Abstract
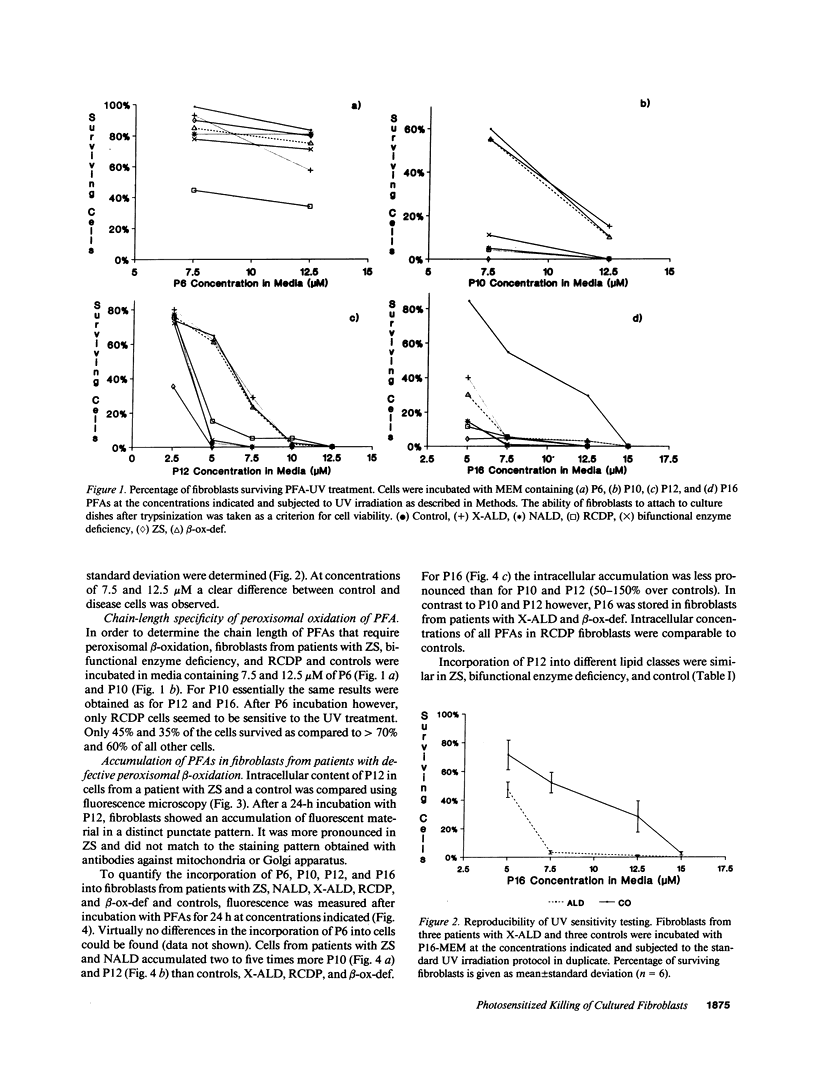
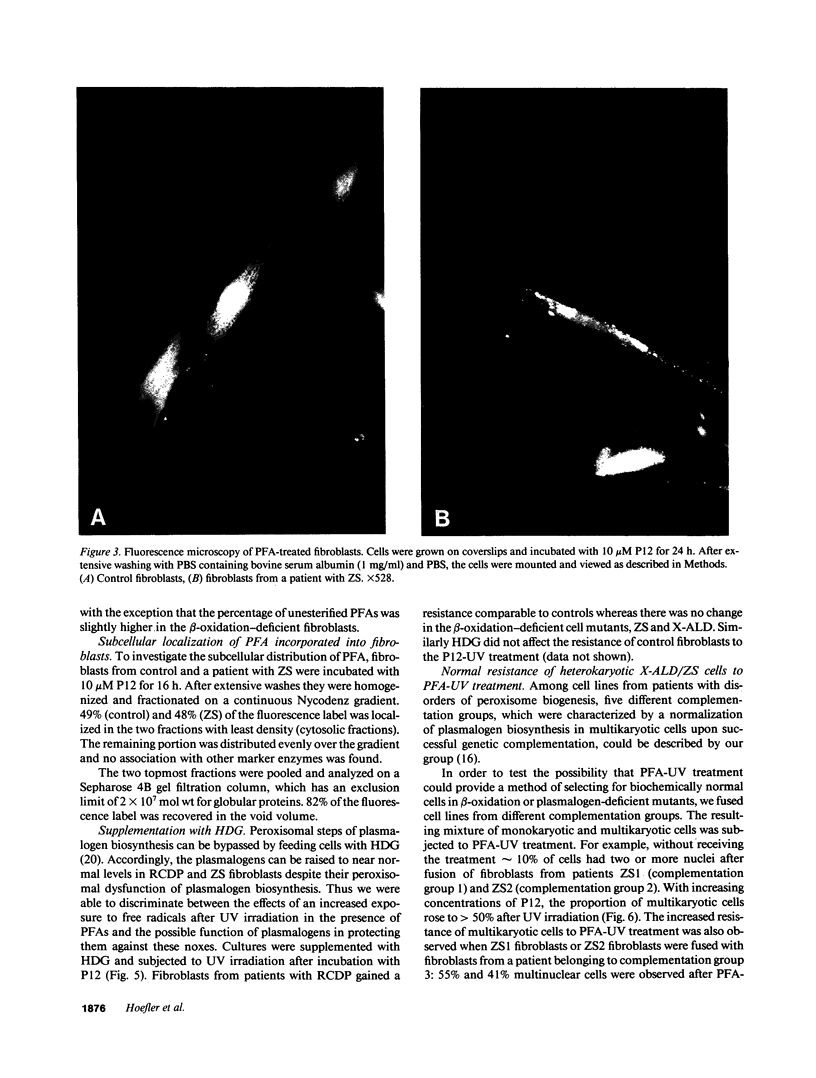
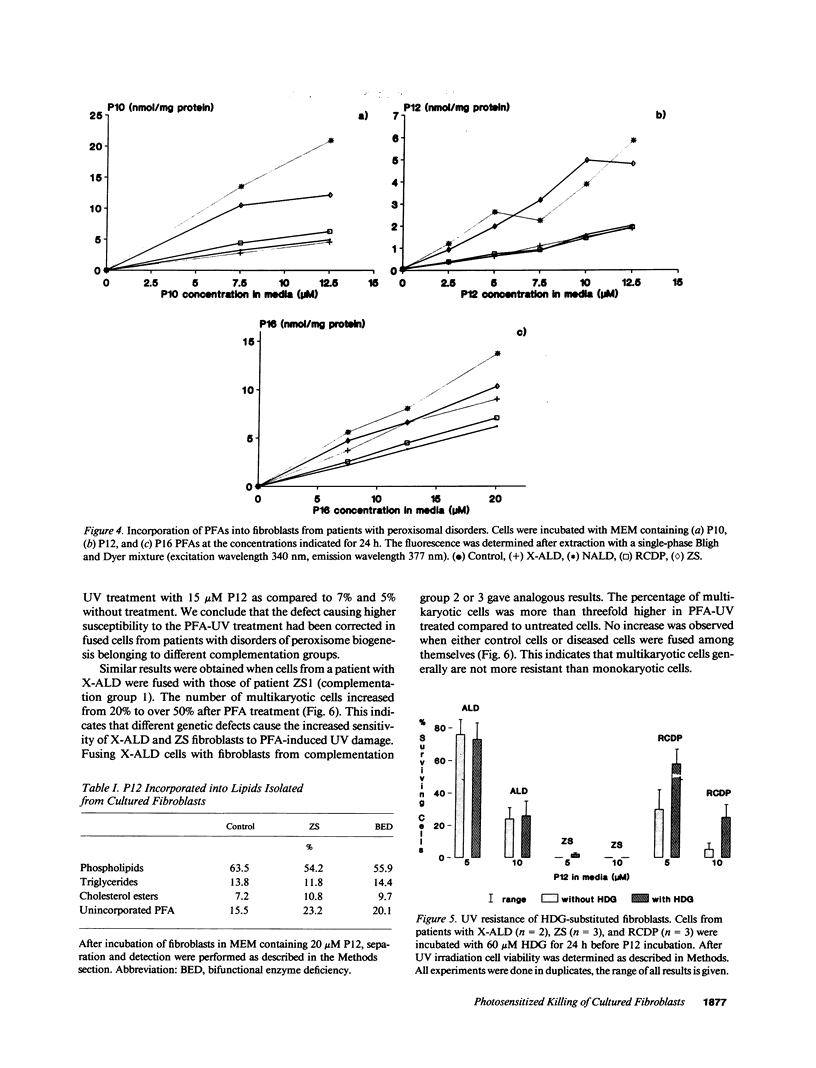
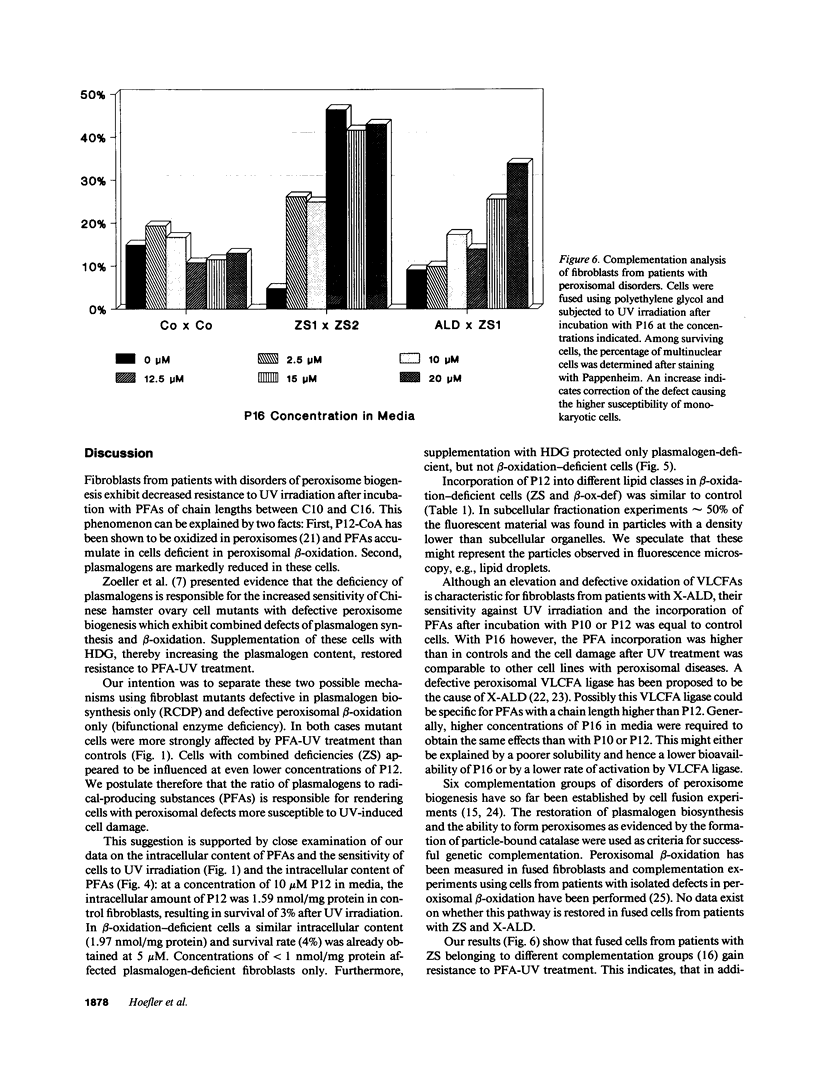
The influence of pyrene-fatty acids on the resistance of cells to ultraviolet (UV) radiation was investigated in cultured fibroblasts from patients with five types of peroxisomal disorders. All showed reduced survival compared to control. The effect varied with the biochemical defect involved and the chain length of the pyrene fatty acid. Reduced survival was observed in cells deficient in plasmalogens (rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata) and in cells deficient in peroxisomal fatty acid oxidation (bifunctional enzyme deficiency), which accumulated pyrene-fatty acids. X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy fibroblasts accumulated pyrene-fatty acids and showed increased UV sensitivity only when exposed to longer-chain pyrene fatty acids. UV radiation resistance was lowest in cells with combined impairment of plasmalogen synthesis and fatty acid oxidation (Zellweger syndrome, neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy), suggesting that UV sensitivity correlates inversely with the ratio of plasmalogens to radical producing substances. Fibroblasts deficient in plasmalogens gained normal UV resistance when their plasmalogen levels were normalized by hexadecylglycerol. UV resistance increased when Zellweger cells were fused with X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy cells, and also when Zellweger cells belonging to different complementation groups were fused. The results provide leads to the pathogenesis of the multiple malformations associated with peroxisomal disorders and a method for the selection of cells in which the metabolic defect has been corrected.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkhem I., Falk O. Assay of the major bile acids in serum by isotope dilution-mass spectrometry. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1983 Apr;43(2):163–170. doi: 10.1080/00365518309168239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brul S., Westerveld A., Strijland A., Wanders R. J., Schram A. W., Heymans H. S., Schutgens R. B., van den Bosch H., Tager J. M. Genetic heterogeneity in the cerebrohepatorenal (Zellweger) syndrome and other inherited disorders with a generalized impairment of peroxisomal functions. A study using complementation analysis. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1710–1715. doi: 10.1172/JCI113510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatt S., Bremer J., Osmundsen H. Pyrene dodecanoic acid coenzyme A ester: peroxisomal oxidation and chain shortening. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jan 19;958(1):130–133. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90254-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermetter A., Rainer B., Ivessa E., Kalb E., Loidl J., Roscher A., Paltauf F. Influence of plasmalogen deficiency on membrane fluidity of human skin fibroblasts: a fluorescence anisotropy study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 16;978(1):151–157. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90510-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heymans H. S., Oorthuys J. W., Nelck G., Wanders R. J., Schutgens R. B. Rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata: another peroxisomal disorder. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jul 18;313(3):187–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoefler G., Hoefler S., Watkins P. A., Chen W. W., Moser A., Baldwin V., McGillivary B., Charrow J., Friedman J. M., Rutledge L. Biochemical abnormalities in rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata. J Pediatr. 1988 May;112(5):726–733. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80689-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarow P. B., Fujiki Y., Small G. M., Watkins P., Moser H. Presence of the peroxisomal 22-kDa integral membrane protein in the liver of a person lacking recognizable peroxisomes (Zellweger syndrome). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9193–9196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazo O., Contreras M., Bhushan A., Stanley W., Singh I. Adrenoleukodystrophy: impaired oxidation of fatty acids due to peroxisomal lignoceroyl-CoA ligase deficiency. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 May 1;270(2):722–728. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90555-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuinness M. C., Moser A. B., Moser H. W., Watkins P. A. Peroxisomal disorders: complementation analysis using beta-oxidation of very long chain fatty acids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Oct 15;172(1):364–369. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80218-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser H. W., Moser A. B., Kawamura N., Murphy J., Suzuki K., Schaumburg H., Kishimoto Y. Adrenoleukodystrophy: elevated C26 fatty acid in cultured skin fibroblasts. Ann Neurol. 1980 Jun;7(6):542–549. doi: 10.1002/ana.410070607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naidu S., Hoefler G., Watkins P. A., Chen W. W., Moser A. B., Hoefler S., Rance N. E., Powers J. M., Beard M., Green W. R. Neonatal seizures and retardation in a girl with biochemical features of X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: a possible new peroxisomal disease entity. Neurology. 1988 Jul;38(7):1100–1107. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.7.1100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulos A., Sharp P., Fellenberg A. J., Danks D. M. Cerebro-hepato-renal (Zellweger) syndrome, adrenoleukodystrophy, and Refsum's disease: plasma changes and skin fibroblast phytanic acid oxidase. Hum Genet. 