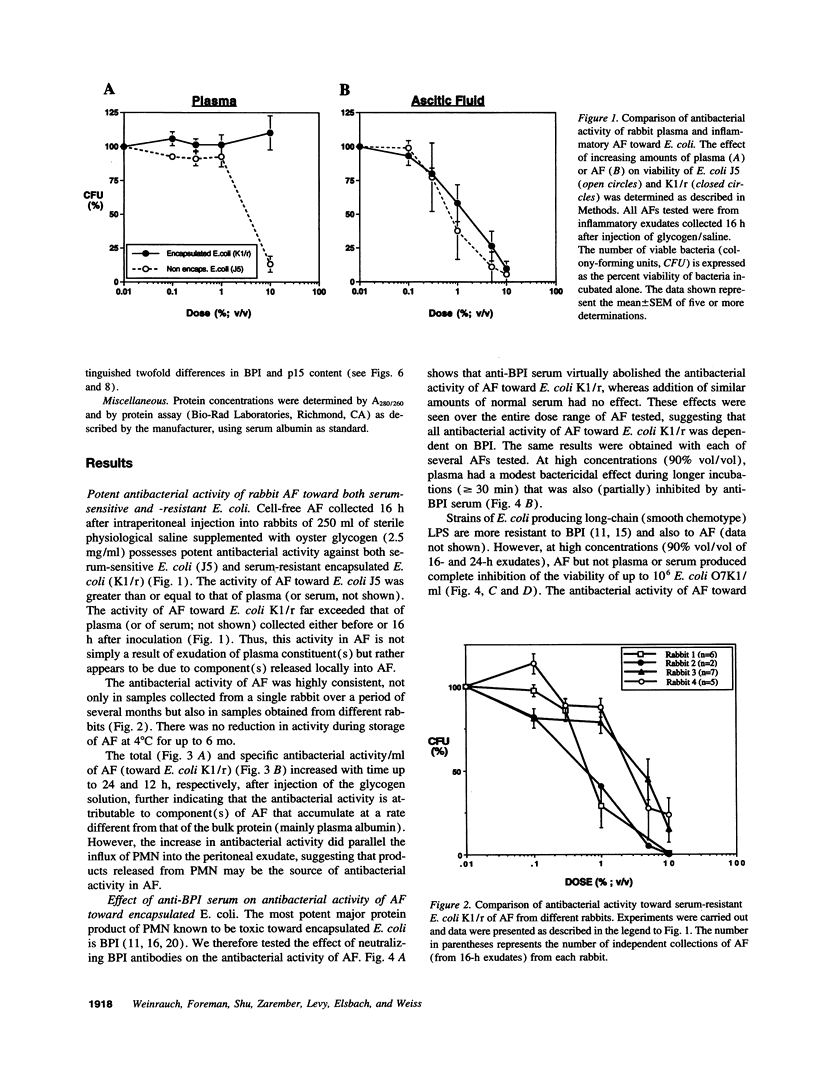
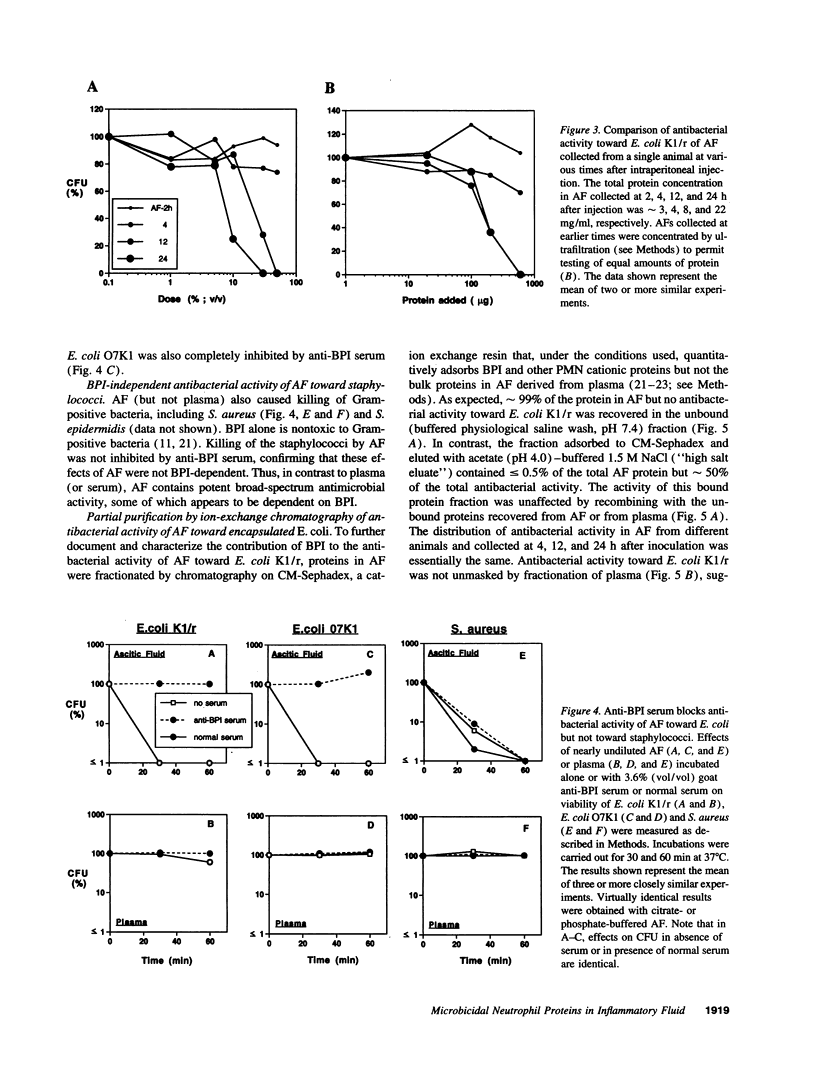
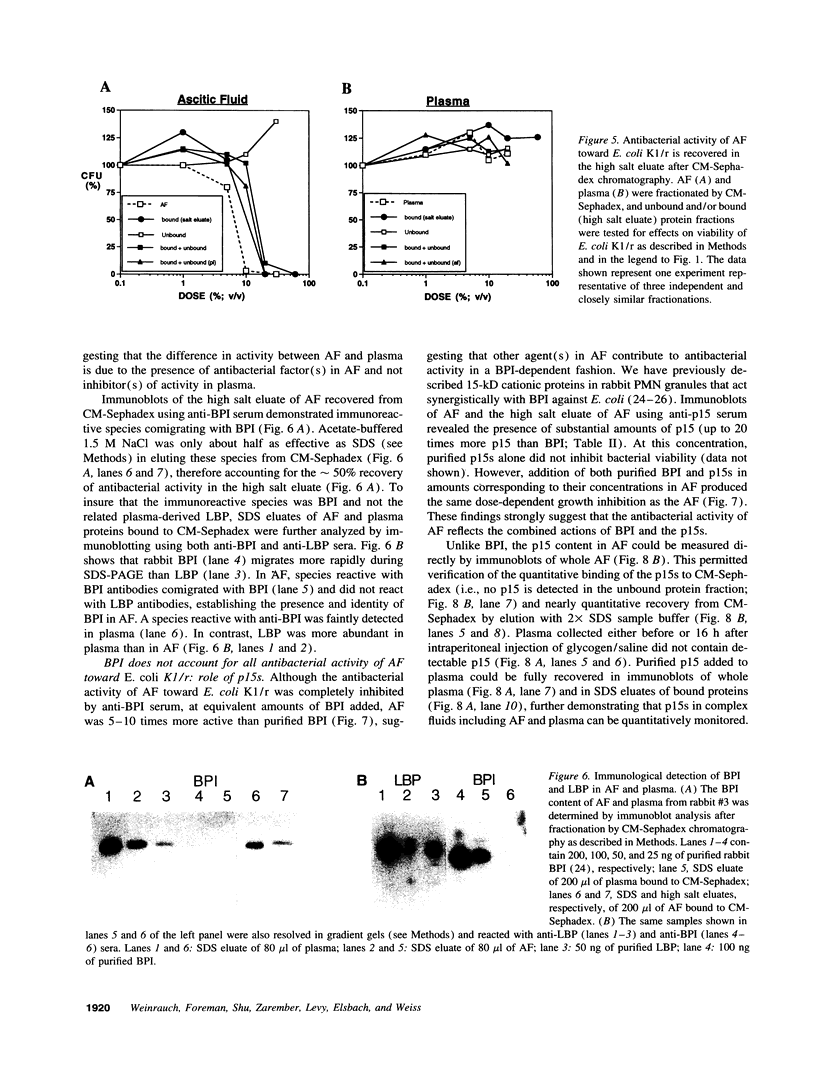
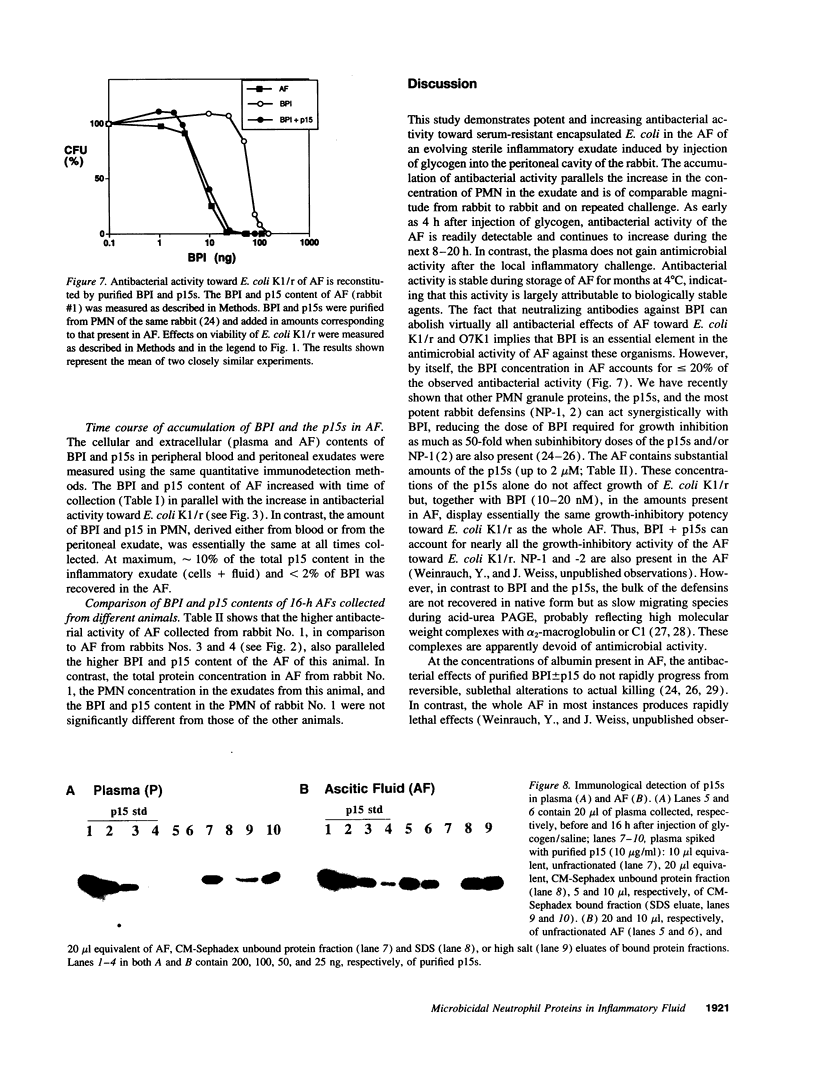
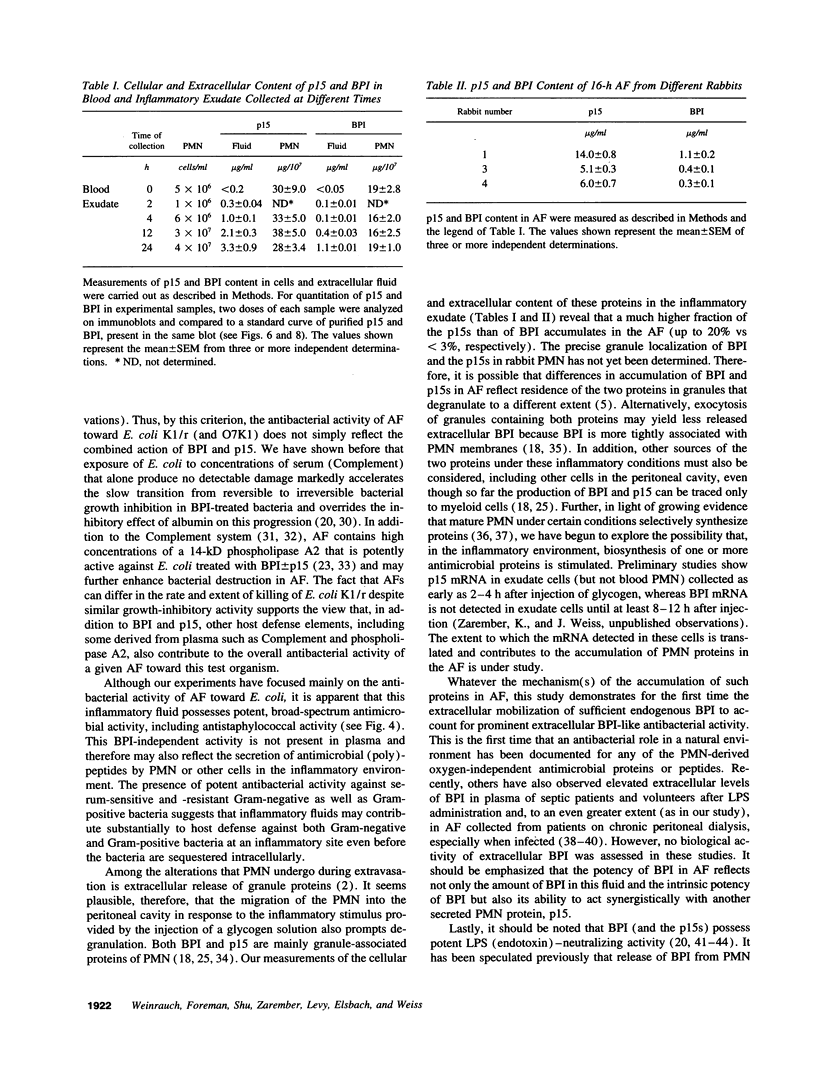
Abstract
To what extent the host defense role of granule-associated antibacterial proteins and peptides of PMN includes extracellular action has not been established. To address this question, we have analyzed the antibacterial activity of cell-free (ascitic) fluid (AF) obtained from glycogen-induced sterile inflammatory rabbit peritoneal exudates in which > 95% of the accumulating cells are PMN. AF, but not plasma collected in parallel, exhibits potent activity toward serum-resistant Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Total and specific antibacterial activity of AF increases during the first 12 h after injection of glycogen in parallel with the influx of PMN. At maximum, > 99% of 10(7) encapsulated Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus are killed in 30 min/ml of AF. Neutralizing antibodies against the bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein (BPI) of PMN abolishes activity of AF toward encapsulated E. coli but has no effect on activity vs staphylococci. However, BPI alone (approximately 1 microgram/ml in AF) can only account for < or = 20% of AF activity toward E. coli. AF also contains 15 kD PMN proteins (p15s) that act in synergy with BPI. Purified BPI and p15s, in amounts present in AF, reconstitute the growth-inhibitory activity of AF toward encapsulated E. coli. These findings show for the first time an extracellular function of endogenous BPI, providing, together with the p15s, a potent microbicidal system toward Gram-negative bacteria resistant to plasma-derived proteins and phagocytes in inflammatory exudates.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akalin H. E., Laleli Y., Telatar H. Bactericidal and opsonic activity of ascitic fluid from cirrhotic and noncirrhotic patients. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jun;147(6):1011–1017. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.6.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bercovici B., Michel J., Miller J., Sacks T. G. Antimicrobial activity of human peritoneal fluid. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1975 Dec;141(6):885–887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borregaard N., Lollike K., Kjeldsen L., Sengeløv H., Bastholm L., Nielsen M. H., Bainton D. F. Human neutrophil granules and secretory vesicles. Eur J Haematol. 1993 Oct;51(4):187–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1993.tb00629.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvano S. E., Thompson W. A., Marra M. N., Coyle S. M., de Riesthal H. F., Trousdale R. K., Barie P. S., Scott R. W., Moldawer L. L., Lowry S. F. Changes in polymorphonuclear leukocyte surface and plasma bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein and plasma lipopolysaccharide binding protein during endotoxemia or sepsis. Arch Surg. 1994 Feb;129(2):220–226. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1994.01420260116016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsbach P., Weiss J. Bactericidal/permeability increasing protein and host defense against gram-negative bacteria and endotoxin. Curr Opin Immunol. 1993 Feb;5(1):103–107. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(93)90088-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsbach P., Weiss J., Franson R. C., Beckerdite-Quagliata S., Schneider A., Harris L. Separation and purification of a potent bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein and a closely associated phospholipase A2 from rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Observations on their relationship. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):11000–11009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsbach P., Weiss J., Levy O. Integration of antimicrobial host defenses: role of the bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein. Trends Microbiol. 1994 Sep;2(9):324–328. doi: 10.1016/0966-842x(94)90449-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forst S., Weiss J., Elsbach P., Maraganore J. M., Reardon I., Heinrikson R. L. Structural and functional properties of a phospholipase A2 purified from an inflammatory exudate. