Abstract
In the title compound, [Ni(C24H43P2)Cl], the Ni atom adopts a distorted square-planar geometry, with the P atoms of the 2,6-bis[(di-tert-butylphosphino)methyl]phenyl ligand trans to one another. The P—Ni—P plane is twisted out of the plane of the aromatic ring by 21.97 (6)°.
Related literature
For the original synthesis and spectroscopic characterization of the title compound, see: Moulton & Shaw (1976 ▶). For the crystallographic characterization of the Pd analogue, see: Kimmich et al. (2002 ▶). For crystallographic characterization of the 2,6-bis[(di-tert-butylphosphino)methyl]benzene ligand, see: Hollink et al. (2003 ▶). For related literature, see: Denney et al. (2006 ▶); Keith et al. (2006 ▶).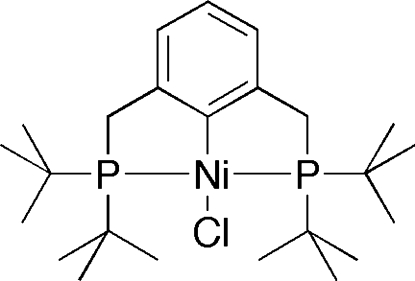
Experimental
Crystal data
[Ni(C24H43P2)Cl]
M r = 487.68
Orthorhombic,

a = 11.3394 (4) Å
b = 15.0463 (5) Å
c = 15.4184 (5) Å
V = 2630.63 (15) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.97 mm−1
T = 225 (2) K
0.50 × 0.50 × 0.40 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2004 ▶) T min = 0.622, T max = 0.679
84881 measured reflections
10074 independent reflections
8461 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.048
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.033
wR(F 2) = 0.084
S = 1.09
10074 reflections
265 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.32 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.50 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), with 4507 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: 0.006 (7)
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2003 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2004 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: DIAMOND (Brandenburg, 1999 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: publCIF (Westrip, 2008 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808029814/pv2105sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808029814/pv2105Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Eileen Duesler and Ana Felix (UNM) for the X-ray data collection. Funding was provided by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC PDF to DAD), and the Department of Energy (DE-FG02-06ER15765). The Bruker X-ray diffractometer was purchased via a National Science Foundation CRIF:MU award to the University of New Mexico (CHE-0443580). Sandia is a multiprogram laboratory operated by Sandia Corporation, a Lockheed Martin Company, for the US Department of Energy under contract No. DE-AC04-94AL85000.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The title compound, (I), was originally prepared by Moulton & Shaw (1976) but its crystal structure was not determined at that time. We have prepared (I) as part of our studies of PCP 'pincer' complexes of divalent late transition metals, which show promise as catalysts for the epoxidation of olefins (Denney et al., 2006; Keith et al., 2006).
In the molecular stucture of (I) (Fig. 1), the nickel adopts a square planar geometry, with the phosphorus atoms trans to one another. The Ni—P bond lengths 2.1921 (4) and 2.1978 (4) Å, are significantly shorter than the corresponding Pd—P bonds [2.3039 (6) and 2.3969 (6) Å] in the analogous palladium complex (Kimmich et al., 2002). Steric hindrance distorts the P—Ni—P bond angle to 169.651 (18)°, while the less constrained C—Ni—Cl angle is much closer to linearity at 176.13 (5)°.
Significant geometrical changes are observed in the 2,6-bis[(di-tert-butylphosphino)methyl]benzene ligand upon binding to nickel. In the free ligand (Hollink et al., 2003), the average P—Cmethylene bond length is 1.870 Å, while in (I), it has decreased to 1.8308 (19) Å (P1—C8) and 1.8341 (18) Å (P2—C7). This bond shortening is accompanied by change in the P—Cmethylene—Cphenyl angle, from 114.5° in the free ligand to 106.23 (12)° (P1—C8—C2) and 106.84 (12)° (P2—C7—C6) in (I).
