Abstract
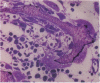
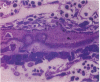
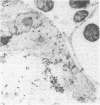
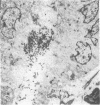
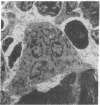
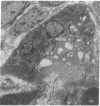
Studies of the mode of action of the bisphosphonate alendronate showed that 1 d after the injection of 0.4 mg/kg [3H]alendronate to newborn rats, 72% of the osteoclastic surface, 2% of the bone forming, and 13% of all other surfaces were densely labeled. Silver grains were seen above the osteoclasts and no other cells. 6 d later the label was 600-1,000 microns away from the epiphyseal plate and buried inside the bone, indicating normal growth and matrix deposition on top of alendronate-containing bone. Osteoclasts from adult animals, infused with parathyroid hormone-related peptide (1-34) and treated with 0.4 mg/kg alendronate subcutaneously for 2 d, all lacked ruffled border but not clear zone. In vitro alendronate bound to bone particles with a Kd of approximately 1 mM and a capacity of 100 nmol/mg at pH 7. At pH 3.5 binding was reduced by 50%. Alendronate inhibited bone resorption by isolated chicken or rat osteoclasts when the amount on the bone surface was around 1.3 x 10(-3) fmol/microns 2, which would produce a concentration of 0.1-1 mM in the resorption space if 50% were released. At these concentrations membrane leakiness to calcium was observed. These findings suggest that alendronate binds to resorption surfaces, is locally released during acidification, the rise in concentration stops resorption and membrane ruffling, without destroying the osteoclasts.
Full text
PDF

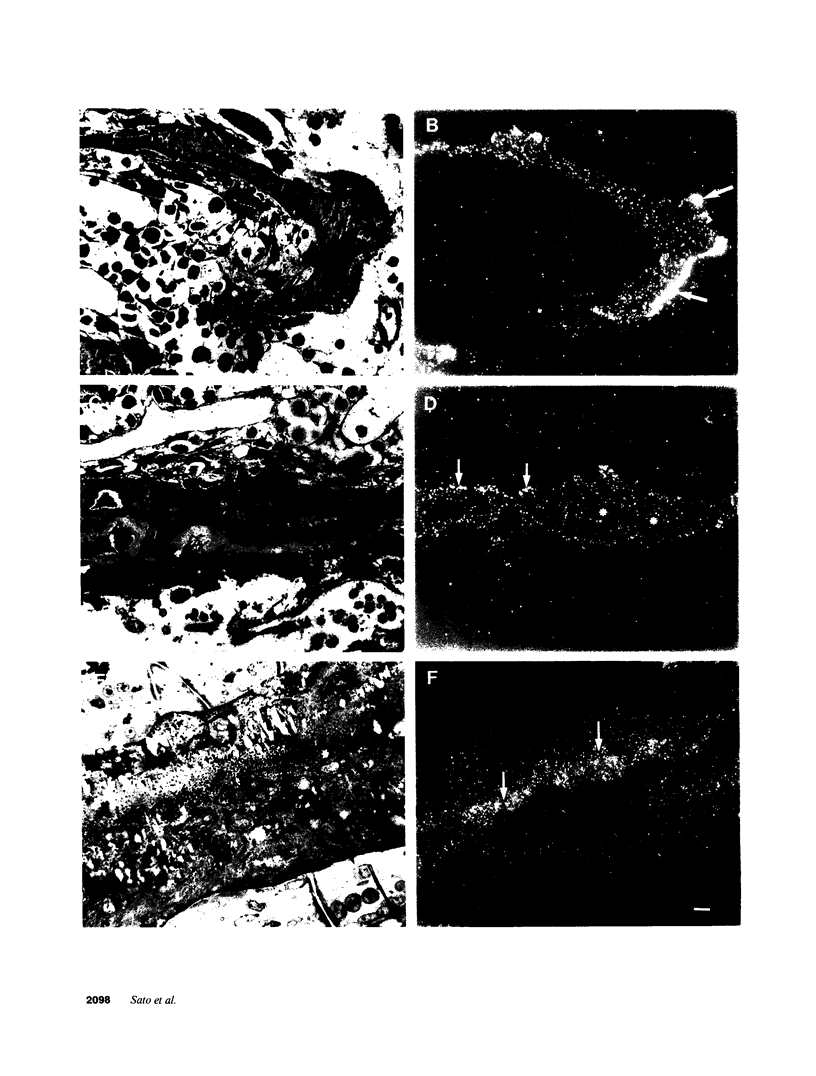
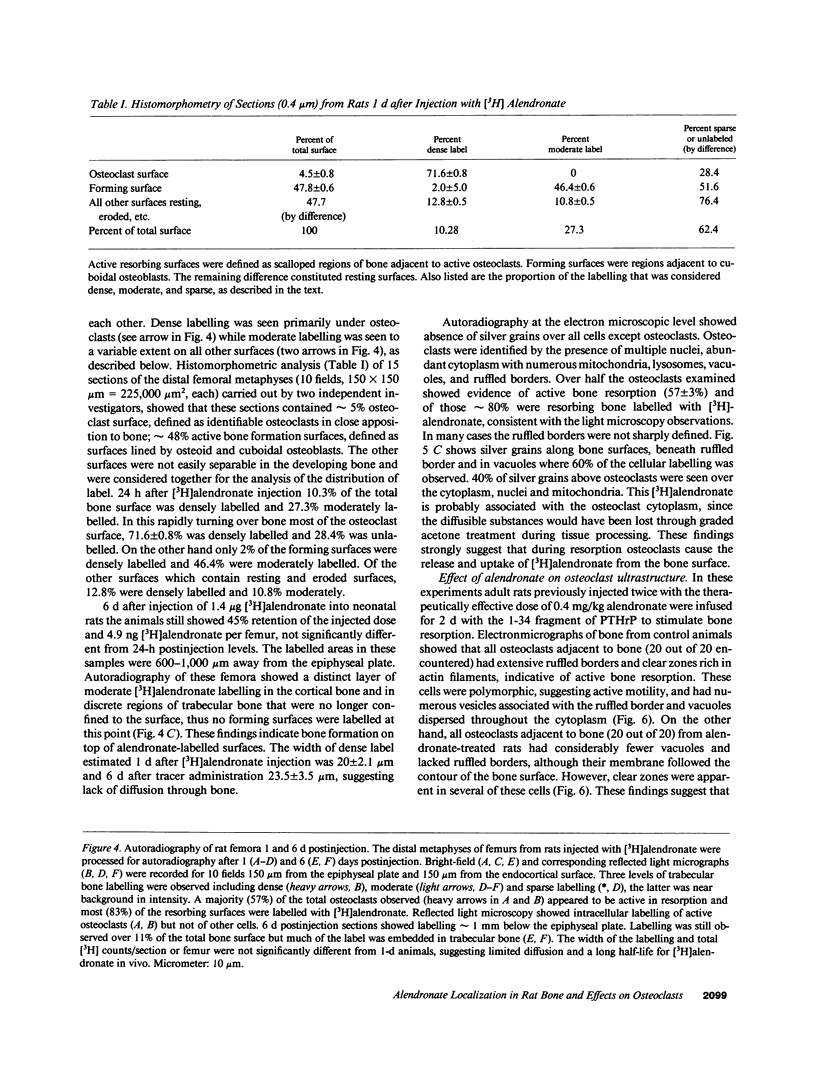

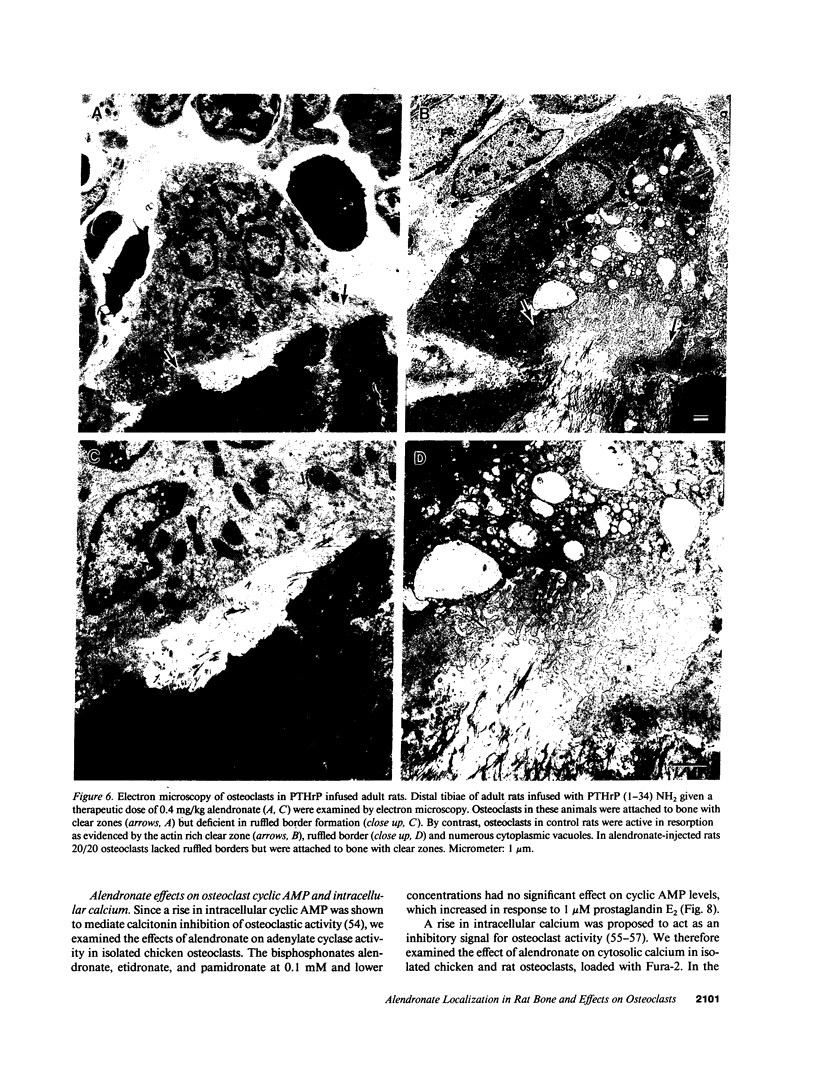
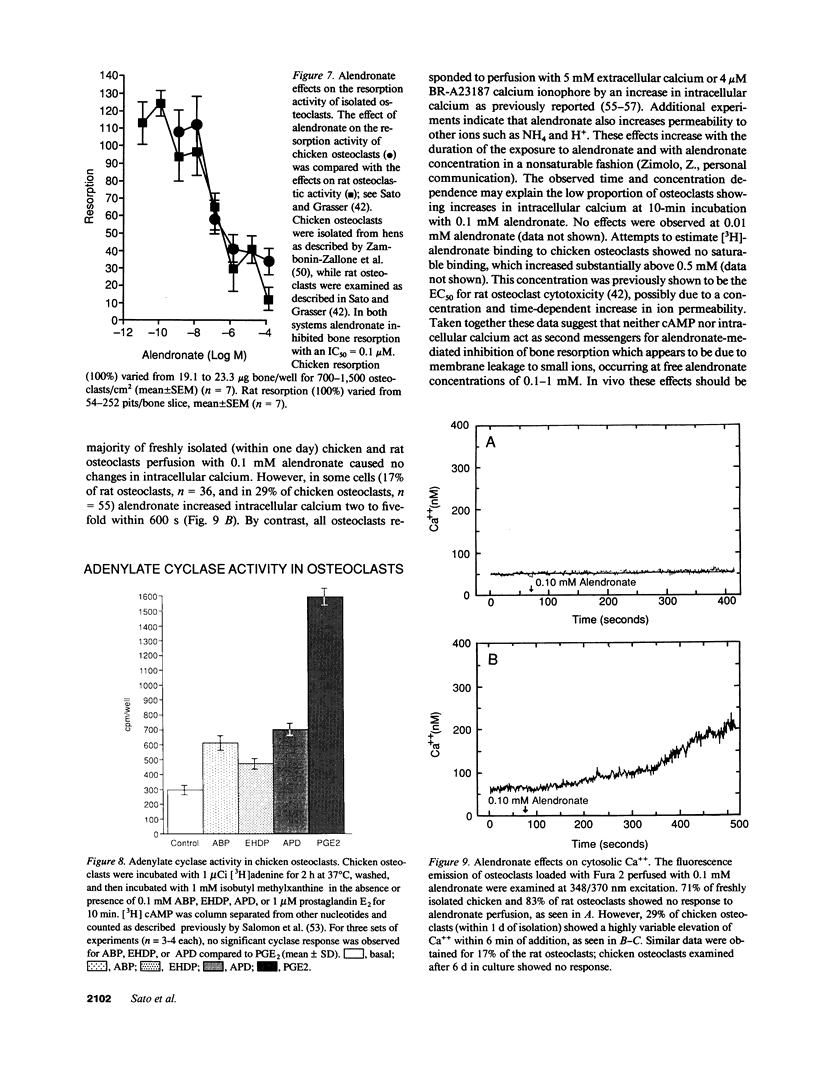



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adami S., Salvagno G., Guarrera G., Montesanti F., Garavelli S., Rosini S., Lo Cascio V. Treatment of Paget's disease of bone with intravenous 4-amino-1-hydroxybutylidene-1,1-bisphosphonate. Calcif Tissue Int. 1986 Oct;39(4):226–229. doi: 10.1007/BF02555208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett T. R., Dempster D. W. A comparative study of disaggregated chick and rat osteoclasts in vitro: effects of calcitonin and prostaglandins. Endocrinology. 1987 Feb;120(2):602–608. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-2-602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attardo-Parrinello G., Merlini G., Pavesi F., Crema F., Fiorentini M. L., Ascari E. Effects of a new aminodiphosphonate (aminohydroxybutylidene diphosphonate) in patients with osteolytic lesions from metastases and myelomatosis. Comparison with dichloromethylene diphosphonate. Arch Intern Med. 1987 Sep;147(9):1629–1633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron R., Neff L., Louvard D., Courtoy P. J. Cell-mediated extracellular acidification and bone resorption: evidence for a low pH in resorbing lacunae and localization of a 100-kD lysosomal membrane protein at the osteoclast ruffled border. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2210–2222. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair H. C., Kahn A. J., Crouch E. C., Jeffrey J. J., Teitelbaum S. L. Isolated osteoclasts resorb the organic and inorganic components of bone. J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;102(4):1164–1172. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.4.1164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair H. C., Teitelbaum S. L., Ghiselli R., Gluck S. Osteoclastic bone resorption by a polarized vacuolar proton pump. Science. 1989 Aug 25;245(4920):855–857. doi: 10.1126/science.2528207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boonekamp P. M., van der Wee-Pals L. J., van Wijk-van Lennep M. M., Thesing C. W., Bijvoet O. L. Two modes of action of bisphosphonates on osteoclastic resorption of mineralized matrix. Bone Miner. 1986 Feb;1(1):27–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canfield R., Rosner W., Skinner J., McWhorter J., Resnick L., Feldman F., Kammerman S., Ryan K., Kunigonis M., Bohne W. Diphosphonate therapy of paget's disease of bone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Jan;44(1):96–106. doi: 10.1210/jcem-44-1-96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carano A., Teitelbaum S. L., Konsek J. D., Schlesinger P. H., Blair H. C. Bisphosphonates directly inhibit the bone resorption activity of isolated avian osteoclasts in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1990 Feb;85(2):456–461. doi: 10.1172/JCI114459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cecchini M. G., Felix R., Fleisch H., Cooper P. H. Effect of bisphosphonates on proliferation and viability of mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages. J Bone Miner Res. 1987 Apr;2(2):135–142. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650020209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cecchini M. G., Fleisch H. Bisphosphonates in vitro specifically inhibit, among the hematopoietic series, the development of the mouse mononuclear phagocyte lineage. J Bone Miner Res. 1990 Oct;5(10):1019–1027. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650051005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. J., Darby J. A., Fuller K. Mammalian collagenase predisposes bone surfaces to osteoclastic resorption. Cell Tissue Res. 1985;241(3):671–675. doi: 10.1007/BF00214590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chappard D., Alexandre C., Palle S., Vico L., Morukov B. V., Rodionova S. S., Minaire P., Riffat G. Effects of a bisphosphonate (1-hydroxy ethylidene-1,1 bisphosphonic acid) on osteoclast number during prolonged bed rest in healthy humans. Metabolism. 