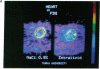
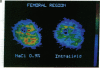
Abstract
Positron emission tomography permits noninvasive measurement of regional glucose uptake in vivo in humans. We employed this technique to determine the effect of FFA on glucose uptake in leg, arm, and heart muscles. Six normal men were studied twice under euglycemic hyperinsulinemic (serum insulin approximately 500 pmol/liter) conditions, once during elevation of serum FFA by infusions of heparin and Intralipid (serum FFA 2.0 +/- 0.4 mmol/liter), and once during infusion of saline (serum FFA 0.1 +/- 0.01 mmol/liter). Regional glucose uptake rates were measured using positron emission tomography-derived 18F-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose kinetics and the three-compartment model described by Sokoloff (Sokoloff, L., M. Reivich, C. Kennedy, M. C. Des Rosiers, C. S. Patlak, K. D. Pettigrew, O. Sakurada, and M. Shinohara. 1977. J. Neurochem. 28: 897-916). Elevation of plasma FFA decreased whole body glucose uptake by 31 +/- 2% (1,960 +/- 130 vs. 2,860 +/- 250 mumol/min, P less than 0.01, FFA vs. saline study). This decrease was due to inhibition of glucose uptake in the heart by 30 +/- 8% (150 +/- 33 vs. 200 +/- 28 mumol/min, P less than 0.02), and in skeletal muscles; both when measured in femoral (1,594 +/- 261 vs. 2,272 +/- 328 mumol/min, 25 +/- 13%) and arm muscles (1,617 +/- 411 to 2,305 +/- 517 mumol/min, P less than 0.02, 31 +/- 6%). Whole body glucose uptake correlated with glucose uptake in femoral (r = 0.75, P less than 0.005), and arm muscles (r = 0.69, P less than 0.05) but not with glucose uptake in the heart (r = 0.04, NS). These data demonstrate that the glucose-FFA cycle operates in vivo in both heart and skeletal muscles in humans.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beatty C. H., Bocek R. M. Interrelation of carbohydrate and palmitate metabolism in skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1971 Jun;220(6):1928–1934. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.6.1928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua S., Buzzigoli G., Bonadonna R., Brandi L. S., Oleggini M., Boni C., Geloni M., Ferrannini E. Operation of Randle's cycle in patients with NIDDM. Diabetes. 1990 Mar;39(3):383–389. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.3.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonadonna R. C., Zych K., Boni C., Ferrannini E., DeFronzo R. A. Time dependence of the interaction between lipid and glucose in humans. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jul;257(1 Pt 1):E49–E56. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1989.257.1.E49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnol A. F., Ferre P., Leturque A., Girard J. Effect of insulin on in vivo glucose utilization in individual tissues of anesthetized lactating rats. Am J Physiol. 1987 Feb;252(2 Pt 1):E183–E188. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.252.2.E183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler P. C., Home P. D. The measurement of metabolite exchange across muscle beds. Baillieres Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Nov;1(4):863–878. doi: 10.1016/s0950-351x(87)80009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassens R. G., Bocek R. M., Beatty C. H. Effect of octanoate on carbohydrate metabolism in red and white muscle of the rhesus monkey. Am J Physiol. 1969 Sep;217(3):715–719. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.3.715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruickshank E. W. On the production and utilisation of glycogen in normal and diabetic animals. J Physiol. 1913 Oct 17;47(1-2):1–14. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1913.sp001608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Jacot E., Jequier E., Maeder E., Wahren J., Felber J. P. The effect of insulin on the disposal of intravenous glucose. Results from indirect calorimetry and hepatic and femoral venous catheterization. Diabetes. 1981 Dec;30(12):1000–1007. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.12.1000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux R. B., Reichek N. Echocardiographic determination of left ventricular mass in man. Anatomic validation of the method. Circulation. 1977 Apr;55(4):613–618. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.55.4.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhawan V., Moeller J. R., Strother S. C., Evans A. C., Rottenberg D. A. Effect of selecting a fixed dephosphorylation rate on the estimation of rate constants and rCMRGlu from dynamic [18F] fluorodeoxyglucose/PET data. J Nucl Med. 1989 Sep;30(9):1483–1488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falholt K., Jensen I., Lindkaer Jensen S., Mortensen H., Vølund A., Heding L. G., Noerskov Petersen P., Falholt W. Carbohydrate and lipid metabolism of skeletal muscle in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabet Med. 1988 Jan;5(1):27–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1988.tb00936.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrannini E., Barrett E. J., Bevilacqua S., DeFronzo R. A. Effect of fatty acids on glucose production and utilization in man. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1737–1747. doi: 10.1172/JCI111133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferré P., Leturque A., Burnol A. F., Penicaud L., Girard J. A method to quantify glucose utilization in vivo in skeletal muscle and white adipose tissue of the anaesthetized rat. Biochem J. 1985 May 15;228(1):103–110. doi: 10.1042/bj2280103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gambhir S. S., Schwaiger M., Huang S. C., Krivokapich J., Schelbert H. R., Nienaber C. A., Phelps M. E. Simple noninvasive quantification method for measuring myocardial glucose utilization in humans employing positron emission tomography and fluorine-18 deoxyglucose. J Nucl Med. 1989 Mar;30(3):359–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland P. B., Randle P. J. Regulation of glucose uptake by muscles. 10. Effects of alloxan-diabetes, starvation, hypophysectomy and adrenalectomy, and of fatty acids, ketone bodies and pyruvate, on the glycerol output and concentrations of free fatty acids, long-chain fatty acyl-coenzyme A, glycerol phosphate and citrate-cycle intermediates in rat heart and diaphragm muscles. Biochem J. 1964 Dec;93(3):678–687. doi: 10.1042/bj0930678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman M. N., Berger M., Ruderman N. B. Glucose metabolism in rat skeletal muscle at rest. Effect of starvation, diabetes, ketone bodies and free fatty acids. Diabetes. 1974 Nov;23(11):881–888. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.11.881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groop L. C., Bonadonna R. C., DelPrato S., Ratheiser K., Zyck K., Ferrannini E., DeFronzo R. A. Glucose and free fatty acid metabolism in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Evidence for multiple sites of insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):205–213. doi: 10.1172/JCI114142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamacher K., Coenen H. H., Stöcklin G. Efficient stereospecific synthesis of no-carrier-added 2-[18F]-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose using aminopolyether supported nucleophilic substitution. J Nucl Med. 1986 Feb;27(2):235–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S. C., Phelps M. E., Hoffman E. J., Sideris K., Selin C. J., Kuhl D. E. Noninvasive determination of local cerebral metabolic rate of glucose in man. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jan;238(1):E69–E82. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.238.1.E69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins A. B., Storlien L. H., Chisholm D. J., Kraegen E. W. Effects of nonesterified fatty acid availability on tissue-specific glucose utilization in rats in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jul;82(1):293–299. doi: 10.1172/JCI113586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krivokapich J., Huang S. C., Selin C. E., Phelps M. E. Fluorodeoxyglucose rate constants, lumped constant, and glucose metabolic rate in rabbit heart. Am J Physiol. 1987 Apr;252(4 Pt 2):H777–H787. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1987.252.4.H777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuzuya H., Blix P. M., Horwitz D. L., Steiner D. F., Rubenstein A. H. Determination of free and total insulin and C-peptide in insulin-treated diabetics. Diabetes. 1977 Jan;26(1):22–29. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.1.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. U., Lee H. K., Koh C. S., Min H. K. Artificial induction of intravascular lipolysis by lipid-heparin infusion leads to insulin resistance in man. Diabetologia. 1988 May;31(5):285–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00277409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles J., Glasscock R., Aikens J., Gerich J., Haymond M. A microfluorometric method for the determination of free fatty acids in plasma. J Lipid Res. 1983 Jan;24(1):96–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mossberg K. A., Rowe R. W., Tewson T. J., Taegtmeyer H. Rabbit hindlimb glucose uptake assessed with positron-emitting fluorodeoxyglucose. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Oct;67(4):1569–1577. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.67.4.1569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott D. M., Lillioja S., Bogardus C. Overnutrition induced decrease in insulin action for glucose storage: in vivo and in vitro in man. Metabolism. 1986 Feb;35(2):160–165. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(86)90118-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy M. L., Thenabadu P. N., de Soyza N., Doherty J. E., Meade J., Baker B. J., Whittle J. L. Reevaluation of electrocardiographic criteria for left, right and combined cardiac ventricular hypertrophy. Am J Cardiol. 1984 Apr 1;53(8):1140–1147. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(84)90651-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mészáros K., Bagby G. J., Lang C. H., Spitzer J. J. Increased uptake and phosphorylation of 2-deoxyglucose by skeletal muscles in endotoxin-treated rats. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jul;253(1 Pt 1):E33–E39. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.253.1.E33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak C. S., Blasberg R. G. Graphical evaluation of blood-to-brain transfer constants from multiple-time uptake data. Generalizations. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1985 Dec;5(4):584–590. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1985.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps M. E., Huang S. C., Hoffman E. J., Selin C., Sokoloff L., Kuhl D. E. Tomographic measurement of local cerebral glucose metabolic rate in humans with (F-18)2-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose: validation of method. Ann Neurol. 