Abstract
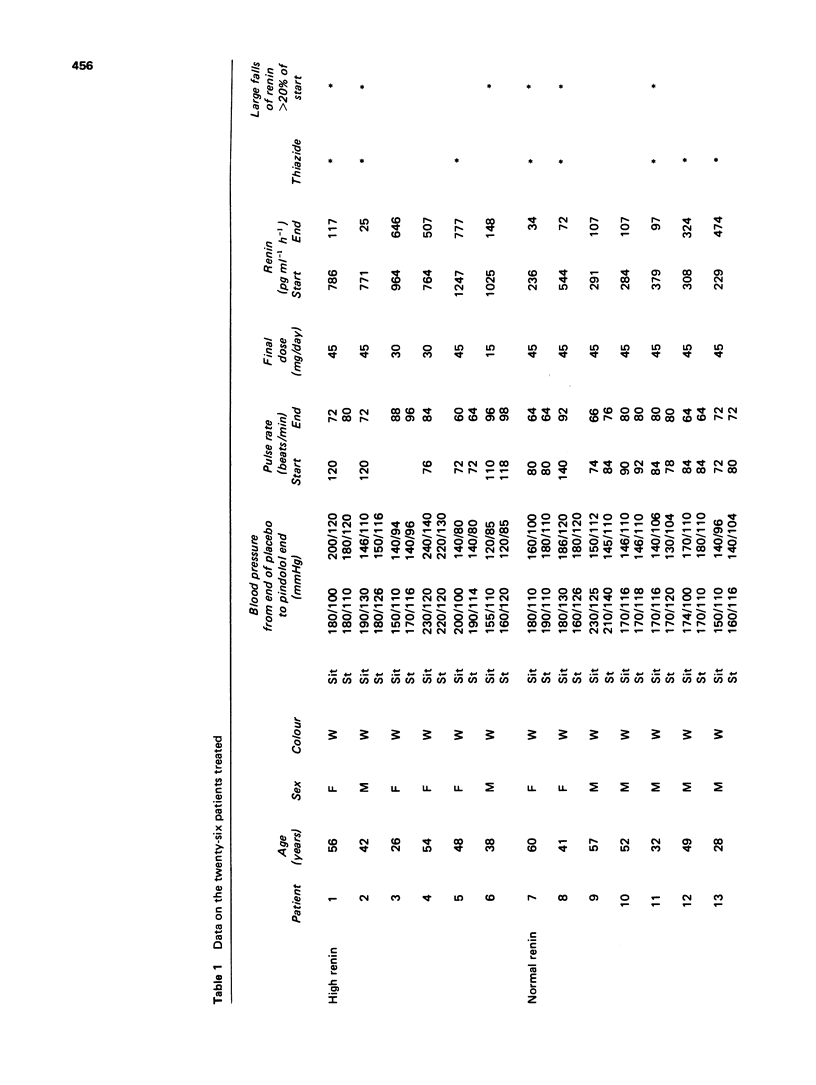
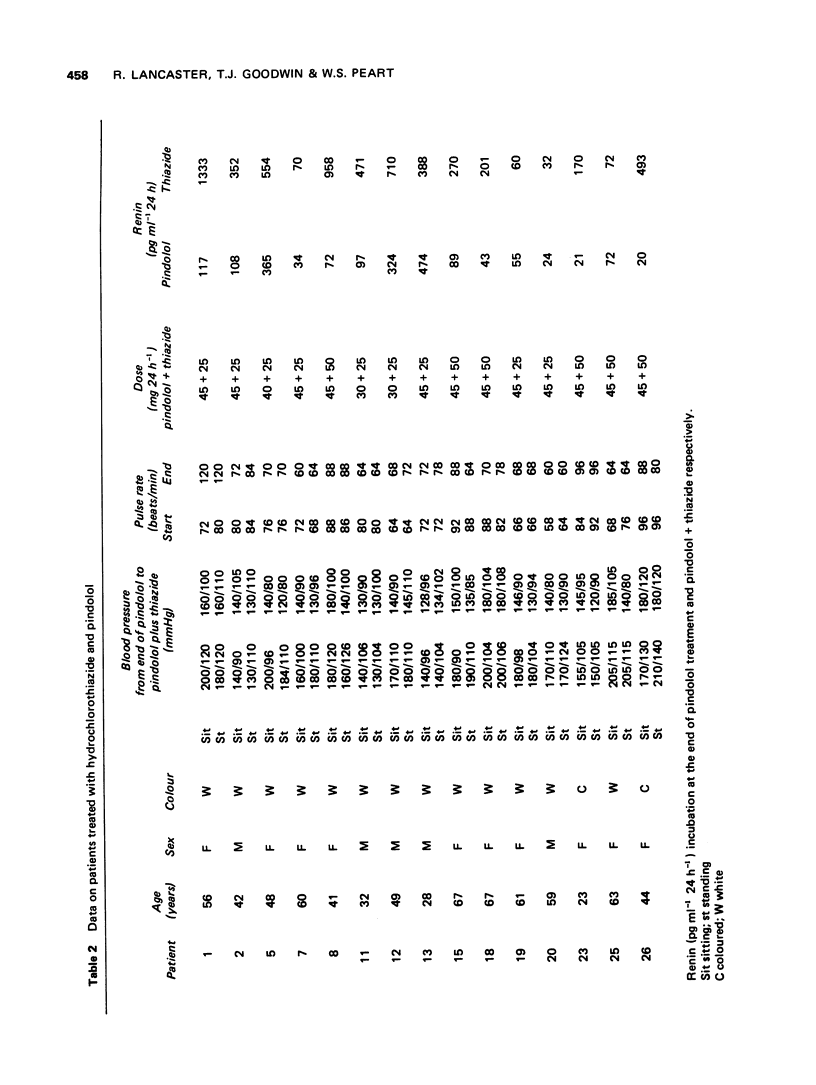
1 The effect of pindolol administered to twenty-six patients with hypertension of unknown origin was compared with respect to blood pressure and plasma renin activity change after increase of the dose over a period of 6 weeks. 2 There was no clear correlation between the fall of plasma renin activity, which in some patients was very marked, and the fall in blood pressure. Some patients with a fall in plasma renin activity did not drop their pressure. Conversely, some with a fall of pressure did not drop their plasma renin activity. 3 The addition of hydrochlorothiazide to the pindolol finally caused further lowering of the blood pressure in all but one patient and the plasma renin activity rose in all but two patinets. There was no clear correlation between change in plasma renin activity and the effect on blood pressure.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amery A., Billiet L., Fagard R. Letter: Beta receptors and renin release. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jan 31;290(5):284–284. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197401312900516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd G. W., Fitz A. E., Adamson A. R., Peart W. S. Radioimmunoassay determination of plasma-renin activity. Lancet. 1969 Feb 1;1(7588):213–218. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo E. L., Tarazi R. C., Dustan H. P. Beta-adrenergic blockade in diuretic-treated patients with essential hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jan 9;292(2):66–70. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197501092920203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bühler F. R., Laragh J. H., Baer L., Vaughan E. D., Jr, Brunner H. R. Propranolol inhibition of renin secretion. A specific approach to diagnosis and treatment of renin-dependent hypertensive diseases. N Engl J Med. 1972 Dec 14;287(24):1209–1214. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197212142872401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bühler F. R., Laragh J. H., Vaughan E. D., Jr, Brunner H. R., Gavras H., Baer L. Antihypertensive action of propranolol. Specific antirenin responses in high and normal renin forms of essential, renal, renovascular and malignant hypertension. Am J Cardiol. 1973 Sep 20;32(4):511–522. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(73)80043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day M. D., Roach A. G. -Adrenergic receptors in the central nervous system of the cat concerned with control of arterial blood pressure and heart rate. Nat New Biol. 1973 Mar 7;242(114):30–31. doi: 10.1038/newbio242030a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollery C. T., Lewis P. H., Myers M. G., Reid J. L. Central hypotensive effect of propranolol in the rabbit. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Jun;48(2):343P–343P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohlich E. D., Tarazi R. C., Dustan H. P., Page I. H. The paradox of beta-adrenergic blockade in hypertension. Circulation. 1968 Mar;37(3):417–423. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.37.3.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson L., Zweifler A. J. The effct of propranolol on plasma renin activity and blood pressure in mild essential hypertension. Acta Med Scand. 1974 May;195(5):397–401. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1974.tb08159.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns E. J., Singer B. Specificity of blockade of renal renin release by propranolol in the cat. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1974 Oct;47(4):331–343. doi: 10.1042/cs0470331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius S., Pascual A. V., Abbrecht P. H., London R. Effect of beta-adrenergic blockade on plasma volume in human subjects. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Jul;140(3):982–985. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelakis A. M., McAllister R. G. The effect of chronic adrenergic receptor blockade on plasma renin activity in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Feb;34(2):386–394. doi: 10.1210/jcem-34-2-386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes G. S., Weber M. A., Thornell I. R. Beta-blockers and plasma renin activity in hypertension. Br Med J. 1974 Jan 12;1(5897):60–62. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5897.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarazi R. C., Dustan H. P. Beta adrenergic blockade in hypertension. Practical and theoretical implications of long-term hemodynamic variations. Am J Cardiol. 1972 May;29(5):633–640. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(72)90164-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandongen R., Peart W. S., Boyd G. W. Andrenergic stimulation of renin secretion in the isolated perfused rat kidney. Circ Res. 1973 Feb;32(2):290–296. doi: 10.1161/01.res.32.2.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber M. A., Thornell I. R., Stokes G. S. Effects of beta adrenergic blocking agents on plasma renin activity in the conscious rabbit. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1974 Jan;188(1):234–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winer N., Chokshi D. S., Walkenhorst W. G. Effects of cyclic AMP, sympathomimetic amines, and adrenergic receptor antagonists on renin secretion. Circ Res. 1971 Sep;29(3):239–248. doi: 10.1161/01.res.29.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