1989 Sep;38(9):822–825. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(89)90226-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. R., Heath D. A. Comparison of different dose regimes of aminohydroxypropylidene-1,1-bisphosphonate (APD) in hypercalcaemia of malignancy. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1989 Sep;28(3):269–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1989.tb05426.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas D. L., Duckworth T., Russell R. G., Kanis J. A., Preston C. J., Preston F. E., Prenton M. A., Woodhead J. S. Effect of dichloromethylene diphosphonate in Paget's disease of bone and in hypercalcaemia due to primary hyperparathyroidism or malignant disease. Lancet. 1980 May 17;1(8177):1043–1047. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91496-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elomaa I., Blomqvist C., Porkka L., Holmström T., Taube T., Lamberg-Allardt C., Borgström G. H. Clodronate for osteolytic metastases due to breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 1988;42(2):111–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fast D. K., Felix R., Dowse C., Neuman W. F., Fleisch H. The effects of diphosphonates on the growth and glycolysis of connective-tissue cells in culture. Biochem J. 1978 Apr 15;172(1):97–107. doi: 10.1042/bj1720097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felix R., Bettex J. D., Fleisch H. Effect of diphosphonates on the synthesis of prostaglandins in cultured calvaria cells. Calcif Tissue Int. 1981;33(5):549–552. doi: 10.1007/BF02409488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felix R., Guenther H. L., Fleisch H. The subcellular distribution of [14C]dichloromethylenebisphosphonate and [14C]1-hydroxyethylidene-1,1-bisphosphonate in cultured calvaria cells. Calcif Tissue Int. 1984 Jan;36(1):108–113. doi: 10.1007/BF02405302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan A. M., Chambers T. J. Dichloromethylenebisphosphonate (Cl2MBP) inhibits bone resorption through injury to osteoclasts that resorb Cl2MBP-coated bone. Bone Miner. 1989 Apr;6(1):33–43. doi: 10.1016/0169-6009(89)90021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleisch H., Russell R. G., Francis M. D. Diphosphonates inhibit hydroxyapatite dissolution in vitro and bone resorption in tissue culture and in vivo. Science. 1969 Sep 19;165(3899):1262–1264. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3899.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frijlink W. B., Bijvoet O. L., te Velde J., Heynen G. Treatment of Paget's disease with (3-amino-1-hydroxypropylidene)-1, 1-bisphosphonate (A.P.D.). Lancet. 1979 Apr 14;1(8120):799–803. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91318-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harinck H. I., Papapoulos S. E., Blanksma H. J., Moolenaar A. J., Vermeij P., Bijvoet O. L. Paget's disease of bone: early and late responses to three different modes of treatment with aminohydroxypropylidene bisphosphonate (APD). Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 Nov 21;295(6609):1301–1305. doi: 10.1136/bmj.295.6609.1301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes D. E., MacDonald B. R., Russell R. G., Gowen M. Inhibition of osteoclast-like cell formation by bisphosphonates in long-term cultures of human bone marrow. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jun;83(6):1930–1935. doi: 10.1172/JCI114100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung A. Comparison of two parenteral diphosphonates in hypercalcemia of malignancy. Am J Med. 1982 Feb;72(2):221–226. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90813-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopriwa B. A comparison of various procedures for fine grain development in electron microscopic radioautography. Histochemistry. 1975 Aug 28;44(3):201–224. doi: 10.1007/BF00491492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. H., Duggan D. E., Chen I. W., Ellsworth R. L. Physiological disposition of alendronate, a potent anti-osteolytic bisphosphonate, in laboratory animals. Drug Metab Dispos. 1991 Sep-Oct;19(5):926–932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löwik C. W., van der Pluijm G., van der Wee-Pals L. J., van Treslong-De Groot H. B., Bijvoet O. L. Migration and phenotypic transformation of osteoclast precursors into mature osteoclasts: the effect of a bisphosphonate. J Bone Miner Res. 1988 Apr;3(2):185–192. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650030210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malgaroli A., Meldolesi J., Zallone A. Z., Teti A. Control of cytosolic free calcium in rat and chicken osteoclasts. The role of extracellular calcium and calcitonin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14342–14347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlini G., Parrinello G. A., Piccinini L., Crema F., Fiorentini M. L., Riccardi A., Pavesi F., Novazzi F., Silingardi V., Ascari E. Long-term effects of parenteral dichloromethylene bisphosphonate (CL2MBP) on bone disease of myeloma patients treated with chemotherapy. Hematol Oncol. 1990 Jan-Feb;8(1):23–30. doi: 10.1002/hon.2900080104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier P. J., Chapuy M. C., Alexandre C., Bressot C., Edouard C., Vignon C., Mathieu L., Trechsel U. Effects of disodium dichloromethylene diphosphonate on Paget's disease of bone. Lancet. 1979 Sep 8;2(8141):489–492. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91551-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. C., Jee W. S. The effect of dichloromethylene diphosphonate, a pyrophosphate analog, on bone and bone cell structure in the growing rat. Anat Rec. 1979 Mar;193(3):439–462. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091930309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyauchi A., Hruska K. A., Greenfield E. M., Duncan R., Alvarez J., Barattolo R., Colucci S., Zambonin-Zallone A., Teitelbaum S. L., Teti A. Osteoclast cytosolic calcium, regulated by voltage-gated calcium channels and extracellular calcium, controls podosome assembly and bone resorption. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 1):2543–2552. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton A. R., Cantrill J. A., Pillai G. V., McMahon A., Anderson D. C., Howell A. Sclerosis of lytic bone metastases after disodium aminohydroxypropylidene bisphosphonate (APD) in patients with breast carcinoma. BMJ. 1988 Sep 24;297(6651):772–773. doi: 10.1136/bmj.297.6651.772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson G. C., Moseley J. M., Sexton P. M., Mendelsohn F. A., Martin T. J. Abundant calcitonin receptors in isolated rat osteoclasts. Biochemical and autoradiographic characterization. J Clin Invest. 1986 Aug;78(2):355–360. doi: 10.1172/JCI112584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Doherty D. P., Bickerstaff D. R., McCloskey E. V., Hamdy N. A., Beneton M. N., Harris S., Mian M., Kanis J. A. Treatment of Paget's disease of bone with aminohydroxybutylidene bisphosphonate. J Bone Miner Res. 1990 May;5(5):483–491. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650050510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papapoulos S. E., Hoekman K., Löwik C. W., Vermeij P., Bijvoet O. L. Application of an in vitro model and a clinical protocol in the assessment of the potency of a new bisphosphonate. J Bone Miner Res. 1989 Oct;4(5):775–781. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650040518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedrazzoni M., Palummeri E., Ciotti G., Davoli L., Pioli G., Girasole G., Passeri M. Short-term effects on bone and mineral metabolism of 4-amino-1-hydroxybutylidene-1,1-diphosphonate (ABDP) in Paget's disease of bone. Bone Miner. 1989 Nov;7(3):301–307. doi: 10.1016/0169-6009(89)90086-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percival R. C., Paterson A. D., Yates A. J., Beard D. J., Douglas D. L., Neal F. E., Russell R. G., Kanis J. A. Treatment of malignant hypercalcaemia with clodronate. Br J Cancer. 1985 May;51(5):665–669. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1985.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plasmans C. M., Jap P. H., Kuijpers W., Slooff T. J. Influence of a diphosphonate on the cellular aspect of young bone tissue. Calcif Tissue Int. 1980;32(3):247–266. doi: 10.1007/BF02408548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralston S. H., Gallacher S. J., Patel U., Dryburgh F. J., Fraser W. D., Cowan R. A., Boyle I. T. Comparison of three intravenous bisphosphonates in cancer-associated hypercalcaemia. Lancet. 