Abstract
Two molecules of the title compound, C15H13N3O3S, are linked by an intermolecular N—H⋯S hydrogen bond. There is also an intramolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bond, forming a six-membered ring. The steric restriction of the m-methyl and p-nitro groups, as well as the intramolecular hydrogen bond, are the main factors influencing the molecular conformation.
Related literature
For general background, see: Su et al. (2006 ▶). For related coordination compounds, see: Su et al. (2005 ▶); Xian et al. (2004 ▶). For related structures, see: Su (2005 ▶, 2007 ▶); Yusof et al. (2007 ▶).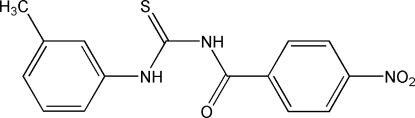
Experimental
Crystal data
C15H13N3O3S
M r = 315.34
Monoclinic,

a = 11.381 (10) Å
b = 8.549 (8) Å
c = 15.653 (12) Å
β = 108.012 (16)°
V = 1448 (3) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.24 mm−1
T = 296 (2) K
0.30 × 0.29 × 0.26 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2000 ▶) T min = 0.609, T max = 1.000 (expected range = 0.572–0.940)
7125 measured reflections
2692 independent reflections
2072 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.059
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.045
wR(F 2) = 0.141
S = 0.89
2692 reflections
201 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.29 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2001 ▶); cell refinement: APEX2 and SAINT (Bruker, 2001 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808029425/bv2107sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808029425/bv2107Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2′⋯S1i | 0.86 | 2.81 | 3.665 (4) | 179 |
| N4—H4′⋯O3 | 0.86 | 1.94 | 2.643 (3) | 138 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Acknowledgments
Financial support of this work by the Foundation of Northwest University for Nationalities is acknowledged.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Thiourea and its derivatives are good ligands for forming coordination compounds with transition metal ions, especially Cu(I). Our previous research showed that coordination compounds of carbonylthiourea derivatives with Cu(I) often adopt a trigonal planar conformation (Xian et al., 2004). In addition, it was found that the reaction of carbonylthiourea derivatives with Cu(I) can also form a metal cluster compound with a complex structure (Su et al., 2005). Apparently, the coordinating ability of carbonylthiorea derivatives is related to their conformation and hydrogen bonds. Herein the structure of N-p-nitrobenzoyl-N'-(m-methylphenyl)thiourea and its FT—IR, 1H NMR was reported.
As shown in Fig. 1, the title compound adopts a trans-conformation similar to the other structures of thiourea derivatives (Su et al., 2006; Su, 2007), i.e. the conformation in which the thiocarbonyl and carbonyl groups are distributed on opposite sides of the main backbone due to steric restriction. On the other hand, steric restriction and hydrogen bond interactions also result in dimer formation through the "head-tail" junction conformation of the title compound (Fig. 2). The thiocarbonyl group forms an intermolecular hydrogen bond with N—H (-x, -y, -z), and the carbonyl group forms intramolecular hydrogen bond with N—H (x, y, z). Apparently, the carbonyl oxygen atom is "locked" in the hydrogen-bonded six-membered ring structure and thus not readily available for coordination with transition metal ions. There are mainly two molecular planes in the structure, two benzene rings almost are in the same plane with the mean deviation 0.078 (4) Å, another plane is the hydrogen-bonding six-membered ring with the mean deviation 0.055 (4) Å. The angle between two benzene planes is 41.39(0.09)°. The above conformation is similar to that observed in previously reported thiourea structures (Su, 2005; Yusof et al., 2007).
