Abstract
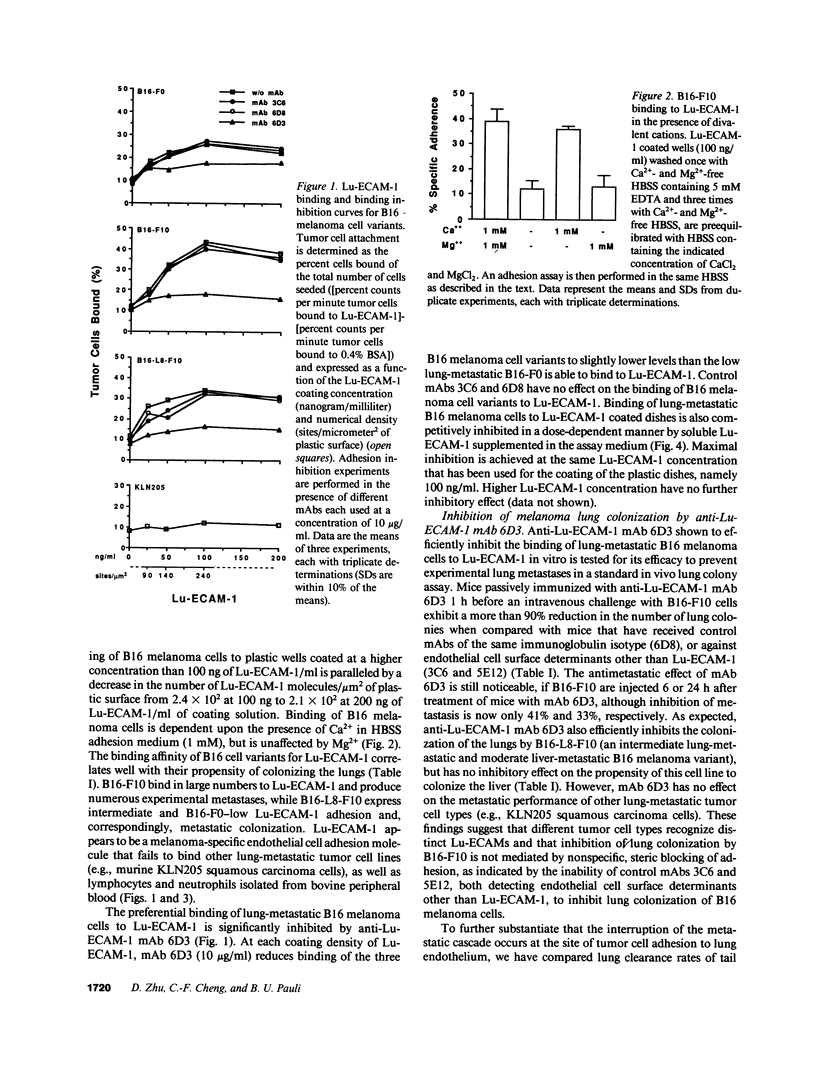
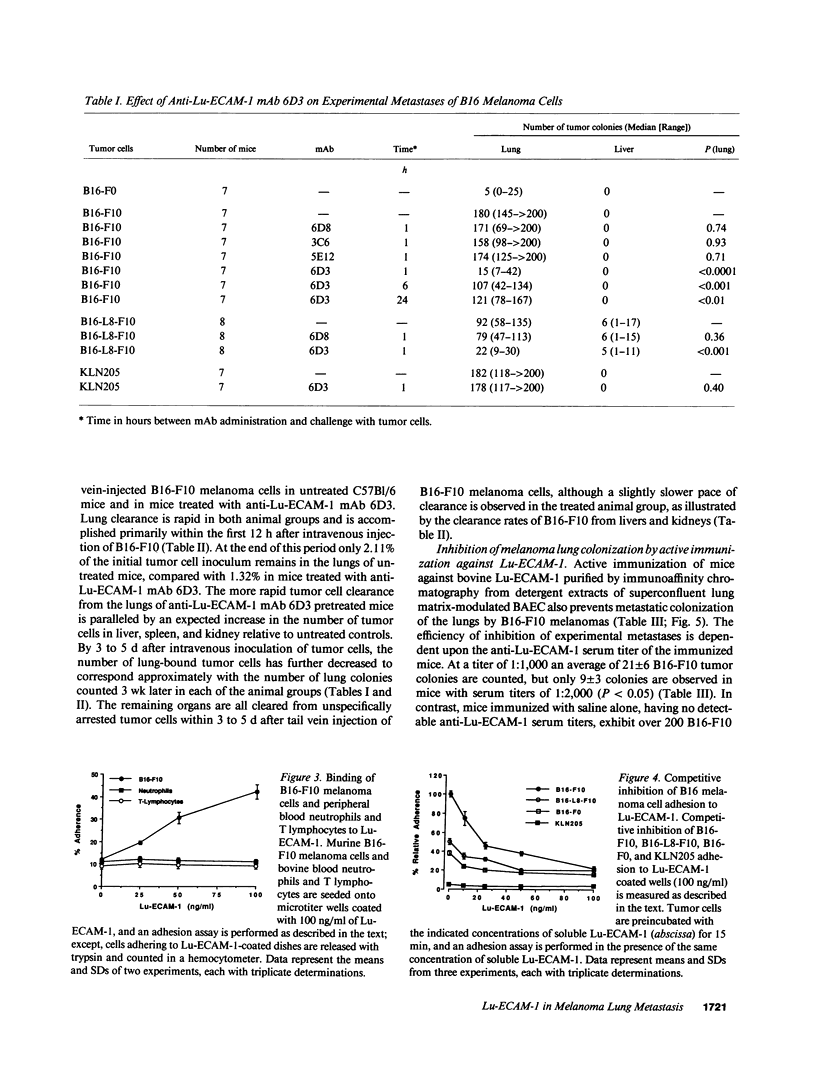
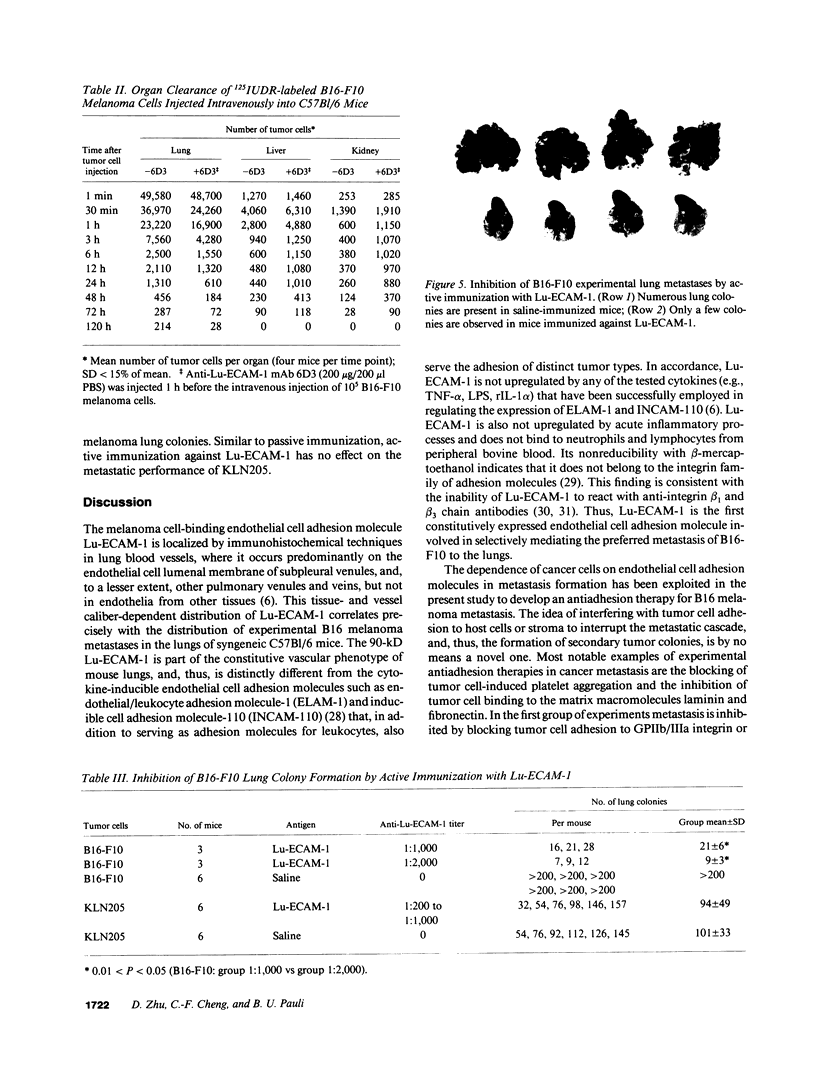
The 90-kD lung endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (Lu-ECAM-1) selectively promotes Ca(2+)-dependent adhesion of lung-metastatic B16 melanoma cells. Corresponding with their metastatic performance, high lung-metastatic B16-F10 melanoma cells bind in significantly higher numbers to Lu-ECAM-1 than their intermediate and low lung-metastatic counterparts B16-L8-F10 and B16-F0, respectively. Maximum attachment is observed at a density of approximately 2.4 x 10(2) Lu-ECAM-1 sites/microns2 of plastic surface. B16 melanoma cell binding to Lu-ECAM-1 is blocked by mAb 6D3 and is competitively inhibited by soluble Lu-ECAM-1. C57B1/6 mice passively immunized with anti-Lu-ECAM-1 mAb 6D3 or actively immunized with purified Lu-ECAM-1 exhibit an anti-Lu-ECAM-1 antibody titer-dependent reduction in the number of B16 experimental metastases. Lu-ECAM-1 promotes neither binding nor metastasis of other lung-metastatic tumor cells (e.g., KLN205). Our data indicate that an "antiadhesion" therapy directed at interfering with the adherence of blood-borne tumor cells to organ-specific vascular endothelium is efficient in the control of metastasis formation in selective organ sites.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alby L., Auerbach R. Differential adhesion of tumor cells to capillary endothelial cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5739–5743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach R., Lu W. C., Pardon E., Gumkowski F., Kaminska G., Kaminski M. Specificity of adhesion between murine tumor cells and capillary endothelium: an in vitro correlate of preferential metastasis in vivo. Cancer Res. 1987 Mar 15;47(6):1492–1496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargatze R. F., Wu N. W., Weissman I. L., Butcher E. C. High endothelial venule binding as a predictor of the dissemination of passaged murine lymphomas. J Exp Med. 1987 Oct 1;166(4):1125–1131. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.4.1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belloni P. N., Tressler R. J. Microvascular endothelial cell heterogeneity: interactions with leukocytes and tumor cells. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1990 Feb;8(4):353–389. doi: 10.1007/BF00052608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg E. L., Goldstein L. A., Jutila M. A., Nakache M., Picker L. J., Streeter P. R., Wu N. W., Zhou D., Butcher E. C. Homing receptors and vascular addressins: cell adhesion molecules that direct lymphocyte traffic. Immunol Rev. 1989 Apr;108:5–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00010.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booyse F. M., Sedlak B. J., Rafelson M. E., Jr Culture of arterial endothelial cells: characterization and growth of bovine aortic cells. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1975 Dec 15;34(3):825–839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlos T. M., Harlan J. M. Membrane proteins involved in phagocyte adherence to endothelium. Immunol Rev. 1990 Apr;114:5–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1990.tb00559.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheresh D. A., Spiro R. C. Biosynthetic and functional properties of an Arg-Gly-Asp-directed receptor involved in human melanoma cell attachment to vitronectin, fibrinogen, and von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17703–17711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Thong Y. H. Simultaneous preparation of mononuclear and polymorphonuclear leucocytes from horse blood on Ficoll-Hypaque medium. J Immunol Methods. 1980;34(4):279–285. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J. Metastasis: quantitative analysis of distribution and fate of tumor emboli labeled with 125 I-5-iodo-2'-deoxyuridine. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1970 Oct;45(4):773–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J. Selection of successive tumour lines for metastasis. Nat New Biol. 1973 Apr 4;242(118):148–149. doi: 10.1038/newbio242148a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günthert U., Hofmann M., Rudy W., Reber S., Zöller M., Haussmann I., Matzku S., Wenzel A., Ponta H., Herrlich P. A new variant of glycoprotein CD44 confers metastatic potential to rat carcinoma cells. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):13–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90403-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakomori S. Possible functions of tumor-associated carbohydrate antigens. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991 Oct;3(5):646–653. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(91)90091-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries M. J., Olden K., Yamada K. M. A synthetic peptide from fibronectin inhibits experimental metastasis of murine melanoma cells. Science. 1986 Jul 25;233(4762):467–470. doi: 10.1126/science.3726541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: a family of cell surface receptors. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto Y., Robey F. A., Graf J., Sasaki M., Kleinman H. K., Yamada Y., Martin G. R. YIGSR, a synthetic laminin pentapeptide, inhibits experimental metastasis formation. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1132–1134. doi: 10.1126/science.2961059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenaga M., Wang C. H., Bell R. G., Zhu D., Ahmad A. Intestinal immunity to Trichinella spiralis is a property of OX8- OX22- T-helper cells that are generated in the intestine. Immunology. 1989 Apr;66(4):588–594. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapis K., Paku S., Liotta L. A. Endothelialization of embolized tumor cells during metastasis formation. Clin Exp Metastasis. 1988 Jan-Feb;6(1):73–89. doi: 10.1007/BF01580408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcantonio E. E., Hynes R. O. Antibodies to the conserved cytoplasmic domain of the integrin beta 1 subunit react with proteins in vertebrates, invertebrates, and fungi. J Cell Biol. 1988 May;106(5):1765–1772. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.5.1765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlin S. D., Springer T. A. Purified intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) is a ligand for lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 (LFA-1). Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):813–819. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90104-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy P., Alexander P., Senior P. V., Fleming J., Kirkham N., Taylor I. Mechanisms of organ selective tumour growth by bloodborne cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 1988 Jan;57(1):19–31. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L., Belloni P. N., Tressler R. J., Dulski K., Inoue T., Cavanaugh P. G. Adhesive, invasive, and growth properties of selected metastatic variants of a murine large-cell lymphoma. Invasion Metastasis. 1989;9(2):102–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. Cancer metastasis: tumor cell and host organ properties important in metastasis to specific secondary sites. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Nov 15;948(2):175–224. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(88)90010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oguchi H., Toyokuni T., Dean B., Ito H., Otsuji E., Jones V. L., Sadozai K. K., Hakomori S. Effect of lactose derivatives on metastatic potential of B16 melanoma cells. Cancer Commun. 1990;2(9):311–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L. Leukocyte adhesion to endothelium in inflammation. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):3–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90230-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauli B. U., Augustin-Voss H. G., el-Sabban M. E., Johnson R. C., Hammer D. A. Organ-preference of metastasis. The role of endothelial cell adhesion molecules. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1990 Nov;9(3):175–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00046359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauli B. U., Lee C. L. Organ preference of metastasis. The role of organ-specifically modulated endothelial cells. Lab Invest. 1988 Apr;58(4):379–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. Cell attachment activity of fibronectin can be duplicated by small synthetic fragments of the molecule. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):30–33. doi: 10.1038/309030a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice G. E., Bevilacqua M. P. An inducible endothelial cell surface glycoprotein mediates melanoma adhesion. Science. 1989 Dec 8;246(4935):1303–1306. doi: 10.1126/science.2588007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojkind M., Gatmaitan Z., Mackensen S., Giambrone M. A., Ponce P., Reid L. M. Connective tissue biomatrix: its isolation and utilization for long-term cultures of normal rat hepatocytes. J Cell Biol. 1980 Oct;87(1):255–263. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.1.