Abstract
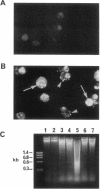
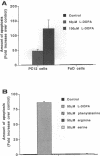
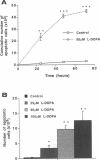
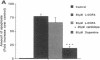
The hypothesis that L-DOPA therapy in Parkinson's disease may augment neuronal damage and thus accelerate the progression of the disease remains controversial. In this study, we demonstrate that L-DOPA induces death of catecholaminergic cells in vitro via an active program of apoptosis. Treatment of PC12 cells with clinically applicable concentrations of L-DOPA (25-100 microM) induced cell death via a mechanism which exhibited morphological and biochemical characteristics of apoptosis, including chromatin condensation, membrane blebbing, and internucleosomal DNA fragmentation. L-DOPA-induced apoptosis was cell and drug-type specific. Toxicity is an intrinsic property of the drug molecule since it was not suppressed by inhibiting conversion of L-DOPA to dopamine. However, L-DOPA toxicity was inhibited by antioxidants, suggesting that activation of apoptosis is mediated by oxygen radicals. Our finding that L-DOPA-induced cell death in vitro occurs via apoptosis explains the lack of evidence supporting its toxicity in vivo, since apoptotic neurons are rapidly phagocytosed in vivo without causing damage to surrounding tissue. Furthermore, since apoptosis is an active cellular program which can be modulated, we suggest clinical approaches for decreasing L-DOPA toxicity, thus preventing acceleration of neuronal damage in Parkinson's disease.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batistatou A., Greene L. A. Aurintricarboxylic acid rescues PC12 cells and sympathetic neurons from cell death caused by nerve growth factor deprivation: correlation with suppression of endonuclease activity. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(2):461–471. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.2.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batistatou A., Greene L. A. Internucleosomal DNA cleavage and neuronal cell survival/death. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(3):523–532. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.3.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin J., Bonnet A. M., Agid Y. Does levodopa aggravate Parkinson's disease? Neurology. 1988 Sep;38(9):1410–1416. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.9.1410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blunt S. B., Jenner P., Marsden C. D. Suppressive effect of L-dopa on dopamine cells remaining in the ventral tegmental area of rats previously exposed to the neurotoxin 6-hydroxydopamine. Mov Disord. 1993 Apr;8(2):129–133. doi: 10.1002/mds.870080202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. G., Sun X. M., Cohen G. M. Dexamethasone-induced apoptosis involves cleavage of DNA to large fragments prior to internucleosomal fragmentation. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3037–3039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. E., Yuan J. Y., Horvitz H. R. Mechanisms and functions of cell death. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:663–698. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A., Sienkiewicz J. Psychotic complications of long-term levodopa treatment of Parkinson's disease. Acta Neurol Scand. 1991 Aug;84(2):111–113. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1991.tb04918.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gervas J. J., Muradás V., Bazán E., Aguado E. G., de Yébenes J. G. Effects of 3-OM-dopa on monoamine metabolism in rat brain. Neurology. 1983 Mar;33(3):278–282. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.3.278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Tischler A. S. Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesser R. P., Fahn S., Snider S. R., Cote L. J., Isgreen W. P., Barrett R. E. Analysis of the clinical problems in parkinsonism and the complications of long-term levodopa therapy. Neurology. 1979 Sep;29(9 Pt 1):1253–1260. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.9_part_1.1253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markham C. H., Diamond S. G. Long-term follow-up of early dopa treatment in Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol. 1986 Apr;19(4):365–372. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markham C. H., Diamond S. G. Modification of Parkinson's disease by long-term levodopa treatment. Arch Neurol. 1986 Apr;43(4):405–407. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1986.00520040083026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Parkes J. D. "On-off" effects in patients with Parkinson's disease on chronic levodopa therapy. Lancet. 1976 Feb 7;1(7954):292–296. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91416-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Parkes J. D. Success and problems of long-term levodopa therapy in Parkinson's disease. Lancet. 1977 Feb 12;1(8007):345–349. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91146-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D. Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1994 Jun;57(6):672–681. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.57.6.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mena M. A., Pardo B., Casarejos M. J., Fahn S., García de Yébenes J. Neurotoxicity of levodopa on catecholamine-rich neurons. Mov Disord. 1992;7(1):23–31. doi: 10.1002/mds.870070105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mena M. A., Pardo B., Paino C. L., De Yebenes J. G. Levodopa toxicity in foetal rat midbrain neurones in culture: modulation by ascorbic acid. Neuroreport. 1993 Apr;4(4):438–440. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199304000-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mytilineou C., Han S. K., Cohen G. Toxic and protective effects of L-dopa on mesencephalic cell cultures. J Neurochem. 