Experimental
All chemicals used for the preparation of the title compound were of reagent grade quality. The infrared spectrum was recorded in the range of 4000–400 cm-1 on a Nicolet NEXUS 670 F T—IR spectrometer, using KBr pellets. 1H NMR spectrum was obtained on an INOVA-400 MHz superconducting spectrometer, CDCl3 was used as the solvent and TMS as internal standard, and the chemical shifts are expressed as delta. Elemental analyses were carried out on a PE-2400 elemental analysis instrument. Melting point determination was performed in YRT-3 melting point instrument (Tianjin) and was uncorrected. The yellow single-crystal was obtained after one week by slow evaporation of the acetone solution of the title compound. N-p-nitrobenzoyl-N'-(m-methylphenyl)thiourea. Color: yellow. Melting Point: 151–153 (°C). Elemental analysis (%) found (calcd.): C, 56.3(61.5); H, 4.11(4.7); N, 10.3(13.2); S, 10.2(10.0). IR (KBr, cm-1): 3244 (N—H), 1675 (C=O), 1521(C=C), 1336, 1264(C=S), 1151. 1H NMR(delta, p.p.m.): 2.40 (s, 3H, CH3); 6.91–9.07 (m, 8H, C6H4, C6H4); 12.30 (s, 1H, NH).
Refinement
The amino hydrogen atoms were found from Fourier difference maps and fixed with N—H bond lengths of 0.86 Å. The H atoms of the aromatic group were geometrically idealized. The methyl H atoms were idealized to tetrahedral geometry and allowed to freely rotate about the C-C vector. All the H atoms were refined isotropically with isotropic vibration parameters related to the atoms to which they are bonded.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level. The intramolecular hydrogen bonds is indicated by dashed lines.
Fig. 2.
View of the dimer of the title compound formed by intermolecular hydrogen bonds (shown as dashed lines).
Crystal data
| C15H13N3O3S | F(000) = 656 |
| Mr = 315.34 | Dx = 1.446 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 11.381 (10) Å | Cell parameters from 2974 reflections |
| b = 8.549 (8) Å | θ = 2.7–29.0° |
| c = 15.653 (12) Å | µ = 0.24 mm−1 |
| β = 108.012 (16)° | T = 296 K |
| V = 1448 (3) Å3 | Block, yellow |
| Z = 4 | 0.30 × 0.29 × 0.26 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer | 2692 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2072 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.059 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 25.5°, θmin = 1.9° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2000) | h = −13→13 |
| Tmin = 0.609, Tmax = 1.000 | k = −5→10 |
| 7125 measured reflections | l = −18→18 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.046 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.141 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.1P)2 + 0.161P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 0.89 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2692 reflections | Δρmax = 0.29 e Å−3 |
| 201 parameters | Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL, Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.038 (4) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.16111 (5) | 0.07187 (6) | 0.10213 (3) | 0.0457 (2) | |