1979 Nov;6(5):371–388. doi: 10.1002/ana.410060502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANDLE P. J., GARLAND P. B., HALES C. N., NEWSHOLME E. A. The glucose fatty-acid cycle. Its role in insulin sensitivity and the metabolic disturbances of diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1963 Apr 13;1(7285):785–789. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)91500-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSSELL J. A., BLOOM W. Hormonal control of glycogen in the heart and other tissues in rats. Endocrinology. 1956 Jan;58(1):83–94. doi: 10.1210/endo-58-1-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randle P. J., Newsholme E. A., Garland P. B. Regulation of glucose uptake by muscle. 8. Effects of fatty acids, ketone bodies and pyruvate, and of alloxan-diabetes and starvation, on the uptake and metabolic fate of glucose in rat heart and diaphragm muscles. Biochem J. 1964 Dec;93(3):652–665. doi: 10.1042/bj0930652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratib O., Phelps M. E., Huang S. C., Henze E., Selin C. E., Schelbert H. R. Positron tomography with deoxyglucose for estimating local myocardial glucose metabolism. J Nucl Med. 1982 Jul;23(7):577–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M., Hollenbeck C., Jeng C. Y., Wu M. S., Chen Y. D. Measurement of plasma glucose, free fatty acid, lactate, and insulin for 24 h in patients with NIDDM. Diabetes. 1988 Aug;37(8):1020–1024. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.8.1020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennie M. J., Holloszy J. O. Inhibition of glucose uptake and glycogenolysis by availability of oleate in well-oxygenated perfused skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1977 Nov 15;168(2):161–170. doi: 10.1042/bj1680161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schelbert H. R., Henze E., Schon H. R., Keen R., Hansen H., Selin C., Huang S. C., Barrio J. R., Phelps M. E. C-11 palmitate for the noninvasive evaluation of regional myocardial fatty acid metabolism with positron computed tomography. III. In vivo demonstration of the effects of substrate availability on myocardial metabolism. Am Heart J. 1983 Mar;105(3):492–504. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(83)90368-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonfeld G., Kipnis D. M. Effects of fatty acids on carbohydrate and fatty acid metabolism of rat diaphragm. Am J Physiol. 1968 Aug;215(2):513–522. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.2.513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman G. I., Rothman D. L., Jue T., Stein P., DeFronzo R. A., Shulman R. G. Quantitation of muscle glycogen synthesis in normal subjects and subjects with non-insulin-dependent diabetes by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jan 25;322(4):223–228. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199001253220403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokoloff L., Reivich M., Kennedy C., Des Rosiers M. H., Patlak C. S., Pettigrew K. D., Sakurada O., Shinohara M. The [14C]deoxyglucose method for the measurement of local cerebral glucose utilization: theory, procedure, and normal values in the conscious and anesthetized albino rat. J Neurochem. 1977 May;28(5):897–916. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb10649.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiébaud D., DeFronzo R. A., Jacot E., Golay A., Acheson K., Maeder E., Jéquier E., Felber J. P. Effect of long chain triglyceride infusion on glucose metabolism in man. Metabolism. 1982 Nov;31(11):1128–1136. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(82)90163-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisneski J. A., Gertz E. W., Neese R. A., Gruenke L. D., Morris D. L., Craig J. C. Metabolic fate of extracted glucose in normal human myocardium. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):1819–1827. doi: 10.1172/JCI112174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yki-Järvinen H., Bogardus C., Foley J. E. Regulation of plasma lactate concentration in resting human subjects. Metabolism. 1990 Aug;39(8):859–864. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(90)90133-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yki-Järvinen H., Puhakainen I., Koivisto V. A. Effect of free fatty acids on glucose uptake and nonoxidative glycolysis across human forearm tissues in the basal state and during insulin stimulation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 Jun;72(6):1268–1277. doi: 10.1210/jcem-72-6-1268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yki-Järvinen H., Puhakainen I., Saloranta C., Groop L., Taskinen M. R. Demonstration of a novel feedback mechanism between FFA oxidation from intracellular and intravascular sources. Am J Physiol. 1991 May;260(5 Pt 1):E680–E689. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1991.260.5.E680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yki-Järvinen H., Sahlin K., Ren J. M., Koivisto V. A. Localization of rate-limiting defect for glucose disposal in skeletal muscle of insulin-resistant type I diabetic patients. Diabetes. 1990 Feb;39(2):157–167. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.2.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yki-Järvinen H., Young A. A., Lamkin C., Foley J. E. Kinetics of glucose disposal in whole body and across the forearm in man. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jun;79(6):1713–1719. doi: 10.1172/JCI113011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]