Abstract
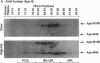
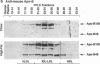
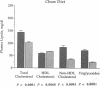
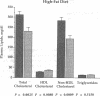
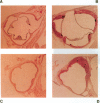
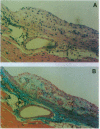
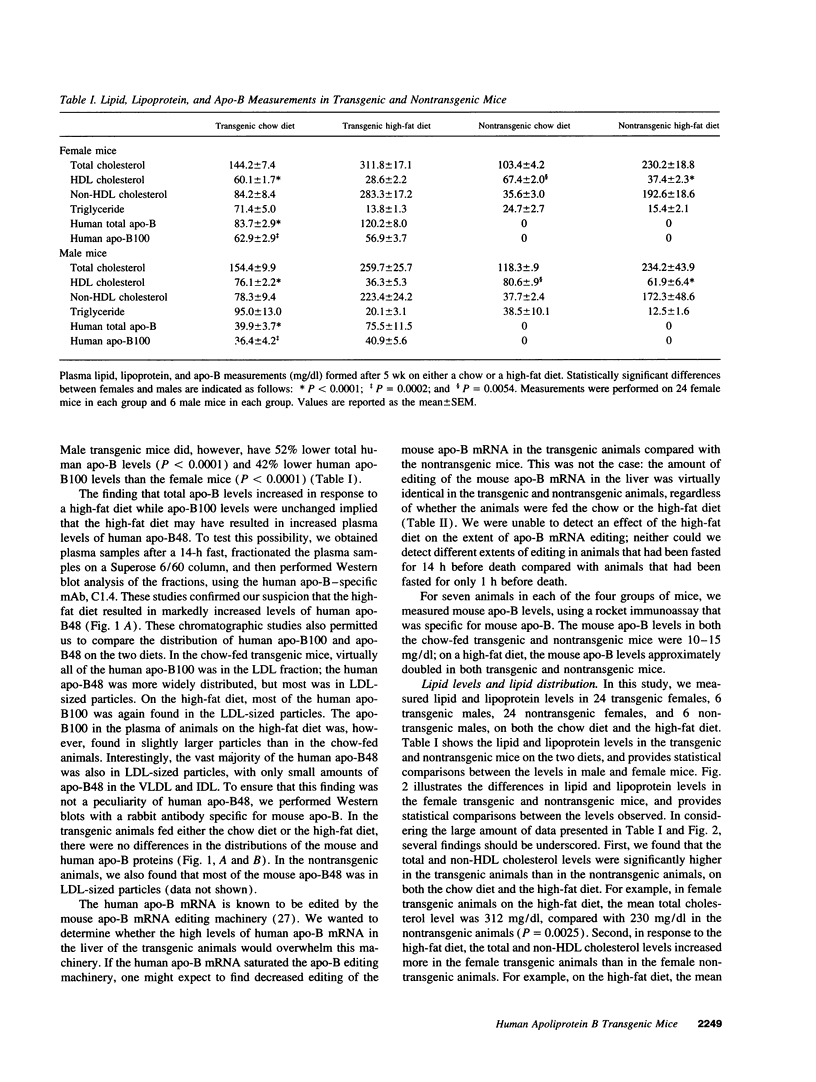
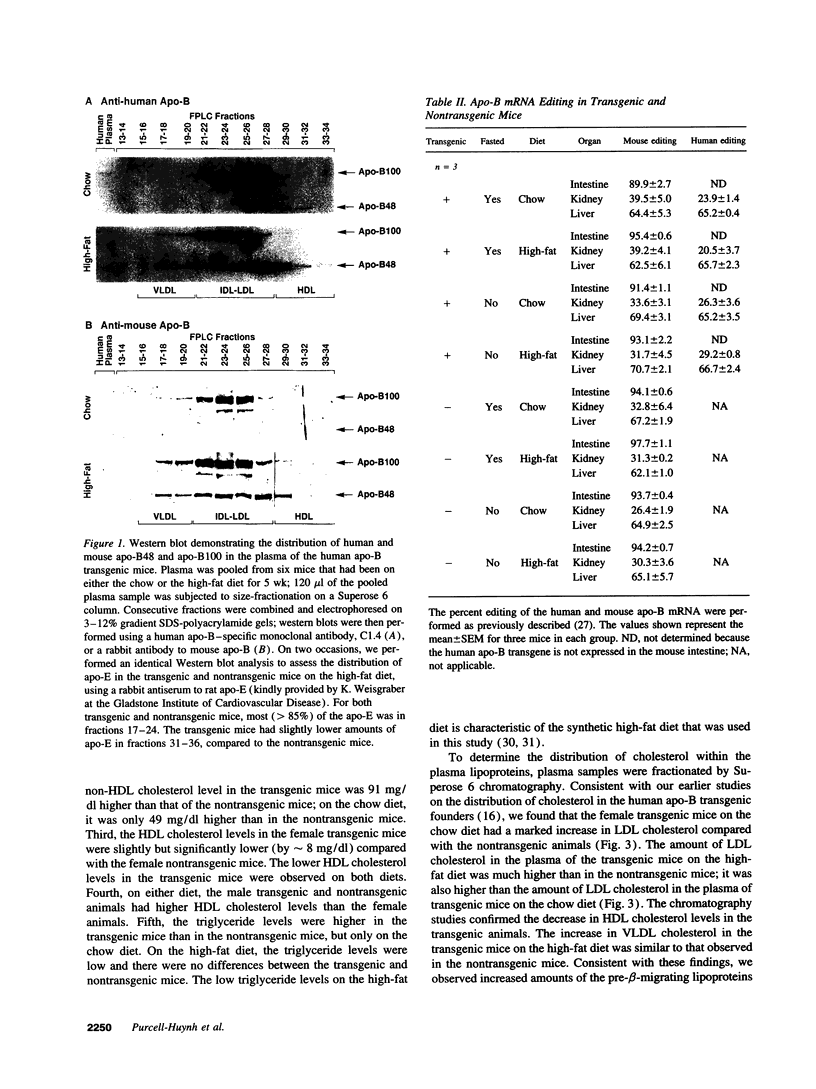
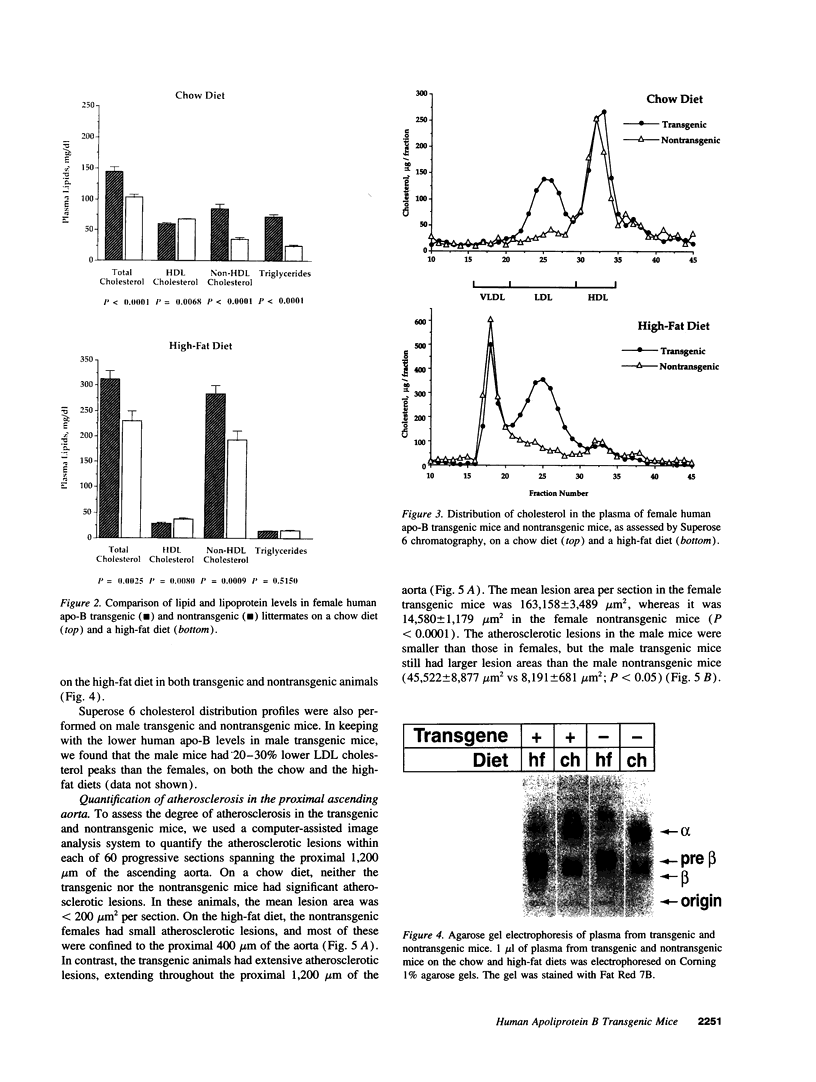
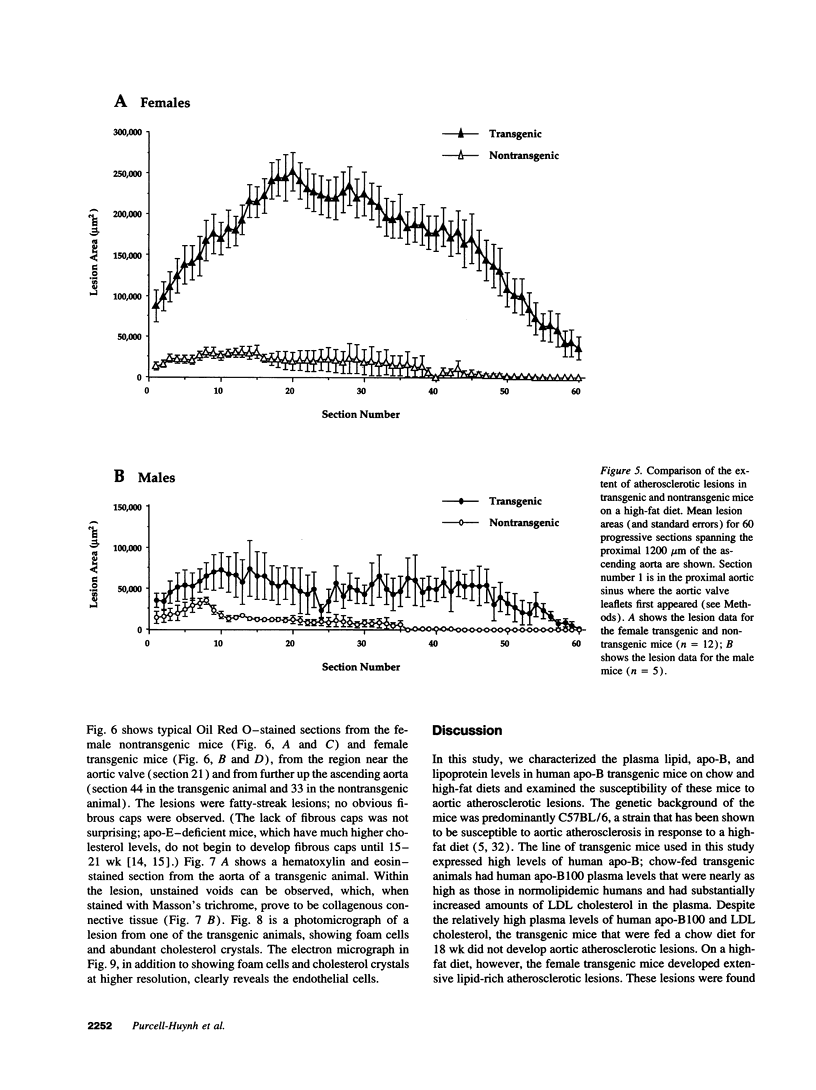
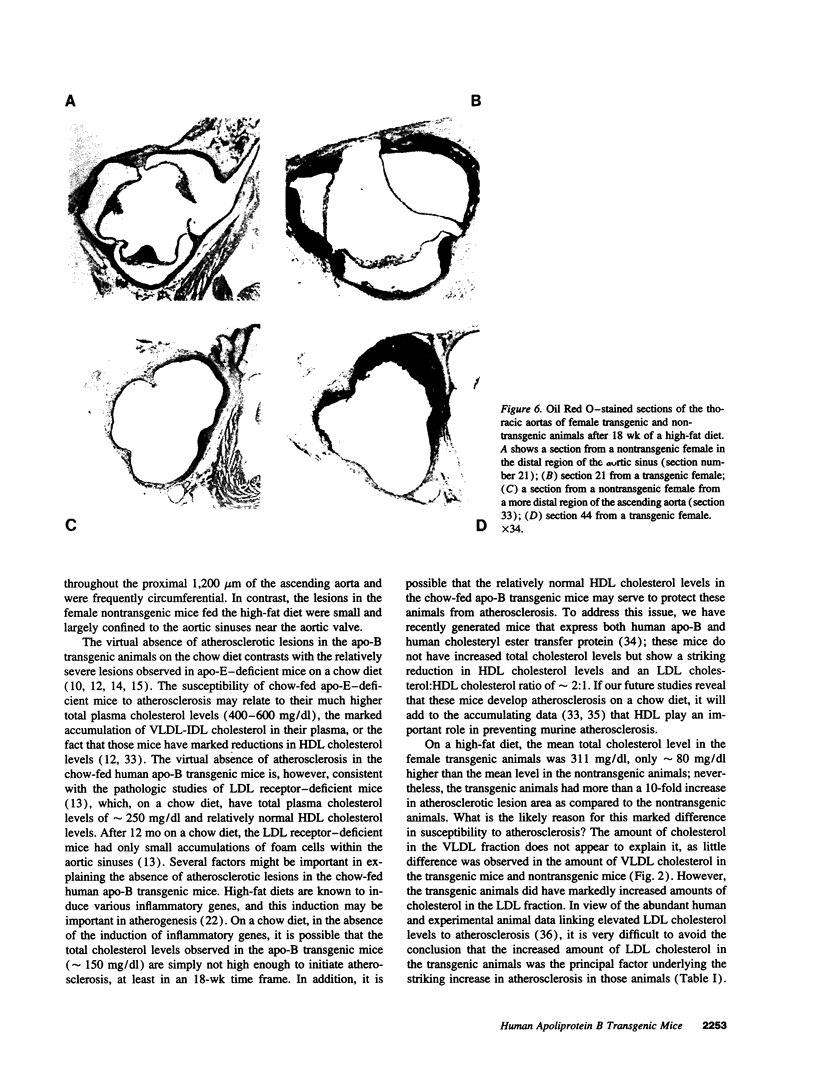
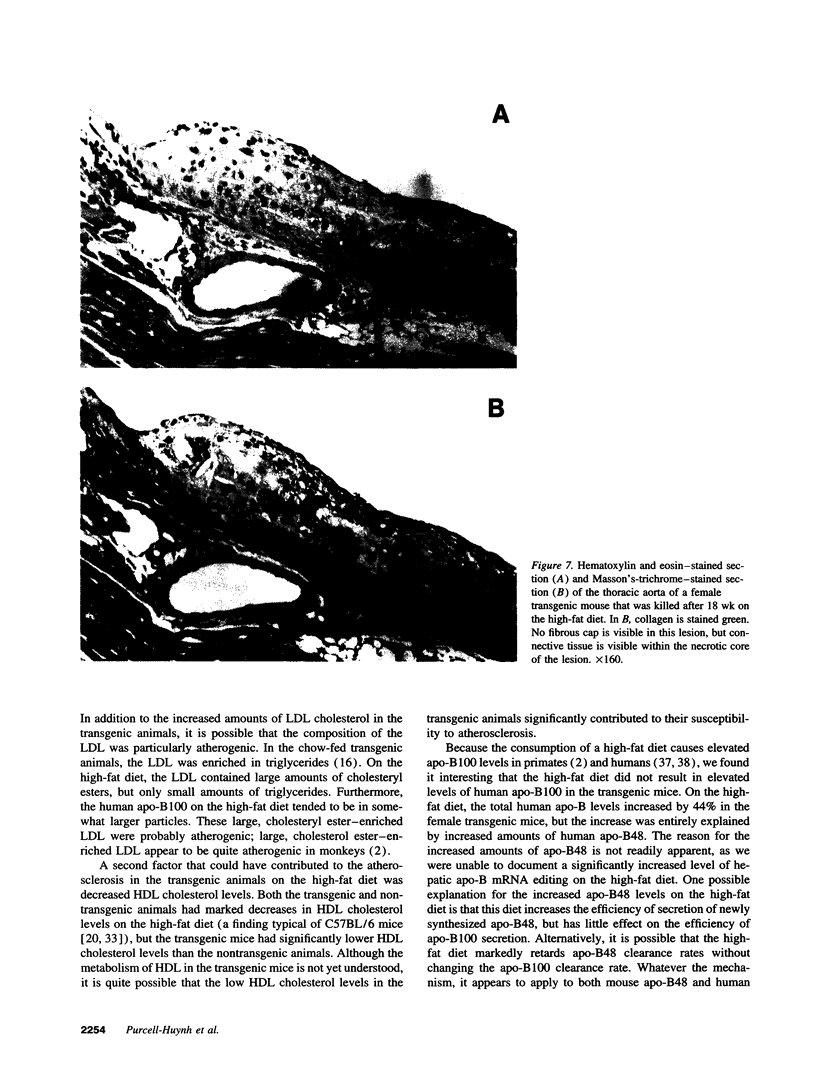
We previously generated transgenic mice expressing human apolipoprotein (apo-) B and demonstrated that the plasma of chow-fed transgenic animals contained markedly increased amounts of LDL (Linton, M. F., R. V. Farese, Jr., G. Chiesa, D. S. Grass, P. Chin, R. E. Hammer, H. H. Hobbs, and S. G. Young 1992. J. Clin. Invest. 92:3029-3037). In this study, we fed groups of transgenic and nontransgenic mice either a chow diet or a diet high in fat (16%) and cholesterol (1.25%). Lipid and lipoprotein levels were assessed, and after 18 wk of diet, the extent of aortic atherosclerotic lesions in each group of animals was quantified. Compared with the female transgenic mice on the chow diet, female transgenic mice on the high-fat diet had higher plasma levels of cholesterol (312 +/- 17 vs 144 +/- 7 mg/dl; P < 0.0001) and human apo-B (120 +/- 8 vs 84 +/- 3 mg/dl; P < 0.0001). The higher human apo-B levels were due to increased plasma levels of human apo-B48; the human apo-B100 levels did not differ in animals on the two diets. In mice on the high-fat diet, most of the human apo-B48 and apo-B100 was found in LDL-sized particles. Compared with nontransgenic mice on the high-fat diet, the transgenic animals on the high-fat diet had significantly increased levels of total cholesterol (312 +/- 17 vs 230 +/- 19 mg/dl; P < 0.0001) and non-HDL cholesterol (283 +/- 17 vs 193 +/- 19 mg/dl; P < 0.0001). The extent of atherosclerotic lesion development within the ascending aorta was quantified by measuring total lesion area in 60 progressive sections, using computer-assisted image analysis. Neither the chow-fed transgenic mice nor the chow-fed nontransgenic mice had significant atherosclerotic lesions. Nontransgenic animals on the high-fat diet had relatively small atherosclerotic lesions (< 15,000 microns 2/section), almost all of which were confined to the proximal 400 microns of the aorta near the aortic valve. In contrast, transgenic animals on the high-fat diet had extensive atherosclerotic lesions (> 160,000 microns 2/section) that were widely distributed throughout the proximal 1,200 microns of the aorta. Thus, human apo-B expression, in the setting of a diet rich in fats, causes severe atherosclerosis in mice.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boström K., Garcia Z., Poksay K. S., Johnson D. F., Lusis A. J., Innerarity T. L. Apolipoprotein B mRNA editing. Direct determination of the edited base and occurrence in non-apolipoprotein B-producing cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22446–22452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):34–47. doi: 10.1126/science.3513311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr T. P., Parks J. S., Rudel L. L. Hepatic ACAT activity in African green monkeys is highly correlated to plasma LDL cholesteryl ester enrichment and coronary artery atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb. 1992 Nov;12(11):1274–1283. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.12.11.1274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle C. K., Colca J. R., Melchior G. W. Lipoprotein profile characterization of the KKA(y) mouse, a rodent model of type II diabetes, before and after treatment with the insulin-sensitizing agent pioglitazone. Arterioscler Thromb. 