| C6 | −0.05997 (17) | 0.3452 (2) | −0.17937 (12) | 0.0385 (5) | |
| C8 | 0.14304 (16) | 0.2443 (2) | 0.05209 (11) | 0.0368 (5) | |
| N2 | 0.05371 (14) | 0.25694 (19) | −0.03121 (10) | 0.0395 (4) | |
| H2' | 0.0037 | 0.1792 | −0.0469 | 0.047* | |
| C9 | 0.30022 (17) | 0.3945 (2) | 0.16605 (12) | 0.0379 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.03499 (18) | 0.3776 (3) | −0.09162 (13) | 0.0413 (5) | |
| O3 | 0.09358 (15) | 0.4980 (2) | −0.07658 (10) | 0.0612 (5) | |
| N4 | 0.20710 (15) | 0.3727 (2) | 0.08184 (10) | 0.0416 (4) | |
| H4' | 0.1908 | 0.4522 | 0.0464 | 0.050* | |
| C10 | 0.28304 (18) | 0.3445 (3) | 0.24483 (12) | 0.0427 (5) | |
| H10 | 0.2111 | 0.2913 | 0.2433 | 0.051* | |
| N1 | −0.30000 (18) | 0.2241 (2) | −0.43126 (12) | 0.0545 (5) | |
| C3 | −0.21803 (18) | 0.2731 (2) | −0.34317 (12) | 0.0406 (5) | |
| C1 | −0.16868 (17) | 0.2707 (2) | −0.18569 (12) | 0.0391 (5) | |
| H1 | −0.1879 | 0.2449 | −0.1338 | 0.047* | |
| C2 | −0.24957 (18) | 0.2339 (2) | −0.26833 (13) | 0.0422 (5) | |
| H2 | −0.3239 | 0.1835 | −0.2733 | 0.051* | |
| C12 | 0.4762 (2) | 0.4543 (3) | 0.32628 (15) | 0.0544 (6) | |
| H12 | 0.5374 | 0.4737 | 0.3804 | 0.065* | |
| C11 | 0.37229 (19) | 0.3729 (3) | 0.32641 (13) | 0.0465 (5) | |
| C5 | −0.03345 (18) | 0.3910 (3) | −0.25606 (13) | 0.0465 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.0384 | 0.4468 | −0.2515 | 0.056* | |
| C4 | −0.11358 (19) | 0.3537 (3) | −0.33902 (13) | 0.0470 (5) | |
| H4 | −0.0967 | 0.3830 | −0.3912 | 0.056* | |
| C14 | 0.40313 (18) | 0.4767 (3) | 0.16660 (14) | 0.0479 (5) | |
| H14 | 0.4140 | 0.5118 | 0.1133 | 0.058* | |
| C13 | 0.49105 (19) | 0.5068 (3) | 0.24843 (16) | 0.0539 (6) | |
| H13 | 0.5613 | 0.5639 | 0.2501 | 0.065* | |
| O1 | −0.27911 (18) | 0.2717 (3) | −0.49730 (10) | 0.0787 (6) | |
| O2 | −0.38159 (19) | 0.1337 (3) | −0.43392 (12) | 0.0918 (7) | |
| C15 | 0.3541 (3) | 0.3154 (4) | 0.41178 (14) | 0.0725 (8) | |
| H15A | 0.3351 | 0.2057 | 0.4065 | 0.109* | |
| H15B | 0.2872 | 0.3715 | 0.4228 | 0.109* | |
| H15C | 0.4284 | 0.3321 | 0.4607 | 0.109* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0441 (4) | 0.0420 (4) | 0.0431 (3) | 0.0008 (2) | 0.0017 (2) | 0.0030 (2) |
| C6 | 0.0384 (10) | 0.0398 (11) | 0.0356 (10) | 0.0041 (9) | 0.0088 (8) | 0.0034 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0325 (9) | 0.0458 (12) | 0.0321 (9) | 0.0017 (8) | 0.0100 (8) | −0.0033 (8) |
| N2 | 0.0390 (9) | 0.0397 (9) | 0.0346 (8) | −0.0011 (7) | 0.0039 (7) | 0.0009 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0325 (9) | 0.0403 (11) | 0.0369 (10) | 0.0032 (8) | 0.0050 (8) | −0.0037 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0398 (11) | 0.0424 (11) | 0.0392 (10) | −0.0006 (9) | 0.0083 (8) | 0.0004 (9) |
| O3 | 0.0644 (10) | 0.0559 (10) | 0.0488 (9) | −0.0186 (9) | −0.0035 (7) | 0.0098 (8) |
| N4 | 0.0423 (9) | 0.0412 (10) | 0.0357 (8) | −0.0034 (8) | 0.0038 (7) | 0.0016 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0379 (10) | 0.0470 (12) | 0.0408 (11) | −0.0010 (9) | 0.0086 (8) | −0.0046 (10) |
| N1 | 0.0497 (11) | 0.0658 (13) | 0.0411 (10) | 0.0018 (10) | 0.0036 (8) | −0.0009 (9) |
