Abstract
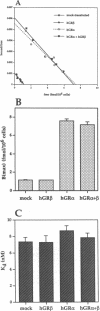
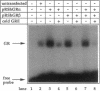
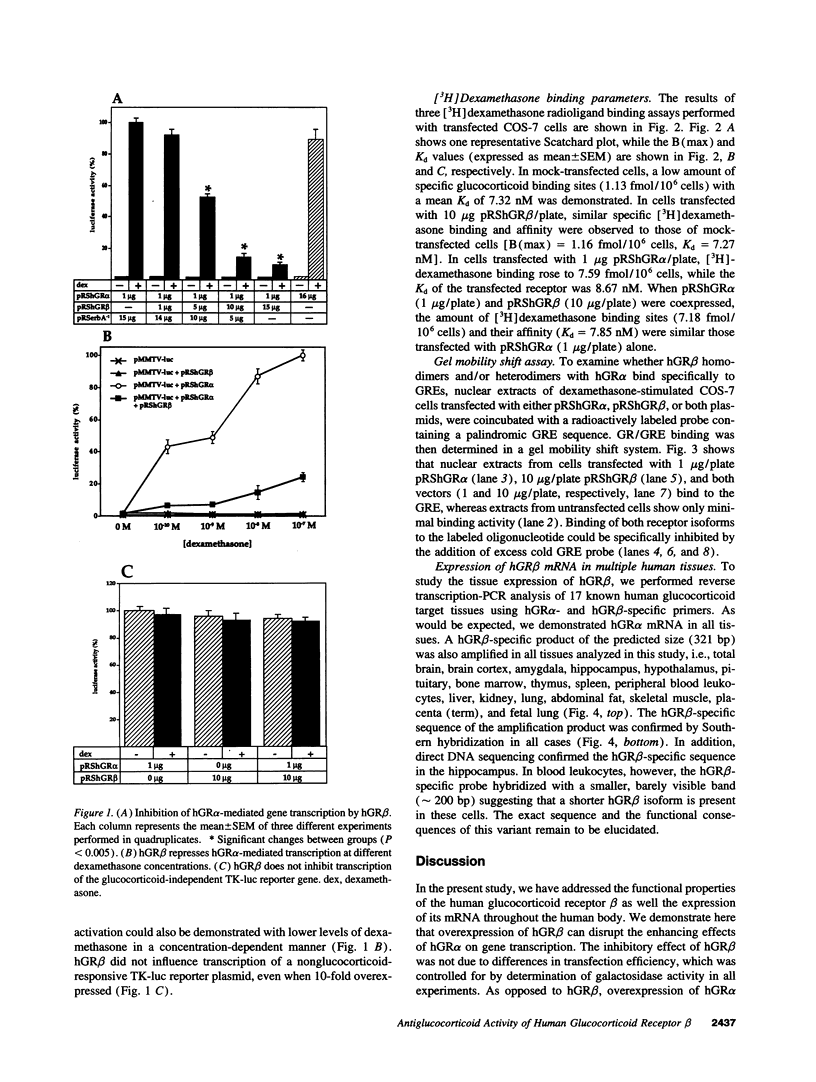
Alternative splicing of the human glucocorticoid receptor (hGR) pre-mRNA generates two highly homologous isoforms, termed hGR alpha and hGR beta. hGR alpha is a ligand-activated transcription factor which, in the hormone-bound state, modulates the expression of glucocorticoid-responsive genes by binding to specific glucocorticoid response element (GRE) DNA sequences. In contrast, hGR beta does not bind glucocorticoids and is transcriptionally inactive. We demonstrate here that hGR beta is able to inhibit the effects of hormone-activated hGR alpha on a glucocorticoid-responsive reporter gene in a concentration-dependent manner. [3H]-Dexamethasone binding studies indicate that hGR beta does not alter the affinity of hGR alpha for its hormonal ligand. The presence of hGR beta in nuclear extracts and its ability to bind to a radiolabeled GRE oligonucleotide suggest that its inhibitory effect may be due to competition for GRE target sites. Reverse transcription-PCR analysis shows expression of hGR beta mRNA in multiple human tissues. These results indicate that hGR beta may be a physiologically and pathophysiologically relevant endogenous inhibitor of glucocorticoid action, which may participate in defining the sensitivity of target tissues to glucocorticoids. They also underline the importance of distinguishing between the two receptor isoforms in all future studies of hGR function and the need to revisit old data.
