Abstract
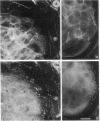
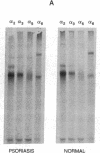
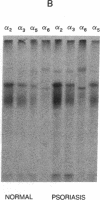
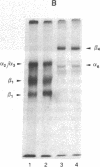
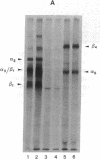
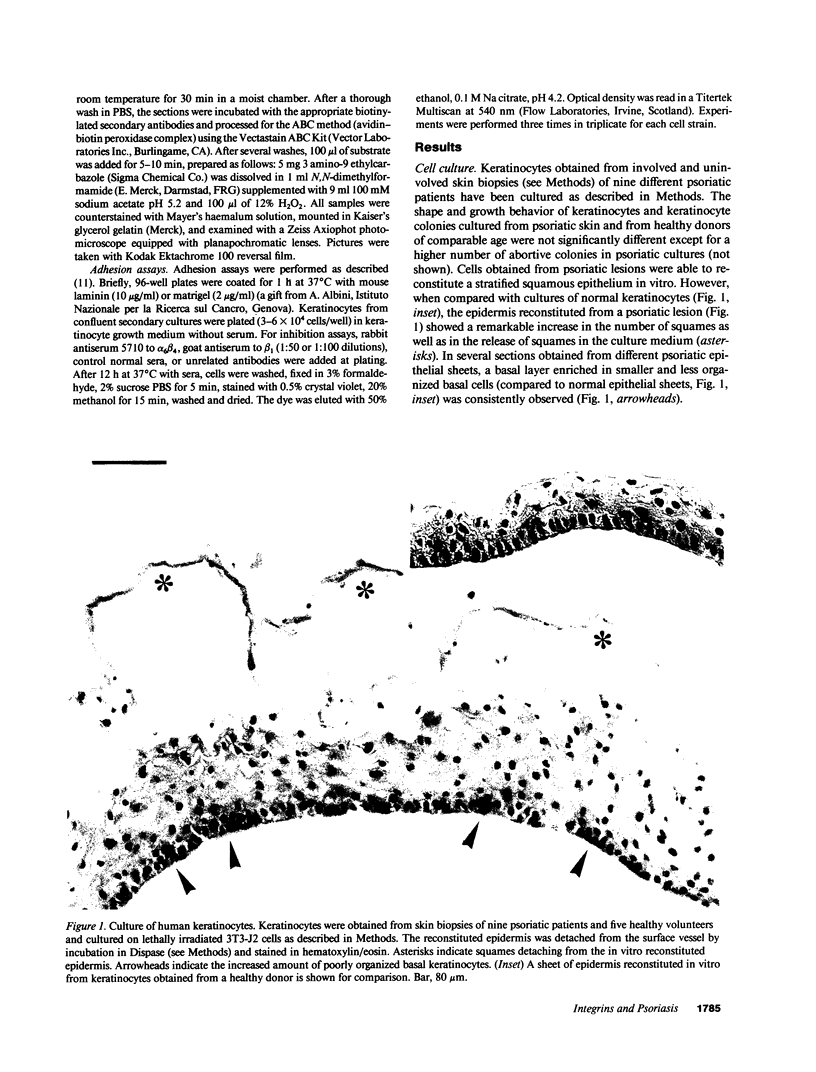
Psoriasis is a hyperproliferative cutaneous disease of unknown etiology and etiopathogenesis. Alteration of keratinocyte adhesiveness to basal lamina has been proposed as the initial disturbance leading to poorly controlled proliferation. Keratinocyte adhesion to basal lamina and lateral interactions among basal epidermal cells are mediated, besides other molecules, by integrin receptors that are segregated to discrete membrane domains. In this paper, the expression and function of integrins in psoriatic keratinocytes were examined, both in vivo and in vitro. We found that: (a) in psoriatic keratinocytes the integrin heterodimers alpha 2 beta 1, alpha 3 beta 1, and alpha 6 beta 4 have lost their polarized distribution on the plasma membrane; (b) the role of these integrins in mediating keratinocyte adhesion in vitro is altered; (c) psoriatic keratinocytes form focal contacts containing both beta 1 and beta 4 integrins. In normal adult keratinocytes the alpha 5 beta 1 fibronectin receptor is poorly expressed and diffusely distributed on the basal keratinocyte plasma membrane and is not organized in defined adhesive structures. In contrast, psoriatic keratinocytes show a clear fibronectin receptor staining in vivo, and organize alpha 5 beta 1 in typical focal contacts in vitro without any obvious increase of its expression and synthesis. These multiple alterations of integrins are also present in uninvolved keratinocytes from psoriatic patients, suggesting a key role for altered integrin-mediated adhesion in the pathogenesis of this disease.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. C., Watt F. M. Changes in keratinocyte adhesion during terminal differentiation: reduction in fibronectin binding precedes alpha 5 beta 1 integrin loss from the cell surface. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):425–435. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90175-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albelda S. M., Buck C. A. Integrins and other cell adhesion molecules. FASEB J. 1990 Aug;4(11):2868–2880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard B. A., Robinson S. M., Vandaele S., Mansbridge J. N., Darmon M. Abnormal maturation pathway of keratinocytes in psoriatic skin. Br J Dermatol. 1985 Jun;112(6):647–653. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1985.tb02332.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck C. A., Horwitz A. F. Cell surface receptors for extracellular matrix molecules. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:179–205. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter W. G., Kaur P., Gil S. G., Gahr P. J., Wayner E. A. Distinct functions for integrins alpha 3 beta 1 in focal adhesions and alpha 6 beta 4/bullous pemphigoid antigen in a new stable anchoring contact (SAC) of keratinocytes: relation to hemidesmosomes. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):3141–3154. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.3141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter W. G., Wayner E. A., Bouchard T. S., Kaur P. The role of integrins alpha 2 beta 1 and alpha 3 beta 1 in cell-cell and cell-substrate adhesion of human epidermal cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):1387–1404. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.1387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A. Fibronectin matrix deposition and fibronectin receptor expression in healing and normal skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Jun;94(6 Suppl):128S–134S. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12876104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper K. D., Hammerberg C., Baadsgaard O., Elder J. T., Chan L. S., Sauder D. N., Voorhees J. J., Fisher G. IL-1 activity is reduced in psoriatic skin. Decreased IL-1 alpha and increased nonfunctional IL-1 beta. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4593–4603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Luca M., Albanese E., Bondanza S., Megna M., Ugozzoli L., Molina F., Cancedda R., Santi P. L., Bormioli M., Stella M. Multicentre experience in the treatment of burns with autologous and allogenic cultured epithelium, fresh or preserved in a frozen state. Burns. 