Experimental
A solution of nickel chloride hexahydrate (0.6 g, 2.5 mmol) dissolved in 2 ml of degassed water was added to a solution of 2,6-bis-[(di-tert-butylphosphino)methyl]benzene (1.02 g, 2.6 mmol) in 10 ml ethanol. The solution was heated to reflux. A golden-yellow precipitate began to form only after 0.5 h. The solution was stirred under gentle reflux overnight. After cooling, the product was collected by filtration and washed with cold ethanol. It was recrystallized from a concentrated solution of pentane at 238 K.
Refinement
Hydrogen atoms were included at geometrically idealized positions with C—H distances 0.94, 0.97 and 0.98 Å, for aryl, methyl and methylene H-atoms in a riding mode on the respective heavy atoms. The isotropic displacement parameters for the hydrogen atoms were fixed at 1.5 and 1.2 times Ueq of the parent methyl and non-methyl C-atoms. An absolute structure was determined (Flack, 1983) employing 4507 Friedel pairs of reflections which were not merged.
Figures
Fig. 1.
View of the title compound showing numbering scheme. Ellipsoids are shown at 50% probability and hydrogen atoms have been removed for clarity.
Crystal data
| [Ni(C24H43P2)Cl] | F(000) = 1048 |
| Mr = 487.68 | Dx = 1.231 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 8656 reflections |
| a = 11.3394 (4) Å | θ = 2.2–32.5° |
| b = 15.0463 (5) Å | µ = 0.97 mm−1 |
| c = 15.4184 (5) Å | T = 225 K |
| V = 2630.63 (15) Å3 | Prism, gold-brown |
| Z = 4 | 0.50 × 0.50 × 0.40 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer | 10074 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 8461 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.048 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 33.2°, θmin = 1.9° |
| Absorption correction: empirical (using intensity measurements) (SADABS; Bruker, 2004) | h = −17→17 |
| Tmin = 0.622, Tmax = 0.679 | k = −23→23 |
| 84881 measured reflections | l = −23→23 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.033 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.084 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0439P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.09 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.002 |
| 10074 reflections | Δρmax = 0.32 e Å−3 |
| 265 parameters | Δρmin = −0.50 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), with 4507 Friedel pairs |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Flack parameter: 0.006 (7) |
Special details
| Experimental. Yield = 60%. 1H NMR (250 MHz, C6D6) δ 7.00 (t, 1H, 3JHH = 7.4 Hz, Ar-Hpara), 6.84 (d, 2H, 3JHH = 7.4 Hz, Ar-Hmeta), 2.91 (virtual t, 4H, JHP = 6.8 Hz, CH2), 1.40 (virtual t, 36H, JHP = 12.7 Hz, CH3) p.p.m. 13C{1H} NMR (63 MHz, C6D6) δ 155.7 (t, 2JCP = 16.7 Hz, Ar-Cipso), 153.0 (virtual t, JCP = 25.5 Hz, Ar-Cortho), 125.2 (s, Ar-Cpara), 121.8 (virtual t, JCP = 16.7 Hz, Ar-Cmeta), 34.9 (virtual t, JCP = 13.4 Hz, PCH2), 34.3 (virtual t, JCP = 22.7 Hz, PC(CH3)3), 29.8 (s, CH3) p.p.m. 31P{1H} NMR (101 MHz, C6D6) δ 66.9 p.p.m. |
