Abstract
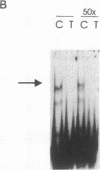
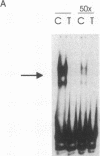
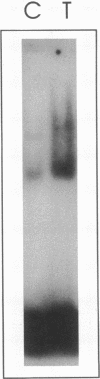
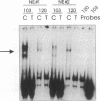
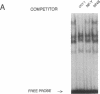
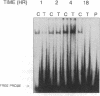
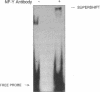
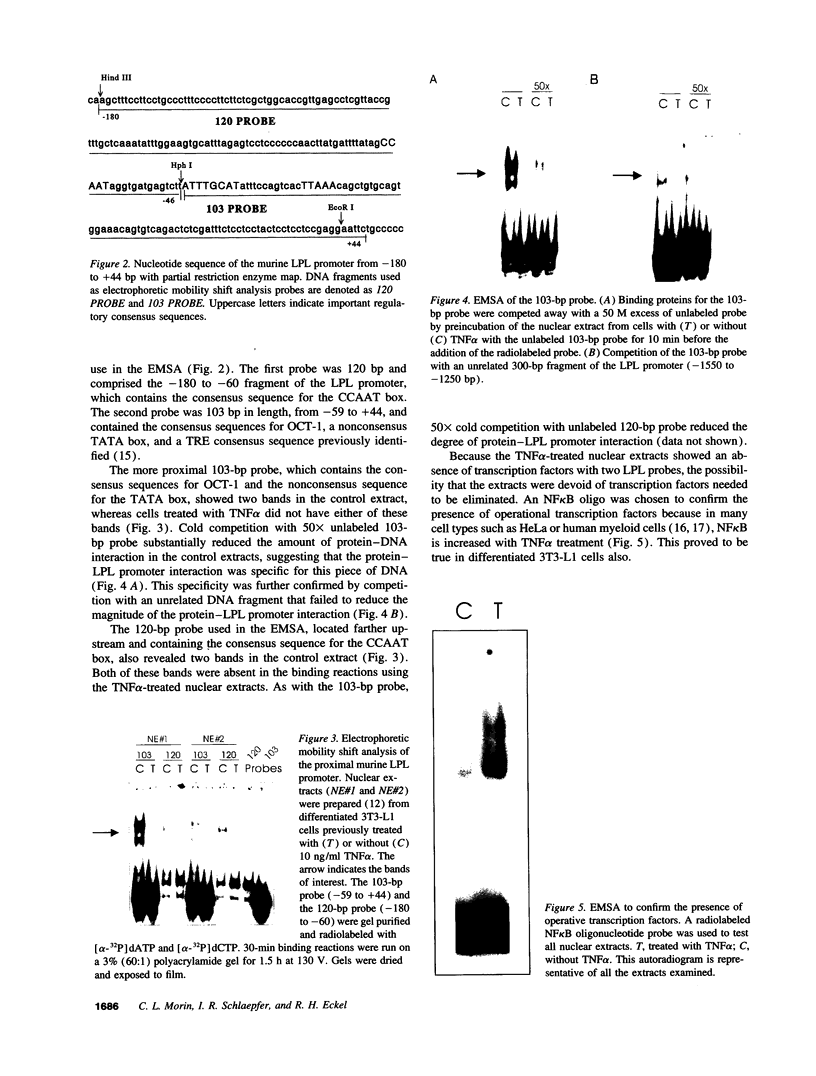
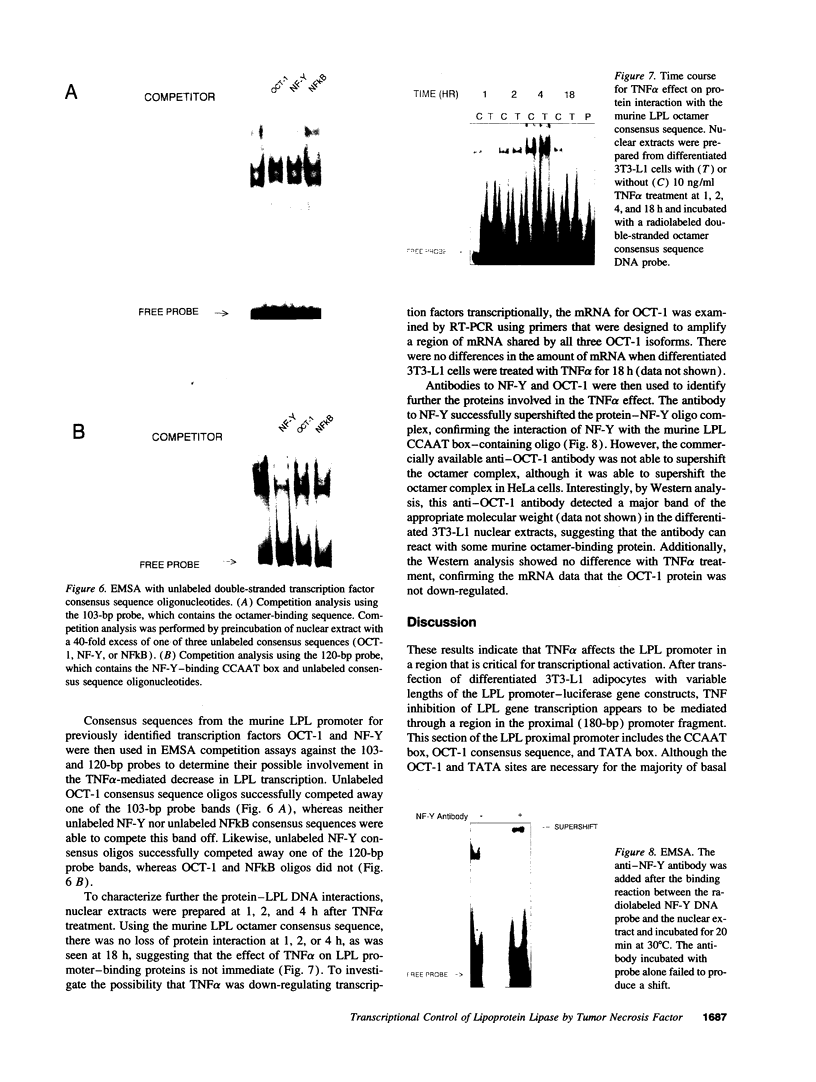
TNF alpha has been shown to reduce lipoprotein lipase (LPL) activity in adipose tissue. Regulation of LPL by TNF alpha occurs at the level of LPL gene transcription and posttranscriptionally. To elucidate further the transcriptional mechanism of TNF alpha inhibition of LPL gene transcription, transfection analysis was used to locate the site(s) of the LPL promoter that imparts the TNF alpha response. Transient transfections using LPL promoter deletions fused to luciferase in differentiated 3T3-L1 cells with and without TNF alpha treatment indicated that a DNA region downstream of -180 bp confers the TNF alpha effect. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays using two 32P-labeled LPL probes spanning the region between -180 and +44 bp revealed the loss of several LPL DNA-protein interactions after TNF alpha treatment, including the binding of NF-Y to the CCAAT box and a protein to the octamer consensus sequence. Protein binding to the OCT-1 consensus sequence is unaffected until after 4 h of TNF alpha treatment. In addition, the amount of mRNA for OCT-1 is not altered with TNF alpha treatment. These results indicate that TNF alpha regulates at least two DNA-binding proteins on the proximal promoter, thereby inhibiting LPL gene transcription.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barcellini-Couget S., Pradines-Figuères A., Roux P., Dani C., Ailhaud G. The regulation by growth hormone of lipoprotein lipase gene expression is mediated by c-fos protooncogene. Endocrinology. 1993 Jan;132(1):53–60. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.1.8419145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B. A., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor: production, distribution, and metabolic fate in vivo. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3972–3977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelius P., Enerback S., Bjursell G., Olivecrona T., Pekala P. H. Regulation of lipoprotein lipase mRNA content in 3T3-L1 cells by tumour necrosis factor. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 1;249(3):765–769. doi: 10.1042/bj2490765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currie R. A., Eckel R. H. Characterization of a high affinity octamer transcription factor binding site in the human lipoprotein lipase promoter. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Nov 1;298(2):630–639. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90459-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distel R. J., Ro H. S., Rosen B. S., Groves D. L., Spiegelman B. M. Nucleoprotein complexes that regulate gene expression in adipocyte differentiation: direct participation of c-fos. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):835–844. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90621-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flink I. L., Morkin E. Interaction of thyroid hormone receptors with strong and weak cis-acting elements in the human alpha-myosin heavy chain gene promoter. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11233–11237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotamisligil G. S., Shargill N. S., Spiegelman B. M. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science. 1993 Jan 1;259(5091):87–91. doi: 10.1126/science.7678183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hua X. X., Enerbäck S., Hudson J., Youkhana K., Gimble J. M. Cloning and characterization of the promoter of the murine lipoprotein lipase-encoding gene: structural and functional analysis. Gene. 1991 Nov 15;107(2):247–258. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90325-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël A., Le Bail O., Hatat D., Piette J., Kieran M., Logeat F., Wallach D., Fellous M., Kourilsky P. TNF stimulates expression of mouse MHC class I genes by inducing an NF kappa B-like enhancer binding activity which displaces constitutive factors. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3793–3800. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08556.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanza-Jacoby S., Lansey S. C., Miller E. E., Cleary M. P. Sequential changes in the activities of lipoprotein lipase and lipogenic enzymes during tumor growth in rats. Cancer Res. 1984 Nov;44(11):5062–5067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M., Tartaglia L. A., Lee A., Bennett G. L., Rice G. C., Wong G. H., Chen E. Y., Goeddel D. V. Cloning and expression of cDNAs for two distinct murine tumor necrosis factor receptors demonstrate one receptor is species specific. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2830–2834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. P., Stashenko P. Characterization of a tumor necrosis factor-responsive element which down-regulates the human osteocalcin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3714–3721. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lähdevirta J., Maury C. P., Teppo A. M., Repo H. Elevated levels of circulating cachectin/tumor necrosis factor in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Med. 1988 Sep;85(3):289–291. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90576-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moldawer L. L., Sherry B., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Endogenous cachectin/tumour necrosis factor-alpha production contributes to experimental cancer-associated cachexia. Cancer Surv. 1989;8(4):853–859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadur C. N., Yost T. J., Eckel R. H. Fat feeding decreases insulin responsiveness of adipose tissue lipoprotein lipase. Metabolism. 1984 Nov;33(11):1043–1047. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(84)90235-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena U., Witte L. D., Goldberg I. J. Tumor necrosis factor induced release of endothelial cell lipoprotein lipase. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 May-Jun;10(3):470–476. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.3.470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segil N., Roberts S. B., Heintz N. Mitotic phosphorylation of the Oct-1 homeodomain and regulation of Oct-1 DNA binding activity. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1814–1816. doi: 10.1126/science.1684878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens J. M., Pekala P. H. Transcriptional repression of the C/EBP-alpha and GLUT4 genes in 3T3-L1 adipocytes by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Regulations is coordinate and independent of protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13580–13584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Student A. K., Hsu R. Y., Lane M. D. Induction of fatty acid synthetase synthesis in differentiating 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4745–4750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Peter W., Ciesiolka T., Gruss P., Schöler H. R. Mouse Oct-1 contains a composite homeodomain of human Oct-1 and Oct-2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jan 25;21(2):245–252. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.2.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada H., Iwase S., Mohri M., Kufe D. Involvement of a nuclear factor-kappa B-like protein in induction of the macrophage colony-stimulating factor gene by tumor necrosis factor. Blood. 1991 Oct 15;78(8):1988–1995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zechner R., Newman T. C., Sherry B., Cerami A., Breslow J. L. Recombinant human cachectin/tumor necrosis factor but not interleukin-1 alpha downregulates lipoprotein lipase gene expression at the transcriptional level in mouse 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2394–2401. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]