1989 Oct;15(5):303–309. doi: 10.1016/0305-4179(89)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Luca M., D'Anna F., Bondanza S., Franzi A. T., Cancedda R. Human epithelial cells induce human melanocyte growth in vitro but only skin keratinocytes regulate its proper differentiation in the absence of dermis. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1919–1926. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Luca M., Tamura R. N., Kajiji S., Bondanza S., Rossino P., Cancedda R., Marchisio P. C., Quaranta V. Polarized integrin mediates human keratinocyte adhesion to basal lamina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6888–6892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dejana E., Colella S., Conforti G., Abbadini M., Gaboli M., Marchisio P. C. Fibronectin and vitronectin regulate the organization of their respective Arg-Gly-Asp adhesion receptors in cultured human endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):1215–1223. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Marco E., Marchisio P. C., Bondanza S., Franzi A. T., Cancedda R., De Luca M. Growth-regulated synthesis and secretion of biologically active nerve growth factor by human keratinocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21718–21722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du X. P., Plow E. F., Frelinger A. L., 3rd, O'Toole T. E., Loftus J. C., Ginsberg M. H. Ligands "activate" integrin alpha IIb beta 3 (platelet GPIIb-IIIa). Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):409–416. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90458-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. Cell adhesion molecules in the regulation of animal form and tissue pattern. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:81–116. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.000501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblom P., Vestweber D., Kemler R. Cell-matrix interactions and cell adhesion during development. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:27–47. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.000331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. T., Fisher G. J., Lindquist P. B., Bennett G. L., Pittelkow M. R., Coffey R. J., Jr, Ellingsworth L., Derynck R., Voorhees J. J. Overexpression of transforming growth factor alpha in psoriatic epidermis. Science. 1989 Feb 10;243(4892):811–814. doi: 10.1126/science.2916128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. T., Tavakkol A., Klein S. B., Zeigler M. E., Wicha M., Voorhees J. J. Protooncogene expression in normal and psoriatic skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Jan;94(1):19–25. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12873313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyrand O. Studies on fibronectin in the skin. II. Indirect immunofluorescence studies in psoriasis vulgaris. Arch Dermatol Res. 1979 Aug;266(1):33–41. doi: 10.1007/BF00412860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaidano G., Bergui L., Schena M., Gaboli M., Cremona O., Marchisio P. C., Caligaris-Cappio F. Integrin distribution and cytoskeleton organization in normal and malignant monocytes. Leukemia. 1990 Oct;4(10):682–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallico G. G., 3rd, O'Connor N. E., Compton C. C., Kehinde O., Green H. Permanent coverage of large burn wounds with autologous cultured human epithelium. N Engl J Med. 1984 Aug 16;311(7):448–451. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198408163110706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green H., Kehinde O., Thomas J. Growth of cultured human epidermal cells into multiple epithelia suitable for grafting. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5665–5668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo M., Kim L. T., Akiyama S. K., Gralnick H. R., Yamada K. M., Grinnell F. Altered processing of integrin receptors during keratinocyte activation. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Aug;195(2):315–322. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertle M. D., Adams J. C., Watt F. M. Integrin expression during human epidermal development in vivo and in vitro. Development. 1991 May;112(1):193–206. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.1.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: a family of cell surface receptors. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajiji S., Tamura R. N., Quaranta V. A novel integrin (alpha E beta 4) from human epithelial cells suggests a fourth family of integrin adhesion receptors. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):673–680. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03425.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane C. J., Knapp A. M., Mansbridge J. N., Hanawalt P. C. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 localization in normal and psoriatic epidermal keratinocytes in situ. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Jul;144(1):144–150. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041440119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King L. E., Jr, Gates R. E., Stoscheck C. M., Nanney L. B. The EGF/TGF alpha receptor in skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Jun;94(6 Suppl):164S–170S. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12876141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein C. E., Steinmayer T., Mattes J. M., Kaufmann R., Weber L. Integrins of normal human epidermis: differential expression, synthesis and molecular structure. Br J Dermatol. 1990 Aug;123(2):171–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1990.tb01844.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konter U., Kellner I., Klein E., Kaufmann R., Mielke V., Sterry W. Adhesion molecule mapping in normal human skin. Arch Dermatol Res. 1989;281(7):454–462. doi: 10.1007/BF00510080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. G., Krane J. F., Carter D. M., Gottlieb A. B. Role of growth factors, cytokines, and their receptors in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Jun;94(6 Suppl):135S–140S. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12876121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampugnani M. G., Resnati M., Dejana E., Marchisio P. C. The role of integrins in the maintenance of endothelial monolayer integrity. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(3):479–490. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.3.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larjava H., Peltonen J., Akiyama S. K., Yamada S. S., Gralnick H. R., Uitto J., Yamada K. M. Novel function for beta 1 integrins in keratinocyte cell-cell interactions. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):803–815. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luger T. A., Schwarz T. Evidence for an epidermal cytokine network. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Dec;95(6 Suppl):100S–104S. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12874944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchisio P. C., Bondanza S., Cremona O., Cancedda R., De Luca M. Polarized expression of integrin receptors (alpha 6 beta 4, alpha 2 beta 1, alpha 3 beta 1, and alpha v beta 5) and their relationship with the cytoskeleton and basement membrane matrix in cultured human keratinocytes. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(4):761–773. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.4.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchisio P. C., Cancedda R., De Luca M. Structural and functional studies of integrin receptors in cultured human keratinocytes. Cell Differ Dev. 1990 Dec 2;32(3):355–359. doi: 10.1016/0922-3371(90)90050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marguerie G. A., Plow E. F., Edgington T. S. Human platelets possess an inducible and saturable receptor specific for fibrinogen. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5357–5363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nazzaro V., Berti E., Cerri A., Brusasco A., Cavalli R., Caputo R. Expression of integrins in junctional and dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Jul;95(1):60–64. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12875994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orfanos C. E., Schaumburg-Lever G., Mahrle G., Lever W. F. Alterations of cell surfaces as a pathogenetic factor in psoriasis. Possible loss of contact inhibition of growth. Arch Dermatol. 1973 Jan;107(1):38–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltonen J., Larjava H., Jaakkola S., Gralnick H., Akiyama S. K., Yamada S. S., Yamada K. M., Uitto J. Localization of integrin receptors for fibronectin, collagen, and laminin in human skin. Variable expression in basal and squamous cell carcinomas. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):1916–1923. doi: 10.1172/JCI114379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkus H., Mehregan A. H. The primary histologic lesion of seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 1966 Jan;46(1):109–116. doi: 10.1038/jid.1966.