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Ni1 | 0.536566 (17) | 0.968358 (13) | 0.925683 (12) | 0.02623 (5) | |
| Cl1 | 0.60025 (5) | 1.02689 (4) | 0.80121 (3) | 0.04914 (12) | |
| P1 | 0.38227 (4) | 0.90497 (3) | 0.86644 (3) | 0.02696 (8) | |
| P2 | 0.67658 (4) | 1.02487 (3) | 1.00738 (3) | 0.02786 (8) | |
| C1 | 0.48595 (14) | 0.91031 (10) | 1.03045 (10) | 0.0278 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.37594 (16) | 0.86671 (11) | 1.03569 (11) | 0.0326 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.34528 (18) | 0.81652 (13) | 1.10805 (13) | 0.0405 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.2723 | 0.7869 | 1.1094 | 0.049* | |
| C4 | 0.4201 (2) | 0.80982 (13) | 1.17718 (13) | 0.0441 (5) | |
| H4 | 0.3992 | 0.7750 | 1.2254 | 0.053* | |
| C5 | 0.52717 (18) | 0.85476 (12) | 1.17589 (11) | 0.0383 (4) | |
| H5 | 0.5780 | 0.8516 | 1.2240 | 0.046* | |
| C6 | 0.55930 (16) | 0.90460 (11) | 1.10322 (11) | 0.0327 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.67683 (17) | 0.95101 (13) | 1.10201 (12) | 0.0391 (4) | |
| H7A | 0.7409 | 0.9076 | 1.0974 | 0.047* | |
| H7B | 0.6879 | 0.9854 | 1.1554 | 0.047* | |
| C8 | 0.29202 (16) | 0.87651 (14) | 0.96090 (12) | 0.0382 (4) | |
| H8A | 0.2345 | 0.9236 | 0.9727 | 0.046* | |
| H8B | 0.2494 | 0.8208 | 0.9508 | 0.046* | |
| C9 | 0.41665 (16) | 0.79598 (10) | 0.81364 (12) | 0.0339 (3) | |
| C10 | 0.5097 (2) | 0.80785 (14) | 0.74313 (14) | 0.0488 (5) | |
| H10A | 0.5784 | 0.8371 | 0.7674 | 0.073* | |
| H10B | 0.4776 | 0.8439 | 0.6966 | 0.073* | |
| H10C | 0.5322 | 0.7501 | 0.7205 | 0.073* | |
| C11 | 0.3068 (2) | 0.75117 (14) | 0.77561 (15) | 0.0497 (5) | |
| H11A | 0.2776 | 0.7861 | 0.7273 | 0.075* | |
| H11B | 0.2463 | 0.7471 | 0.8199 | 0.075* | |
| H11C | 0.3271 | 0.6920 | 0.7556 | 0.075* | |
| C12 | 0.4694 (2) | 0.73571 (12) | 0.88360 (14) | 0.0471 (5) | |
| H12A | 0.4934 | 0.6798 | 0.8577 | 0.071* | |
| H12B | 0.4108 | 0.7245 | 0.9281 | 0.071* | |
| H12C | 0.5374 | 0.7646 | 0.9093 | 0.071* | |
| C13 | 0.28236 (17) | 0.97553 (14) | 0.79810 (13) | 0.0422 (4) | |
| C14 | 0.15386 (19) | 0.94355 (18) | 0.79892 (18) | 0.0618 (6) | |
| H14A | 0.1057 | 0.9840 | 0.7651 | 0.093* | |
| H14B | 0.1252 | 0.9420 | 0.8582 | 0.093* | |
| H14C | 0.1494 | 0.8844 | 0.7740 | 0.093* | |
| C15 | 0.3241 (2) | 0.98364 (15) | 0.70379 (13) | 0.0539 (5) | |
| H15A | 0.3162 | 0.9266 | 0.6751 | 0.081* | |
| H15B | 0.4061 | 1.0020 | 0.7028 | 0.081* | |
| H15C | 0.2764 | 1.0275 | 0.6738 | 0.081* | |
| C16 | 0.2868 (3) | 1.06881 (15) | 0.83988 (18) | 0.0642 (7) | |
| H16A | 0.2328 | 1.1081 | 0.8098 | 0.096* | |
| H16B | 0.3663 | 1.0923 | 0.8357 | 0.096* | |
| H16C | 0.2643 | 1.0646 | 0.9004 | 0.096* | |
| C17 | 0.83287 (16) | 1.01907 (13) | 0.96814 (12) | 0.0369 (4) | |
| C18 | 0.84152 (19) | 0.92899 (15) | 0.92080 (17) | 0.0524 (5) | |
| H18A | 0.9217 | 0.9200 | 0.9007 | 0.079* | |
| H18B | 0.7882 | 0.9288 | 0.8716 | 0.079* | |
| H18C | 0.8201 | 0.8815 | 0.9604 | 0.079* | |
