Abstract
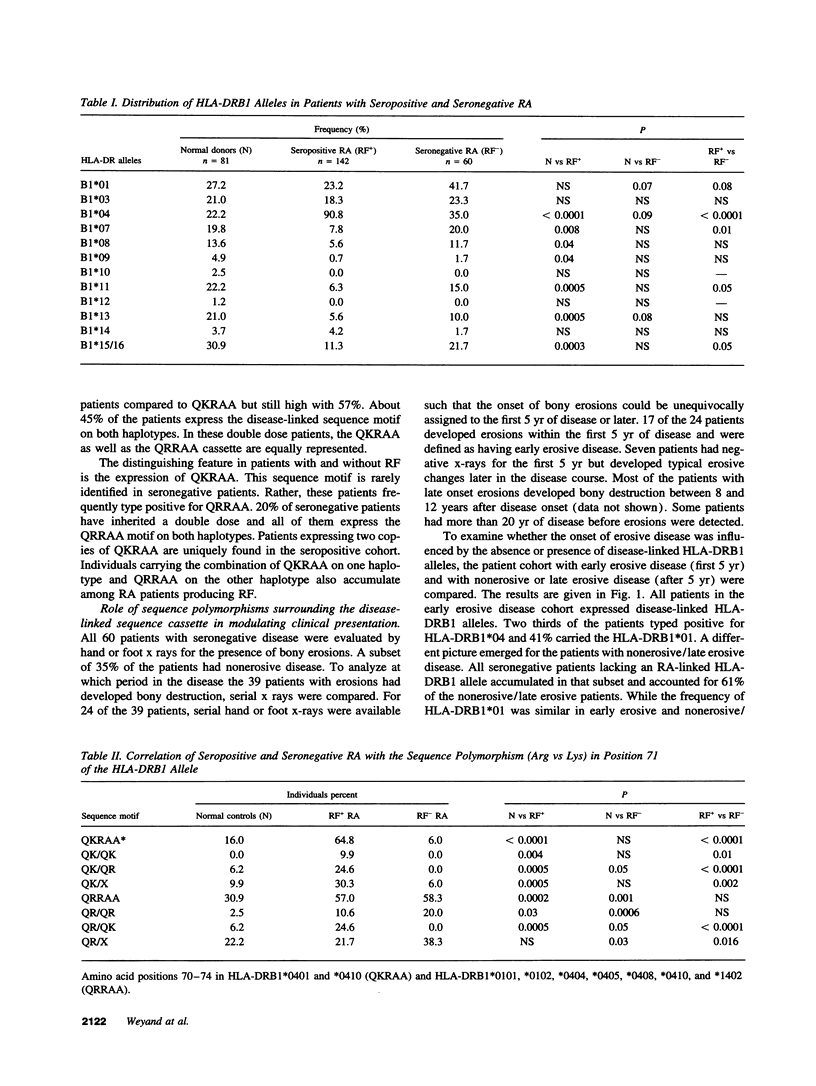
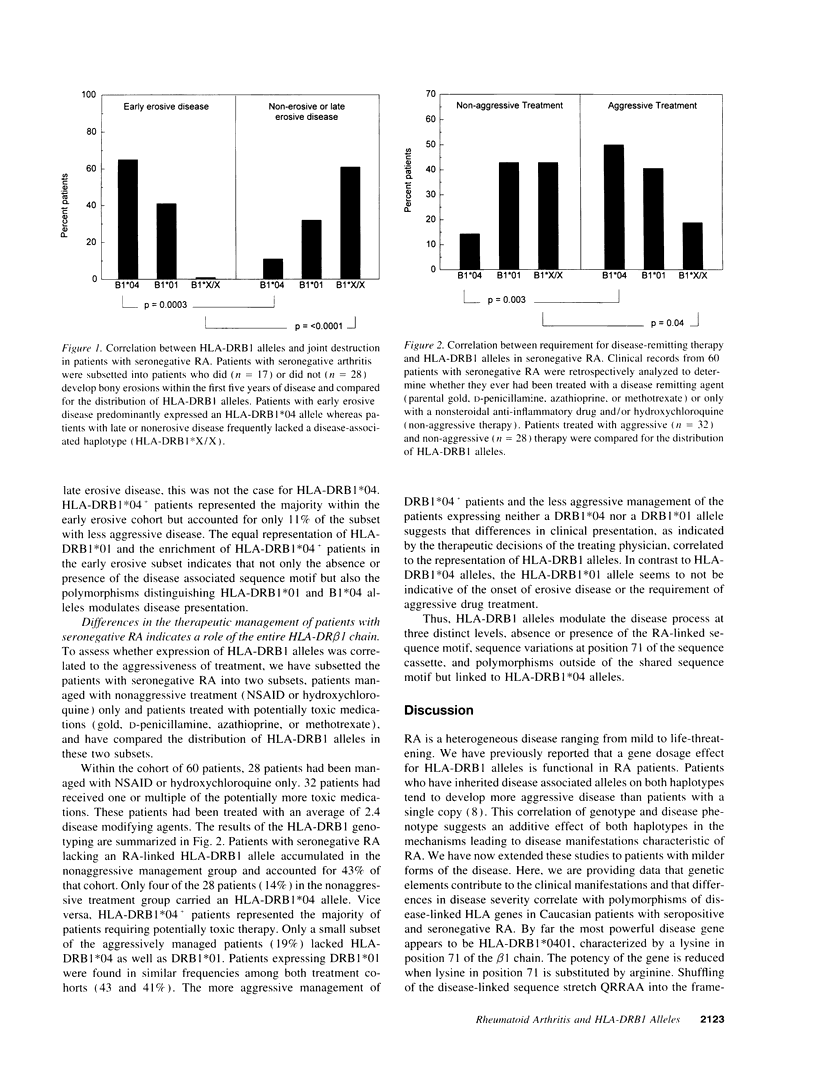
RA is a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by variations in clinical manifestations, disease course, and probably response to therapeutic interventions. We have addressed the question whether genetically and potentially etiologically more homogeneous subgroups of RA patients can be defined based upon the expression of the RA-linked sequence motif in the third hypervariable region of the HLA-DRB1 gene. Genetic comparison of patients classified upon clinical manifestation and disease course demonstrated that patients with mild disease were genetically distinct from those progressing to severe and destructive disease. Specifically, rheumatoid factor (RF) negative patients preferentially expressed RA-linked HLA-DRB1 alleles with an arginine substitution in position 71, whereas the alleles with a lysine substitution in position 71 accumulated in RF+ patients. RF- patients were further subdivided based on clinical markers (time of onset of erosive disease and requirement for aggressive therapy). Clinical heterogeneity correlated with genetic heterogeneity. Patients with early erosive disease and patients requiring aggressive therapy frequently typed HLA-DRB1*04+. Patients with late erosive/nonerosive disease or a benign disease course manageable with nonaggressive treatment preferentially expressed HLA-DRB1*01 or lacked an RA-linked haplotype. These data indicate that the heterogeneity of RA reflects genetic differences. Sequence variations within the disease-linked sequence motif, as well as polymorphisms surrounding the candidate genetic element, affect pattern, course, and treatment response of RA. Amino acid position 71 in the HLA-DRB1 gene has a unique role, the understanding of which may provide important clues to disease etiology.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albani S., Tuckwell J. E., Esparza L., Carson D. A., Roudier J. The susceptibility sequence to rheumatoid arthritis is a cross-reactive B cell epitope shared by the Escherichia coli heat shock protein dnaJ and the histocompatibility leukocyte antigen DRB10401 molecule. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jan;89(1):327–331. doi: 10.1172/JCI115580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goronzy J. J., Weyand C. M. Interplay of T lymphocytes and HLA-DR molecules in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 1993 Mar;5(2):169–177. doi: 10.1097/00002281-199305020-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goronzy J. J., Xie C., Hu W., Lundy S. K., Weyand C. M. Restrictions in the repertoire of allospecific T cells. Contribution of the alpha-helical sequence polymorphism of HLA-DR molecules. J Immunol. 