| C3 | 0.0378 (10) | 0.0457 (12) | 0.0339 (10) | 0.0052 (9) | 0.0045 (8) | −0.0005 (9) |
| C1 | 0.0433 (11) | 0.0407 (11) | 0.0342 (9) | 0.0019 (9) | 0.0134 (8) | 0.0035 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0349 (10) | 0.0448 (11) | 0.0458 (11) | 0.0011 (9) | 0.0108 (8) | 0.0029 (9) |
| C12 | 0.0398 (12) | 0.0633 (15) | 0.0474 (12) | 0.0050 (11) | −0.0051 (9) | −0.0084 (11) |
| C11 | 0.0470 (12) | 0.0497 (12) | 0.0379 (10) | 0.0091 (10) | 0.0058 (9) | −0.0015 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0362 (10) | 0.0610 (14) | 0.0415 (11) | −0.0053 (10) | 0.0110 (9) | 0.0039 (10) |
| C4 | 0.0450 (11) | 0.0609 (14) | 0.0365 (10) | 0.0010 (10) | 0.0145 (9) | 0.0052 (10) |
| C14 | 0.0391 (11) | 0.0546 (13) | 0.0490 (12) | 0.0009 (10) | 0.0120 (9) | 0.0014 (10) |
| C13 | 0.0313 (10) | 0.0620 (15) | 0.0617 (13) | −0.0068 (10) | 0.0046 (9) | −0.0052 (12) |
| O1 | 0.0929 (14) | 0.0997 (16) | 0.0343 (8) | −0.0134 (12) | 0.0062 (8) | 0.0072 (9) |
| O2 | 0.0754 (12) | 0.1309 (19) | 0.0583 (11) | −0.0485 (14) | 0.0046 (9) | −0.0138 (12) |
| C15 | 0.0825 (18) | 0.090 (2) | 0.0401 (12) | −0.0026 (16) | 0.0122 (12) | 0.0013 (13) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| S1—C8 | 1.652 (3) | C3—C4 | 1.358 (3) |
| C6—C1 | 1.368 (3) | C3—C2 | 1.369 (3) |
| C6—C5 | 1.382 (3) | C1—C2 | 1.372 (3) |
| C6—C7 | 1.488 (3) | C1—H1 | 0.9300 |
| C8—N4 | 1.320 (3) | C2—H2 | 0.9300 |
| C8—N2 | 1.388 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.358 (4) |
| N2—C7 | 1.371 (3) | C12—C11 | 1.372 (3) |
| N2—H2' | 0.8600 | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C9—C14 | 1.364 (3) | C11—C15 | 1.497 (3) |
| C9—C10 | 1.375 (3) | C5—C4 | 1.374 (3) |
| C9—N4 | 1.425 (3) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| C7—O3 | 1.210 (3) | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| N4—H4' | 0.8600 | C14—C13 | 1.384 (3) |
| C10—C11 | 1.385 (3) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C10—H10 | 0.9300 | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| N1—O2 | 1.199 (3) | C15—H15A | 0.9600 |
| N1—O1 | 1.201 (3) | C15—H15B | 0.9600 |
| N1—C3 | 1.467 (3) | C15—H15C | 0.9600 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 120.32 (18) | C2—C1—H1 | 119.9 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 122.42 (18) | C3—C2—C1 | 118.3 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 117.25 (19) | C3—C2—H2 | 120.9 |
| N4—C8—N2 | 115.52 (18) | C1—C2—H2 | 120.9 |
| N4—C8—S1 | 126.90 (15) | C13—C12—C11 | 121.0 (2) |
| N2—C8—S1 | 117.56 (15) | C13—C12—H12 | 119.5 |
| C7—N2—C8 | 128.27 (18) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.5 |
| C7—N2—H2' | 115.9 | C12—C11—C10 | 118.3 (2) |
| C8—N2—H2' | 115.9 | C12—C11—C15 | 121.7 (2) |
| C14—C9—C10 | 120.97 (18) | C10—C11—C15 | 120.1 (2) |
| C14—C9—N4 | 117.68 (18) | C4—C5—C6 | 119.7 (2) |
| C10—C9—N4 | 121.17 (19) | C4—C5—H5 | 120.1 |
| O3—C7—N2 | 123.19 (19) | C6—C5—H5 | 120.1 |
| O3—C7—C6 | 122.51 (19) | C3—C4—C5 | 118.59 (19) |
| N2—C7—C6 | 114.24 (18) | C3—C4—H4 | 120.7 |