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 30;25(26):8381–8385. doi: 10.1021/bi00374a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabay J. E., Almeida R. P. Antibiotic peptides and serine protease homologs in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: defensins and azurocidin. Curr Opin Immunol. 1993 Feb;5(1):97–102. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(93)90087-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH J. G. Phagocytin: a bactericidal substance from polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Exp Med. 1956 May 1;103(5):589–611. doi: 10.1084/jem.103.5.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehr H. A., Arfors K. E. Mechanisms of tissue damage by leukocytes. Curr Opin Hematol. 1994 Jan;1(1):92–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Lichtenstein A. K., Ganz T. Defensins: antimicrobial and cytotoxic peptides of mammalian cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:105–128. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.000541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy O., Ooi C. E., Weiss J., Lehrer R. I., Elsbach P. Individual and synergistic effects of rabbit granulocyte proteins on Escherichia coli. J Clin Invest. 1994 Aug;94(2):672–682. doi: 10.1172/JCI117384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy O., Weiss J., Zarember K., Ooi C. E., Elsbach P. Antibacterial 15-kDa protein isoforms (p15s) are members of a novel family of leukocyte proteins. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):6058–6063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd A. R., Oppenheim J. J. Poly's lament: the neglected role of the polymorphonuclear neutrophil in the afferent limb of the immune response. Immunol Today. 1992 May;13(5):169–172. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90121-M. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannion B. A., Weiss J., Elsbach P. Separation of sublethal and lethal effects of polymorphonuclear leukocytes on Escherichia coli. J Clin Invest. 1990 Aug;86(2):631–641. doi: 10.1172/JCI114755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannion B. A., Weiss J., Elsbach P. Separation of sublethal and lethal effects of the bactericidal/permeability increasing protein on Escherichia coli. J Clin Invest. 