Abstract
7-Dimethylamino-2-phenyl-1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-a][1,3,5]triazin-5-amine crystallized with one molecule of methanol to give the title compound, C12H13N7·CH3OH. The triazolo[1,5-a][1,3,5]triazine heterocyclic core is essentially planar as are both amino groups that are involved in π-electron delocalization with the triazolo[1,5-a][1,3,5]triazine nucleus. The methyl groups of the dimethylamino fragment are involved in the formation of weak intramolecular C—H⋯N hydrogen bonds with the N atoms of the heterocyclic system. The crystal packing is stabilized by intermolecular N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds between the triazolo[1,5-a][1,3,5]triazine molecules. The methanol solvent molecule also participates in the formation of the crystal structure via intermolecular O—H⋯N, N—H⋯O and weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, linking the layers of triazolo[1,5-a][1,3,5]triazine molecules.
Related literature
The 1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-a][1,3,5]triazine (5-azapurine) heterocyclic system has been reviewed by Dolzhenko et al. (2006 ▶). For investigations on 5,7-diamino-1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-a][1,3,5]triazines, see Dolzhenko et al. (2007 ▶). For a similar structure, see: Gilardi (1973 ▶). For related literature, see: Dolzhenko et al. (2008 ▶)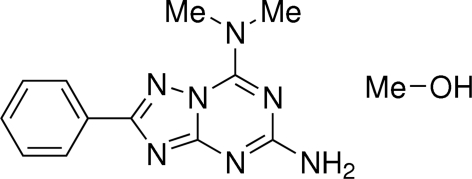
Experimental
Crystal data
C12H13N7·CH4O
M r = 287.34
Triclinic,

a = 6.9963 (5) Å
b = 8.0435 (5) Å
c = 13.0942 (9) Å
α = 93.493 (1)°
β = 93.972 (1)°
γ = 102.883 (1)°
V = 714.39 (8) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 223 (2) K
0.74 × 0.68 × 0.40 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2001 ▶) T min = 0.935, T max = 0.964
9183 measured reflections
3256 independent reflections
2870 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.023
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.047
wR(F 2) = 0.139
S = 1.07
3256 reflections
205 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.26 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2001 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2001 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808030481/fb2109sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808030481/fb2109Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1S—H1S⋯N1 | 0.92 (2) | 1.97 (2) | 2.8861 (16) | 172.8 (18) |
| N6—H6NB⋯N4i | 0.86 (2) | 2.11 (2) | 2.9679 (17) | 178.8 (18) |
| N6—H6NA⋯O1Si | 0.89 (2) | 2.398 (19) | 3.0280 (18) | 128.3 (16) |
| C6—H6C⋯N2 | 0.97 | 2.08 | 2.8753 (18) | 138 |
| C6—H6C⋯N3 | 0.97 | 2.54 | 2.9484 (17) | 105 |
| C7—H7A⋯N5 | 0.97 | 2.22 | 2.6788 (18) | 108 |
| C7—H7C⋯O1Sii | 0.97 | 2.48 | 3.4438 (19) | 176 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Academic Research Fund of the National University of Singapore (WBS R-148-000-069-112) and the National Medical Research Council, Singapore (NMRC/NIG/0019/2008 and NMRC/NIG/0020/2008).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
1,2,4-Triazolo[1,5-a][1,3,5]triazine system is known as 5-aza-isostere of the purine core. Compounds based on this skeleton have been shown to possess a wide range of biological activities (Dolzhenko et al., 2006). In continuation of our investigations on 5,7-diamino-1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-a][1,3,5]triazines (Dolzhenko et al., 2007), we report herein the structural study of 7-dimethylamino-2-phenyl-1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-a][1,3,5]triazin-5-amine (Fig. 1).
The fused triazine and triazole rings are located practically in the same plane (the angle between the mean planes of these rings makes 1.66 (4)°). The phenyl ring makes a dihedral angle of 22.70 (5)° with the mean plane of the 1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-a][1,3,5]triazine core. Similarity of the lengths of C3—N4, C3—N5, C3—N6, C4—N3, C4—N5 and C4—N7 makes evidence for π-electron delocalization of the amino groups with the 1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-a][1,3,5]triazine core.
The dimethylamino group (C6—N7—C7) has an out-of-plane twist (4.3 (8)°). The nitrogen atom of dimethylamino group (N7) has a slightly pyramidal stereochemistry [C6-N7-C7 = 115.0 (1)°] and it is located 0.039 (1) Å above the C4/C6/C7 plane. These data are in good agreement with previously reported results on the similar structure of 5,7-bis(dimethylamino)-2-methylthio-1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-a][1,3,5]triazine (Gilardi, 1973).
