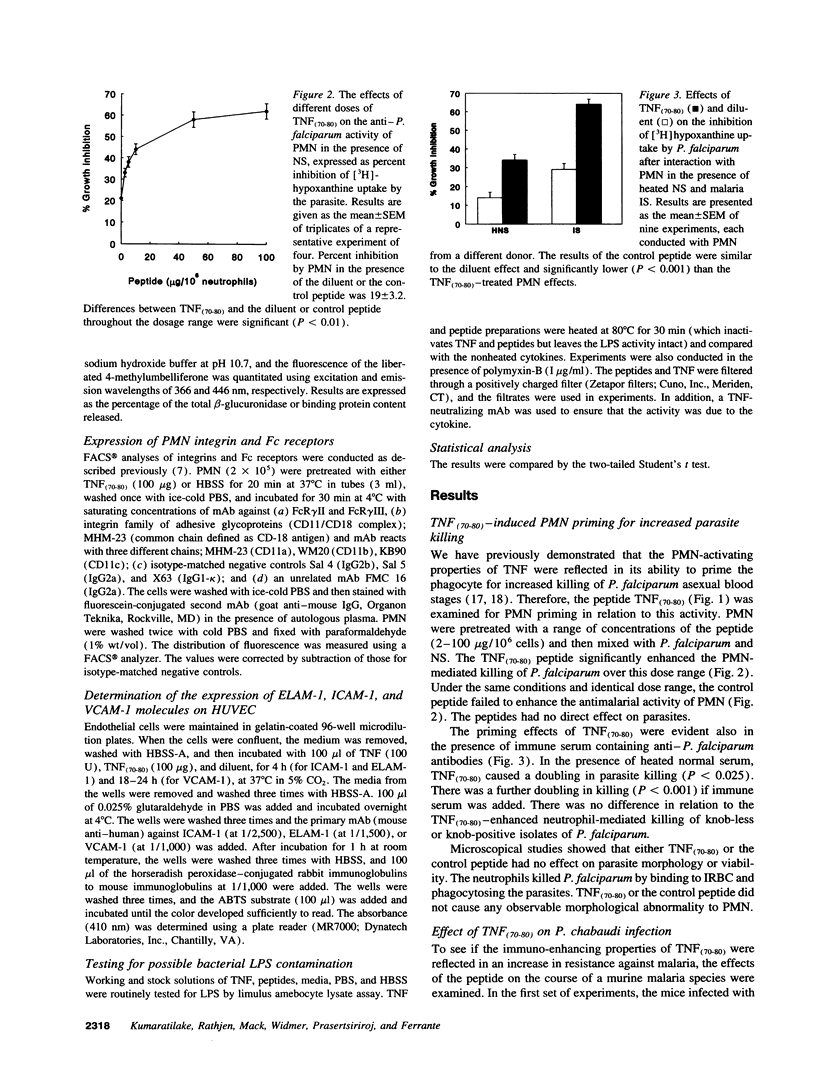
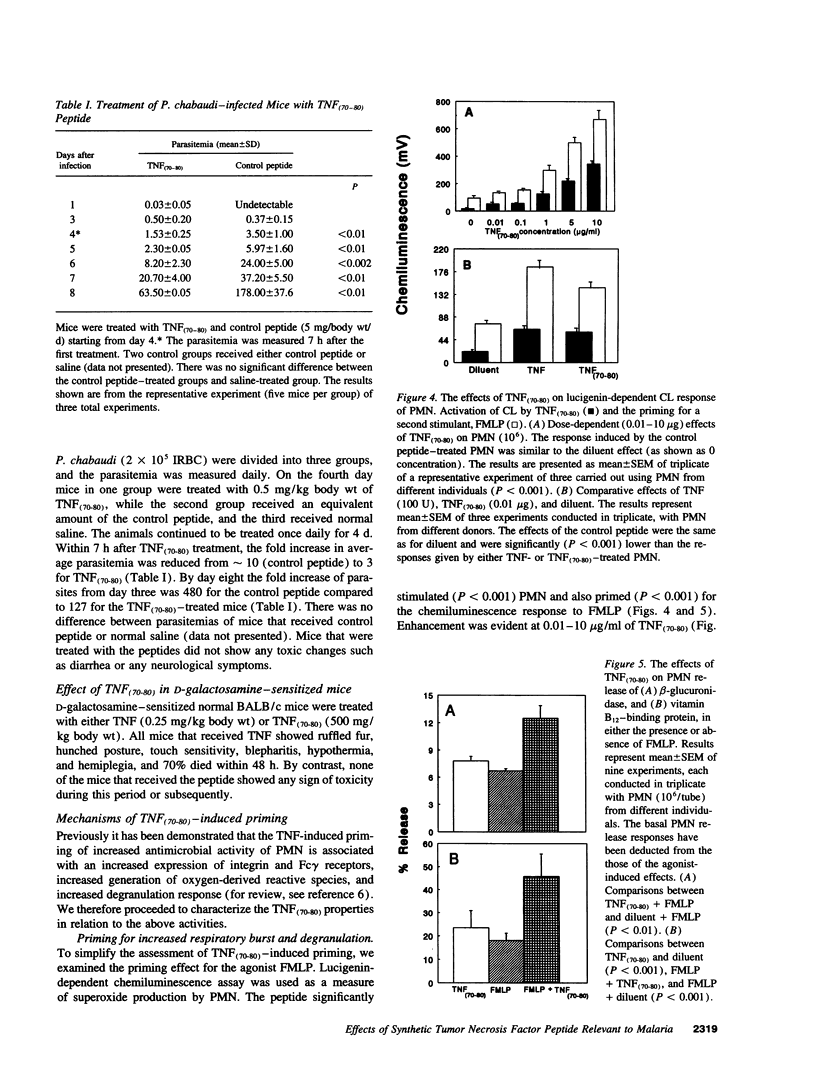
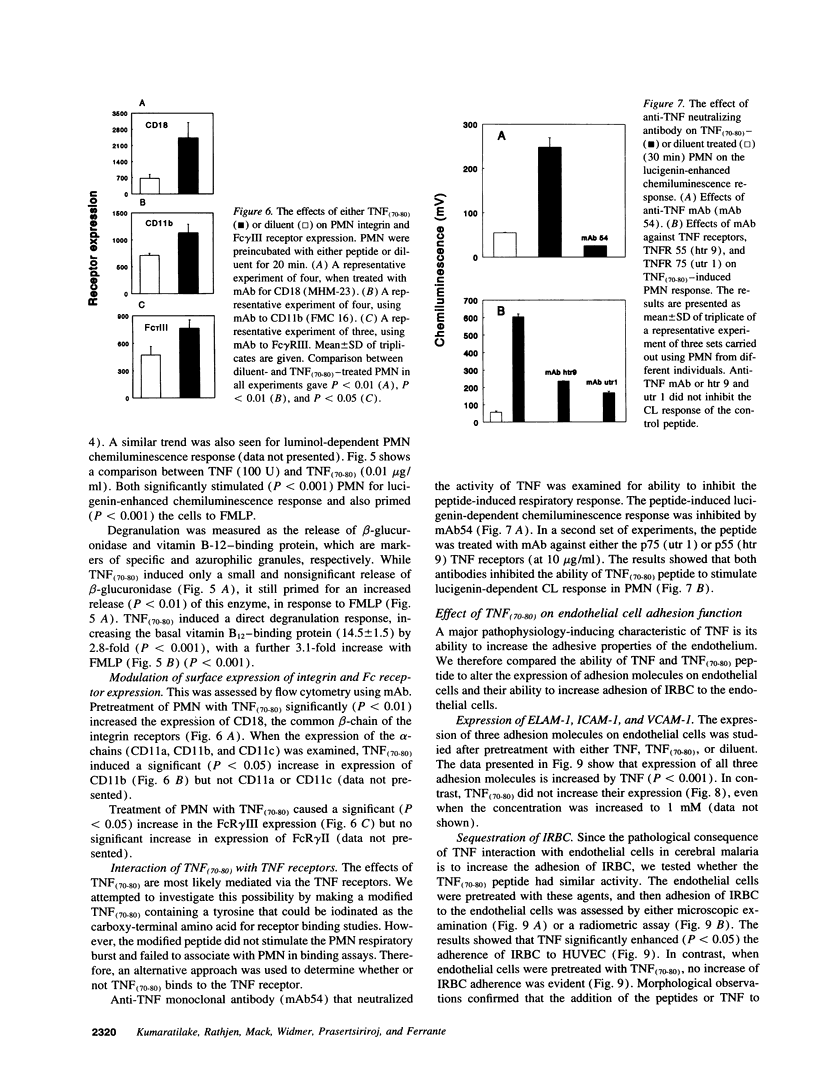
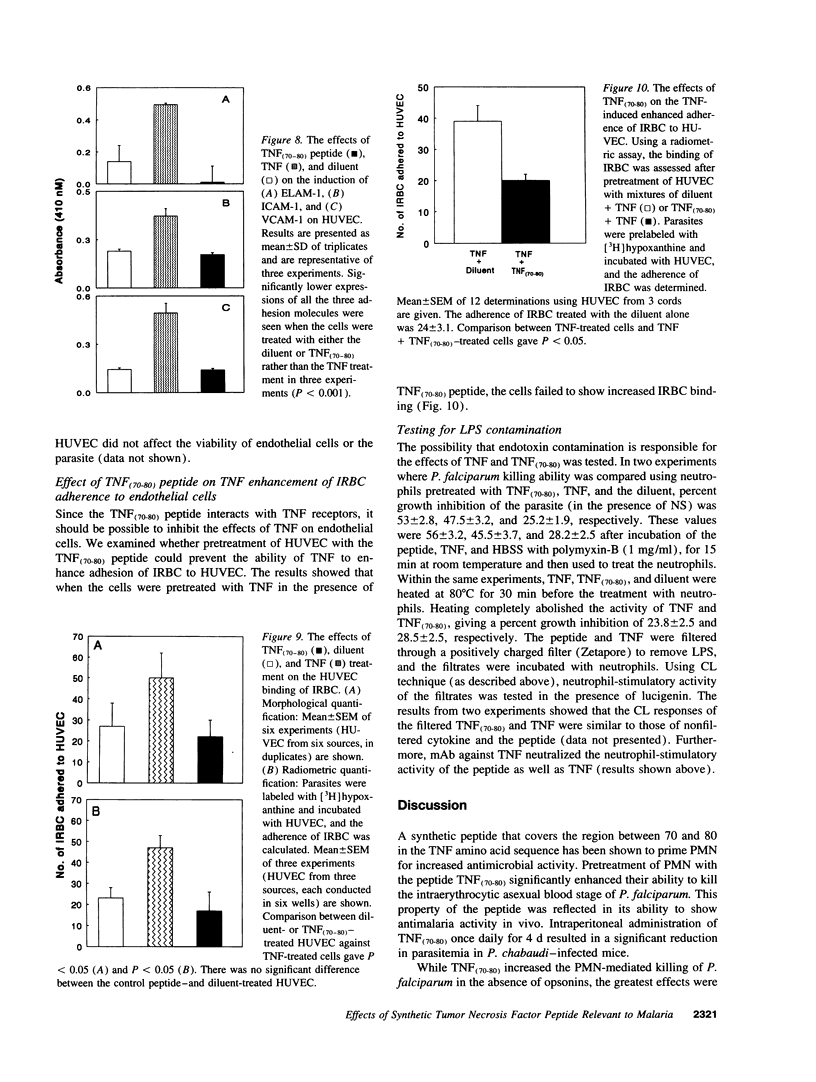
Abstract
A peptide corresponding to residues 70-80 of the TNF-alpha polypeptide was synthesized and shown to enhance human PMN-mediated killing of Plasmodium falciparum in vitro and reduced the Plasmodium chabaudi parasitemia in mice. Studies of the mechanism of action showed that the peptide, TNF(70-80), stimulated and primed PMN for an increased respiratory burst and release of granule constituents in response to a second agonist. The PMN-stimulatory activity of the peptide was inhibited by mAbs against the p55 and p75 TNF receptors and a TNF-neutralizing mAb. Analysis of PMN receptor expression showed that CR3 (CD18/CD11b) and Fc gamma RIII were upregulated by TNF(70-80), which was consistent with the peptide's ability to enhance parasite killing by PMN. The peptide, unlike TNF, did not increase the expression of adhesion molecules on endothelial cells and failed to promote binding of P. falciparum-infected erythrocytes to endothelial cells. TNF(70-80) also inhibited the TNF-induced increase in adhesion of P. falciparum-infected erythrocytes to endothelial cells. The results demonstrate that the host-protective effects of TNF can be retained while toxic effects are eliminated using a selected, characterized subunit of the cytokine.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balkwill F. Tumour necrosis factor. Improving on the formula. Nature. 1993 Jan 21;361(6409):206–207. doi: 10.1038/361206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger M., Wetzler E. M., Wallis R. S. Tumor necrosis factor is the major monocyte product that increases complement receptor expression on mature human neutrophils. Blood. 1988 Jan;71(1):151–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. The common mediator of shock, cachexia, and tumor necrosis. Adv Immunol. 1988;42:213–231. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60846-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.3895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Chadee K. Human neutrophils activated by interferon-gamma and tumour necrosis factor-alpha kill Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites in vitro. J Leukoc Biol. 1989 Sep;46(3):270–274. doi: 10.1002/jlb.46.3.270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espevik T., Nissen-Meyer J. A highly sensitive cell line, WEHI 164 clone 13, for measuring cytotoxic factor/tumor necrosis factor from human monocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Dec 4;95(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90322-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Martin A. J., Bates E. J., Goh D. H., Harvey D. P., Parsons D., Rathjen D. A., Russ G., Dayer J. M. Killing of Staphylococcus aureus by tumor necrosis factor-alpha-activated neutrophils. The role of serum opsonins, integrin receptors, respiratory burst, and degranulation. J Immunol. 1993 Nov 1;151(9):4821–4828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Nandoskar M., Walz A., Goh D. H., Kowanko I. C. Effects of tumour necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1 alpha and beta on human neutrophil migration, respiratory burst and degranulation. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1988;86(1):82–91. doi: 10.1159/000234610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Thong Y. H. Separation of mononuclear and polymorphonuclear leucocytes from human blood by the one-step Hypaque-Ficoll method is dependent on blood column height. J Immunol Methods. 1982;48(1):81–85. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90212-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A. Tumor necrosis factor alpha potentiates neutrophil antimicrobial activity: increased fungicidal activity against Torulopsis glabrata and Candida albicans and associated increases in oxygen radical production and lysosomal enzyme release. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2115–2122. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2115-2122.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figari I. S., Mori N. A., Palladino M. A., Jr Regulation of neutrophil migration and superoxide production by recombinant tumor necrosis factors-alpha and -beta: comparison to recombinant interferon-gamma and interleukin-1 alpha. Blood. 