Full text
PDF

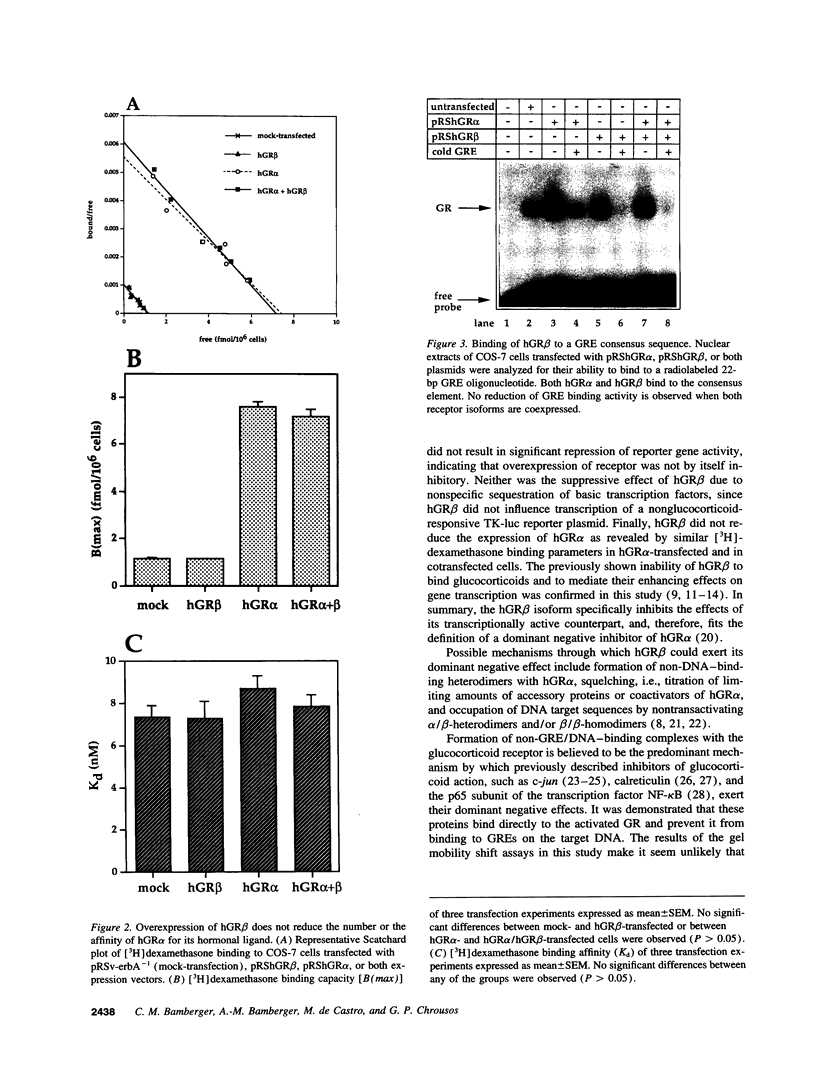
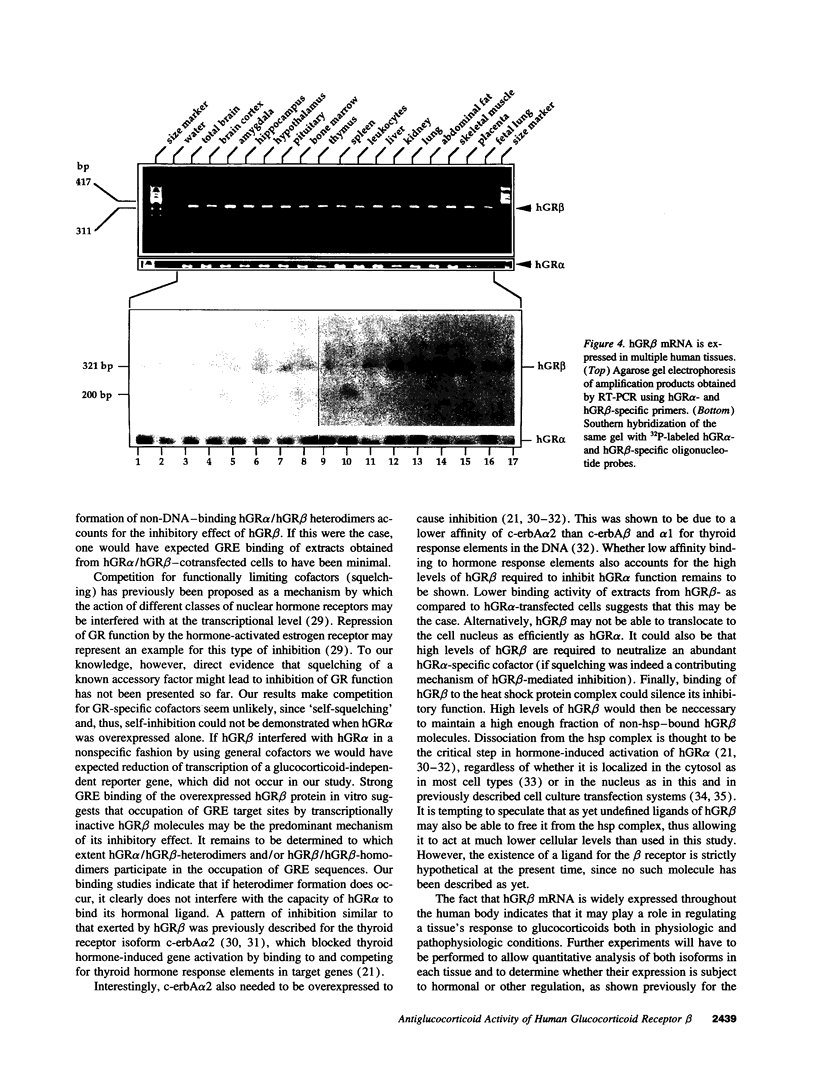


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brasier A. R., Tate J. E., Habener J. F. Optimized use of the firefly luciferase assay as a reporter gene in mammalian cell lines. Biotechniques. 1989 Nov-Dec;7(10):1116–1122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnick E. H., John S., Berard D. S., LeFebvre P., Hager G. L. Glucocorticoid receptor-dependent disruption of a specific nucleosome on the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter is prevented by sodium butyrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3977–3981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns K., Duggan B., Atkinson E. A., Famulski K. S., Nemer M., Bleackley R. C., Michalak M. Modulation of gene expression by calreticulin binding to the glucocorticoid receptor. Nature. 1994 Feb 3;367(6462):476–480. doi: 10.1038/367476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrousos G. P., Detera-Wadleigh S. D., Karl M. Syndromes of glucocorticoid resistance. Ann Intern Med. 1993 Dec 1;119(11):1113–1124. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-119-11-199312010-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czar M. J., Owens-Grillo J. K., Dittmar K. D., Hutchison K. A., Zacharek A. M., Leach K. L., Deibel M. R., Jr, Pratt W. B. Characterization of the protein-protein interactions determining the heat shock protein (hsp90.hsp70.hsp56) heterocomplex. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 15;269(15):11155–11161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedhar S., Rennie P. S., Shago M., Hagesteijn C. Y., Yang H., Filmus J., Hawley R. G., Bruchovsky N., Cheng H., Matusik R. J. Inhibition of nuclear hormone receptor activity by calreticulin. Nature. 1994 Feb 3;367(6462):480–483. doi: 10.1038/367480a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBattista J. A., Martel-Pelletier J., Antakly T., Tardif G., Cloutier J. M., Pelletier J. P. Reduced expression of glucocorticoid receptor levels in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Role in the suppression of metalloprotease synthesis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993 May;76(5):1128–1134. doi: 10.1210/jcem.76.5.8496302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Encío I. J., Detera-Wadleigh S. D. The genomic structure of the human glucocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):7182–7188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguère V., Hollenberg S. M., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Functional domains of the human glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):645–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I. Functional inactivation of genes by dominant negative mutations. Nature. 1987 Sep 17;329(6136):219–222. doi: 10.1038/329219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodin R. A., Lazar M. A., Chin W. W. Differential and tissue-specific regulation of the multiple rat c-erbA messenger RNA species by thyroid hormone. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jan;85(1):101–105. doi: 10.1172/JCI114398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg S. M., Weinberger C., Ong E. S., Cerelli G., Oro A., Lebo R., Thompson E. B., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Primary structure and expression of a functional human glucocorticoid receptor cDNA. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):635–641. doi: 10.1038/318635a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley D. M., Accili D., Stratakis C. A., Karl M., Vamvakopoulos N., Rorer E., Constantine K., Taylor S. I., Chrousos G. P. Point mutation causing a single amino acid substitution in the hormone binding domain of the glucocorticoid receptor in familial glucocorticoid resistance. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):680–686. doi: 10.1172/JCI115046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison K. A., Scherrer L. C., Czar M. J., Stancato L. F., Chow Y. H., Jove R., Pratt W. B. Regulation of glucocorticoid receptor function through assembly of a receptor-heat shock protein complex. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993 Jun 11;684:35–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb32269.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida S., Nakamura Y., Fujii H., Nishimura J., Tsugawa M., Gomi M., Fukata J., Tarui S., Moriwaki K., Kitani T. A patient with hypocortisolism and Cushing's syndrome-like manifestations: cortisol hyperreactive syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 Mar;70(3):729–737. doi: 10.1210/jcem-70-3-729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonat C., Rahmsdorf H. J., Park K. K., Cato A. C., Gebel S., Ponta H., Herrlich P. Antitumor promotion and antiinflammation: down-modulation of AP-1 (Fos/Jun) activity by glucocorticoid hormone. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1189–1204. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90395-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karl M., Lamberts S. W., Detera-Wadleigh S. D., Encio I. J., Stratakis C. A., Hurley D. M., Accili D., Chrousos G. P. Familial glucocorticoid resistance caused by a splice site deletion in the human glucocorticoid receptor gene. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993 Mar;76(3):683–689. doi: 10.1210/jcem.76.3.8445027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D., Berrodin T. J., Lazar M. A. The unique C-termini of the thyroid hormone receptor variant, c-erbA alpha 2, and thyroid hormone receptor alpha 1 mediate different DNA-binding and heterodimerization properties. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 May;6(5):805–814. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.5.1318505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D., Lazar M. A. Dominant negative activity of an endogenous thyroid hormone receptor variant (alpha 2) is due to competition for binding sites on target genes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):20904–20910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig R. J., Lazar M. A., Hodin R. A., Brent G. A., Larsen P. R., Chin W. W., Moore D. D. Inhibition of thyroid hormone action by a non-hormone binding c-erbA protein generated by alternative mRNA splicing. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):659–661. doi: 10.1038/337659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazar M. A., Hodin R. A., Chin W. W. Human carboxyl-terminal variant of alpha-type c-erbA inhibits trans-activation by thyroid hormone receptors without binding thyroid hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7771–7774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martins V. R., Pratt W. B., Terracio L., Hirst M. A., Ringold G. M., Housley P. R. Demonstration by confocal microscopy that unliganded overexpressed glucocorticoid receptors are distributed in a nonrandom manner throughout all planes of the nucleus. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Feb;5(2):217–225. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-2-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer M. E., Gronemeyer H., Turcotte B., Bocquel M. T., Tasset D., Chambon P. Steroid hormone receptors compete for factors that mediate their enhancer function. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):433–442. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90918-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norbiato G., Bevilacqua M., Vago T., Baldi G., Chebat E., Bertora P., Moroni M., Galli M., Oldenburg N. Cortisol resistance in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 Mar;74(3):608–613. doi: 10.1210/jcem.74.3.1740494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfahl M. Nuclear receptor/AP-1 interaction. Endocr Rev. 1993 Oct;14(5):651–658. doi: 10.1210/edrv-14-5-651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt W. B. The role of heat shock proteins in regulating the function, folding, and trafficking of the glucocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):21455–21458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray A., Prefontaine K. E. Physical association and functional antagonism between the p65 subunit of transcription factor NF-kappa B and the glucocorticoid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):752–756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez E. R., Hirst M., Scherrer L. C., Tang H. Y., Welsh M. J., Harmon J. M., Simons S. S., Jr, Ringold G. M., Pratt W. B. Hormone-free mouse glucocorticoid receptors overexpressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells are localized to the nucleus and are associated with both hsp70 and hsp90. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20123–20130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaghecke R., Kornely E., Wollenhaupt J., Specker C. Glucocorticoid receptors in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Jul;35(7):740–744. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schaffner W. Rapid detection of octamer binding proteins with 'mini-extracts', prepared from a small number of cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6419–6419. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sher E. R., Leung D. Y., Surs W., Kam J. C., Zieg G., Kamada A. K., Szefler S. J. Steroid-resistant asthma. Cellular mechanisms contributing to inadequate response to glucocorticoid therapy. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jan;93(1):33–39. doi: 10.1172/JCI116963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. F., Toft D. O. Steroid receptors and their associated proteins. Mol Endocrinol. 1993 Jan;7(1):4–11. doi: 10.1210/mend.7.1.8446107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truss M., Beato M. Steroid hormone receptors: interaction with deoxyribonucleic acid and transcription factors. Endocr Rev. 1993 Aug;14(4):459–479. doi: 10.1210/edrv-14-4-459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikström A. C., Bakke O., Okret S., Brönnegård M., Gustafsson J. A. Intracellular localization of the glucocorticoid receptor: evidence for cytoplasmic and nuclear localization. Endocrinology. 1987 Apr;120(4):1232–1242. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-4-1232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R. Steroid receptor regulated transcription of specific genes and gene networks. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:209–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Chambard J. C., Sun Y. L., Smeal T., Schmidt T. J., Drouin J., Karin M. Transcriptional interference between c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor: mutual inhibition of DNA binding due to direct protein-protein interaction. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1205–1215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90396-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen P. M., Chin W. W. Molecular mechanisms of dominant negative activity by nuclear hormone receptors. Mol Endocrinol. 1994 Nov;8(11):1450–1454. doi: 10.1210/mend.8.11.7877614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]