The methyl groups of dimethylamino fragment are involved in the formation of weak C-H···N intramolecular hydrogen-bonds with the nitrogen atoms of the heterocyclic system (Tab. 1).
7-Dimethylamino-2-phenyl-1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-a][1,3,5]triazin-5-amine crystallizes together with one molecule of methanol (Fig. 1). The methanol molecule participates in the formation of the crystalline structure via intermolecular O-H···N, N-H···O and weak C-H···O hydrogen-bonds linking the layers of the molecules of 7-dimethylamino-2-phenyl-1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-a][1,3,5]triazin-5-amine (Tab. 1, Fig. 2).
Experimental
2-Phenyl-7-trichloromethyl-1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-a][1,3,5]triazin-5-amine (0.66 g, 2.0 mmol) was added to cold (0–5 °C) dimethylamine (5 ml). The mixture was stirred first in ice-bath for 20 min and then for another 60 min at room temperature. Cold water (20 ml) was added and the product was filtered and recrystallized from methanol (m.p. 521 K).
Refinement
All the hydrogen atoms could have been discerned in the difference electron density map, nevertheless, all the H atoms attached to the carbon atoms were constrained in a riding motion approximation [0.94 Å for Caryl-H and 0.97 Å for methyl groups; Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(Caryl) and Uiso(H) =1.5Ueq(Cmethyl)] while the hydroxyl and the amino H atoms were refined freely.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title molecules with the atomic numbering scheme. The displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
Molecular packing viewed along the axis c.
Crystal data
| C12H13N7·CH4O | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 287.34 | F(000) = 304 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.336 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Melting point: 521 K |
| a = 6.9963 (5) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 8.0435 (5) Å | Cell parameters from 5236 reflections |
| c = 13.0942 (9) Å | θ = 2.6–27.5° |
| α = 93.493 (1)° | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| β = 93.972 (1)° | T = 223 K |
| γ = 102.883 (1)° | Block, colourless |
| V = 714.39 (8) Å3 | 0.74 × 0.68 × 0.40 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer | 3256 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2870 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.023 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 2.6° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2001) | h = −9→9 |
| Tmin = 0.935, Tmax = 0.964 | k = −10→10 |
| 9183 measured reflections | l = −16→16 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.047 | Hydrogen site location: difference Fourier map |
| wR(F2) = 0.139 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.07 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0789P)2 + 0.1582P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3256 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 205 parameters | Δρmax = 0.26 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3 |
| 53 constraints |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| N1 | 0.81509 (16) | 0.63570 (13) | 0.67882 (8) | 0.0325 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.66405 (16) | 0.37327 (13) | 0.60113 (8) | 0.0322 (3) | |