| C19 | 0.92396 (18) | 1.02033 (17) | 1.04173 (15) | 0.0514 (5) | |
| H19A | 1.0020 | 1.0103 | 1.0180 | 0.077* | |
| H19B | 0.9055 | 0.9739 | 1.0832 | 0.077* | |
| H19C | 0.9219 | 1.0776 | 1.0705 | 0.077* | |
| C20 | 0.63680 (18) | 1.13804 (12) | 1.04915 (13) | 0.0403 (4) | |
| C21 | 0.5238 (2) | 1.12685 (15) | 1.10274 (17) | 0.0593 (6) | |
| H21A | 0.5401 | 1.0901 | 1.1530 | 0.089* | |
| H21B | 0.4636 | 1.0987 | 1.0674 | 0.089* | |
| H21C | 0.4962 | 1.1847 | 1.1217 | 0.089* | |
| C22 | 0.7314 (2) | 1.17943 (16) | 1.10738 (16) | 0.0585 (6) | |
| H22A | 0.8020 | 1.1907 | 1.0735 | 0.088* | |
| H22B | 0.7500 | 1.1389 | 1.1543 | 0.088* | |
| H22C | 0.7023 | 1.2349 | 1.1312 | 0.088* | |
| C23 | 0.6101 (3) | 1.19968 (14) | 0.97333 (16) | 0.0571 (6) | |
| H23A | 0.5786 | 1.2553 | 0.9951 | 0.086* | |
| H23B | 0.5527 | 1.1719 | 0.9354 | 0.086* | |
| H23C | 0.6821 | 1.2111 | 0.9412 | 0.086* | |
| C24 | 0.86278 (18) | 1.09373 (16) | 0.90427 (14) | 0.0491 (5) | |
| H24A | 0.8597 | 1.1505 | 0.9340 | 0.074* | |
| H24B | 0.8062 | 1.0936 | 0.8571 | 0.074* | |
| H24C | 0.9414 | 1.0844 | 0.8812 | 0.074* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Ni1 | 0.02964 (9) | 0.02516 (9) | 0.02389 (9) | −0.00470 (8) | −0.00320 (8) | 0.00305 (7) |
| Cl1 | 0.0605 (3) | 0.0569 (3) | 0.02997 (19) | −0.0283 (3) | −0.00855 (19) | 0.0151 (2) |
| P1 | 0.02591 (18) | 0.02588 (17) | 0.02911 (19) | −0.00090 (15) | −0.00127 (15) | −0.00323 (15) |
| P2 | 0.03048 (18) | 0.02878 (18) | 0.02431 (17) | −0.00396 (16) | −0.00252 (14) | 0.00080 (16) |
| C1 | 0.0318 (8) | 0.0261 (6) | 0.0256 (7) | −0.0007 (6) | 0.0043 (6) | 0.0008 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0343 (8) | 0.0312 (8) | 0.0321 (8) | −0.0005 (7) | 0.0090 (7) | −0.0036 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0416 (10) | 0.0390 (9) | 0.0411 (9) | −0.0050 (8) | 0.0187 (8) | −0.0025 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0579 (12) | 0.0399 (9) | 0.0345 (9) | 0.0028 (9) | 0.0192 (9) | 0.0076 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0465 (10) | 0.0410 (9) | 0.0273 (8) | 0.0087 (8) | 0.0051 (8) | 0.0062 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0394 (9) | 0.0319 (8) | 0.0268 (7) | 0.0021 (7) | 0.0030 (6) | 0.0027 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0393 (9) | 0.0472 (10) | 0.0309 (8) | −0.0033 (8) | −0.0079 (7) | 0.0094 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0301 (8) | 0.0469 (10) | 0.0377 (9) | −0.0050 (7) | 0.0061 (7) | −0.0095 (8) |
| C9 | 0.0396 (9) | 0.0247 (7) | 0.0375 (9) | −0.0030 (6) | 0.0075 (7) | −0.0057 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0569 (13) | 0.0432 (10) | 0.0465 (11) | 0.0010 (9) | 0.0210 (9) | −0.0067 (8) |
| C11 | 0.0562 (12) | 0.0374 (10) | 0.0556 (12) | −0.0123 (9) | 0.0036 (10) | −0.0146 (9) |
| C12 | 0.0604 (12) | 0.0281 (8) | 0.0529 (11) | 0.0085 (9) | 0.0101 (11) | 0.0009 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0421 (9) | 0.0404 (9) | 0.0442 (10) | 0.0116 (8) | −0.0140 (8) | −0.0054 (9) |