1989 Nov 18;2(8673):1180–1182. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91791-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralston S. H., Gardner M. D., Dryburgh F. J., Jenkins A. S., Cowan R. A., Boyle I. T. Comparison of aminohydroxypropylidene diphosphonate, mithramycin, and corticosteroids/calcitonin in treatment of cancer-associated hypercalcaemia. Lancet. 1985 Oct 26;2(8461):907–910. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90848-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reginster J. Y., Lecart M. P., Deroisy R., Sarlet N., Denis D., Ethgen D., Collette J., Franchimont P. Prevention of postmenopausal bone loss by tiludronate. Lancet. 1989 Dec 23;2(8678-8679):1469–1471. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92927-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid I. R., King A. R., Alexander C. J., Ibbertson H. K. Prevention of steroid-induced osteoporosis with (3-amino-1-hydroxypropylidene)-1,1-bisphosphonate (APD). Lancet. 1988 Jan 23;1(8578):143–146. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92721-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid I. R., Schooler B. A., Stewart A. W. Prevention of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res. 1990 Jun;5(6):619–623. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650050611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitsma P. H., Teitelbaum S. L., Bijvoet O. L., Kahn A. J. Differential action of the bisphosphonates (3-amino-1-hydroxypropylidene)-1,1-bisphosphonate (APD) and disodium dichloromethylidene bisphosphonate (Cl2MDP) on rat macrophage-mediated bone resorption in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1982 Nov;70(5):927–933. doi: 10.1172/JCI110704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouleau M. F., Warshawsky H., Goltzman D. Parathyroid hormone binding in vivo to renal, hepatic, and skeletal tissues of the rat using a radioautographic approach. Endocrinology. 1986 Mar;118(3):919–931. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-3-919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. G., Smith R., Preston C., Walton R. J., Woods C. G. Diphosphonates in Paget's disease. Lancet. 1974 May 11;1(7863):894–898. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90347-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato M., Grasser W. Effects of bisphosphonates on isolated rat osteoclasts as examined by reflected light microscopy. J Bone Miner Res. 1990 Jan;5(1):31–40. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650050107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato M., Sardana M. K., Grasser W. A., Garsky V. M., Murray J. M., Gould R. J. Echistatin is a potent inhibitor of bone resorption in culture. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1713–1723. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenk R., Eggli P., Fleisch H., Rosini S. Quantitative morphometric evaluation of the inhibitory activity of new aminobisphosphonates on bone resorption in the rat. Calcif Tissue Int. 1986 Jun;38(6):342–349. doi: 10.1007/BF02555748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seedor J. G., Quartuccio H. A., Thompson D. D. The bisphosphonate alendronate (MK-217) inhibits bone loss due to ovariectomy in rats. J Bone Miner Res. 1991 Apr;6(4):339–346. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650060405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sietsema W. K., Ebetino F. H., Salvagno A. M., Bevan J. A. Antiresorptive dose-response relationships across three generations of bisphosphonates. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1989;15(9):389–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siris E. S., Sherman W. H., Baquiran D. C., Schlatterer J. P., Osserman E. F., Canfield R. E. Effects of dichloromethylene diphosphonate on skeletal mobilization of calcium in multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 1980 Feb 7;302(6):310–315. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198002073020602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleeboom H. P., Bijvoet O. L., van Oosterom A. T., Gleed J. H., O'Riordan J. L. Comparison of intravenous (3-amino-1-hydroxypropylidene)-1, 1-bisphosphonate and volume repletion in tumour-induced hypercalcaemia. Lancet. 1983 Jul 30;2(8344):239–243. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90231-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R., Russell R. G., Bishop M. Diphosphonates and Page's disease of bone. Lancet. 1971 May 8;1(7706):945–947. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91447-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson P. H., Stevenson J. R. Cytotoxic and migration inhibitory effects of bisphosphonates on macrophages. Calcif Tissue Int. 1986 Apr;38(4):227–233. doi: 10.1007/BF02556715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone M. D., Hawthorne A. B., Kerr D., Webster G., Hosking D. J. Treatment of Paget's disease with intermittent low-dose infusions of disodium pamidronate (APD). J Bone Miner Res. 1990 Dec;5(12):1231–1235. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650051207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storm T., Thamsborg G., Steiniche T., Genant H. K., Sørensen O. H. Effect of intermittent cyclical etidronate therapy on bone mass and fracture rate in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 1990 May 3;322(18):1265–1271. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199005033221803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson D. D., Seedor J. G., Fisher J. E., Rosenblatt M., Rodan G. A. Direct action of the parathyroid hormone-like human hypercalcemic factor on bone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5673–5677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson D. D., Seedor J. G., Weinreb M., Rosini S., Rodan G. A. Aminohydroxybutane bisphosphonate inhibits bone loss due to immobilization in rats. J Bone Miner Res. 1990 Mar;5(3):279–286. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650050312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VENABLE J. H., COGGESHALL R. A SIMPLIFIED LEAD CITRATE STAIN FOR USE IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Cell Biol. 1965 May;25:407–408. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valkema R., Vismans F. J., Papapoulos S. E., Pauwels E. K., Bijvoet O. L. Maintained improvement in calcium balance and bone mineral content in patients with osteoporosis treated with the bisphosphonate APD. Bone Miner. 1989 Jan;5(2):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0169-6009(89)90095-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vänänen H. K., Karhukorpi E. K., Sundquist K., Wallmark B., Roininen I., Hentunen T., Tuukkanen J., Lakkakorpi P. Evidence for the presence of a proton pump of the vacuolar H(+)-ATPase type in the ruffled borders of osteoclasts. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1305–1311. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts N. B., Harris S. T., Genant H. K., Wasnich R. D., Miller P. D., Jackson R. D., Licata A. A., Ross P., Woodson G. C., 3rd, Yanover M. J. Intermittent cyclical etidronate treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jul 12;323(2):73–79. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199007123230201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaidi M., Moonga B., Moss D. W., MacIntyre I. Inhibition of osteoclastic acid phosphatase abolishes bone resorption. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Feb 28;159(1):68–71. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92405-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambonin Zallone A., Teti A., Primavera M. V. Isolated osteoclasts in primary culture: first observations on structure and survival in culture media. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1982 Dec;165(3):405–413. doi: 10.1007/BF00305576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Holten-Verzantvoort A. T., Bijvoet O. L., Cleton F. J., Hermans J., Kroon H. M., Harinck H. I., Vermey P., Elte J. W., Neijt J. P., Beex L. V. Reduced morbidity from skeletal metastases in breast cancer patients during long-term bisphosphonate (APD) treatment. Lancet. 1987 Oct 31;2(8566):983–985. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92555-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]