Abstract
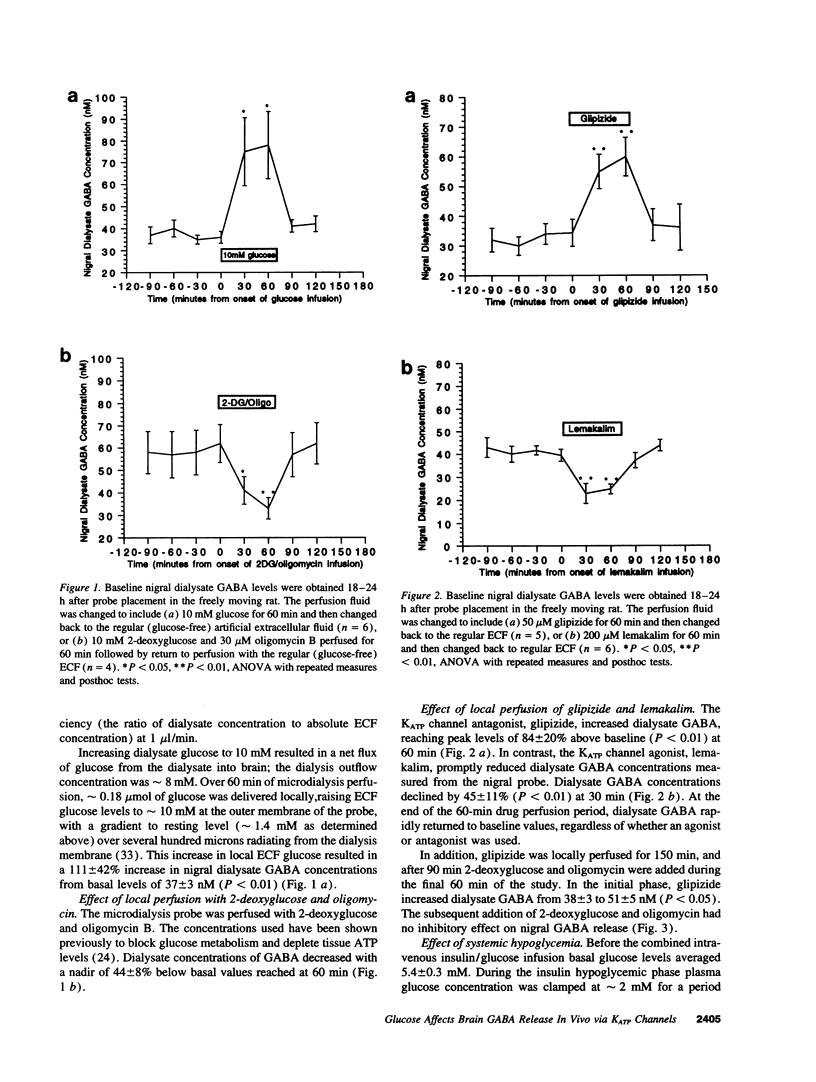
Glucose modulates beta cell insulin secretion via effects on ATP-sensitive potassium (KATP) channels. To test the hypothesis that glucose exerts a similar effect on neuronal function, local glucose availability was varied in awake rats using microdialysis in the substantia nigra, the brain region with the highest density of KATP channels. 10 mM glucose perfusion increased GABA release by 111 +/- 42%, whereas the sulfonylurea, glipizide, increased GABA release by 84 +/- 20%. In contrast, perfusion of the KATP channel activator, lemakalim, or depletion of ATP by perfusion of 2-deoxyglucose with oligomycin inhibited GABA release by 44 +/- 8 and 45 +/- 11%, respectively. Moreover, the inhibition of GABA release by 2-deoxyglucose and oligomycin was blocked by glipizide. During systemic insulin-induced hypoglycemia (1.8 +/- 0.3 mM), nigral dialysate GABA concentrations decreased by 49 +/- 4% whereas levels of dopamine in striatal dialysates increased by 119 +/- 18%. We conclude that both local and systemic glucose availability influences nigral GABA release via an effect on KATP channels and that inhibition of GABA release may in part mediate the hyperexcitability associated with hypoglycemia. These data support the hypothesis that glucose acts as a signaling molecule, and not simply as an energy-yielding fuel, for neurons.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguilar-Bryan L., Nichols C. G., Rajan A. S., Parker C., Bryan J. Co-expression of sulfonylurea receptors and KATP channels in hamster insulinoma tumor (HIT) cells. Evidence for direct association of the receptor with the channel. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14934–14940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amoroso S., Schmid-Antomarchi H., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. Glucose, sulfonylureas, and neurotransmitter release: role of ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Science. 1990 Feb 16;247(4944):852–854. doi: 10.1126/science.2305257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben Ari Y. Effect of glibenclamide, a selective blocker of an ATP-K+ channel, on the anoxic response of hippocampal neurones. Pflugers Arch. 1989;414 (Suppl 1):S111–S114. doi: 10.1007/BF00582258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi H., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. ATP/ADP binding sites are present in the sulfonylurea binding protein associated with brain ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Biochemistry. 1992 Jul 14;31(27):6328–6332. doi: 10.1021/bi00142a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daut J., Maier-Rudolph W., von Beckerath N., Mehrke G., Günther K., Goedel-Meinen L. Hypoxic dilation of coronary arteries is mediated by ATP-sensitive potassium channels. Science. 1990 Mar 16;247(4948):1341–1344. doi: 10.1126/science.2107575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detimary P., Gilon P., Nenquin M., Henquin J. C. Two sites of glucose control of insulin release with distinct dependence on the energy state in pancreatic B-cells. Biochem J. 1994 Feb 1;297(Pt 3):455–461. doi: 10.1042/bj2970455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- During M. J., Craig J. S., Hernandez T. D., Anderson G. M., Gallager D. W. Effect of amygdala kindling on the in vivo release of GABA and 5-HT in the dorsal raphe nucleus in freely moving rats. Brain Res. 1992 Jul 3;584(1-2):36–44. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90875-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- During M. J., Naegele J. R., O'Malley K. L., Geller A. I. Long-term behavioral recovery in parkinsonian rats by an HSV vector expressing tyrosine hydroxylase. Science. 1994 Nov 25;266(5189):1399–1403. doi: 10.1126/science.266.5189.1399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- During M. J., Spencer D. D. Adenosine: a potential mediator of seizure arrest and postictal refractoriness. Ann Neurol. 1992 Nov;32(5):618–624. doi: 10.1002/ana.410320504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- During M. J., Spencer D. D. Extracellular hippocampal glutamate and spontaneous seizure in the conscious human brain. Lancet. 1993 Jun 26;341(8861):1607–1610. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90754-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durkin T. A., Anderson G. M., Cohen D. J. High-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of neurotransmitter amino acids in brain. J Chromatogr. 1988 Jun 24;428(1):9–15. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)83885-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellows L. K., Boutelle M. G., Fillenz M. Extracellular brain glucose levels reflect local neuronal activity: a microdialysis study in awake, freely moving rats. J Neurochem. 