1993 Jul 15;151(2):825–836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregersen P. K., Silver J., Winchester R. J. The shared epitope hypothesis. An approach to understanding the molecular genetics of susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Nov;30(11):1205–1213. doi: 10.1002/art.1780301102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley J. B., Reichlin M., Arnett F. C., Alexander E. L., Bias W. B., Provost T. T. Gene interaction at HLA-DQ enhances autoantibody production in primary Sjögren's syndrome. Science. 1986 May 30;232(4754):1145–1147. doi: 10.1126/science.3458307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley J. B., Sestak A. L., Willis L. G., Fu S. M., Hansen J. A., Reichlin M. A model for disease heterogeneity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Relationships between histocompatibility antigens, autoantibodies, and lymphopenia or renal disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Jul;32(7):826–836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. M., Liu A., Marshall K. W., Mayer J., Jorgensen B., Yuan B., Cubbon R. M., Nichols E. A., Wicker L. S., Rothbard J. B. Exploration of requirements for peptide binding to HLA DRB1*0101 and DRB1*0401. J Immunol. 1994 Mar 15;152(6):2890–2898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh S. G., Bodmer J. G. HLA class II nucleotide sequences, 1991. Immunogenetics. 1991;33(5-6):321–334. doi: 10.1007/BF00216691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. L., Dugowson C. E., Koepsell T. D., Voigt L. F., Branchaud A. M., Barrington R. A., Wener M. H., Hansen J. A. Rheumatoid factor, HLA-DR4, and allelic variants of DRB1 in women with recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 May;37(5):673–680. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reveille J. D., Durban E., MacLeod-St Clair M. J., Goldstein R., Moreda R., Altman R. D., Arnett F. C. Association of amino acid sequences in the HLA-DQB1 first domain with antitopoisomerase I autoantibody response in scleroderma (progressive systemic sclerosis). J Clin Invest. 1992 Sep;90(3):973–980. doi: 10.1172/JCI115974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roudier J., Rhodes G., Petersen J., Vaughan J. H., Carson D. A. The Epstein-Barr virus glycoprotein gp110, a molecular link between HLA DR4, HLA DR1, and rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Immunol. 1988 Apr;27(4):367–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb02359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp J. T., Wolfe F., Mitchell D. M., Bloch D. A. The progression of erosion and joint space narrowing scores in rheumatoid arthritis during the first twenty-five years of disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Jun;34(6):660–668. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens H. A., Sakkas L. I., Vaughan R. W., Teitsson I., Welsh K. I., Panayi G. S. HLA-DQw7 is a disease severity marker in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Immunogenetics. 1989;30(2):119–122. doi: 10.1007/BF02421540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. A., Acha-Orbea H., Bell J. I., Chao N., Fronek Z., Jacob C. O., McDermott M., Sinha A. A., Timmerman L., Steinman L. A molecular basis for MHC class II--associated autoimmunity. Science. 1988 May 20;240(4855):1003–1009. doi: 10.1126/science.3368786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weyand C. M., Goronzy J. J. Disease-associated human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen determinants in patients with seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. Functional role in antigen-specific and allogeneic T cell recognition. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1051–1057. doi: 10.1172/JCI114535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weyand C. M., Hicok K. C., Conn D. L., Goronzy J. J. The influence of HLA-DRB1 genes on disease severity in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 1992 Nov 15;117(10):801–806. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-117-10-801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weyand C. M., Xie C., Goronzy J. J. Homozygosity for the HLA-DRB1 allele selects for extraarticular manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jun;89(6):2033–2039. doi: 10.1172/JCI115814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willkens R. F., Nepom G. T., Marks C. R., Nettles J. W., Nepom B. S. Association of HLA-Dw16 with rheumatoid arthritis in Yakima Indians. Further evidence for the "shared epitope" hypothesis. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Jan;34(1):43–47. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R., Dwyer E., Rose S. The genetic basis of rheumatoid arthritis. The shared epitope hypothesis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1992 Nov;18(4):761–783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jongh B. M., van Romunde L. K., Valkenburg H. A., de Lange G. G., van Rood J. J. Epidemiological study of HLA and GM in rheumatoid arthritis and related symptoms in an open Dutch population. Ann Rheum Dis. 1984 Aug;43(4):613–619. doi: 10.1136/ard.43.4.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijde D. M., van Riel P. L., van Rijswijk M. H., van de Putte L. B. Influence of prognostic features on the final outcome in rheumatoid arthritis: a review of the literature. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1988 May;17(4):284–292. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(88)90013-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