1993 Feb;13(2):302–309. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.13.2.302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiesa G., Johnson D. F., Yao Z., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W., Young S. G., Hammer R. H., Hobbs H. H. Expression of human apolipoprotein B100 in transgenic mice. Editing of human apolipoprotein B100 mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):23747–23750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W., Weisgraber K. H., Bersot T. P., Krauss R. M., Vega G. L., Grundy S. M., Friedl W., Davignon J., McCarthy B. J. Familial defective apolipoprotein B-100: a mutation of apolipoprotein B that causes hypercholesterolemia. J Lipid Res. 1990 Aug;31(8):1337–1349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi S., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Gerard R. D., Hammer R. E., Herz J. Hypercholesterolemia in low density lipoprotein receptor knockout mice and its reversal by adenovirus-mediated gene delivery. J Clin Invest. 1993 Aug;92(2):883–893. doi: 10.1172/JCI116663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi S., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Herz J., Burns D. K. Massive xanthomatosis and atherosclerosis in cholesterol-fed low density lipoprotein receptor-negative mice. J Clin Invest. 1994 May;93(5):1885–1893. doi: 10.1172/JCI117179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida B. Y., Blanche P. J., Nichols A. V., Yashar M., Paigen B. Effects of atherogenic diet consumption on lipoproteins in mouse strains C57BL/6 and C3H. J Lipid Res. 1991 Apr;32(4):559–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krul E. S., Kleinman Y., Kinoshita M., Pfleger B., Oida K., Law A., Scott J., Pease R., Schonfeld G. Regional specificities of monoclonal anti-human apolipoprotein B antibodies. J Lipid Res. 1988 Jul;29(7):937–947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn R. M., Wade D. P., Hammer R. E., Chiesa G., Verstuyft J. G., Rubin E. M. Atherogenesis in transgenic mice expressing human apolipoprotein(a) Nature. 