1993 Oct;61(4):1470–1478. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb13642.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhammer F., Wilson J. W., Dive C., Morris I. D., Hickman J. A., Wakeling A. E., Walker P. R., Sikorska M. Apoptotic death in epithelial cells: cleavage of DNA to 300 and/or 50 kb fragments prior to or in the absence of internucleosomal fragmentation. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3679–3684. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06042.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa N., Asanuma M., Kondo Y., Kawada Y., Yamamoto M., Mori A. Differential effects of chronic L-dopa treatment on lipid peroxidation in the mouse brain with or without pretreatment with 6-hydroxydopamine. Neurosci Lett. 1994 Apr 25;171(1-2):55–58. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(94)90603-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olney J. W., Zorumski C. F., Stewart G. R., Price M. T., Wang G. J., Labruyere J. Excitotoxicity of L-dopa and 6-OH-dopa: implications for Parkinson's and Huntington's diseases. Exp Neurol. 1990 Jun;108(3):269–272. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(90)90134-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim R. W. Cell death during development of the nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1991;14:453–501. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.14.030191.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry T. L., Godin D. V., Hansen S. Parkinson's disease: a disorder due to nigral glutathione deficiency? Neurosci Lett. 1982 Dec 13;33(3):305–310. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90390-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry T. L., Yong V. W., Ito M., Foulks J. G., Wall R. A., Godin D. V., Clavier R. M. Nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons remain undamaged in rats given high doses of L-DOPA and carbidopa chronically. J Neurochem. 1984 Oct;43(4):990–993. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb12834.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn N., Parkes D., Janota I., Marsden C. D. Preservation of the substantia nigra and locus coeruleus in a patient receiving levodopa (2 kg) plus decarboxylase inhibitor over a four-year period. Mov Disord. 1986;1(1):65–68. doi: 10.1002/mds.870010109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rukenstein A., Rydel R. E., Greene L. A. Multiple agents rescue PC12 cells from serum-free cell death by translation- and transcription-independent mechanisms. J Neurosci. 1991 Aug;11(8):2552–2563. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-08-02552.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savill J., Fadok V., Henson P., Haslett C. Phagocyte recognition of cells undergoing apoptosis. Immunol Today. 1993 Mar;14(3):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90215-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scigliano G., Musicco M., Soliveri P., Piccolo I., Girotti F., Giovannini P., Caraceni T. Mortality associated with early and late levodopa therapy initiation in Parkinson's disease. Neurology. 1990 Feb;40(2):265–269. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.2.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. S., Parker W. D., Jr, Bennett J. P., Jr L-dopa increases nigral production of hydroxyl radicals in vivo: potential L-dopa toxicity? Neuroreport. 1994 Apr 14;5(8):1009–1011. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199404000-00039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steece-Collier K., Collier T. J., Sladek C. D., Sladek J. R., Jr Chronic levodopa impairs morphological development of grafted embryonic dopamine neurons. Exp Neurol. 1990 Nov;110(2):201–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(90)90031-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Sotomatsu A., Kanai H., Hirai S. Dopa and dopamine cause cultured neuronal death in the presence of iron. J Neurol Sci. 1991 Feb;101(2):198–203. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(91)90046-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uitti R. J., Ahlskog J. E., Maraganore D. M., Muenter M. D., Atkinson E. J., Cha R. H., O'Brien P. C. Levodopa therapy and survival in idiopathic Parkinson's disease: Olmsted County project. Neurology. 1993 Oct;43(10):1918–1926. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.10.1918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walkinshaw G., Waters C. M. Neurotoxin-induced cell death in neuronal PC12 cells is mediated by induction of apoptosis. Neuroscience. 1994 Dec;63(4):975–987. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)90566-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H. Glucocorticoid-induced thymocyte apoptosis is associated with endogenous endonuclease activation. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):555–556. doi: 10.1038/284555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Kerr J. F., Currie A. R. Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol. 1980;68:251–306. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62312-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yurek D. M., Steece-Collier K., Collier T. J., Sladek J. R., Jr Chronic levodopa impairs the recovery of dopamine agonist-induced rotational behavior following neural grafting. Exp Brain Res. 1991;86(1):97–107. doi: 10.1007/BF00231044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziv I., Melamed E., Nardi N., Luria D., Achiron A., Offen D., Barzilai A. Dopamine induces apoptosis-like cell death in cultured chick sympathetic neurons--a possible novel pathogenetic mechanism in Parkinson's disease. Neurosci Lett. 1994 Mar 28;170(1):136–140. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(94)90258-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]