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos E., Tulp A., Middelkoop O. P., van de Pavert I. V. Interactions between lymphoid tumor cells and isolated liver endothelial cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1984 May;72(5):1173–1180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. Arg-Gly-Asp: a versatile cell recognition signal. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):517–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90259-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):425–434. doi: 10.1038/346425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao T., Matter A., Vogel K., Burger M. M. Liver-colonizing melanoma cells selected from B-16 melanoma. Int J Cancer. 1979 Jun 15;23(6):854–857. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910230618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terranova V. P., Williams J. E., Liotta L. A., Martin G. R. Modulation of the metastatic activity of melanoma cells by laminin and fibronectin. Science. 1984 Nov 23;226(4677):982–985. doi: 10.1126/science.6505678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollmers H. P., Birchmeier W. Monoclonal antibodies inhibit the adhesion of mouse B 16 melanoma cells in vitro and block lung metastasis in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3729–3733. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegner C. D., Gundel R. H., Reilly P., Haynes N., Letts L. G., Rothlein R. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in the pathogenesis of asthma. Science. 1990 Jan 26;247(4941):456–459. doi: 10.1126/science.1967851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L., Dimitrov D. S. Mechanical aspects of the lungs as cancer cell-killing organs during hematogenous metastasis. J Theor Biol. 1986 Aug 7;121(3):307–321. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(86)80110-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. The hemodynamic destruction of circulating cancer cells. Biorheology. 1987;24(2):105–115. doi: 10.3233/bir-1987-24204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yednock T. A., Rosen S. D. Lymphocyte homing. Adv Immunol. 1989;44:313–378. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60645-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu D. Z., Bell R. G. Trichinella spiralis: murine strain variation in response to monoclonally defined, protective, nonstage-specific antigens. Exp Parasitol. 1990 Apr;70(3):330–343. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(90)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu D. Z., Cheng C. F., Pauli B. U. Mediation of lung metastasis of murine melanomas by a lung-specific endothelial cell adhesion molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9568–9572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu D. Z., Pauli B. U. Generation of monoclonal antibodies directed against organ-specific endothelial cell surface determinants. J Histochem Cytochem. 1991 Aug;39(8):1137–1142. doi: 10.1177/39.8.1856462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]