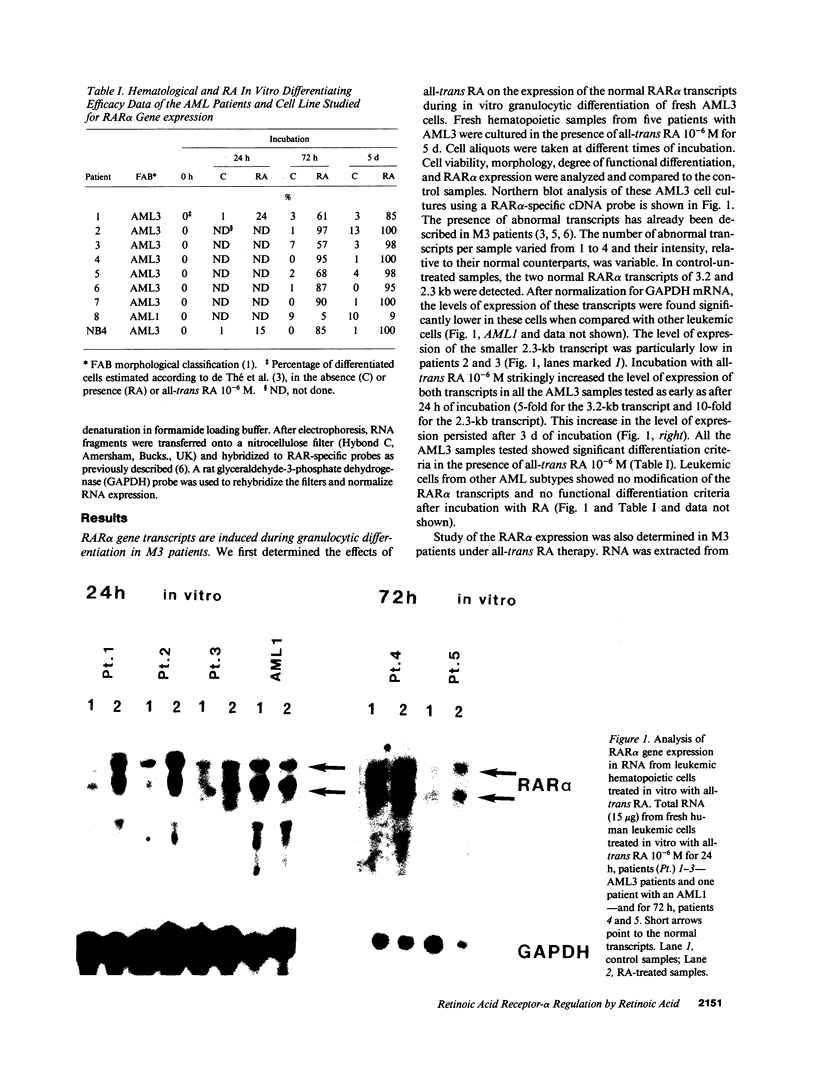
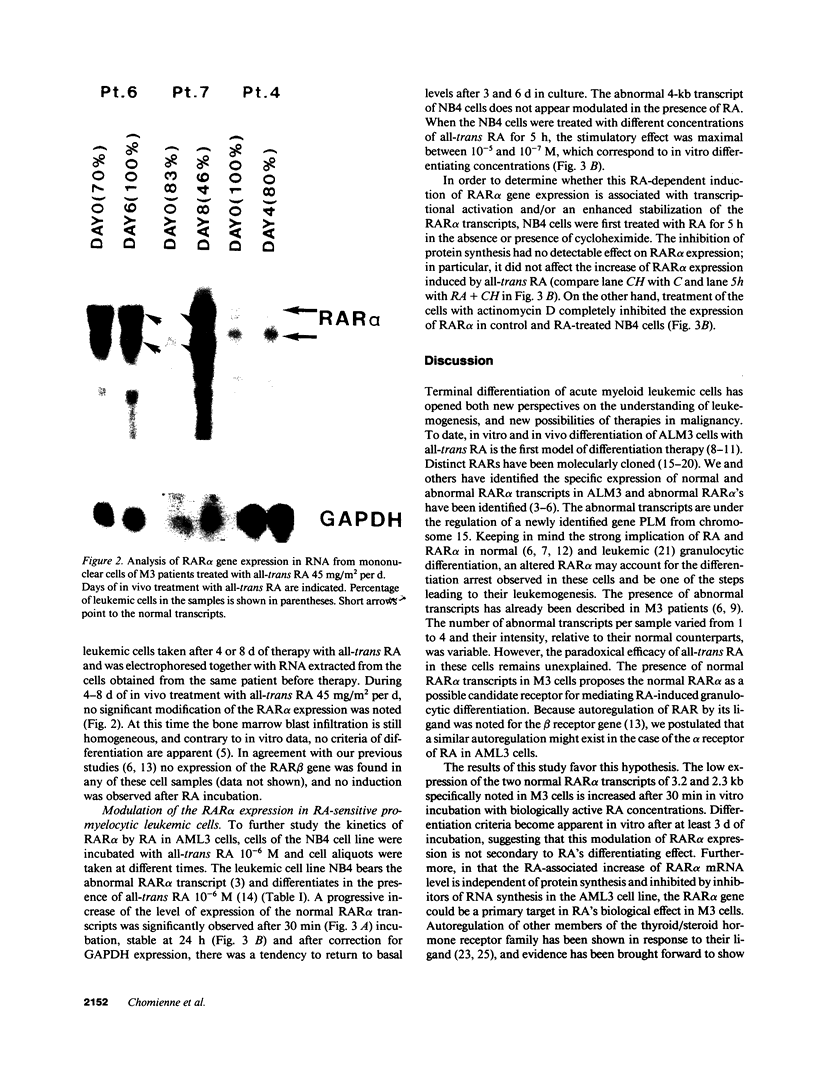
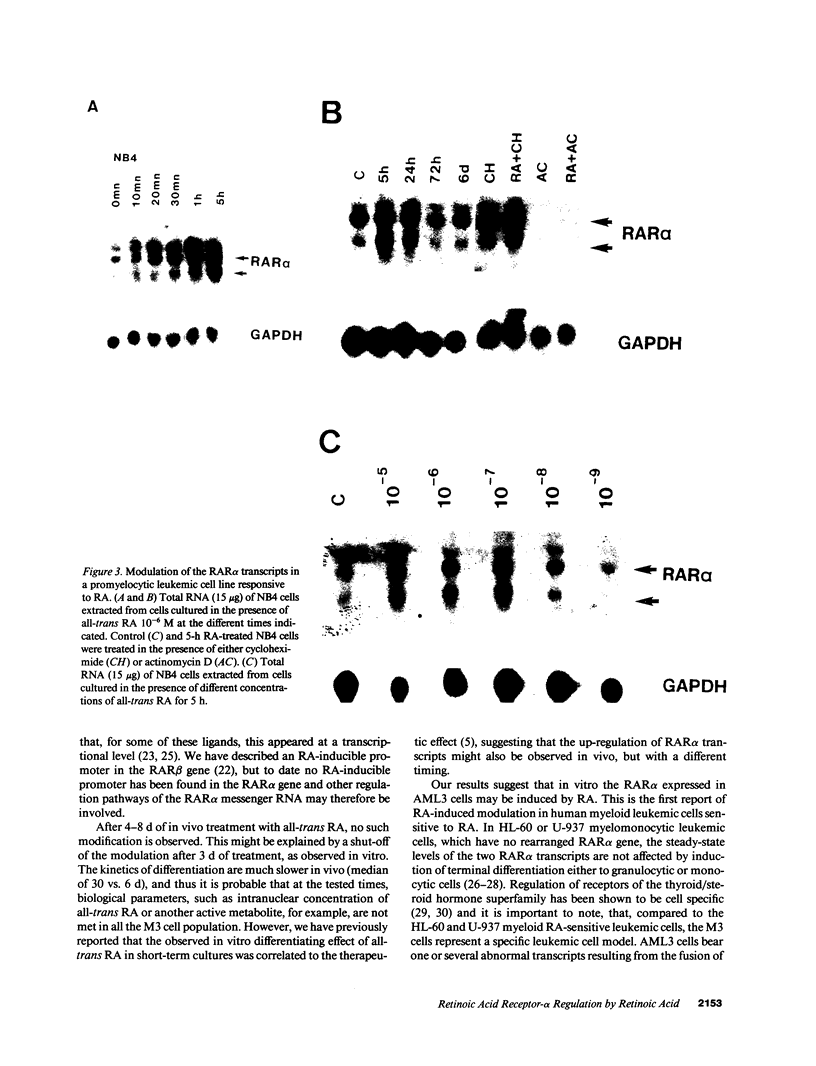
Abstract
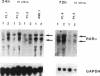
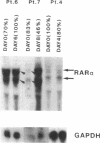
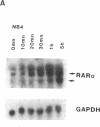
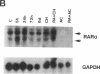
We have recently demonstrated that all-trans retinoic acid (RA), the active metabolite of vitamin A, is an efficient alternative to chemotherapy in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia (AML3). We have further shown that, in these AML3 cells, the gene of the retinoic acid receptor-alpha (RAR alpha) is translocated from chromosome 17 to chromosome 15, and fused to a new gene, PLM. This results in the expression of both normal and chimeric RAR alpha transcripts in AML3 cells. The PLM-RAR alpha protein may account for the impairment of differentiation and thus leukemogenesis, but not for the paradoxical efficacy of RA in these cells. In an attempt to elucidate RA's differentiative effect in AML3 patients, the present work examined the in vitro and in vivo modulation of the normal RAR alpha transcripts by all-trans RA in seven cases of AML3. In all samples, Northern blot analysis revealed a low expression of the two normal RAR alpha transcripts compared with other human myeloid leukemic cells. No modulation was observed after 4-8 d of in vivo therapy with all-trans RA 45 mg/m2 per d. In vitro incubation with all-trans RA, however, increased the level of expression of the normal RAR alpha transcripts in AML3 cells but not in other AML leukemic subtypes. This modulation of the two normal RAR alpha transcripts appeared to be an early and primary event of RA's differentiating effect. We therefore suggest that up-regulation of the normal RAR alpha gene expression by pharmacological concentrations of all-trans RA may restore the normal differentiation pathway in these cells.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett J. M., Catovsky D., Daniel M. T., Flandrin G., Galton D. A., Gralnick H. R., Sultan C. Proposals for the classification of the acute leukaemias. French-American-British (FAB) co-operative group. Br J Haematol. 1976 Aug;33(4):451–458. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1976.tb03563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrow J., Goddard A. D., Sheer D., Solomon E. Molecular analysis of acute promyelocytic leukemia breakpoint cluster region on chromosome 17. Science. 