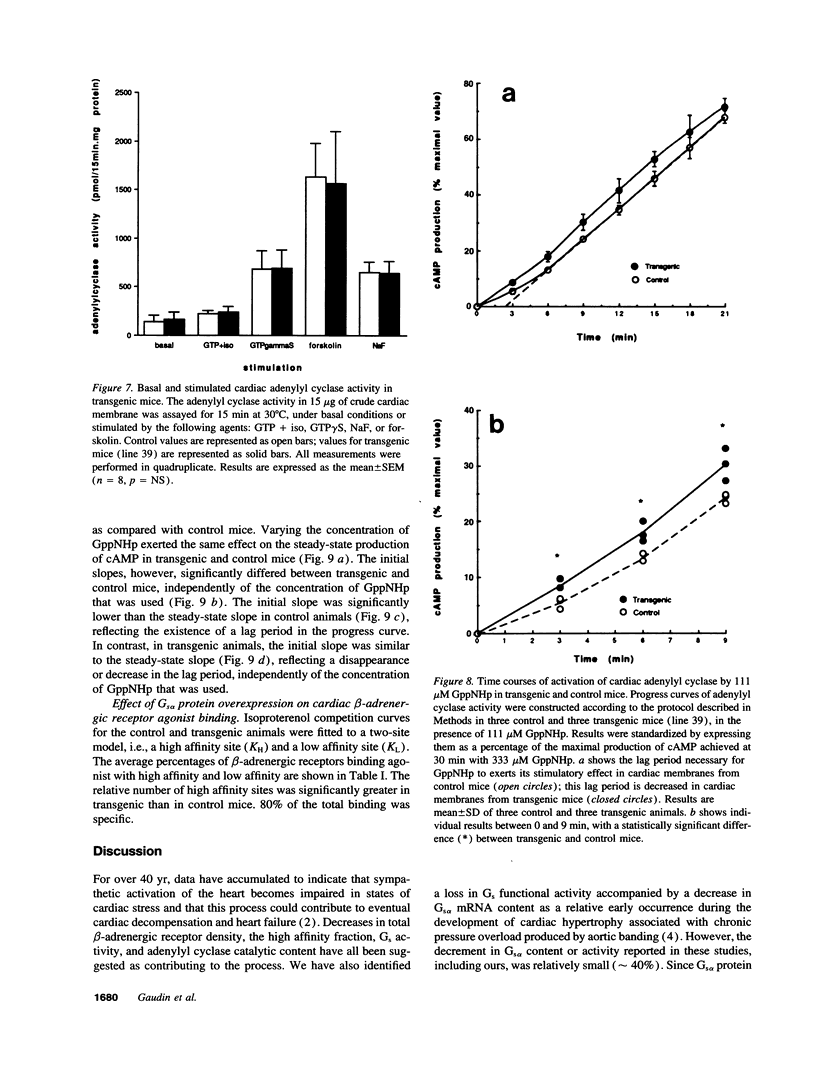
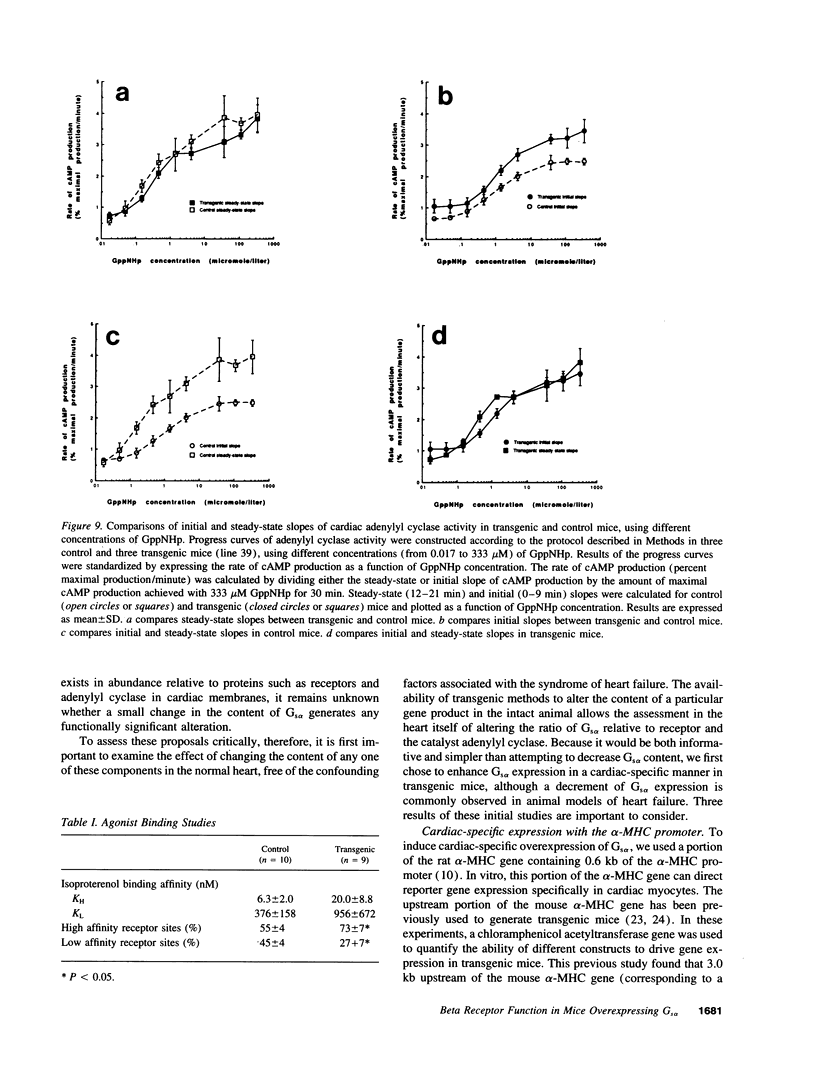
Alterations in beta-adrenergic receptor-Gs-adenylyl cyclase coupling underlie the reduced catecholamine responsiveness that is a hallmark of human and animal models of heart failure. To study the effect of altered expression of Gs alpha, we overexpressed the short isoform of Gs alpha in the hearts of transgenic mice, using a rat alpha-myosin heavy chain promoter. Gs alpha mRNA levels were increased selectively in the hearts of transgenic mice, with a level 38 times the control. Despite this marked increase in mRNA, Western blotting identified only a 2.8-fold increase in the content of the Gs alpha short isoform, whereas Gs activity was increased by 88%. The discrepancy between Gs alpha mRNA and Gs alpha protein levels suggests that the membrane content of Gs alpha is posttranscriptionally regulated. The steady-state adenylyl cyclase catalytic activity was not altered under either basal or stimulated conditions (GTP + isoproterenol, GTP gamma S, NaF, or forskolin). However, progress curve studies did show a significant decrease in the lag period necessary for GppNHp to stimulate adenylyl cyclase activity. Furthermore, the relative number of beta-adrenergic receptors binding agonist with high affinity was significantly increased. Our data demonstrate that a relatively small increase in the amount of the coupling protein Gs alpha can modify the rate of catalyst activation and the formation of agonist high affinity receptors.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alousi A. A., Jasper J. R., Insel P. A., Motulsky H. J. Stoichiometry of receptor-Gs-adenylate cyclase interactions. FASEB J. 1991 Jun;5(9):2300–2303. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.9.1650314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L., Swartz T. L., Abramowitz J., Mintz P. W., Iyengar R. Transient and steady state kinetics of the interaction of guanyl nucleotides with the adenylyl cyclase system from rat liver plasma membranes. Interpretation in terms of a simple two-state model. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3542–3551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Allen J. M., Behringer R. R., Gelinas R. E., Palmiter R. D. Introns increase transcriptional efficiency in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):836–840. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. A., Vatner D. E., Vatner S. F., Hittinger L., Homcy C. J. Decreased Gs alpha mRNA levels accompany the fall in Gs and adenylyl cyclase activities in compensated left ventricular hypertrophy. In heart failure, only the impairment in adenylyl cyclase activation progresses. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jan;87(1):293–298. doi: 10.1172/JCI114985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulick J., Subramaniam A., Neumann J., Robbins J. Isolation and characterization of the mouse cardiac myosin heavy chain genes. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9180–9185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homcy C. J., Vatner S. F., Vatner D. E. Beta-adrenergic receptor regulation in the heart in pathophysiologic states: abnormal adrenergic responsiveness in cardiac disease. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:137–159. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.001033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. R., Maddock S. W., Besch H. R., Jr Unmasking effect of alamethicin on the (Na+,K+)-ATPase, beta-adrenergic receptor-coupled adenylate cyclase, and cAMP-dependent protein kinase activities of cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9971–9980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz E. B., Steinhelper M. E., Delcarpio J. B., Daud A. I., Claycomb W. C., Field L. J. Cardiomyocyte proliferation in mice expressing alpha-cardiac myosin heavy chain-SV40 T-antigen transgenes. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jun;262(6 Pt 2):H1867–H1876. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.262.6.H1867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiuchi K., Shannon R. P., Komamura K., Cohen D. J., Bianchi C., Homcy C. J., Vatner S. F., Vatner D. E. Myocardial beta-adrenergic receptor function during the development of pacing-induced heart failure. J Clin Invest. 1993 Mar;91(3):907–914. doi: 10.1172/JCI116312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosaki T., Gander I., Ravetch J. V. A subunit common to an IgG Fc receptor and the T-cell receptor mediates assembly through different interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3837–3841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis M. J., Bourne H. R. Activation of the alpha subunit of Gs in intact cells alters its abundance, rate of degradation, and membrane avidity. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(5):1297–1307. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.5.1297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao J. K., Homcy C. J. Specific receptor-guanine nucleotide binding protein interaction mediates the release of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Circ Res. 1992 May;70(5):1018–1026. doi: 10.1161/01.res.70.5.1018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder M. E., Middleton P., Hepler J. R., Taussig R., Gilman A. G., Mumby S. M. Lipid modifications of G proteins: alpha subunits are palmitoylated. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3675–3679. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longabaugh J. P., Vatner D. E., Vatner S. F., Homcy C. J. Decreased stimulatory guanosine triphosphate binding protein in dogs with pressure-overload left ventricular failure. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):420–424. doi: 10.1172/JCI113335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Maguire M. E., Sturgill T. W., Biltonen R. L., Gilman A. G. Relationship between the beta-adrenergic receptor and adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 25;252(16):5761–5775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y. Adenylate cyclase assay. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:35–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. Reconstitution of catecholamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase. Reconstitution of the uncoupled variant of the S40 lymphoma cell. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3333–3340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramaniam A., Jones W. K., Gulick J., Wert S., Neumann J., Robbins J. Tissue-specific regulation of the alpha-myosin heavy chain gene promoter in transgenic mice. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24613–24620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Susanni E. E., Manders W. T., Knight D. R., Vatner D. E., Vatner S. F., Homcy C. J. One hour of myocardial ischemia decreases the activity of the stimulatory guanine-nucleotide regulatory protein Gs. Circ Res. 1989 Oct;65(4):1145–1150. doi: 10.1161/01.res.65.4.1145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taussig R., Iñiguez-Lluhi J. A., Gilman A. G. Inhibition of adenylyl cyclase by Gi alpha. Science. 1993 Jul 9;261(5118):218–221. doi: 10.1126/science.8327893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vatner D. E., Homcy C. J., Sit S. P., Manders W. T., Vatner S. F. Effects of pressure overload, left ventricular hypertrophy on beta-adrenergic receptors, and responsiveness to catecholamines. J Clin Invest. 1984 May;73(5):1473–1482. doi: 10.1172/JCI111351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vatner D. E., Vatner S. F., Fujii A. M., Homcy C. J. Loss of high affinity cardiac beta adrenergic receptors in dogs with heart failure. J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;76(6):2259–2264. doi: 10.1172/JCI112235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vatner D. E., Vatner S. F., Nejima J., Uemura N., Susanni E. E., Hintze T. H., Homcy C. J. Chronic norepinephrine elicits desensitization by uncoupling the beta-receptor. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):1741–1748. doi: 10.1172/JCI114357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner T. E., Hoppe P. C., Jollick J. D., Scholl D. R., Hodinka R. L., Gault J. B. Microinjection of a rabbit beta-globin gene into zygotes and its subsequent expression in adult mice and their offspring. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6376–6380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woon C. W., Soparkar S., Heasley L., Johnson G. L. Expression of a G alpha s/G alpha i chimera that constitutively activates cyclic AMP synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5687–5693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Shawi R., Kinnaird J., Burke J., Bishop J. O. Expression of a foreign gene in a line of transgenic mice is modulated by a chromosomal position effect. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1192–1198. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]