1990 Mar;85(3):853–860. doi: 10.1172/JCI114512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marra M. N., Wilde C. G., Collins M. S., Snable J. L., Thornton M. B., Scott R. W. The role of bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein as a natural inhibitor of bacterial endotoxin. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 15;148(2):532–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marra M. N., Wilde C. G., Griffith J. E., Snable J. L., Scott R. W. Bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein has endotoxin-neutralizing activity. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 15;144(2):662–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F. Neutrophil activation on biological surfaces. Massive secretion of hydrogen peroxide in response to products of macrophages and lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1550–1560. doi: 10.1172/JCI113241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi C. E., Weiss J., Doerfler M. E., Elsbach P. Endotoxin-neutralizing properties of the 25 kD N-terminal fragment and a newly isolated 30 kD C-terminal fragment of the 55-60 kD bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein of human neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1991 Sep 1;174(3):649–655. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.3.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi C. E., Weiss J., Levy O., Elsbach P. Isolation of two isoforms of a novel 15-kDa protein from rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes that modulate the antibacterial actions of other leukocyte proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15956–15962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opal S. M., Palardy J. E., Marra M. N., Fisher C. J., Jr, McKelligon B. M., Scott R. W. Relative concentrations of endotoxin-binding proteins in body fluids during infection. Lancet. 1994 Aug 13;344(8920):429–431. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)91767-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyutich A., Ganz T. Activated alpha 2-macroglobulin is a principal defensin-binding protein. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Aug;5(2):101–106. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/5.2.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira H. A., Shafer W. M., Pohl J., Martin L. E., Spitznagel J. K. CAP37, a human neutrophil-derived chemotactic factor with monocyte specific activity. J Clin Invest. 1990 May;85(5):1468–1476. doi: 10.1172/JCI114593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Traffic signals for lymphocyte recirculation and leukocyte emigration: the multistep paradigm. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):301–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90337-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobias P. S., Mathison J., Mintz D., Lee J. D., Kravchenko V., Kato K., Pugin J., Ulevitch R. J. Participation of lipopolysaccharide-binding protein in lipopolysaccharide-dependent macrophage activation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1992 Sep;7(3):239–245. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/7.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbanac D., Zanetti M., Romeo D. Chemotactic and protease-inhibiting activities of antibiotic peptide precursors. FEBS Lett. 1993 Feb 15;317(3):255–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81287-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman Y., Golde D. W., Savion N., Fabian I. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor enhances cationic antimicrobial protein synthesis by human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3437–3443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weersink A. J., van Kessel K. P., van den Tol M. E., van Strijp J. A., Torensma R., Verhoef J., Elsbach P., Weiss J. Human granulocytes express a 55-kDa lipopolysaccharide-binding protein on the cell surface that is identical to the bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 1;150(1):253–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Beckerdite-Quagliata S., Elsbach P. Resistance of gram-negative bacteria to purified bactericidal leukocyte proteins: relation to binding and bacterial lipopolysaccharide structure. J Clin Invest. 