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prens E. P., Benne K., van Damme J., Bakkus M., Brakel K., Benner R., van Joost T. Interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 in psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Dec;95(6 Suppl):121S–124S. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12874991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rheinwald J. G., Green H. Serial cultivation of strains of human epidermal keratinocytes: the formation of keratinizing colonies from single cells. Cell. 1975 Nov;6(3):331–343. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(75)80001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romagnoli G., De Luca M., Faranda F., Bandelloni R., Franzi A. T., Cataliotti F., Cancedda R. Treatment of posterior hypospadias by the autologous graft of cultured urethral epithelium. N Engl J Med. 1990 Aug 23;323(8):527–530. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199008233230806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman J., LaChance R. M., Broekelmann T. J., Kennedy C. J., Wayner E. A., Carter W. G., McDonald J. A. The fibronectin receptor is organized by extracellular matrix fibronectin: implications for oncogenic transformation and for cell recognition of fibronectin matrices. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2529–2543. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E. Integrins. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jan;87(1):1–5. doi: 10.1172/JCI114957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. New perspectives in cell adhesion: RGD and integrins. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):491–497. doi: 10.1126/science.2821619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryynänen J., Jaakkola S., Engvall E., Peltonen J., Uitto J. Expression of beta 4 integrins in human skin: comparison of epidermal distribution with beta 1-integrin epitopes, and modulation by calcium and vitamin D3 in cultured keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Sep;97(3):562–567. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12481896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. A., Lechene C., Ingber D. E. Insoluble fibronectin activates the Na/H antiporter by clustering and immobilizing integrin alpha 5 beta 1, independent of cell shape. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7849–7853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu Y., Van Seventer G. A., Horgan K. J., Shaw S. Regulated expression and binding of three VLA (beta 1) integrin receptors on T cells. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):250–253. doi: 10.1038/345250a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg A., Calafat J., Janssen H., Daams H., van der Raaij-Helmer L. M., Falcioni R., Kennel S. J., Aplin J. D., Baker J., Loizidou M. Integrin alpha 6/beta 4 complex is located in hemidesmosomes, suggesting a major role in epidermal cell-basement membrane adhesion. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(4):907–917. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.4.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stepp M. A., Spurr-Michaud S., Tisdale A., Elwell J., Gipson I. K. Alpha 6 beta 4 integrin heterodimer is a component of hemidesmosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8970–8974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura R. N., Rozzo C., Starr L., Chambers J., Reichardt L. F., Cooper H. M., Quaranta V. Epithelial integrin alpha 6 beta 4: complete primary structure of alpha 6 and variant forms of beta 4. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1593–1604. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turbitt M. L., Akhurst R. J., White S. I., MacKie R. M. Localization of elevated transforming growth factor-alpha in psoriatic epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Aug;95(2):229–232. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12478077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt F. M. Terminal differentiation of epidermal keratinocytes. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;1(6):1107–1115. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(89)80058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Luca M., Albanese E., Megna M., Cancedda R., Mangiante P. E., Cadoni A., Franzi A. T. Evidence that human oral epithelium reconstituted in vitro and transplanted onto patients with defects in the oral mucosa retains properties of the original donor site. Transplantation. 1990 Sep;50(3):454–459. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199009000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]