1990 Sep 28;249(4976):1577–1580. doi: 10.1126/science.2218500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand N., Petkovich M., Krust A., Chambon P., de Thé H., Marchio A., Tiollais P., Dejean A. Identification of a second human retinoic acid receptor. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):850–853. doi: 10.1038/332850a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaigne S., Chomienne C., Daniel M. T., Ballerini P., Berger R., Fenaux P., Degos L. All-trans retinoic acid as a differentiation therapy for acute promyelocytic leukemia. I. Clinical results. Blood. 1990 Nov 1;76(9):1704–1709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomienne C., Ballerini P., Balitrand N., Amar M., Bernard J. F., Boivin P., Daniel M. T., Berger R., Castaigne S., Degos L. Retinoic acid therapy for promyelocytic leukaemia. Lancet. 1989 Sep 23;2(8665):746–747. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90812-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomienne C., Ballerini P., Balitrand N., Daniel M. T., Fenaux P., Castaigne S., Degos L. All-trans retinoic acid in acute promyelocytic leukemias. II. In vitro studies: structure-function relationship. Blood. 1990 Nov 1;76(9):1710–1717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomienne C., Ballerini P., Balitrand N., Huang M. E., Krawice I., Castaigne S., Fenaux P., Tiollais P., Dejean A., Degos L. The retinoic acid receptor alpha gene is rearranged in retinoic acid-sensitive promyelocytic leukemias. Leukemia. 1990 Dec;4(12):802–807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Robertson K. A., Mueller L. Retinoic acid-induced granulocytic differentiation of HL-60 myeloid leukemia cells is mediated directly through the retinoic acid receptor (RAR-alpha). Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2154–2163. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degos L., Chomienne C., Daniel M. T., Berger R., Dombret H., Fenaux P., Castaigne S. Treatment of first relapse in acute promyelocytic leukaemia with all-trans retinoic acid. Lancet. 1990 Dec 8;336(8728):1440–1441. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)93135-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher R. E., Said F., Pua I., Papenhausen P. R., Paietta E., Wiernik P. H. Expression of retinoic acid receptor-alpha mRNA in human leukemia cells with variable responsiveness to retinoic acid. Leukemia. 1989 Nov;3(11):789–795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguere V., Ong E. S., Segui P., Evans R. M. Identification of a receptor for the morphogen retinoic acid. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):624–629. doi: 10.1038/330624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. E., Ye Y. C., Chen S. R., Chai J. R., Lu J. X., Zhoa L., Gu L. J., Wang Z. Y. Use of all-trans retinoic acid in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood. 1988 Aug;72(2):567–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Januszewicz E., Cooper I. A. Inhibition of normal human macrophage progenitors by retinoic acid. Br J Haematol. 1984 Sep;58(1):119–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1984.tb06066.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalinyak J. E., Dorin R. I., Hoffman A. R., Perlman A. J. Tissue-specific regulation of glucocorticoid receptor mRNA by dexamethasone. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10441–10444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kizaki M., Koeffler H. P., Lin C. W., Miller C. W. Expression of retinoic acid receptor mRNA in hematopoietic cells. Leuk Res. 1990;14(7):645–655. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(90)90020-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krust A., Kastner P., Petkovich M., Zelent A., Chambon P. A third human retinoic acid receptor, hRAR-gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5310–5314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanotte M., Martin-Thouvenin V., Najman S., Balerini P., Valensi F., Berger R. NB4, a maturation inducible cell line with t(15;17) marker isolated from a human acute promyelocytic leukemia (M3). Blood. 1991 Mar 1;77(5):1080–1086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Largman C., Detmer K., Corral J. C., Hack F. M., Lawrence H. J. Expression of retinoic acid receptor alpha mRNA in human leukemia cells. Blood. 1989 Jul;74(1):99–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson R. A., Kondo K., Vardiman J. W., Butler A. E., Golomb H. M., Rowley J. D. Evidence for a 15;17 translocation in every patient with acute promyelocytic leukemia. Am J Med. 1984 May;76(5):827–841. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90994-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longo L., Pandolfi P. P., Biondi A., Rambaldi A., Mencarelli A., Lo Coco F., Diverio D., Pegoraro L., Avanzi G., Tabilio A. Rearrangements and aberrant expression of the retinoic acid receptor alpha gene in acute promyelocytic leukemias. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1571–1575. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Ong E. S., Dyck J. A., Evans R. M. Nuclear receptor that identifies a novel retinoic acid response pathway. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):224–229. doi: 10.1038/345224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell D. P., Mangelsdorf D. J., Pike J. W., Haussler M. R., O'Malley B. W. Molecular cloning of complementary DNA encoding the avian receptor for vitamin D. Science. 1987 Mar 6;235(4793):1214–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.3029866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okret S., Poellinger L., Dong Y., Gustafsson J. A. Down-regulation of glucocorticoid receptor mRNA by glucocorticoid hormones and recognition by the receptor of a specific binding sequence within a receptor cDNA clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5899–5903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petkovich M., Brand N. J., Krust A., Chambon P. A human retinoic acid receptor which belongs to the family of nuclear receptors. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):444–450. doi: 10.1038/330444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saceda M., Lippman M. E., Chambon P., Lindsey R. L., Ponglikitmongkol M., Puente M., Martin M. B. Regulation of the estrogen receptor in MCF-7 cells by estradiol. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Dec;2(12):1157–1162. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-12-1157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de The H., Marchio A., Tiollais P., Dejean A. Differential expression and ligand regulation of the retinoic acid receptor alpha and beta genes. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):429–433. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03394.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Thé H., Chomienne C., Lanotte M., Degos L., Dejean A. The t(15;17) translocation of acute promyelocytic leukaemia fuses the retinoic acid receptor alpha gene to a novel transcribed locus. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):558–561. doi: 10.1038/347558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Thé H., Marchio A., Tiollais P., Dejean A. A novel steroid thyroid hormone receptor-related gene inappropriately expressed in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):667–670. doi: 10.1038/330667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Thé H., Vivanco-Ruiz M. M., Tiollais P., Stunnenberg H., Dejean A. Identification of a retinoic acid responsive element in the retinoic acid receptor beta gene. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):177–180. doi: 10.1038/343177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]