1992 Dec 17;360(6405):670–672. doi: 10.1038/360670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBoeuf R. C., Caldwell M., Kirk E. Regulation by nutritional status of lipids and apolipoproteins A-I, A-II, and A-IV in inbred mice. J Lipid Res. 1994 Jan;35(1):121–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBoeuf R. C., Doolittle M. H., Montcalm A., Martin D. C., Reue K., Lusis A. J. Phenotypic characterization of the Ath-1 gene controlling high density lipoprotein levels and susceptibility to atherosclerosis. J Lipid Res. 1990 Jan;31(1):91–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao F., Andalibi A., deBeer F. C., Fogelman A. M., Lusis A. J. Genetic control of inflammatory gene induction and NF-kappa B-like transcription factor activation in response to an atherogenic diet in mice. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jun;91(6):2572–2579. doi: 10.1172/JCI116495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linton M. F., Farese R. V., Jr, Chiesa G., Grass D. S., Chin P., Hammer R. E., Hobbs H. H., Young S. G. Transgenic mice expressing high plasma concentrations of human apolipoprotein B100 and lipoprotein(a). J Clin Invest. 1993 Dec;92(6):3029–3037. doi: 10.1172/JCI116927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusis A. J., Taylor B. A., Quon D., Zollman S., LeBoeuf R. C. Genetic factors controlling structure and expression of apolipoproteins B and E in mice. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7594–7604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W. Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):622–630. doi: 10.1126/science.3283935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marotti K. R., Castle C. K., Boyle T. P., Lin A. H., Murray R. W., Melchior G. W. Severe atherosclerosis in transgenic mice expressing simian cholesteryl ester transfer protein. Nature. 1993 Jul 1;364(6432):73–75. doi: 10.1038/364073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattson F. H., Grundy S. M. Comparison of effects of dietary saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated fatty acids on plasma lipids and lipoproteins in man. J Lipid Res. 1985 Feb;26(2):194–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima Y., Plump A. S., Raines E. W., Breslow J. L., Ross R. ApoE-deficient mice develop lesions of all phases of atherosclerosis throughout the arterial tree. Arterioscler Thromb. 1994 Jan;14(1):133–140. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.14.1.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishina P. M., Verstuyft J., Paigen B. Synthetic low and high fat diets for the study of atherosclerosis in the mouse. J Lipid Res. 1990 May;31(5):859–869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paigen B., Ishida B. Y., Verstuyft J., Winters R. B., Albee D. Atherosclerosis susceptibility differences among progenitors of recombinant inbred strains of mice. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 Mar-Apr;10(2):316–323. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.2.316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paigen B., Mitchell D., Reue K., Morrow A., Lusis A. J., LeBoeuf R. C. Ath-1, a gene determining atherosclerosis susceptibility and high density lipoprotein levels in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3763–3767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paigen B., Morrow A., Holmes P. A., Mitchell D., Williams R. A. Quantitative assessment of atherosclerotic lesions in mice. Atherosclerosis. 