| N3 | 0.73812 (15) | 0.48432 (13) | 0.52921 (8) | 0.0296 (2) | |
| N4 | 0.90611 (16) | 0.77645 (13) | 0.52784 (9) | 0.0343 (3) | |
| N5 | 0.81734 (16) | 0.59004 (13) | 0.37296 (8) | 0.0327 (3) | |
| N6 | 0.9623 (2) | 0.87296 (16) | 0.36975 (11) | 0.0432 (3) | |
| H6NA | 0.954 (3) | 0.859 (2) | 0.3018 (16) | 0.053 (5)* | |
| H6NB | 1.001 (3) | 0.975 (3) | 0.3987 (15) | 0.055 (5)* | |
| N7 | 0.65525 (16) | 0.30863 (13) | 0.37239 (8) | 0.0343 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.71566 (17) | 0.47092 (16) | 0.68750 (10) | 0.0309 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.82710 (17) | 0.64251 (15) | 0.57841 (10) | 0.0304 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.89340 (18) | 0.74312 (16) | 0.42567 (10) | 0.0330 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.73645 (17) | 0.45873 (15) | 0.42375 (10) | 0.0291 (3) | |
| C6 | 0.5786 (2) | 0.14747 (17) | 0.41673 (12) | 0.0439 (3) | |
| H6A | 0.6609 | 0.0681 | 0.4018 | 0.066* | |
| H6B | 0.4452 | 0.0991 | 0.3874 | 0.066* | |
| H6C | 0.5789 | 0.1681 | 0.4905 | 0.066* | |
| C7 | 0.6562 (2) | 0.29631 (19) | 0.26060 (11) | 0.0428 (3) | |
| H7A | 0.6950 | 0.4101 | 0.2371 | 0.064* | |
| H7B | 0.5255 | 0.2413 | 0.2299 | 0.064* | |
| H7C | 0.7489 | 0.2293 | 0.2406 | 0.064* | |
| C8 | 0.66609 (18) | 0.40434 (16) | 0.78684 (10) | 0.0333 (3) | |
| C9 | 0.7706 (2) | 0.4838 (2) | 0.87779 (11) | 0.0431 (3) | |
| H9 | 0.8728 | 0.5815 | 0.8760 | 0.052* | |
| C10 | 0.7244 (3) | 0.4193 (2) | 0.97062 (12) | 0.0517 (4) | |
| H10 | 0.7960 | 0.4728 | 1.0318 | 0.062* | |
| C11 | 0.5733 (3) | 0.2762 (2) | 0.97403 (12) | 0.0512 (4) | |
| H11 | 0.5433 | 0.2323 | 1.0374 | 0.061* | |
| C12 | 0.4663 (2) | 0.1978 (2) | 0.88451 (12) | 0.0456 (4) | |
| H12 | 0.3624 | 0.1016 | 0.8870 | 0.055* | |
| C13 | 0.5127 (2) | 0.26140 (17) | 0.79114 (11) | 0.0386 (3) | |
| H13 | 0.4402 | 0.2078 | 0.7302 | 0.046* | |
| O1S | 1.00567 (17) | 0.92566 (15) | 0.81876 (10) | 0.0530 (3) | |
| H1S | 0.936 (3) | 0.838 (3) | 0.7737 (16) | 0.061 (6)* | |
| C1S | 0.8695 (3) | 0.9935 (3) | 0.86937 (19) | 0.0739 (6) | |
| H1S1 | 0.8051 | 0.9119 | 0.9148 | 0.111* | |
| H1S2 | 0.7720 | 1.0174 | 0.8195 | 0.111* | |
| H1S3 | 0.9360 | 1.0986 | 0.9092 | 0.111* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N1 | 0.0333 (5) | 0.0275 (5) | 0.0349 (6) | 0.0040 (4) | 0.0007 (4) | 0.0013 (4) |
| N2 | 0.0341 (5) | 0.0271 (5) | 0.0341 (5) | 0.0038 (4) | 0.0024 (4) | 0.0047 (4) |
| N3 | 0.0296 (5) | 0.0238 (5) | 0.0336 (5) | 0.0028 (4) | 0.0011 (4) | 0.0019 (4) |
| N4 | 0.0364 (6) | 0.0256 (5) | 0.0383 (6) | 0.0017 (4) | 0.0027 (4) | 0.0021 (4) |
| N5 | 0.0333 (5) | 0.0287 (5) | 0.0353 (6) | 0.0054 (4) | 0.0039 (4) | 0.0019 (4) |
| N6 | 0.0550 (8) | 0.0304 (6) | 0.0409 (7) | 0.0007 (5) | 0.0081 (5) | 0.0054 (5) |
| N7 | 0.0370 (6) | 0.0277 (5) | 0.0355 (6) | 0.0036 (4) | 0.0005 (4) | −0.0014 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0279 (6) | 0.0288 (6) | 0.0356 (6) | 0.0056 (4) | 0.0009 (5) | 0.0032 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0279 (6) | 0.0249 (6) | 0.0370 (6) | 0.0048 (4) | −0.0005 (5) | −0.0006 (5) |