| C14 | 0.0352 (10) | 0.0807 (17) | 0.0696 (15) | 0.0119 (10) | −0.0166 (10) | −0.0113 (13) |
| C15 | 0.0648 (14) | 0.0528 (12) | 0.0441 (11) | 0.0079 (11) | −0.0195 (10) | 0.0053 (9) |
| C16 | 0.0812 (18) | 0.0433 (11) | 0.0682 (16) | 0.0299 (12) | −0.0268 (14) | −0.0098 (11) |
| C17 | 0.0303 (8) | 0.0426 (9) | 0.0378 (9) | −0.0044 (7) | −0.0011 (7) | 0.0008 (8) |
| C18 | 0.0414 (10) | 0.0530 (12) | 0.0627 (13) | 0.0072 (9) | 0.0048 (10) | −0.0128 (11) |
| C19 | 0.0348 (9) | 0.0644 (13) | 0.0551 (12) | −0.0068 (9) | −0.0094 (9) | 0.0041 (11) |
| C20 | 0.0479 (11) | 0.0351 (9) | 0.0378 (9) | −0.0036 (8) | 0.0014 (8) | −0.0089 (7) |
| C21 | 0.0600 (14) | 0.0528 (12) | 0.0650 (14) | 0.0047 (11) | 0.0205 (12) | −0.0166 (11) |
| C22 | 0.0662 (15) | 0.0557 (13) | 0.0535 (13) | −0.0148 (11) | −0.0036 (12) | −0.0227 (11) |
| C23 | 0.0776 (17) | 0.0351 (10) | 0.0586 (14) | 0.0104 (11) | −0.0019 (13) | 0.0007 (9) |
| C24 | 0.0399 (10) | 0.0612 (12) | 0.0462 (11) | −0.0106 (9) | 0.0041 (8) | 0.0102 (10) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Ni1—C1 | 1.9239 (15) | C13—C15 | 1.534 (3) |
| Ni1—P1 | 2.1921 (4) | C13—C14 | 1.535 (3) |
| Ni1—P2 | 2.1978 (4) | C13—C16 | 1.545 (3) |
| Ni1—Cl1 | 2.2317 (5) | C14—H14A | 0.9700 |
| P1—C8 | 1.8308 (19) | C14—H14B | 0.9700 |
| P1—C9 | 1.8720 (16) | C14—H14C | 0.9700 |
| P1—C13 | 1.8763 (18) | C15—H15A | 0.9700 |
| P2—C7 | 1.8341 (18) | C15—H15B | 0.9700 |
| P2—C17 | 1.8746 (19) | C15—H15C | 0.9700 |
| P2—C20 | 1.8756 (19) | C16—H16A | 0.9700 |
| C1—C6 | 1.399 (2) | C16—H16B | 0.9700 |
| C1—C2 | 1.412 (2) | C16—H16C | 0.9700 |
| C2—C3 | 1.391 (2) | C17—C24 | 1.532 (3) |
| C2—C8 | 1.502 (3) | C17—C19 | 1.534 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.366 (3) | C17—C18 | 1.543 (3) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9400 | C18—H18A | 0.9700 |
| C4—C5 | 1.390 (3) | C18—H18B | 0.9700 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9400 | C18—H18C | 0.9700 |
| C5—C6 | 1.397 (2) | C19—H19A | 0.9700 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9400 | C19—H19B | 0.9700 |
| C6—C7 | 1.505 (3) | C19—H19C | 0.9700 |
| C7—H7A | 0.9800 | C20—C23 | 1.523 (3) |
| C7—H7B | 0.9800 | C20—C22 | 1.532 (3) |
| C8—H8A | 0.9800 | C20—C21 | 1.534 (3) |
| C8—H8B | 0.9800 | C21—H21A | 0.9700 |
| C9—C10 | 1.525 (3) | C21—H21B | 0.9700 |
| C9—C12 | 1.531 (3) | C21—H21C | 0.9700 |
| C9—C11 | 1.533 (3) | C22—H22A | 0.9700 |
| C10—H10A | 0.9700 | C22—H22B | 0.9700 |
| C10—H10B | 0.9700 | C22—H22C | 0.9700 |
| C10—H10C | 0.9700 | C23—H23A | 0.9700 |
| C11—H11A | 0.9700 | C23—H23B | 0.9700 |
| C11—H11B | 0.9700 | C23—H23C | 0.9700 |
| C11—H11C | 0.9700 | C24—H24A | 0.9700 |
| C12—H12A | 0.9700 | C24—H24B | 0.9700 |
| C12—H12B | 0.9700 | C24—H24C | 0.9700 |
| C12—H12C | 0.9700 | ||
| C1—Ni1—P1 | 85.08 (5) | C15—C13—C14 | 109.01 (18) |
| C1—Ni1—P2 | 84.83 (5) | C15—C13—C16 | 108.2 (2) |
| P1—Ni1—P2 | 169.651 (18) | C14—C13—C16 | 108.22 (19) |
| C1—Ni1—Cl1 | 176.13 (5) | C15—C13—P1 | 113.01 (14) |
