Abstract
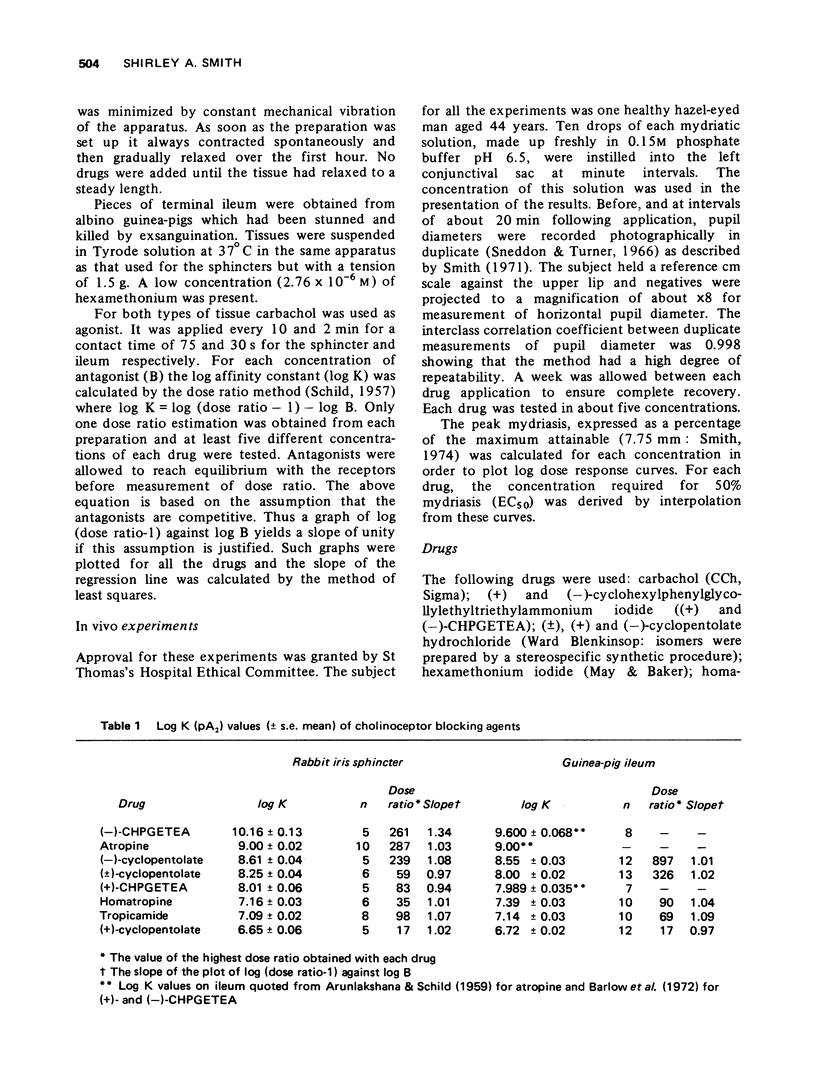
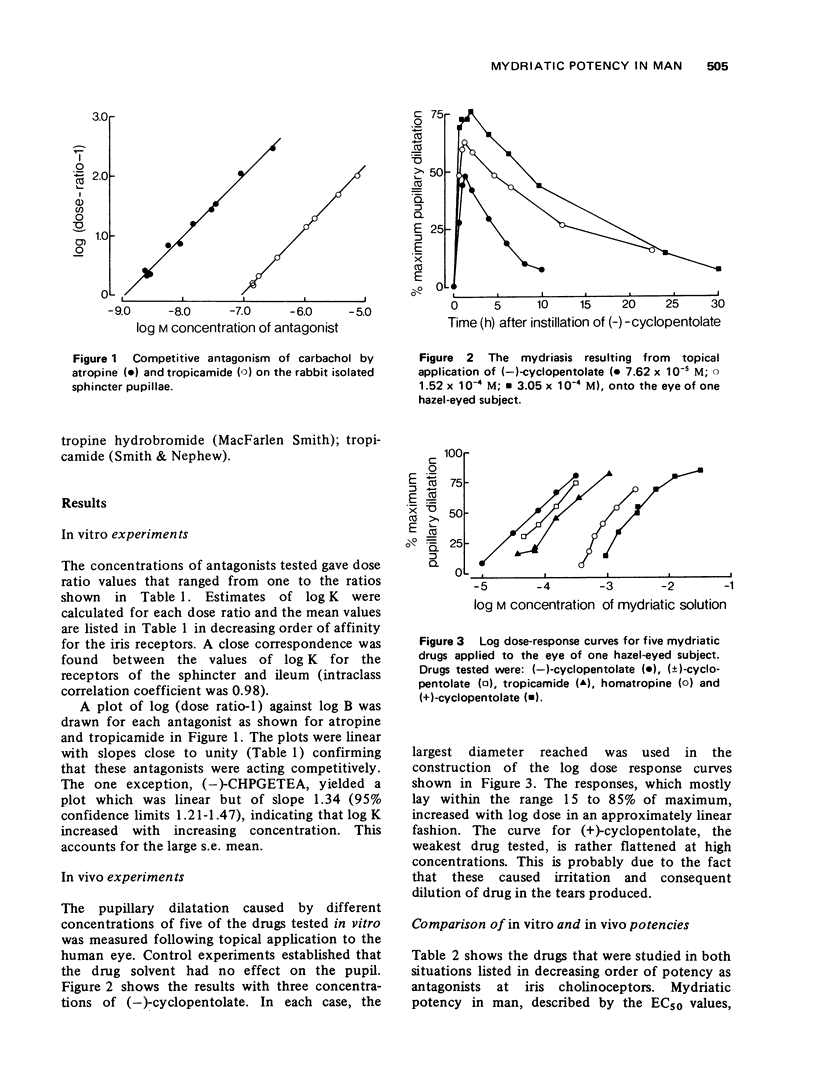
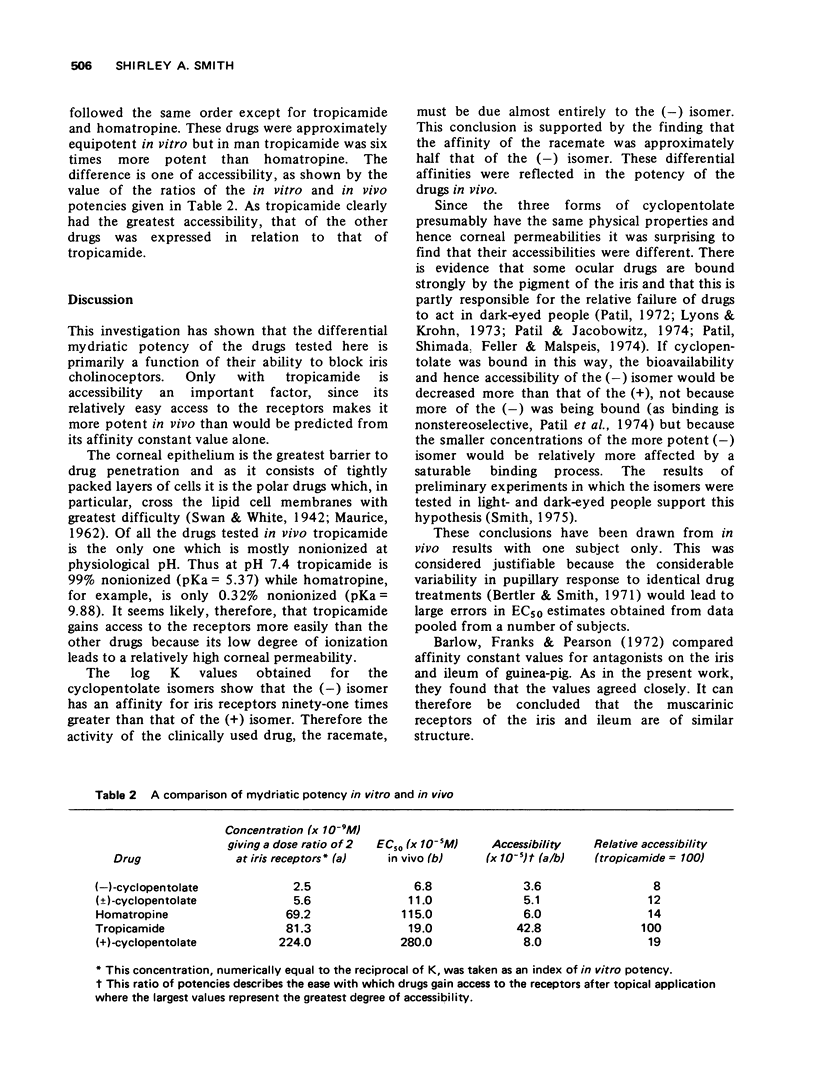
1 The mydriasis resulting from topical application of five atropine-like drugs was measured photographically in man. Drug potency was obtained from log dose-response curves. 2 The in vitro potency of eight cholinoceptor blocking drugs, including those studied in man, was obtained by measuring their affinity constants for binding to the receptors of an isolated preparation of the rabbit sphincter pupillae. Values agreed closely with those obtained for the muscarinic receptors of guinea-pig ileum. 3 In vitro and in vivo potency was compared to obtain a quantitative measure of the relative ease with which drugs gain access to the receptors after topical application. 4 The large differences that occur in the intensity and duration of the mydriatic response to atropine-like drugs is primarily the result of differences in their ability to blcok the receptors. Only with tropicamide does its relatively high accessibility affect its potency in man.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow R. B., Franks F. M., Pearson J. D. A comparison of the affinities of antagonists for acetylcholine receptors in the ileum, bronchial muscle and iris of the guinea-pig. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Oct;46(2):300–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb06875.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertler A., Smith S. E. Genetic influences in drug responses of the eye and the heart. Clin Sci. 1971 May;40(5):403–410. doi: 10.1042/cs0400403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Thiéry J., Tung Y., Kittel C. On the cooperativity of biological membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):335–341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gambill H. D., Ogle K. N., Kearns T. P. Mydriatic effect of four drugs determined with pupillograph. Arch Ophthalmol. 1967 Jun;77(6):740–746. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1967.00980020742005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons J. S., Krohn D. L. Pilocarpine uptake by pigmented uveal tissue. Am J Ophthalmol. 1973 May;75(5):885–888. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(73)90898-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattila M. J., Takki S., Idänpän-Heikkilä J. E. Actions of some autonomic drugs on the human eye. Experiments on medical students. Ann Med Exp Biol Fenn. 1967;45(4):412–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patil P. M., Jacobowitz D. Unequal accumulation of adrenergic drugs by pigmented and nonpigmented iris. Am J Ophthalmol. 1974 Sep;78(3):470–477. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(74)90233-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patil P. N. Cocaine-binding by the pigmented and the nonpigmented iris and its relevance to the mydriatic effect. Invest Ophthalmol. 1972 Sep;11(9):739–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patil P. N., Shimada K., Feller D. R., Malspeis L. Accumulation of (-)-14C-ephedrine by the pigmented and the nonpigmented iris. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1974 Feb;188(2):342–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHILD H. O. Drug antagonism and pAx. Pharmacol Rev. 1957 Jun;9(2):242–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. E. Mydriatic drugs for routine fundal inspection. A reappraisal. Lancet. 1971 Oct 16;2(7729):837–839. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90218-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon J. M., Turner P. Adrenergic blockade and the eye signs of thyrotoxicosis. Lancet. 1966 Sep 3;2(7462):525–527. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)92881-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