1992 Dec;59(6):2141–2147. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb10105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellows L. K., Boutelle M. G. Rapid changes in extracellular glucose levels and blood flow in the striatum of the freely moving rat. Brain Res. 1993 Feb 26;604(1-2):225–231. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)90373-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay I., Dunne M. J., Petersen O. H. ATP-sensitive inward rectifier and voltage- and calcium-activated K+ channels in cultured pancreatic islet cells. J Membr Biol. 1985;88(2):165–172. doi: 10.1007/BF01868430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale K. Mechanisms of seizure control mediated by gamma-aminobutyric acid: role of the substantia nigra. Fed Proc. 1985 May;44(8):2414–2424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale K. Role of the substantia nigra in GABA-mediated anticonvulsant actions. Adv Neurol. 1986;44:343–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandolfo G., Gottesmann C., Bidard J. N., Lazdunski M. K+ channels openers prevent epilepsy induced by the bee venom peptide MCD. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Jan 17;159(3):329–330. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90169-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandolfo G., Romettino S., Gottesmann C., van Luijtelaar G., Coenen A., Bidard J. N., Lazdunski M. K+ channel openers decrease seizures in genetically epileptic rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Aug 11;167(1):181–183. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90762-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta G., Azam M., Baquer N. Z. Effect of experimental diabetes on the catecholamine metabolism in rat brain. J Neurochem. 1992 Jan;58(1):95–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb09282.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberger A., Jacobson I., Nyström B., Sandberg M. Microdialysis sampling of the neuronal environment in basic and clinical research. J Intern Med. 1991 Oct;230(4):375–380. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.1991.tb00460.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. Adenosine triphosphate-sensitive K+ channels may not be the sole regulators of glucose-induced electrical activity in pancreatic B-cells. Endocrinology. 1992 Jul;131(1):127–131. doi: 10.1210/endo.131.1.1611991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heurteaux C., Bertaina V., Widmann C., Lazdunski M. K+ channel openers prevent global ischemia-induced expression of c-fos, c-jun, heat shock protein, and amyloid beta-protein precursor genes and neuronal death in rat hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9431–9435. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang C., Haddad G. G. Effect of anoxia on intracellular and extracellular potassium activity in hypoglossal neurons in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1991 Jul;66(1):103–111. doi: 10.1152/jn.1991.66.1.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang C., Xia Y., Haddad G. G. Role of ATP-sensitive K+ channels during anoxia: major differences between rat (newborn and adult) and turtle neurons. J Physiol. 1992 Mar;448:599–612. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakei M., Noma A., Shibasaki T. Properties of adenosine-triphosphate-regulated potassium channels in guinea-pig ventricular cells. J Physiol. 1985 Jun;363:441–462. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund-Andersen H. Transport of glucose from blood to brain. Physiol Rev. 1979 Apr;59(2):305–352. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.2.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnroth P., Jansson P. A., Smith U. A microdialysis method allowing characterization of intercellular water space in humans. Am J Physiol. 1987 Aug;253(2 Pt 1):E228–E231. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.253.2.E228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milusheva E., Doda M., Pasztor E., Lajtha A., Sershen H., Vizi E. S. Regulatory interactions among axon terminals affecting the release of different transmitters from rat striatal slices under hypoxic and hypoglycemic conditions. J Neurochem. 1992 Sep;59(3):946–952. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb08335.