1985;70(2):172–177. doi: 10.1007/BF00273077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roscher A. A., Hoefler S., Hoefler G., Paschke E., Paltauf F., Moser A., Moser H. Genetic and phenotypic heterogeneity in disorders of peroxisome biogenesis--a complementation study involving cell lines from 19 patients. Pediatr Res. 1989 Jul;26(1):67–72. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198907000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roscher A., Molzer B., Bernheimer H., Stöckler S., Mutz I., Paltauf F. The cerebrohepatorenal (Zellweger) syndrome: an improved method for the biochemical diagnosis and its potential value for prenatal detection. Pediatr Res. 1985 Sep;19(9):930–933. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198509000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schram A. W., Goldfischer S., van Roermund C. W., Brouwer-Kelder E. M., Collins J., Hashimoto T., Heymans H. S., van den Bosch H., Schutgens R. B., Tager J. M. Human peroxisomal 3-oxoacyl-coenzyme A thiolase deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2494–2496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater T. F. Free-radical mechanisms in tissue injury. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 15;222(1):1–15. doi: 10.1042/bj2220001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Miura N., Satokata I., Miyamoto I., Yoshida M. C., Satoh Y., Kondo S., Yasui A., Okayama H., Okada Y. Analysis of a human DNA excision repair gene involved in group A xeroderma pigmentosum and containing a zinc-finger domain. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):73–76. doi: 10.1038/348073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitz T., Naiman T., Avissar S. S., Bar S., Okayama H., Canaani D. Complementation of the UV-sensitive phenotype of a xeroderma pigmentosum human cell line by transfection with a cDNA clone library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8801–8804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanders R. J., van Roermund C. W., van Wijland M. J., Schutgens R. B., Heikoop J., van den Bosch H., Schram A. W., Tager J. M. Peroxisomal fatty acid beta-oxidation in relation to the accumulation of very long chain fatty acids in cultured skin fibroblasts from patients with Zellweger syndrome and other peroxisomal disorders. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1778–1783. doi: 10.1172/JCI113271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins P. A., Chen W. W., Harris C. J., Hoefler G., Hoefler S., Blake D. C., Jr, Balfe A., Kelley R. I., Moser A. B., Beard M. E. Peroxisomal bifunctional enzyme deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1989 Mar;83(3):771–777. doi: 10.1172/JCI113956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. N., Holmes R. G., Custer J., Lipkowitz J. L., Stover J., Datta N., Hajra A. Zellweger syndrome: diagnostic assays, syndrome delineation, and potential therapy. Am J Med Genet. 1986 May;24(1):69–82. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320240109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoeller R. A., Allen L. A., Santos M. J., Lazarow P. B., Hashimoto T., Tartakoff A. M., Raetz C. R. Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants defective in peroxisome biogenesis. Comparison to Zellweger syndrome. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21872–21878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoeller R. A., Morand O. H., Raetz C. R. A possible role for plasmalogens in protecting animal cells against photosensitized killing. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11590–11596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg G. A., Breukelman H., Elzinga H., Trijbels J. M., Monnens L. A., Muskiet F. A. Determination of pipecolic acid in urine and plasma by isotope dilution mass fragmentography. Clin Chim Acta. 1986 Sep 30;159(3):229–237. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(86)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]