Abstract
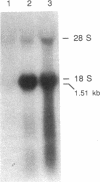
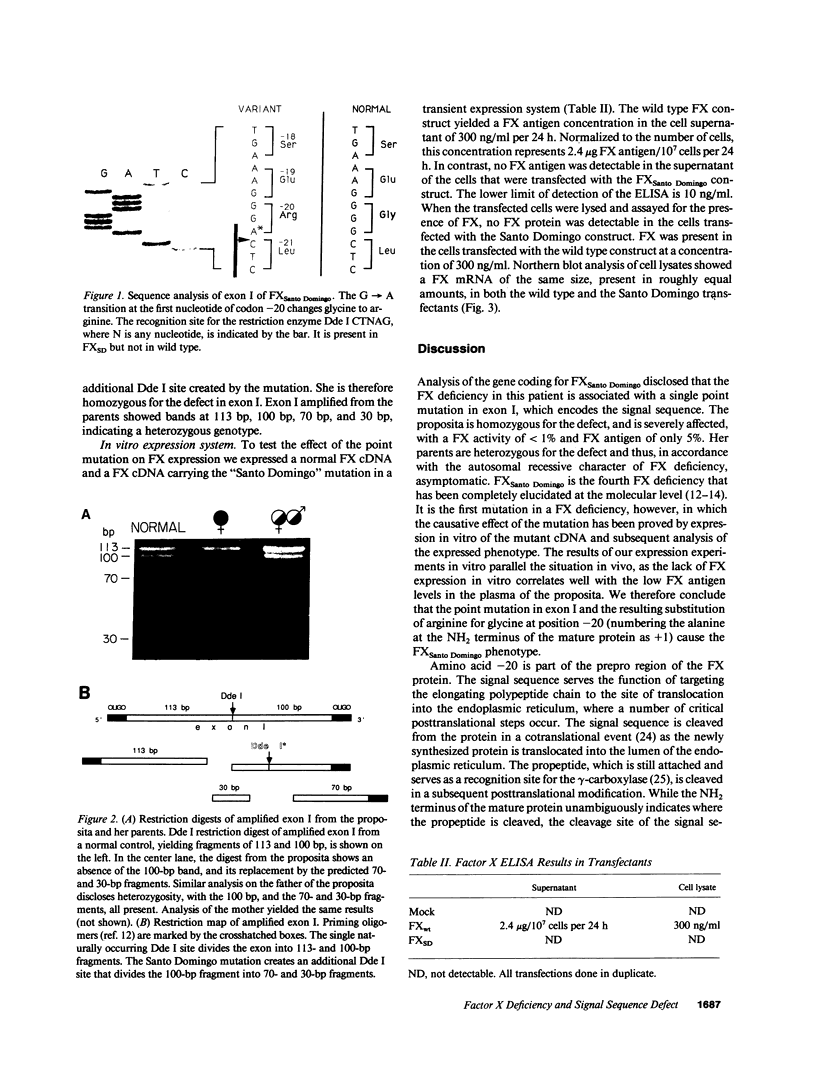
Factor X (FX) is a vitamin K-dependent plasma protein required for the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of blood coagulation. FXSanto Domingo is a hereditary FX deficiency which is characterized clinically by a severe bleeding diathesis. The proposita has a FX activity of less than 1% and a FX antigen of less than 5%. We have determined the molecular basis of the defect in the FXSanto Domingo gene by amplification of all eight exons with polymerase chain reaction and subsequent sequence analysis. The patient is homozygous for a G----A transition in exon I at codon -20 (numbering the alanine at the NH2 terminus of the mature protein as +1), resulting in the substitution of arginine for glycine in the carboxy-terminal part of the signal peptide. This amino acid change occurs near the presumed cleavage site of the signal peptidase. We hypothesized that the mutation might prevent cleavage by the signal peptidase which in turn would impair proper secretion of the FX protein. To test this hypothesis, we compared the expression of wild type and mutant FX cDNA in a human kidney cell line. Wild type and mutant constructs in the expression vector pCMV4 were introduced into the human embryonic kidney cell line 293 by calcium phosphate transfection. FX antigen levels in the supernatant of the cells harboring the wild type construct were 2.4 micrograms/10(7) cells per 24 h, whereas antigen levels in media from cells containing the FXSanto Domingo construct were undetectable. No FX antigen was detected in the cell lysates of cells transfected with the mutant construct. To insure that the difference in protein levels was not due to a difference in steady state levels of mRNA, Northern analysis was performed on RNA from the cell lysates of both constructs. The results showed a transcript of the same size, present in roughly equal amounts, in both cases. Thus, the defect in the signal sequence of FXSanto Domingo exerts its effect posttranscriptionally. FXSanto Domingo is the first described example of a bleeding diathesis due to a mutation in the signal sequence.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson S., Davis D. L., Dahlbäck H., Jörnvall H., Russell D. W. Cloning, structure, and expression of the mitochondrial cytochrome P-450 sterol 26-hydroxylase, a bile acid biosynthetic enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8222–8229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold A., Horst S. A., Gardella T. J., Baba H., Levine M. A., Kronenberg H. M. Mutation of the signal peptide-encoding region of the preproparathyroid hormone gene in familial isolated hypoparathyroidism. J Clin Invest. 1990 Oct;86(4):1084–1087. doi: 10.1172/JCI114811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan S. O., Myles T., Peach R. J., Donaldson D., George P. M. Albumin Redhill (-1 Arg, 320 Ala----Thr): a glycoprotein variant of human serum albumin whose precursor has an aberrant signal peptidase cleavage site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):26–30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church W. R., Messier T. L., Tucker M. M., Mann K. G. An inhibitory monoclonal antibody to factor X that blocks prothrombin activation but not prothrombinase enzyme assembly. Blood. 1988 Dec;72(6):1911–1921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denson K. W., Lurie A., De Cataldo F., Mannucci P. M. The factor-X defect: recognition of abnormal forms of factor X. Br J Haematol. 1970 Mar;18(3):317–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb01446.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fair D. S., Edgington T. S. Heterogeneity of hereditary and acquired factor X deficiencies by combined immunochemical and functional analyses. Br J Haematol. 1985 Feb;59(2):235–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1985.tb02990.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fair D. S., Plow E. F., Edgington T. S. Combined functional and immunochemical analysis of normal and abnormal human factor X. J Clin Invest. 1979 Oct;64(4):884–894. doi: 10.1172/JCI109554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikes J. D., Barkocy-Gallagher G. A., Klapper D. G., Bassford P. J., Jr Maturation of Escherichia coli maltose-binding protein by signal peptidase I in vivo. Sequence requirements for efficient processing and demonstration of an alternate cleavage site. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3417–3423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung M. R., Hay C. W., MacGillivray R. T. Characterization of an almost full-length cDNA coding for human blood coagulation factor X. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3591–3595. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannelli F., Green P. M., High K. A., Lozier J. N., Lillicrap D. P., Ludwig M., Olek K., Reitsma P. H., Goossens M., Yoshioka A. Haemophilia B: database of point mutations and short additions and deletions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 25;18(14):4053–4059. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.14.4053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOUGIE C., BARROW E. M., GRAHAM J. B. Stuart clotting defect. I. Segregation of an hereditary hemorrhagic state from the heterogeneous group heretofore called stable factor (SPCA, proconvertin, factor VII) deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1957 Mar;36(3):485–496. doi: 10.1172/JCI103446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. N., Kasper C. K., Roberts H. R., Stafford D. W., High K. A. Molecular defect in factor IXHilo, a hemophilia Bm variant: Arg----Gln at the carboxyterminal cleavage site of the activation peptide. Blood. 1989 Feb 15;73(3):718–721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. M., Nemerson Y. Blood coagulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:765–811. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James H. L., Girolami A., Fair D. S. Molecular defect in coagulation factor XFriuli results from a substitution of serine for proline at position 343. Blood. 1991 Jan 15;77(2):317–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaul R. K., Hildebrand B., Roberts S., Jagadeeswaran P. Isolation and characterization of human blood-coagulation factor X cDNA. Gene. 1986;41(2-3):311–314. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knobloch J. E., Suttie J. W. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Control of enzyme activity by the "propeptide" region of factor X. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15334–15337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leytus S. P., Chung D. W., Kisiel W., Kurachi K., Davie E. W. Characterization of a cDNA coding for human factor X. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3699–3702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leytus S. P., Foster D. C., Kurachi K., Davie E. W. Gene for human factor X: a blood coagulation factor whose gene organization is essentially identical with that of factor IX and protein C. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 9;25(18):5098–5102. doi: 10.1021/bi00366a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMullen B. A., Fujikawa K., Kisiel W., Sasagawa T., Howald W. N., Kwa E. Y., Weinstein B. Complete amino acid sequence of the light chain of human blood coagulation factor X: evidence for identification of residue 63 as beta-hydroxyaspartic acid. Biochemistry. 1983 Jun 7;22(12):2875–2884. doi: 10.1021/bi00281a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy S. V., Zhou Z. Q., Rao K. J., Scott J. P., Watzke H., High K. A., Jagadeeswaran P. Molecular characterization of human factor XSan Antonio. Blood. 1989 Oct;74(5):1486–1490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royle N. J., Fung M. R., MacGillivray R. T., Hamerton J. L. The gene for clotting factor 10 is mapped to 13q32----qter. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1986;41(3):185–188. doi: 10.1159/000132225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verner K., Schatz G. Protein translocation across membranes. Science. 1988 Sep 9;241(4871):1307–1313. doi: 10.1126/science.2842866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvikis S., Chan L., Siest G., Drouin P., Boerwinkle E. An insertion deletion polymorphism in the signal peptide of the human apolipoprotein B gene. Hum Genet. 1990 Mar;84(4):373–375. doi: 10.1007/BF00196239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watzke H. H., Lechner K., Roberts H. R., Reddy S. V., Welsch D. J., Friedman P., Mahr G., Jagadeeswaran P., Monroe D. M., High K. A. Molecular defect (Gla+14----Lys) and its functional consequences in a hereditary factor X deficiency (factor X "Vorarlberg"). J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11982–11989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):17–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]