1980 Mar;65(3):619–628. doi: 10.1172/JCI109707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Elsbach P., Shu C., Castillo J., Grinna L., Horwitz A., Theofan G. Human bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein and a recombinant NH2-terminal fragment cause killing of serum-resistant gram-negative bacteria in whole blood and inhibit tumor necrosis factor release induced by the bacteria. J Clin Invest. 1992 Sep;90(3):1122–1130. doi: 10.1172/JCI115930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Franson R. C., Beckerdite S., Schmeidler K., Elsbach P. Partial characterization and purification of a rabbit granulocyte factor that increases permeability of Escherichia coli. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jan;55(1):33–42. doi: 10.1172/JCI107915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Kao L., Victor M., Elsbach P. Oxygen-independent intracellular and oxygen-dependent extracellular killing of Escherichia coli S15 by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):206–212. doi: 10.1172/JCI111947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Olsson I. Cellular and subcellular localization of the bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein of neutrophils. Blood. 1987 Feb;69(2):652–659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Victor M., Cross A. S., Elsbach P. Sensitivity of K1-encapsulated Escherichia coli to killing by the bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein of rabbit and human neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):1149–1153. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.1149-1153.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J. Tissue destruction by neutrophils. N Engl J Med. 1989 Feb 9;320(6):365–376. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198902093200606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright G. W., Ooi C. E., Weiss J., Elsbach P. Purification of a cellular (granulocyte) and an extracellular (serum) phospholipase A2 that participate in the destruction of Escherichia coli in a rabbit inflammatory exudate. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6675–6681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]