| P1—Ni1—Cl1 | 94.109 (18) | C14—C13—P1 | 113.03 (17) |
| P2—Ni1—Cl1 | 96.109 (17) | C16—C13—P1 | 105.07 (13) |
| C8—P1—C9 | 104.92 (9) | C13—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| C8—P1—C13 | 103.98 (9) | C13—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C9—P1—C13 | 112.16 (9) | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C8—P1—Ni1 | 102.50 (6) | C13—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C9—P1—Ni1 | 113.34 (6) | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C13—P1—Ni1 | 118.02 (7) | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C7—P2—C17 | 103.12 (9) | C13—C15—H15A | 109.5 |
| C7—P2—C20 | 106.10 (9) | C13—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C17—P2—C20 | 112.36 (9) | H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C7—P2—Ni1 | 102.87 (6) | C13—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C17—P2—Ni1 | 118.68 (6) | H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C20—P2—Ni1 | 111.98 (7) | H15B—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C2 | 116.79 (15) | C13—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—Ni1 | 121.59 (12) | C13—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—Ni1 | 121.51 (12) | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 121.26 (17) | C13—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C8 | 120.69 (17) | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—C8 | 118.05 (15) | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 120.70 (18) | C24—C17—C19 | 108.50 (16) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.6 | C24—C17—C18 | 109.02 (17) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.6 | C19—C17—C18 | 108.54 (18) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.69 (17) | C24—C17—P2 | 112.50 (14) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.2 | C19—C17—P2 | 113.40 (13) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.2 | C18—C17—P2 | 104.70 (13) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.04 (18) | C17—C18—H18A | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.0 | C17—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.0 | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 121.42 (16) | C17—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 119.36 (17) | H18A—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 119.21 (14) | H18B—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—P2 | 106.84 (12) | C17—C19—H19A | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7A | 110.4 | C17—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| P2—C7—H7A | 110.4 | H19A—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7B | 110.4 | C17—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| P2—C7—H7B | 110.4 | H19A—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| H7A—C7—H7B | 108.6 | H19B—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C2—C8—P1 | 106.23 (12) | C23—C20—C22 | 109.96 (19) |
| C2—C8—H8A | 110.5 | C23—C20—C21 | 108.3 (2) |
| P1—C8—H8A | 110.5 | C22—C20—C21 | 108.32 (18) |