| C3 | 0.0302 (6) | 0.0286 (6) | 0.0402 (7) | 0.0059 (5) | 0.0042 (5) | 0.0041 (5) |
| C4 | 0.0253 (5) | 0.0280 (6) | 0.0339 (6) | 0.0068 (4) | 0.0009 (4) | 0.0008 (5) |
| C6 | 0.0527 (8) | 0.0260 (6) | 0.0473 (8) | −0.0013 (6) | 0.0026 (6) | −0.0023 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0503 (8) | 0.0391 (7) | 0.0357 (7) | 0.0062 (6) | 0.0021 (6) | −0.0066 (5) |
| C8 | 0.0330 (6) | 0.0326 (6) | 0.0348 (7) | 0.0081 (5) | 0.0020 (5) | 0.0042 (5) |
| C9 | 0.0414 (7) | 0.0436 (7) | 0.0394 (7) | 0.0010 (6) | −0.0008 (6) | 0.0031 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0558 (9) | 0.0599 (10) | 0.0340 (7) | 0.0036 (7) | −0.0015 (6) | 0.0021 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0560 (9) | 0.0599 (10) | 0.0368 (7) | 0.0074 (7) | 0.0106 (6) | 0.0109 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0446 (8) | 0.0442 (8) | 0.0462 (8) | 0.0029 (6) | 0.0098 (6) | 0.0095 (6) |
| C13 | 0.0394 (7) | 0.0355 (7) | 0.0388 (7) | 0.0046 (5) | 0.0017 (5) | 0.0034 (5) |
| O1S | 0.0485 (6) | 0.0470 (6) | 0.0569 (7) | −0.0004 (5) | 0.0067 (5) | −0.0090 (5) |
| C1S | 0.0679 (12) | 0.0663 (12) | 0.0864 (14) | 0.0126 (10) | 0.0233 (11) | −0.0111 (11) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| N1—C2 | 1.3269 (17) | C7—H7A | 0.9700 |
| N1—C1 | 1.3681 (16) | C7—H7B | 0.9700 |
| N2—C1 | 1.3172 (17) | C7—H7C | 0.9700 |
| N2—N3 | 1.3846 (14) | C8—C9 | 1.393 (2) |
| N3—C4 | 1.3826 (16) | C8—C13 | 1.3939 (19) |
| N3—C2 | 1.3830 (15) | C9—C10 | 1.381 (2) |
| N4—C2 | 1.3330 (16) | C9—H9 | 0.9400 |
| N4—C3 | 1.3412 (18) | C10—C11 | 1.384 (2) |
| N5—C4 | 1.3226 (16) | C10—H10 | 0.9400 |
| N5—C3 | 1.3524 (16) | C11—C12 | 1.382 (2) |
| N6—C3 | 1.3330 (17) | C11—H11 | 0.9400 |
| N6—H6NA | 0.89 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.385 (2) |
| N6—H6NB | 0.86 (2) | C12—H12 | 0.9400 |
| N7—C4 | 1.3323 (16) | C13—H13 | 0.9400 |
| N7—C6 | 1.4594 (17) | O1S—C1S | 1.386 (2) |
| N7—C7 | 1.4617 (18) | O1S—H1S | 0.92 (2) |
| C1—C8 | 1.4709 (18) | C1S—H1S1 | 0.9700 |
| C6—H6A | 0.9700 | C1S—H1S2 | 0.9700 |
| C6—H6B | 0.9700 | C1S—H1S3 | 0.9700 |
| C6—H6C | 0.9700 | ||
| C2—N1—C1 | 103.31 (10) | N7—C7—H7A | 109.5 |
| C1—N2—N3 | 101.79 (10) | N7—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| C4—N3—C2 | 119.85 (11) | H7A—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| C4—N3—N2 | 130.72 (10) | N7—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C2—N3—N2 | 109.43 (10) | H7A—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C2—N4—C3 | 113.98 (11) | H7B—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C4—N5—C3 | 118.92 (11) | C9—C8—C13 | 119.13 (13) |
| C3—N6—H6NA | 121.0 (13) | C9—C8—C1 | 120.54 (12) |
| C3—N6—H6NB | 120.1 (13) | C13—C8—C1 | 120.33 (12) |
| H6NA—N6—H6NB | 118.3 (18) | C10—C9—C8 | 120.14 (14) |
| C4—N7—C6 | 126.56 (12) | C10—C9—H9 | 119.9 |
| C4—N7—C7 | 118.21 (11) | C8—C9—H9 | 119.9 |
| C6—N7—C7 | 115.01 (11) | C9—C10—C11 | 120.31 (15) |
| N2—C1—N1 | 116.27 (11) | C9—C10—H10 | 119.8 |
| N2—C1—C8 | 121.01 (11) | C11—C10—H10 | 119.8 |
| N1—C1—C8 | 122.72 (12) | C12—C11—C10 | 120.14 (14) |
| N1—C2—N4 | 128.12 (11) | C12—C11—H11 | 119.9 |
| N1—C2—N3 | 109.21 (11) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.9 |
| N4—C2—N3 | 122.66 (12) | C11—C12—C13 | 119.79 (14) |