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mourre C., Ben Ari Y., Bernardi H., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. Antidiabetic sulfonylureas: localization of binding sites in the brain and effects on the hyperpolarization induced by anoxia in hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 1989 May 1;486(1):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91288-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mourre C., Widmann C., Lazdunski M. Specific hippocampal lesions indicate the presence of sulfonylurea binding sites associated to ATP-sensitive K+ channels both post-synaptically and on mossy fibers. Brain Res. 1991 Feb 1;540(1-2):340–344. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90533-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noma A. ATP-regulated K+ channels in cardiac muscle. Nature. 1983 Sep 8;305(5930):147–148. doi: 10.1038/305147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H., Dunne M. J. Regulation of K+ channels plays a crucial role in the control of insulin secretion. Pflugers Arch. 1989;414 (Suppl 1):S115–S120. doi: 10.1007/BF00582259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H., Findlay I. Electrophysiology of the pancreas. Physiol Rev. 1987 Jul;67(3):1054–1116. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.3.1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Politi D. M., Rogawski M. A. Glyburide-sensitive K+ channels in cultured rat hippocampal neurons: activation by cromakalim and energy-depleting conditions. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;40(2):308–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post J. M., Stevens R. J., Sanders K. M., Hume J. R. Effect of cromakalim and lemakalim on slow waves and membrane currents in colonic smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1991 Feb;260(2 Pt 1):C375–C382. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.260.2.C375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saller C. F., Chiodo L. A. Glucose suppresses basal firing and haloperidol-induced increases in the firing rate of central dopaminergic neurons. Science. 1980 Dec 12;210(4475):1269–1271. doi: 10.1126/science.6254155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid-Antomarchi H., De Weille J., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. The receptor for antidiabetic sulfonylureas controls the activity of the ATP-modulated K+ channel in insulin-secreting cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):15840–15844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sofue M., Yoshimura Y., Nishida M., Kawada J. Uptake of nicotinamide by rat pancreatic beta cells with regard to streptozotocin action. J Endocrinol. 1991 Oct;131(1):135–138. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1310135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spruce A. E., Standen N. B., Stanfield P. R. Voltage-dependent ATP-sensitive potassium channels of skeletal muscle membrane. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):736–738. doi: 10.1038/316736a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B., Quayle J. M., Davies N. W., Brayden J. E., Huang Y., Nelson M. T. Hyperpolarizing vasodilators activate ATP-sensitive K+ channels in arterial smooth muscle. Science. 1989 Jul 14;245(4914):177–180. doi: 10.1126/science.2501869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay E., Zini S., Ben-Ari Y. Autoradiographic study of the cellular localization of [3H]glibenclamide binding sites in the rat hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Jun 10;127(1):21–24. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90884-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia Y., Haddad G. G. Major differences in CNS sulfonylurea receptor distribution between the rat (newborn, adult) and turtle. J Comp Neurol. 1991 Dec 8;314(2):278–289. doi: 10.1002/cne.903140206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zini S., Ben-Ari Y., Ashford M. L. Characterization of sulfonylurea receptors and the action of potassium channel openers on cholinergic neurotransmission in guinea pig isolated small intestine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Nov;259(2):566–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zini S., Tremblay E., Pollard H., Moreau J., Ben-Ari Y. Regional distribution of sulfonylurea receptors in the brain of rodent and primate. Neuroscience. 1993 Aug;55(4):1085–1091. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90322-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zini S., Tremblay E., Roisin M. P., Ben-Ari Y. Two binding sites for [3H]glibenclamide in the rat brain. Brain Res. 1991 Feb 22;542(1):151–154. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Kuil J. H., Korf J. On-line monitoring of extracellular brain glucose using microdialysis and a NADPH-linked enzymatic assay. J Neurochem. 1991 Aug;57(2):648–654. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb03796.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