1987 Dec;68(3):231–240. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(87)90202-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pease R. J., Milne R. W., Jessup W. K., Law A., Provost P., Fruchart J. C., Dean R. T., Marcel Y. L., Scott J. Use of bacterial expression cloning to localize the epitopes for a series of monoclonal antibodies against apolipoprotein B100. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):553–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piedrahita J. A., Zhang S. H., Hagaman J. R., Oliver P. M., Maeda N. Generation of mice carrying a mutant apolipoprotein E gene inactivated by gene targeting in embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4471–4475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plump A. S., Smith J. D., Hayek T., Aalto-Setälä K., Walsh A., Verstuyft J. G., Rubin E. M., Breslow J. L. Severe hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice created by homologous recombination in ES cells. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):343–353. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90362-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pászty C., Maeda N., Verstuyft J., Rubin E. M. Apolipoprotein AI transgene corrects apolipoprotein E deficiency-induced atherosclerosis in mice. J Clin Invest. 1994 Aug;94(2):899–903. doi: 10.1172/JCI117412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddick R. L., Zhang S. H., Maeda N. Atherosclerosis in mice lacking apo E. Evaluation of lesional development and progression. Arterioscler Thromb. 1994 Jan;14(1):141–147. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.14.1.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin E. M., Krauss R. M., Spangler E. A., Verstuyft J. G., Clift S. M. Inhibition of early atherogenesis in transgenic mice by human apolipoprotein AI. Nature. 