Abstract
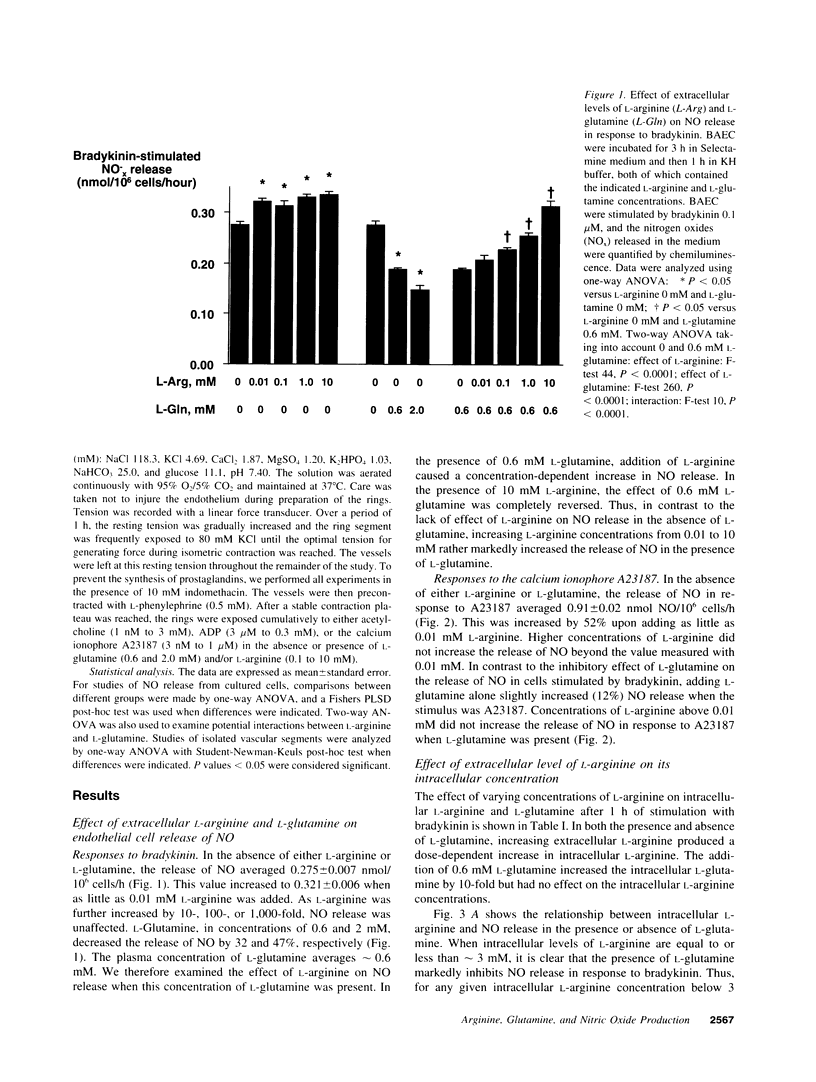
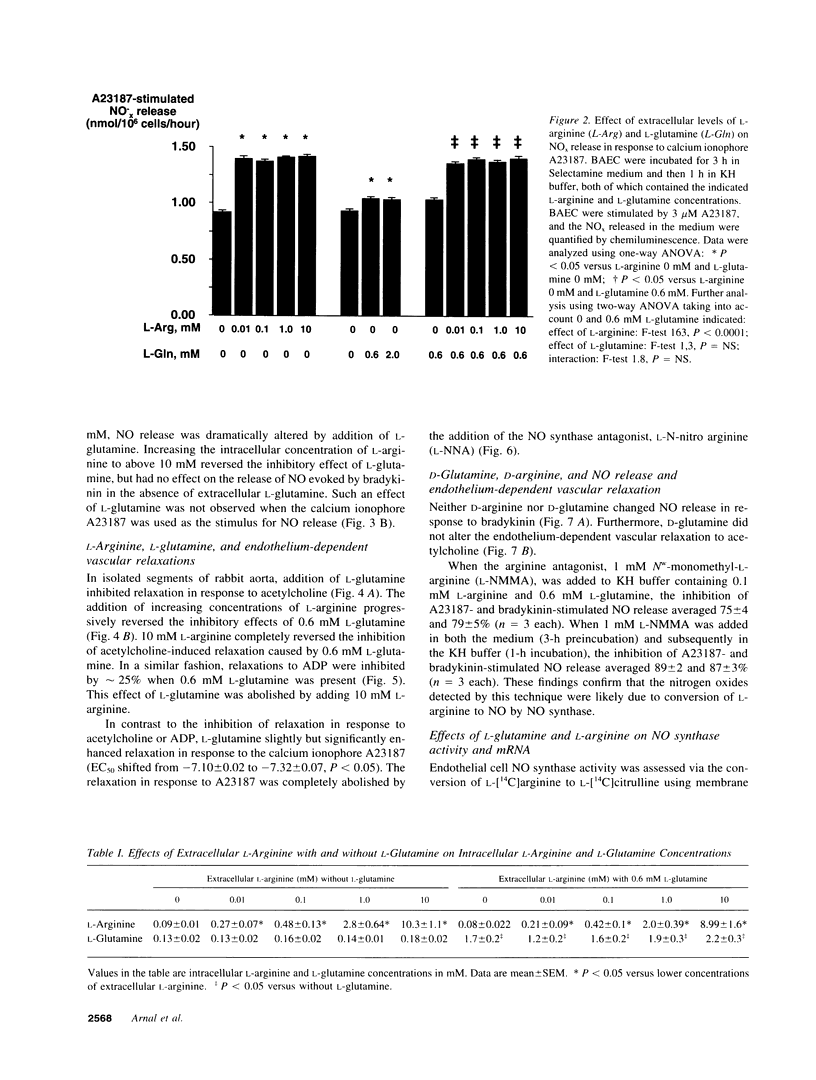
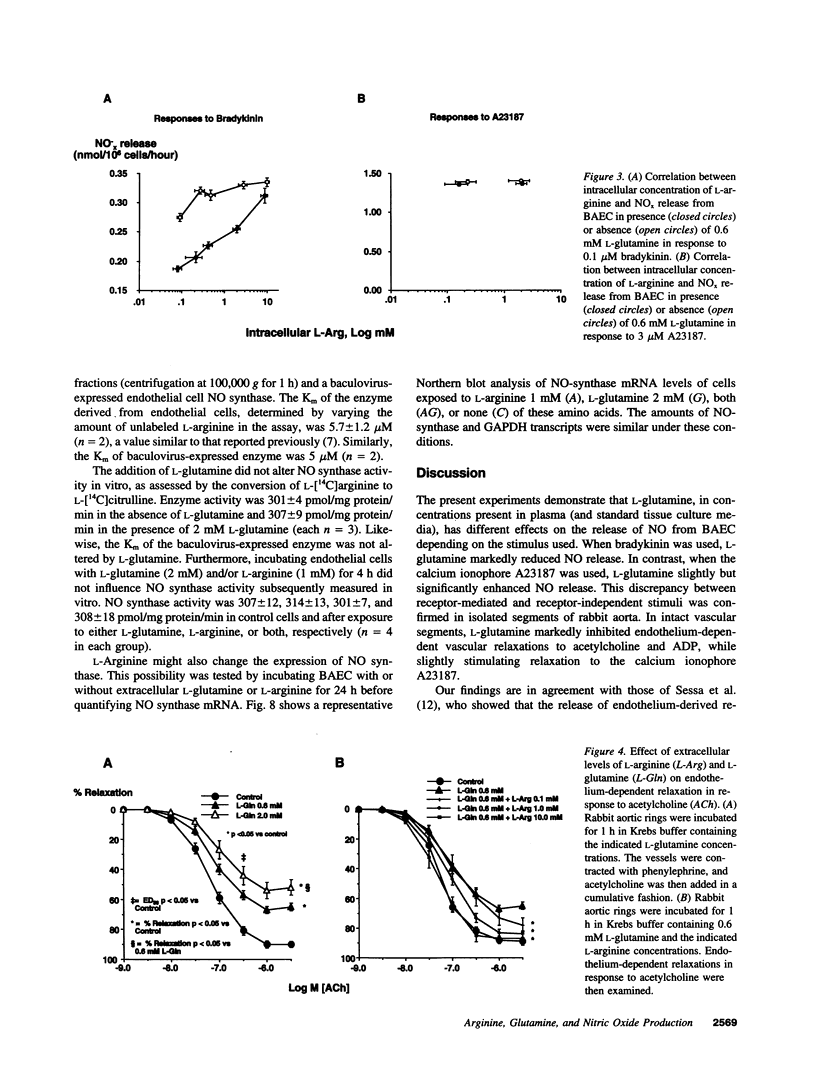
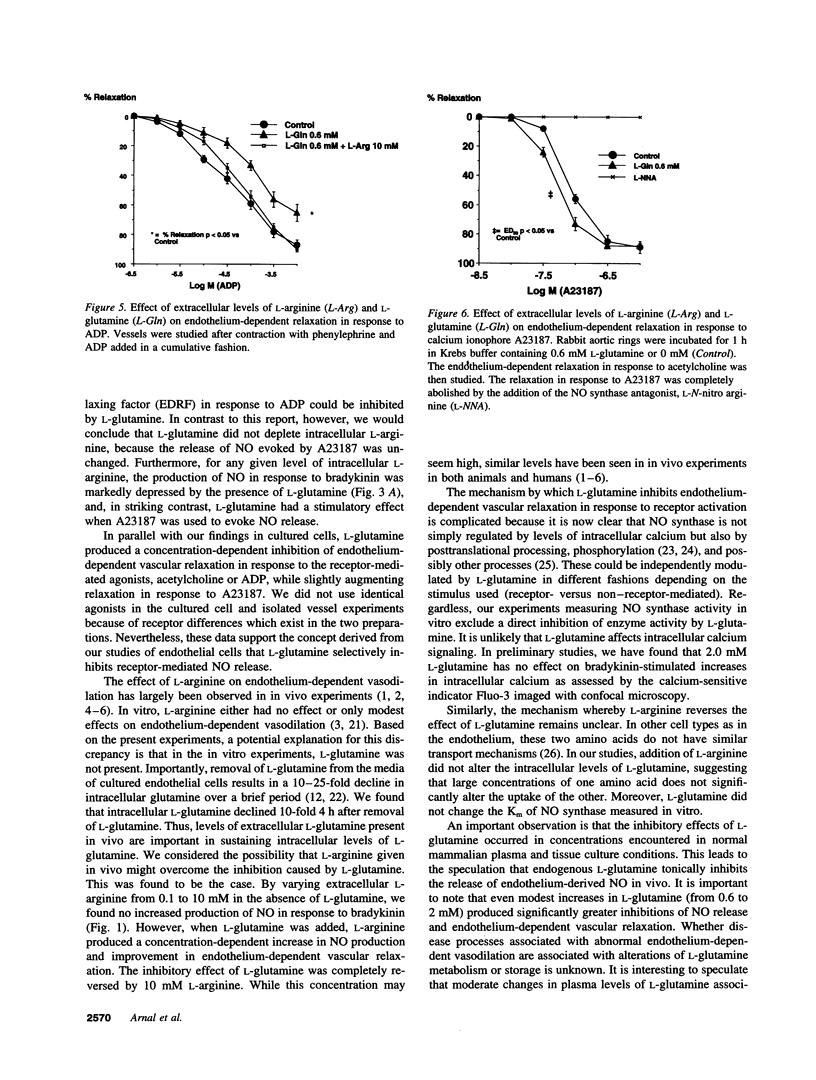
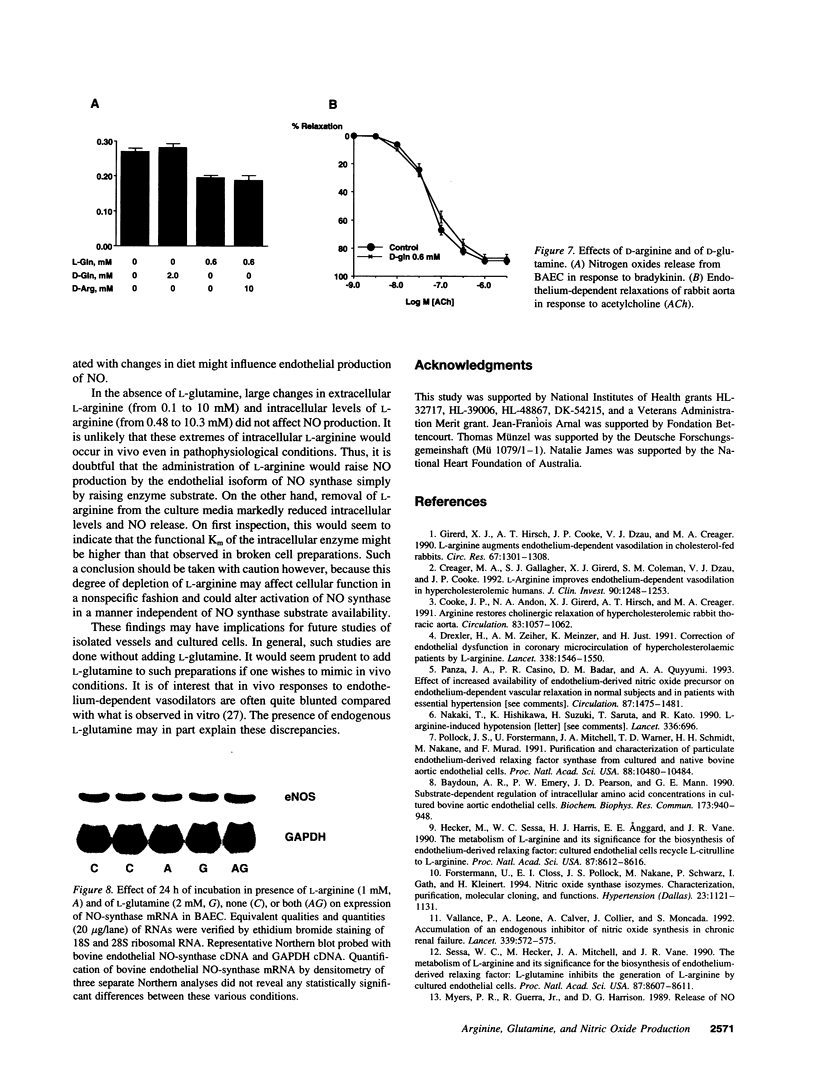
The effect of extracellular L-arginine and L-glutamine on nitric oxide (NO) release was studied in cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells and in rabbit aortic rings. Increasing L-arginine (0.01 to 10 mM) did not alter NO release from cultured endothelial cells or modify endothelium-dependent relaxation to acetylcholine in isolated vessels. L-Glutamine (0.6 and 2 mM) inhibited NO release from cultured cells (in response to bradykinin) and from aortic rings (in response to acetylcholine or ADP). L-Arginine (0.1-10 mM) dose-dependently reversed the L-glutamine inhibition of receptor-stimulated NO release in both models. In contrast to its inhibitory response to receptor-mediated stimuli, glutamine alone slightly potentiated NO release in both models when the calcium ionophore, A23187, was added. Furthermore, cultured cells incubated with L-arginine (0.01-10 mM), in the presence or absence of glutamine, released similar amounts of NO in response to A23187. L-Glutamine did not affect intracellular L-arginine levels. Neither D-glutamine nor D-arginine affected NO release or endothelium-dependent vascular relaxation. L-Glutamine had no effect on the activity of endothelial NOS assessed by L-arginine to L-citrulline conversion. These findings show that in the absence of L-glutamine, manipulating intracellular L-arginine levels over a wide range does not affect NO release. L-Glutamine in concentrations circulating in vivo may tonically inhibit receptor-mediated NO release by interfering with signal transduction. One mechanism by which L-arginine may enhance NO release is via reversal of the inhibitory effect of L-glutamine, but apparently independently of enhancing NO synthase substrate.