| N6—C3—N4 | 117.28 (12) | C11—C12—H12 | 120.1 |
| N6—C3—N5 | 116.20 (13) | C13—C12—H12 | 120.1 |
| N4—C3—N5 | 126.52 (12) | C12—C13—C8 | 120.48 (13) |
| N5—C4—N7 | 119.54 (12) | C12—C13—H13 | 119.8 |
| N5—C4—N3 | 117.96 (11) | C8—C13—H13 | 119.8 |
| N7—C4—N3 | 122.50 (12) | C1S—O1S—H1S | 107.0 (13) |
| N7—C6—H6A | 109.5 | O1S—C1S—H1S1 | 109.5 |
| N7—C6—H6B | 109.5 | O1S—C1S—H1S2 | 109.5 |
| H6A—C6—H6B | 109.5 | H1S1—C1S—H1S2 | 109.5 |
| N7—C6—H6C | 109.5 | O1S—C1S—H1S3 | 109.5 |
| H6A—C6—H6C | 109.5 | H1S1—C1S—H1S3 | 109.5 |
| H6B—C6—H6C | 109.5 | H1S2—C1S—H1S3 | 109.5 |
| C1—N2—N3—C4 | 178.41 (12) | C6—N7—C4—N5 | 173.18 (12) |
| C1—N2—N3—C2 | −0.83 (12) | C7—N7—C4—N5 | −1.02 (18) |
| N3—N2—C1—N1 | 0.51 (14) | C6—N7—C4—N3 | −7.5 (2) |
| N3—N2—C1—C8 | 179.98 (10) | C7—N7—C4—N3 | 178.25 (11) |
| C2—N1—C1—N2 | 0.03 (14) | C2—N3—C4—N5 | −1.60 (17) |
| C2—N1—C1—C8 | −179.44 (11) | N2—N3—C4—N5 | 179.22 (11) |
| C1—N1—C2—N4 | 178.09 (12) | C2—N3—C4—N7 | 179.11 (11) |
| C1—N1—C2—N3 | −0.57 (13) | N2—N3—C4—N7 | −0.1 (2) |
| C3—N4—C2—N1 | −179.24 (12) | N2—C1—C8—C9 | 159.09 (13) |
| C3—N4—C2—N3 | −0.74 (18) | N1—C1—C8—C9 | −21.47 (19) |
| C4—N3—C2—N1 | −178.42 (10) | N2—C1—C8—C13 | −21.37 (18) |
| N2—N3—C2—N1 | 0.92 (13) | N1—C1—C8—C13 | 158.07 (12) |
| C4—N3—C2—N4 | 2.83 (18) | C13—C8—C9—C10 | 1.2 (2) |
| N2—N3—C2—N4 | −177.83 (11) | C1—C8—C9—C10 | −179.30 (14) |
| C2—N4—C3—N6 | 177.38 (11) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −0.5 (3) |
| C2—N4—C3—N5 | −2.68 (19) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −0.6 (3) |
| C4—N5—C3—N6 | −176.15 (11) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.9 (3) |
| C4—N5—C3—N4 | 3.9 (2) | C11—C12—C13—C8 | −0.2 (2) |
| C3—N5—C4—N7 | 177.83 (11) | C9—C8—C13—C12 | −0.8 (2) |
| C3—N5—C4—N3 | −1.48 (17) | C1—C8—C13—C12 | 179.66 (12) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1S—H1S···N1 | 0.92 (2) | 1.97 (2) | 2.8861 (16) | 172.8 (18) |
| N6—H6NB···N4i | 0.86 (2) | 2.11 (2) | 2.9679 (17) | 178.8 (18) |
| N6—H6NA···O1Si | 0.89 (2) | 2.398 (19) | 3.0280 (18) | 128.3 (16) |
| C6—H6C···N2 | 0.97 | 2.08 | 2.8753 (18) | 138. |
| C6—H6C···N3 | 0.97 | 2.54 | 2.9484 (17) | 105. |
| C7—H7A···N5 | 0.97 | 2.22 | 2.6788 (18) | 108. |
| C7—H7C···O1Sii | 0.97 | 2.48 | 3.4438 (19) | 176. |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, −y+2, −z+1; (ii) −x+2, −y+1, −z+1.
Footnotes
Part 11 in the series ‘Fused heterocyclic systems with an s-triazine ring’. For Part 10, see Dolzhenko et al. (2008).
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: FB2109).
References
- Bruker (2001). SMART and SAINT Bruker AXS GmbH, Karlsruhe, Germany.
- Dolzhenko, A. V., Dolzhenko, A. V. & Chui, W. K. (2006). Heterocycles, 68, 1723–1759.
- Dolzhenko, A. V., Dolzhenko, A. V. & Chui, W. K. (2007). Heterocycles, 71, 429–436.
- Dolzhenko, A. V., Tan, B. J., Dolzhenko, A. V., Chiu, G. N. C. & Chui, W. K. (2008). J. Fluorine Chem.129, 429–434.
- Gilardi, R. D. (1973). Acta Cryst. B29, 2089–2095.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2001). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808030481/fb2109sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808030481/fb2109Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