1987 Oct;70(4):979–984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford M. J., Taylor M. G., McHugh S. M., Wilson R. A., Hughes D. L. Studies on heterologous resistance between Schistosoma mansoni and Fasciola hepatica in inbred rats. Parasitology. 1987 Feb;94(Pt 1):55–67. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000053452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTLIEBLAU K. S., WASSERMAN L. R., HERBERT V. RAPID CHARCOAL ASSAY FOR INTRINSIC FACTOR (IF), GASTRIC JUICE UNSATURATED B12 BINDING CAPACITY, ANTIBODY TO IF, AND SERUM UNSATURATED B12 BINDING CAPACITY. Blood. 1965 Jun;25:875–884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau G. E., Piguet P. F., Vassalli P., Lambert P. H. Tumor-necrosis factor and other cytokines in cerebral malaria: experimental and clinical data. Immunol Rev. 1989 Dec;112:49–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00552.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jupin C., Parant M., Chedid L. Involvement of reactive oxygen metabolites in the candidacidal activity of human neutrophils stimulated by muramyl dipeptide or tumor necrosis factor. Immunobiology. 1989 Nov;180(1):68–79. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(89)80031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keffer J., Probert L., Cazlaris H., Georgopoulos S., Kaslaris E., Kioussis D., Kollias G. Transgenic mice expressing human tumour necrosis factor: a predictive genetic model of arthritis. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4025–4031. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04978.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kharazmi A., Jepsen S. Enhanced inhibition of in vitro multiplication of Plasmodium falciparum by stimulated human polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Aug;57(2):287–292. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J., Vadas M. A., Harlan J. M., Sparks L. H., Gamble J. R., Agosti J. M., Waltersdorph A. M. Stimulation of neutrophils by tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 1;136(11):4220–4225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodny E. H., Mumford R. A. Human leukocyte acid hydrolases: characterization of eleven lysosomal enzymes and study of reaction conditions for their automated analysis. Clin Chim Acta. 1976 Jul 15;70(2):247–257. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(76)90426-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumaratilake L. M., Ferrante A., Bates E. J., Kowanko I. C. Augmentation of the human monocyte/macrophage chemiluminescence response during short-term exposure to interferon-gamma and tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 May;80(2):257–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05244.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumaratilake L. M., Ferrante A., Jaeger T., Rzepczyk C. M. Effects of cytokines, complement, and antibody on the neutrophil respiratory burst and phagocytic response to Plasmodium falciparum merozoites. Infect Immun. 1992 Sep;60(9):3731–3738. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.9.3731-3738.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumaratilake L. M., Ferrante A., Rzepczyk C. M. Tumor necrosis factor enhances neutrophil-mediated killing of Plasmodium falciparum. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):788–793. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.788-793.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumaratilake L. M., Ferrante A., Rzepczyk C. The role of T lymphocytes in immunity to Plasmodium falciparum. Enhancement of neutrophil-mediated parasite killing by lymphotoxin and IFN-gamma: comparisons with tumor necrosis factor effects. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 15;146(2):762–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutner S., Breuer W. V., Ginsburg H., Aley S. B., Cabantchik Z. I. Characterization of permeation pathways in the plasma membrane of human erythrocytes infected with early stages of Plasmodium falciparum: association with parasite development. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Dec;125(3):521–527. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041250323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F. Neutrophil activation on biological surfaces. Massive secretion of hydrogen peroxide in response to products of macrophages and lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1550–1560. doi: 10.1172/JCI113241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockenhouse C. F., Ho M., Tandon N. N., Van Seventer G. A., Shaw S., White N. J., Jamieson G. A., Chulay J. D., Webster H. K. Molecular basis of sequestration in severe and uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria: differential adhesion of infected erythrocytes to CD36 and ICAM-1. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jul;164(1):163–169. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.1.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Kobayashi M., Rossi M. E., Anegon I., Trinchieri G. Immune interferon enhances functional properties of human granulocytes: role of Fc receptors and effect of lymphotoxin, tumor necrosis factor, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):765–774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Playfair J. H., Taverne J. Antiparasitic effects of tumour necrosis factor in vivo and in vitro. Ciba Found Symp. 1987;131:192–205. doi: 10.1002/9780470513521.ch13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rathjen D. A., Cowan K., Furphy L. J., Aston R. Antigenic structure of human tumour necrosis factor: recognition of distinct regions of TNF alpha by different tumour cell receptors. Mol Immunol. 1991 Jan-Feb;28(1-2):79–86. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(91)90089-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rathjen D. A., Ferrante A., Aston R. Differential effects of small tumour necrosis factor-alpha peptides on tumour cell cytotoxicity, neutrophil activation and endothelial cell procoagulant activity. Immunology. 1993 Oct;80(2):293–299. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby M. R., Aggarwal B. B., Rinderknecht E., Svedersky L. P., Finkle B. S., Palladino M. A., Jr Activation of human polymorphonuclear neutrophil functions by interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factors. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2069–2073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman I. W., Crandall I., Smith H. Membrane proteins involved in the adherence of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes to the endothelium. Biol Cell. 1992;74(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0248-4900(92)90022-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



