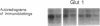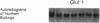Abstract
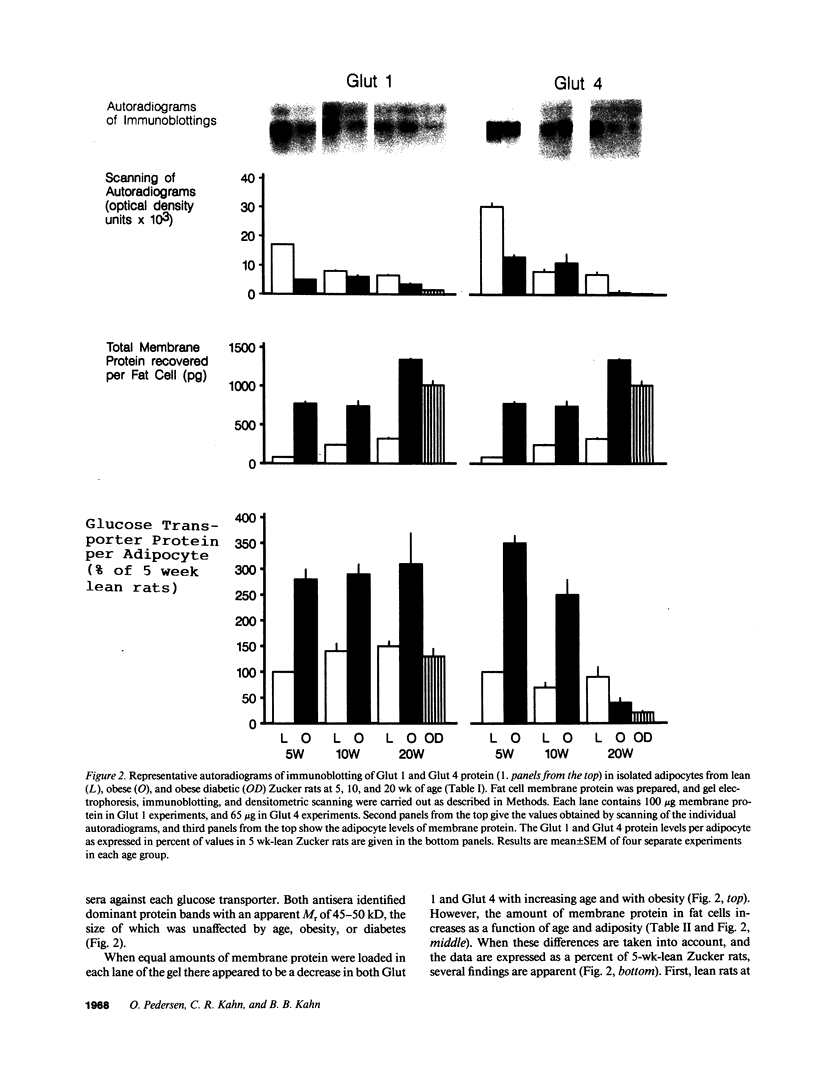
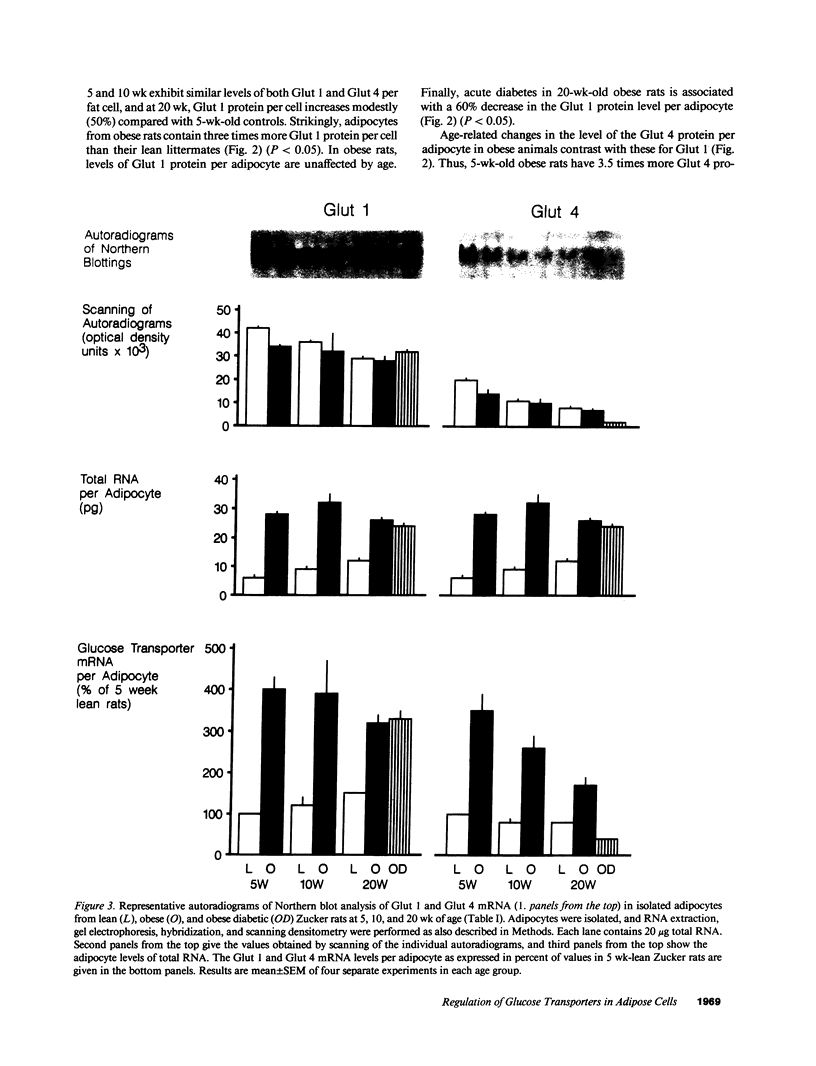
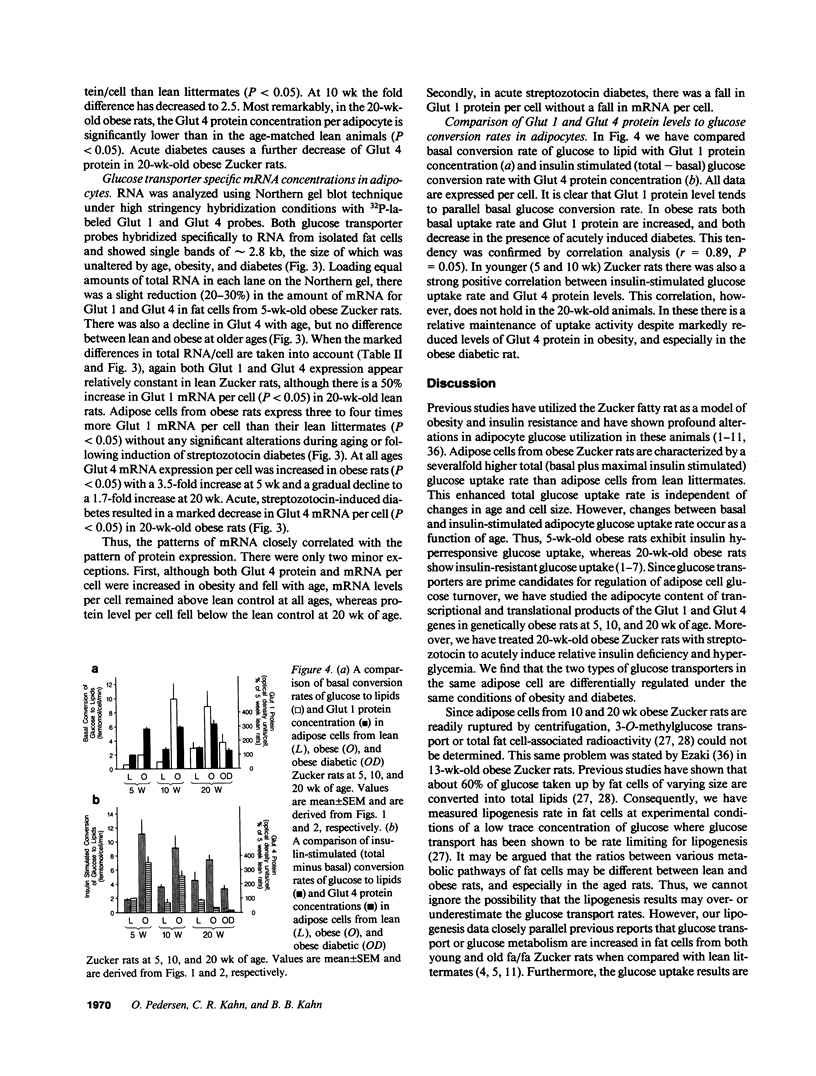
We have studied the relationship between glucose uptake rate and Glut 1 and Glut 4 protein and mRNA levels per fat cell in lean (FA/FA) and obese (fa/fa) Zucker rats at 5, 10, and 20 wk of age, and after induction of acute diabetes with streptozotocin. 5 wk obese rats exhibit insulin hyperresponsive glucose uptake, whereas 20 wk obese rats show insulin resistant glucose uptake. The relative abundance of Glut 1 and Glut 4 mRNA and protein per equal amount of total RNA and total membrane protein, respectively, is lower in adipocytes from obese rats. However, at all ages the enlargement of fat cells from obese rats is accompanied by a severalfold increase in total RNA and total membrane protein per cell. Thus, on a cellular basis, mRNA and protein levels of Glut 4 increases in young obese rats and gradually declines as a function of age. Basal glucose uptake is increased severalfold in fat cells from obese rats, and in parallel Glut 1 expression per cell in obese rats is two- to threefold increased over lean rats at all ages. Acute diabetes in 20 wk obese rats causes a profound downregulation of glucose uptake and a concomitant reduction of both Glut 1 and Glut 4 protein levels. Thus, changes in Glut 4 expression are a major cause of alteration in insulin-stimulated glucose uptake of adipocytes during evolution of obesity and diabetes in Zucker rats.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnbaum M. J., Haspel H. C., Rosen O. M. Cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding the rat brain glucose-transporter protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5784–5788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray G. A., York D. A. Genetically transmitted obesity in rodents. Physiol Rev. 1971 Jul;51(3):598–646. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1971.51.3.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman S. W., Zarnowski M. J., Franzusoff A. J., Salans L. B. Alterations in glucose metabolism and its stimulation by insulin in isolated adipose cells during the development of genetic obesity in the Zucker fatty rat. Metabolism. 1978 Dec;27(12 Suppl 2):1930–1940. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(78)80010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P., Richardson D. K., Becker S. G., Walters C. G., Gitomer W., Heinrich J. Insulin response in skeletal muscle and fat cells of the genetically obese Zucker rat. Metabolism. 1978 Dec;27(12 Suppl 2):1967–1981. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(78)80013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugail I., Quignard-Boulange A., Bazin R., Le Liepvre X., Lavau M. Adipose-tissue-specific increase in glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase activity and mRNA amounts in suckling pre-obese Zucker rats. Effect of weaning. Biochem J. 1988 Sep 1;254(2):483–487. doi: 10.1042/bj2540483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezaki O., Fukuda N., Itakura H. Role of two types of glucose transporters in enlarged adipocytes from aged obese rats. Diabetes. 1990 Dec;39(12):1543–1549. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.12.1543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezaki O. Mechanism for increased insulin-stimulated glucose metabolism in adipocytes from 13-week-old obese Zucker rats. Diabetologia. 1989 May;32(5):290–294. doi: 10.1007/BF00265544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flier J. S., Mueckler M., McCall A. L., Lodish H. F. Distribution of glucose transporter messenger RNA transcripts in tissues of rat and man. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):657–661. doi: 10.1172/JCI112864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumoto H., Seino S., Imura H., Seino Y., Eddy R. L., Fukushima Y., Byers M. G., Shows T. B., Bell G. I. Sequence, tissue distribution, and chromosomal localization of mRNA encoding a human glucose transporter-like protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5434–5438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvey W. T., Huecksteadt T. P., Birnbaum M. J. Pretranslational suppression of an insulin-responsive glucose transporter in rats with diabetes mellitus. Science. 1989 Jul 7;245(4913):60–63. doi: 10.1126/science.2662408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gliemann J., Rees W. D., Foley J. A. The fate of labelled glucose molecules in the rat adipocyte. Dependence on glucose concentration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 May 22;804(1):68–76. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(84)90100-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godbole V., York D. A. Lipogenesis in situ in the genetically obese Zucker fatty rat (fa/fa): role of hyperphagia and hyperinsulinaemia. Diabetologia. 1978 Mar;14(3):191–197. doi: 10.1007/BF00429780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerre-Millo M., Lavau M., Horne J. S., Wardzala L. J. Proposed mechanism for increased insulin-mediated glucose transport in adipose cells from young, obese Zucker rats. Large intracellular pool of glucose transporters. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2197–2201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hainault I., Guerre-Millo M., Guichard C., Lavau M. Differential regulation of adipose tissue glucose transporters in genetic obesity (fatty rat). Selective increase in the adipose cell/muscle glucose transporter (GLUT 4) expression. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):1127–1131. doi: 10.1172/JCI115077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjøllund E., Pedersen O. Transport and metabolism of D-glucose in human adipocytes. Studies of the dependence on medium glucose and insulin concentrations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jan 13;937(1):93–102. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90231-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Brown R., Navarro J., Pilch P. F. Insulin-regulatable tissues express a unique insulin-sensitive glucose transport protein. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):183–185. doi: 10.1038/333183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Strube M., Mueckler M. Molecular cloning and characterization of an insulin-regulatable glucose transporter. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):83–87. doi: 10.1038/338083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joost H. G., Steinfelder H. J. Modulation of insulin sensitivity by adenosine. Effects on glucose transport, lipid synthesis, and insulin receptors of the adipocyte. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Nov;22(3):614–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn B. B., Charron M. J., Lodish H. F., Cushman S. W., Flier J. S. Differential regulation of two glucose transporters in adipose cells from diabetic and insulin-treated diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1989 Aug;84(2):404–411. doi: 10.1172/JCI114180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn B. B., Cushman S. W., Flier J. S. Regulation of glucose transporter-specific mRNA levels in rat adipose cells with fasting and refeeding. Implications for in vivo control of glucose transporter number. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jan;83(1):199–204. doi: 10.1172/JCI113859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn B. B., Flier J. S. Regulation of glucose-transporter gene expression in vitro and in vivo. Diabetes Care. 1990 Jun;13(6):548–564. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.6.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. J. In vivo lipogenesis and enzyme levels in adipose and liver tissues from pair-fed genetically obese and lean rats. Life Sci. 1974 Apr 16;14(8):1447–1453. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90155-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueckler M., Caruso C., Baldwin S. A., Panico M., Blench I., Morris H. R., Allard W. J., Lienhard G. E., Lodish H. F. Sequence and structure of a human glucose transporter. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):941–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3839598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueckler M. Family of glucose-transporter genes. Implications for glucose homeostasis and diabetes. Diabetes. 1990 Jan;39(1):6–11. doi: 10.2337/diacare.39.1.