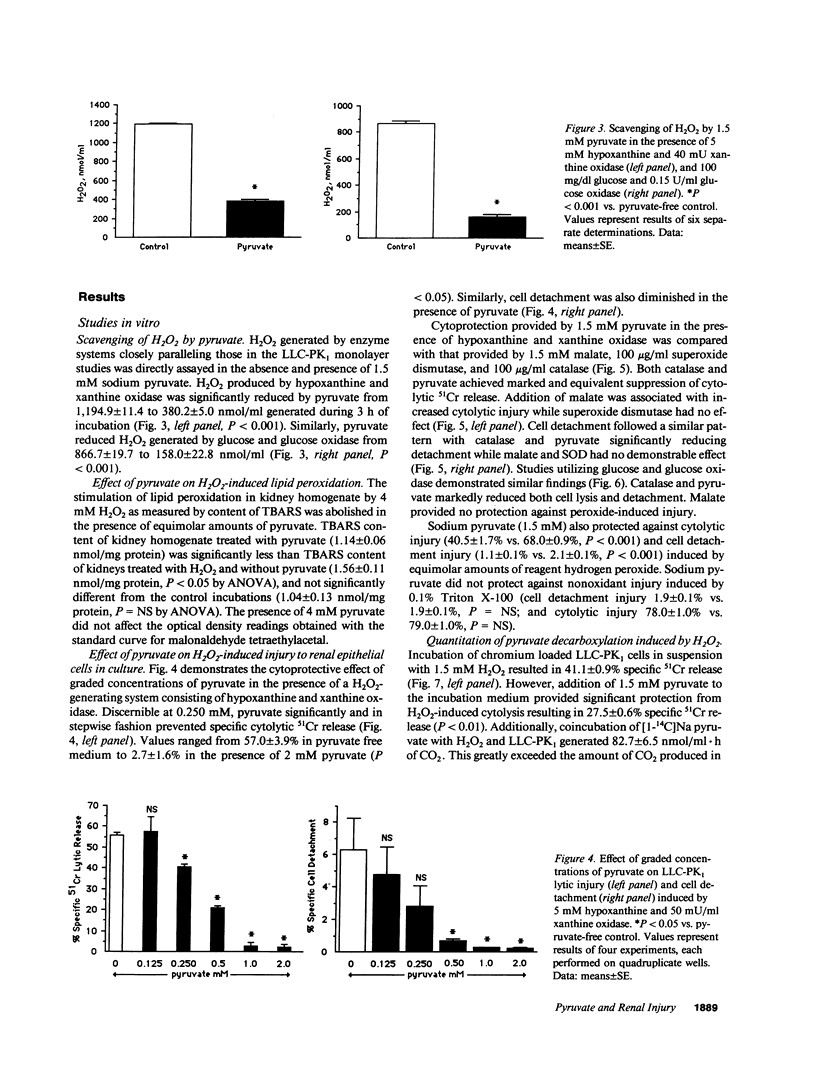
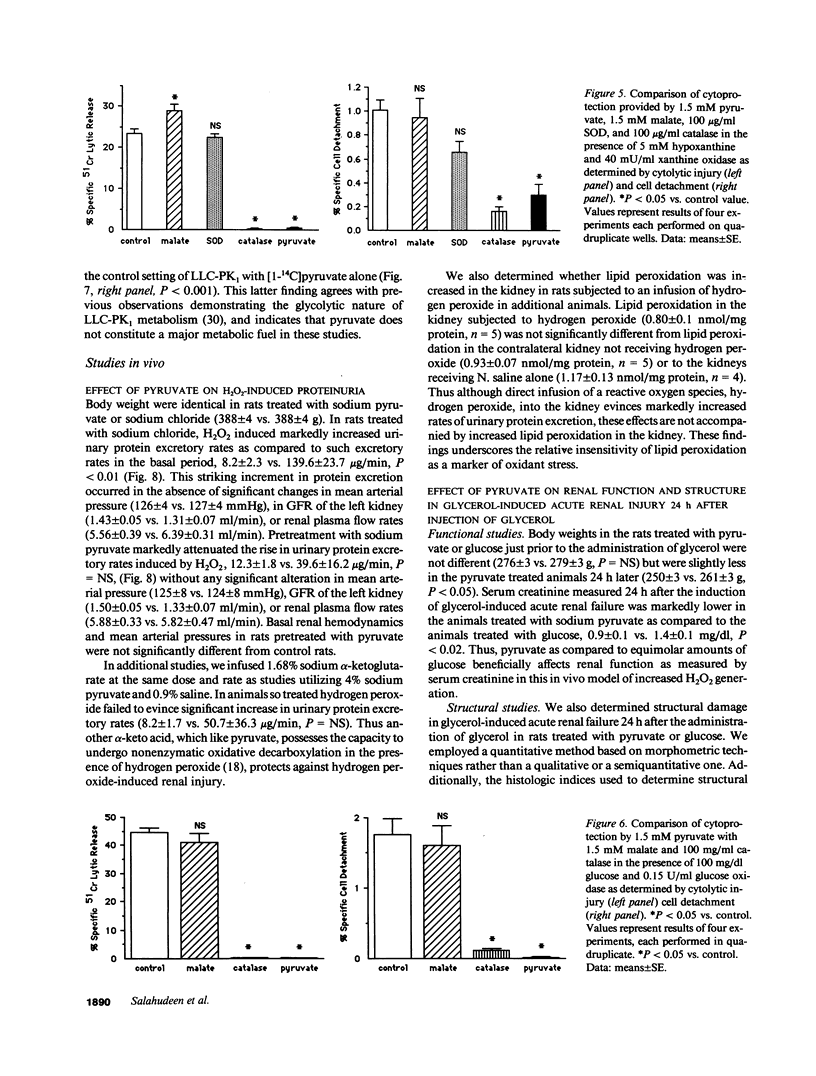
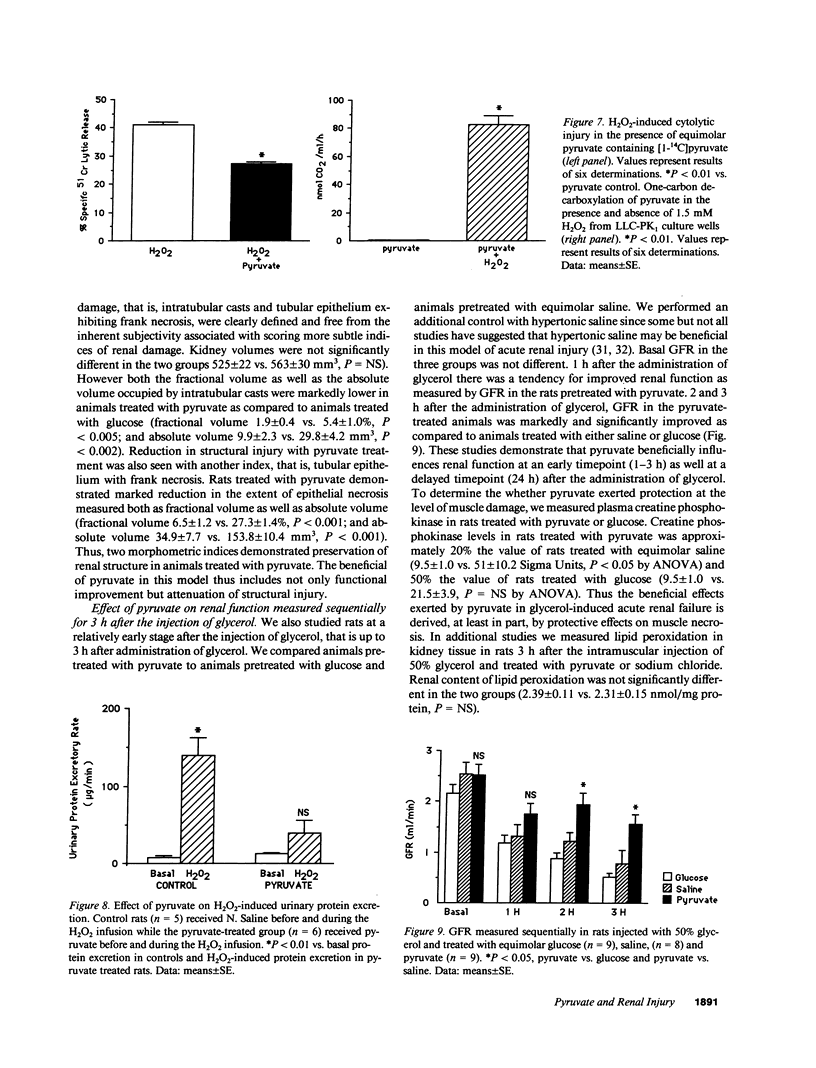
Abstract
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) contributes to renal cellular injury. alpha-Keto acids nonenzymatically reduce H2O2 to water while undergoing decarboxylation at the 1-carbon (1-C) position. We examined, in vitro and in vivo, the protective role of sodium pyruvate in H2O2-induced renal injury. Pyruvate effectively scavenged H2O2 in vitro, and suppressed H2O2-induced renal lipid peroxidation. Injury to LLC-PK1 cells induced by hydrogen peroxide was attenuated by pyruvate to an extent comparable to that seen with catalase. Studies utilizing [1-14C]pyruvate further demonstrated 1-C decarboxylation concurrent with cytoprotection by pyruvate from H2O2-induced injury. Pyruvate was also protective in vivo. Infusion of pyruvate before and during the intrarenal infusion of H2O2 attenuated H2O2-induced proteinuria. Systemic administration of pyruvate was also protective in the glycerol model of acute renal failure, a model also characterized by increased generation of H2O2. These findings indicate that pyruvate, a ubiquitous alpha-keto acid, scavenges H2O2 and protects renal tissue in vitro and in vivo from H2O2-mediated injury. These data suggest a potential therapeutic role for pyruvate in diseases in which increased generation of H2O2 is incriminated in renal damage.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreoli S. P., Baehner R. L., Bergstein J. M. In vitro detection of endothelial cell damage using 2-deoxy-D-3H-glucose: comparison with chromium 51, 3H-leucine, 3H-adenine, and lactate dehydrogenase. J Lab Clin Med. 1985 Sep;106(3):253–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabili S., Charney A. N. Lack of an effect of saline loading on glycerol-induced acute renal failure. Nephron. 1982;30(1):73–76. doi: 10.1159/000182436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantopoulos G., Barranger J. A. Nonenzymatic decarboxylation of pyruvate. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jun;139(2):353–358. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushner H. M., Barnes J. L., Stein J. H., Reineck H. J. Role of volume depletion in the glycerol model of acute renal failure. Am J Physiol. 1986 Feb;250(2 Pt 2):F315–F321. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.2.F315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra U., Gabreëls F., Joosten E., Wevers R., Lamers K., Doesburg W., Renier W. Friedreich's ataxia: intravenous pyruvate load to demonstrate a defect in pyruvate metabolism. Neurology. 1984 Nov;34(11):1493–1497. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.11.1493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamelin L. M., Zager R. A. Evidence against oxidant injury as a critical mediator of postischemic acute renal failure. Am J Physiol. 