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnal J. F., Yamin J., Dockery S., Harrison D. G. Regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase mRNA, protein, and activity during cell growth. Am J Physiol. 1994 Nov;267(5 Pt 1):C1381–C1388. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.267.5.C1381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baydoun A. R., Emery P. W., Pearson J. D., Mann G. E. Substrate-dependent regulation of intracellular amino acid concentrations in cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Dec 31;173(3):940–948. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80876-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braman R. S., Hendrix S. A. Nanogram nitrite and nitrate determination in environmental and biological materials by vanadium (III) reduction with chemiluminescence detection. Anal Chem. 1989 Dec 15;61(24):2715–2718. doi: 10.1021/ac00199a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Ferris C. D., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide synthase regulatory sites. Phosphorylation by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, protein kinase C, and calcium/calmodulin protein kinase; identification of flavin and calmodulin binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):10976–10981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Isolation of nitric oxide synthetase, a calmodulin-requiring enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):682–685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussolati O., Sala R., Astorri A., Rotoli B. M., Dall'Asta V., Gazzola G. C. Characterization of amino acid transport in human endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1993 Oct;265(4 Pt 1):C1006–C1014. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.4.C1006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke J. P., Andon N. A., Girerd X. J., Hirsch A. T., Creager M. A. Arginine restores cholinergic relaxation of hypercholesterolemic rabbit thoracic aorta. Circulation. 1991 Mar;83(3):1057–1062. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.83.3.1057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creager M. A., Gallagher S. J., Girerd X. J., Coleman S. M., Dzau V. J., Cooke J. P. L-arginine improves endothelium-dependent vasodilation in hypercholesterolemic humans. J Clin Invest. 1992 Oct;90(4):1248–1253. doi: 10.1172/JCI115987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drexler H., Zeiher A. M., Meinzer K., Just H. Correction of endothelial dysfunction in coronary microcirculation of hypercholesterolaemic patients by L-arginine. Lancet. 1991 Dec 21;338(8782-8783):1546–1550. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92372-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förstermann U., Closs E. I., Pollock J. S., Nakane M., Schwarz P., Gath I., Kleinert H. Nitric oxide synthase isozymes. Characterization, purification, molecular cloning, and functions. Hypertension. 1994 Jun;23(6 Pt 2):1121–1131. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.23.6.1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girerd X. J., Hirsch A. T., Cooke J. P., Dzau V. J., Creager M. A. L-arginine augments endothelium-dependent vasodilation in cholesterol-fed rabbits. Circ Res. 1990 Dec;67(6):1301–1308. doi: 10.1161/01.res.67.6.1301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecker M., Sessa W. C., Harris H. J., Anggård E. E., Vane J. R. The metabolism of L-arginine and its significance for the biosynthesis of endothelium-derived relaxing factor: cultured endothelial cells recycle L-citrulline to L-arginine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8612–8616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leighton B., Curi R., Hussein A., Newsholme E. A. Maximum activities of some key enzymes of glycolysis, glutaminolysis, Krebs cycle and fatty acid utilization in bovine pulmonary endothelial cells. FEBS Lett. 1987 Dec 10;225(1-2):93–96. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81137-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludmer P. L., Selwyn A. P., Shook T. L., Wayne R. R., Mudge G. H., Alexander R. W., Ganz P. Paradoxical vasoconstriction induced by acetylcholine in atherosclerotic coronary arteries. N Engl J Med. 1986 Oct 23;315(17):1046–1051. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198610233151702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel T., Li G. K., Busconi L. Phosphorylation and subcellular translocation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6252–6256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers P. R., Guerra R., Jr, Harrison D. G. Release of NO and EDRF from cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Apr;256(4 Pt 2):H1030–H1037. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.256.4.H1030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mügge A., Harrison D. G. L-arginine does not restore endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerotic rabbit aorta in vitro. Blood Vessels. 1991;28(5):354–357. doi: 10.1159/000158881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mügge A., Peterson T., Harrison D. G. Release of nitrogen oxides from cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells is not impaired by calcium channel antagonists. Circulation. 1991 Apr;83(4):1404–1409. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.83.4.1404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaki T., Hishikawa K., Suzuki H., Saruta T., Kato R. L-arginine-induced hypotension. Lancet. 1990 Sep 15;336(8716):696–696. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92196-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C., Xie Q. W. Regulation of biosynthesis of nitric oxide. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 13;269(19):13725–13728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida K., Harrison D. G., Navas J. P., Fisher A. A., Dockery S. P., Uematsu M., Nerem R. M., Alexander R. W., Murphy T. J. Molecular cloning and characterization of the constitutive bovine aortic endothelial cell nitric oxide synthase. J Clin Invest. 1992 Nov;90(5):2092–2096. doi: 10.1172/JCI116092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panza J. A., Casino P. R., Badar D. M., Quyyumi A. A. Effect of increased availability of endothelium-derived nitric oxide precursor on endothelium-dependent vascular relaxation in normal subjects and in patients with essential hypertension. Circulation. 1993 May;87(5):1475–1481. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.87.5.1475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock J. S., Förstermann U., Mitchell J. A., Warner T. D., Schmidt H. H., Nakane M., Murad F. Purification and characterization of particulate endothelium-derived relaxing factor synthase from cultured and native bovine aortic endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10480–10484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sessa W. C., Hecker M., Mitchell J. A., Vane J. R. The metabolism of L-arginine and its significance for the biosynthesis of endothelium-derived relaxing factor: L-glutamine inhibits the generation of L-arginine by cultured endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8607–8611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallance P., Leone A., Calver A., Collier J., Moncada S. Accumulation of an endogenous inhibitor of nitric oxide synthesis in chronic renal failure. Lancet. 1992 Mar 7;339(8793):572–575. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90865-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