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen O., Gliemann J. Hexose transport in human adipocytes: factors influencing the response to insulin and kinetics of methylglucose and glucose transport. Diabetologia. 1981 Jun;20(6):630–635. doi: 10.1007/BF00257432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen O., Hjøllund E., Beck-Nielsen H., Lindskov H. O., Sonne O., Gliemann J. Insulin receptor binding and receptor-mediated insulin degradation in human adipocytes. Diabetologia. 1981 Jun;20(6):636–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richelsen B., Hjøllund E., Pedersen O., Sørensen N. S. Effects of prostaglandin E2, indomethacin and adenosine deaminase on basal and insulin-stimulated glucose metabolism in human adipocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Mar 21;844(3):359–366. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(85)90138-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohner-Jeanrenaud F., Hochstrasser A. C., Jeanrenaud B. Hyperinsulinemia of preobese and obese fa/fa rats is partly vagus nerve mediated. Am J Physiol. 1983 Apr;244(4):E317–E322. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.244.4.E317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivitz W. I., DeSautel S. L., Kayano T., Bell G. I., Pessin J. E. Regulation of glucose transporter messenger RNA in insulin-deficient states. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):72–74. doi: 10.1038/340072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern J. S., Johnson P. R., Batchelor B. R., Zucker L. M., Hirsch J. Pancreatic insulin release and peripheral tissue resistance in Zucker obese rats fed high- and low-carbohydrate diets. Am J Physiol. 1975 Feb;228(2):543–548. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.2.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub R., Roy A., Dieter R., Koontz J. Insulin as a growth factor in rat hepatoma cells. Stimulation of proto-oncogene expression. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10893–10897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- York D. A., Steinke J., Bray G. A. Hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance in genetically obese rats. Metabolism. 1972 Apr;21(4):277–284. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(72)90070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorzano A., Wilkinson W., Kotliar N., Thoidis G., Wadzinkski B. E., Ruoho A. E., Pilch P. F. Insulin-regulated glucose uptake in rat adipocytes is mediated by two transporter isoforms present in at least two vesicle populations. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12358–12363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
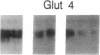
- Zucker L. M., Antoniades H. N. Insulin and obesity in the Zucker genetically obese rat "fatty". Endocrinology. 1972 May;90(5):1320–1330. doi: 10.1210/endo-90-5-1320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]