| C2—C8—H8B | 110.5 | C23—C20—P2 | 109.70 (13) |
| P1—C8—H8B | 110.5 | C22—C20—P2 | 113.70 (16) |
| H8A—C8—H8B | 108.7 | C21—C20—P2 | 106.63 (13) |
| C10—C9—C12 | 107.52 (16) | C20—C21—H21A | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—C11 | 109.93 (16) | C20—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C12—C9—C11 | 109.06 (16) | H21A—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—P1 | 110.57 (12) | C20—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C12—C9—P1 | 107.09 (12) | H21A—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C11—C9—P1 | 112.49 (13) | H21B—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C9—C10—H10A | 109.5 | C20—C22—H22A | 109.5 |
| C9—C10—H10B | 109.5 | C20—C22—H22B | 109.5 |
| H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 | H22A—C22—H22B | 109.5 |
| C9—C10—H10C | 109.5 | C20—C22—H22C | 109.5 |
| H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 | H22A—C22—H22C | 109.5 |
| H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 | H22B—C22—H22C | 109.5 |
| C9—C11—H11A | 109.5 | C20—C23—H23A | 109.5 |
| C9—C11—H11B | 109.5 | C20—C23—H23B | 109.5 |
| H11A—C11—H11B | 109.5 | H23A—C23—H23B | 109.5 |
| C9—C11—H11C | 109.5 | C20—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| H11A—C11—H11C | 109.5 | H23A—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| H11B—C11—H11C | 109.5 | H23B—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| C9—C12—H12A | 109.5 | C17—C24—H24A | 109.5 |
| C9—C12—H12B | 109.5 | C17—C24—H24B | 109.5 |
| H12A—C12—H12B | 109.5 | H24A—C24—H24B | 109.5 |
| C9—C12—H12C | 109.5 | C17—C24—H24C | 109.5 |
| H12A—C12—H12C | 109.5 | H24A—C24—H24C | 109.5 |
| H12B—C12—H12C | 109.5 | H24B—C24—H24C | 109.5 |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: PV2105).
References
- Brandenburg, K. (1999). DIAMOND Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Bruker (2003). SMART Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2004). SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Denney, M. C., Smythe, N. A., Cetto, K. L., Kemp, R. A. & Goldberg, K. I. (2006). J. Am. Chem. Soc.128, 2508–2509. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Hollink, E., Stewart, J. C., Wei, P. & Stephan, D. W. (2003). J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. pp. 3968–3974.
- Keith, J. M., Muller, R. P., Kemp, R. A., Goldberg, K. I., Goddard, W. A. III & Oxgaard, J. (2006). Inorg. Chem.45, 9631–9633. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kimmich, B. F. M., Marshall, W. J., Fagan, P. J., Hauptman, E. & Bullock, R. M. (2002). Inorg. Chim. Acta, 330, 52–58.
- Moulton, C. J. & Shaw, B. L. (1976). J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. pp. 1020–1024.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2008). publCIF In preparation.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808029814/pv2105sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808029814/pv2105Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