1991 Sep 19;353(6341):265–267. doi: 10.1038/353265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vega G. L., Groszek E., Wolf R., Grundy S. M. Influence of polyunsaturated fats on composition of plasma lipoproteins and apolipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1982 Aug;23(6):811–822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe M. S., Parks J. S., Morgan T. M., Rudel L. L. Childhood consumption of dietary polyunsaturated fat lowers risk for coronary artery atherosclerosis in African green monkeys. Arterioscler Thromb. 1993 Jun;13(6):863–875. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.13.6.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. G., Bertics S. J., Scott T. M., Dubois B. W., Curtiss L. K., Witztum J. L. Parallel expression of the MB19 genetic polymorphism in apoprotein B-100 and apoprotein B-48. Evidence that both apoproteins are products of the same gene. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):2995–2998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. G., Farese R. V., Jr, Pierotti V. R., Taylor S., Grass D. S., Linton M. F. Transgenic mice expressing human apoB100 and apoB48. Curr Opin Lipidol. 1994 Apr;5(2):94–101. doi: 10.1097/00041433-199404000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. G. Recent progress in understanding apolipoprotein B. Circulation. 1990 Nov;82(5):1574–1594. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.82.5.1574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S. H., Reddick R. L., Piedrahita J. A., Maeda N. Spontaneous hypercholesterolemia and arterial lesions in mice lacking apolipoprotein E. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):468–471. doi: 10.1126/science.1411543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]