| C8—N4—C9 | 127.32 (17) | C5—C4—H4 | 120.7 |
| C8—N4—H4' | 116.3 | C9—C14—C13 | 118.4 (2) |
| C9—N4—H4' | 116.3 | C9—C14—H14 | 120.8 |
| C9—C10—C11 | 120.3 (2) | C13—C14—H14 | 120.8 |
| C9—C10—H10 | 119.8 | C12—C13—C14 | 120.9 (2) |
| C11—C10—H10 | 119.8 | C12—C13—H13 | 119.5 |
| O2—N1—O1 | 123.1 (2) | C14—C13—H13 | 119.5 |
| O2—N1—C3 | 118.5 (2) | C11—C15—H15A | 109.5 |
| O1—N1—C3 | 118.3 (2) | C11—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 122.73 (18) | H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—N1 | 118.87 (18) | C11—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—N1 | 118.4 (2) | H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C2 | 120.21 (18) | H15B—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—H1 | 119.9 | ||
| N4—C8—N2—C7 | 9.9 (3) | C5—C6—C1—C2 | 3.3 (3) |
| S1—C8—N2—C7 | −168.46 (16) | C7—C6—C1—C2 | −175.48 (19) |
| C8—N2—C7—O3 | −4.2 (3) | C4—C3—C2—C1 | −3.5 (3) |
| C8—N2—C7—C6 | 173.12 (17) | N1—C3—C2—C1 | 175.73 (18) |
| C1—C6—C7—O3 | −141.1 (2) | C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.2 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—O3 | 40.1 (3) | C13—C12—C11—C10 | 0.5 (3) |
| C1—C6—C7—N2 | 41.5 (3) | C13—C12—C11—C15 | −179.4 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7—N2 | −137.3 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 1.2 (3) |
| N2—C8—N4—C9 | 177.28 (17) | C9—C10—C11—C15 | −178.8 (2) |
| S1—C8—N4—C9 | −4.5 (3) | C1—C6—C5—C4 | −3.6 (3) |
| C14—C9—N4—C8 | 138.7 (2) | C7—C6—C5—C4 | 175.16 (19) |
| C10—C9—N4—C8 | −46.1 (3) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | 3.1 (3) |
| C14—C9—C10—C11 | −2.0 (3) | N1—C3—C4—C5 | −176.1 (2) |
| N4—C9—C10—C11 | −177.11 (18) | C6—C5—C4—C3 | 0.5 (3) |
| O2—N1—C3—C4 | 169.0 (2) | C10—C9—C14—C13 | 1.0 (3) |
| O1—N1—C3—C4 | −8.1 (3) | N4—C9—C14—C13 | 176.2 (2) |
| O2—N1—C3—C2 | −10.3 (3) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −1.5 (4) |
| O1—N1—C3—C2 | 172.6 (2) | C9—C14—C13—C12 | 0.8 (4) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2'···S1i | 0.86 | 2.81 | 3.665 (4) | 179. |
| N4—H4'···O3 | 0.86 | 1.94 | 2.643 (3) | 138. |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y, −z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BV2107).
References
- Bruker (2001). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2000). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Su, B.-Q. (2005). Acta Cryst. E61, o3492–o3494.
- Su, B. Q. (2007). J. Chem. Crystallogr.37, 87–90.
- Su, B. Q., Liu, G. L., Sheng, L., Wang, X. Q. & Xian, L. (2006). Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon, 181, 745–750.
- Su, B. Q., Xian, L., Zhang, B. & Song, H. B. (2005). J. Chem. Res.(S.), 2, 101–102.
- Xian, L., Wei, T. B. & Zhang, Y. M. (2004). J. Coord. Chem.57, 453–457.
- Yusof, M. S. M., Pazil, A. M., Kadir, M. A. & Yamin, B. M. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o1302–o1303.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808029425/bv2107sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808029425/bv2107Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