1988 Sep;255(3 Pt 2):F450–F460. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.3.F450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gstraunthaler G., Pfaller W., Kotanko P. Biochemical characterization of renal epithelial cell cultures (LLC-PK1 and MDCK). Am J Physiol. 1985 Apr;248(4 Pt 2):F536–F544. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.4.F536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidet B. R., Shah S. V. In vivo generation of hydrogen peroxide by rat kidney cortex and glomeruli. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jan;256(1 Pt 2):F158–F164. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.1.F158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidet B., Shah S. V. Enhanced in vivo H2O2 generation by rat kidney in glycerol-induced renal failure. Am J Physiol. 1989 Sep;257(3 Pt 2):F440–F445. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.257.3.F440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halestrap A. P., Scott R. D., Thomas A. P. Mitochondrial pyruvate transport and its hormonal regulation. Int J Biochem. 1980;11(2):97–105. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(80)90241-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hems D. A., Brosnan J. T. Effects of metabolic acidosis and starvation on the content of intermediary metabolites in rat kidney. Biochem J. 1971 Jul;123(3):391–397. doi: 10.1042/bj1230391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kako K., Kato M., Matsuoka T., Mustapha A. Depression of membrane-bound Na+-K+-ATPase activity induced by free radicals and by ischemia of kidney. Am J Physiol. 1988 Feb;254(2 Pt 1):C330–C337. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.254.2.C330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linas S. L., Shanley P. F., White C. W., Parker N. P., Repine J. E. O2 metabolite-mediated injury in perfused kidneys is reflected by consumption of DMTU and glutathione. Am J Physiol. 1987 Oct;253(4 Pt 2):F692–F701. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.4.F692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCoy R. N., Hill K. E., Ayon M. A., Stein J. H., Burk R. F. Oxidant stress following renal ischemia: changes in the glutathione redox ratio. Kidney Int. 1988 Apr;33(4):812–817. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan H. J., Schwappach J. R., Enquist E. G., Walden D. L., Terada L. S., Reiss O. K., Leff J. A., Repine J. E. Xanthine oxidase-derived H2O2 contributes to reperfusion injury of ischemic skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 2):H1415–H1419. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.258.5.H1415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melzer E., Schmidt H. L. Carbon isotope effects on the decarboxylation of carboxylic acids. Comparison of the lactate oxidase reaction and the degradation of pyruvate by H2O2. Biochem J. 1988 Jun 15;252(3):913–915. doi: 10.1042/bj2520913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitch W. E. The influence of the diet on the progression of renal insufficiency. Annu Rev Med. 1984;35:249–264. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.35.020184.001341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitch W. E., Walser M., Steinman T. I., Hill S., Zeger S., Tungsanga K. The effect of a keto acid-amino acid supplement to a restricted diet on the progression of chronic renal failure. N Engl J Med. 1984 Sep 6;311(10):623–629. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198409063111002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murer H., Burckhardt G. Membrane transport of anions across epithelia of mammalian small intestine and kidney proximal tubule. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1983;96:1–51. doi: 10.1007/BFb0031006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nath K. A., Croatt A. J., Hostetter T. H. Oxygen consumption and oxidant stress in surviving nephrons. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 2):F1354–F1362. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.5.F1354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nath K. A., Hostetter M. K., Hostetter T. H. Pathophysiology of chronic tubulo-interstitial disease in rats. Interactions of dietary acid load, ammonia, and complement component C3. J Clin Invest. 1985 Aug;76(2):667–675. doi: 10.1172/JCI112020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nath K. A., Paller M. S. Dietary deficiency of antioxidants exacerbates ischemic injury in the rat kidney. Kidney Int. 1990 Dec;38(6):1109–1117. doi: 10.1038/ki.1990.320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nath K. A., Salahudeen A. K. Induction of renal growth and injury in the intact rat kidney by dietary deficiency of antioxidants. J Clin Invest. 1990 Oct;86(4):1179–1192. doi: 10.1172/JCI114824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell-Tormey J., Nathan C. F., Lanks K., DeBoer C. J., de la Harpe J. Secretion of pyruvate. An antioxidant defense of mammalian cells. J Exp Med. 1987 Feb 1;165(2):500–514. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.2.500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkawa H., Ohishi N., Yagi K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jun;95(2):351–358. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90738-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paller M. S. Hemoglobin- and myoglobin-induced acute renal failure in rats: role of iron in nephrotoxicity. Am J Physiol. 1988 Sep;255(3 Pt 2):F539–F544. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.3.F539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick E., Keisari Y. A simple colorimetric method for the measurement of hydrogen peroxide produced by cells in culture. J Immunol Methods. 1980;38(1-2):161–170. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90340-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RONDONI P., CUDKOWICZ G. Hydrogen peroxide in tumours; its possible significance in carcinogenesis. Experientia. 1953 Sep;9(9):348–349. doi: 10.1007/BF02155843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schraufstätter I. U., Browne K., Harris A., Hyslop P. A., Jackson J. H., Quehenberger O., Cochrane C. G. Mechanisms of hypochlorite injury of target cells. J Clin Invest. 1990 Feb;85(2):554–562. doi: 10.1172/JCI114472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah S. V., Baricos W. H., Basci A. Degradation of human glomerular basement membrane by stimulated neutrophils. Activation of a metalloproteinase(s) by reactive oxygen metabolites. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):25–31. doi: 10.1172/JCI112790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah S. V. Role of reactive oxygen metabolites in experimental glomerular disease. Kidney Int. 1989 May;35(5):1093–1106. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah S. V., Walker P. D. Evidence suggesting a role for hydroxyl radical in glycerol-induced acute renal failure. Am J Physiol. 1988 Sep;255(3 Pt 2):F438–F443. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.3.F438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varma S. D., Morris S. M. Peroxide damage to the eye lens in vitro prevention by pyruvate. Free Radic Res Commun. 1988;4(5):283–290. doi: 10.3109/10715768809066893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veech R. L., Lawson J. W., Cornell N. W., Krebs H. A. Cytosolic phosphorylation potential. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6538–6547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P. D., Shah S. V. Gentamicin enhanced production of hydrogen peroxide by renal cortical mitochondria. Am J Physiol. 1987 Oct;253(4 Pt 1):C495–C499. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.4.C495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka T., Bills T., Moore-Jarrett T., Greene H. L., Burr I. M., Ichikawa I. Role of intrinsic antioxidant enzymes in renal oxidant injury. Kidney Int. 1990 Aug;38(2):282–288. doi: 10.1038/ki.1990.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka T., Ichikawa I. Glomerular dysfunction induced by polymorphonuclear leukocyte-derived reactive oxygen species. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jul;257(1 Pt 2):F53–F59. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.257.1.F53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




