Abstract
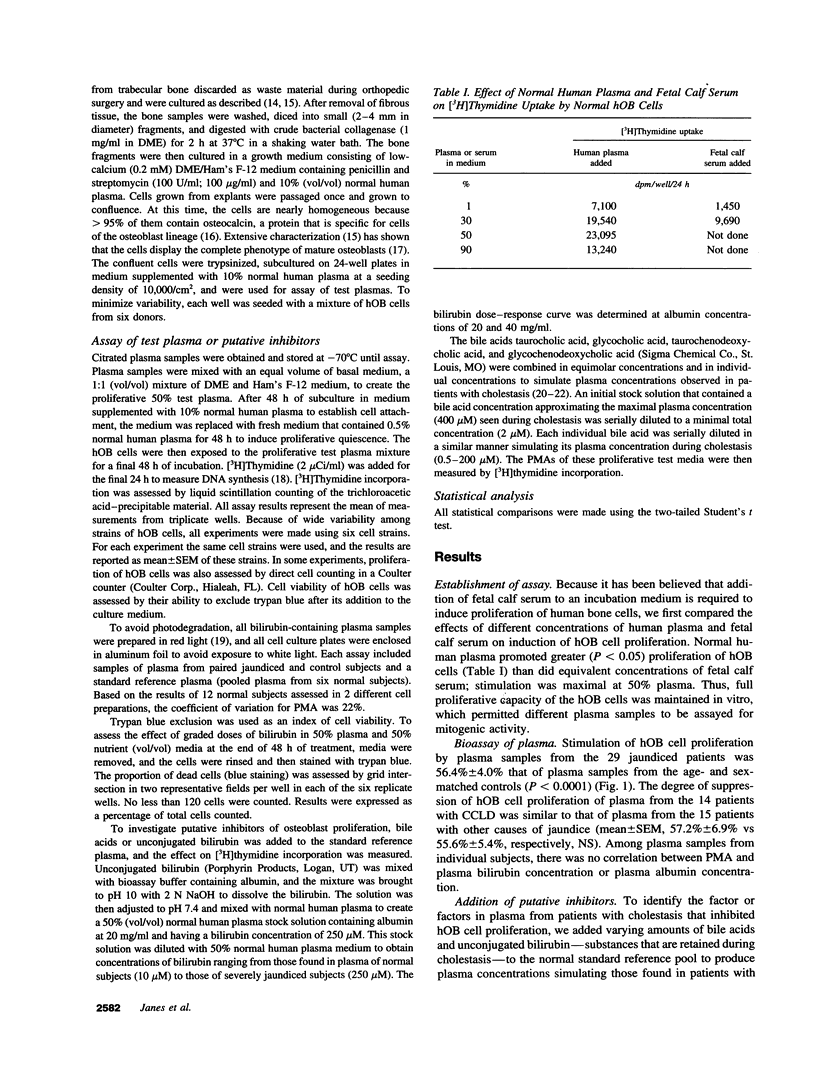
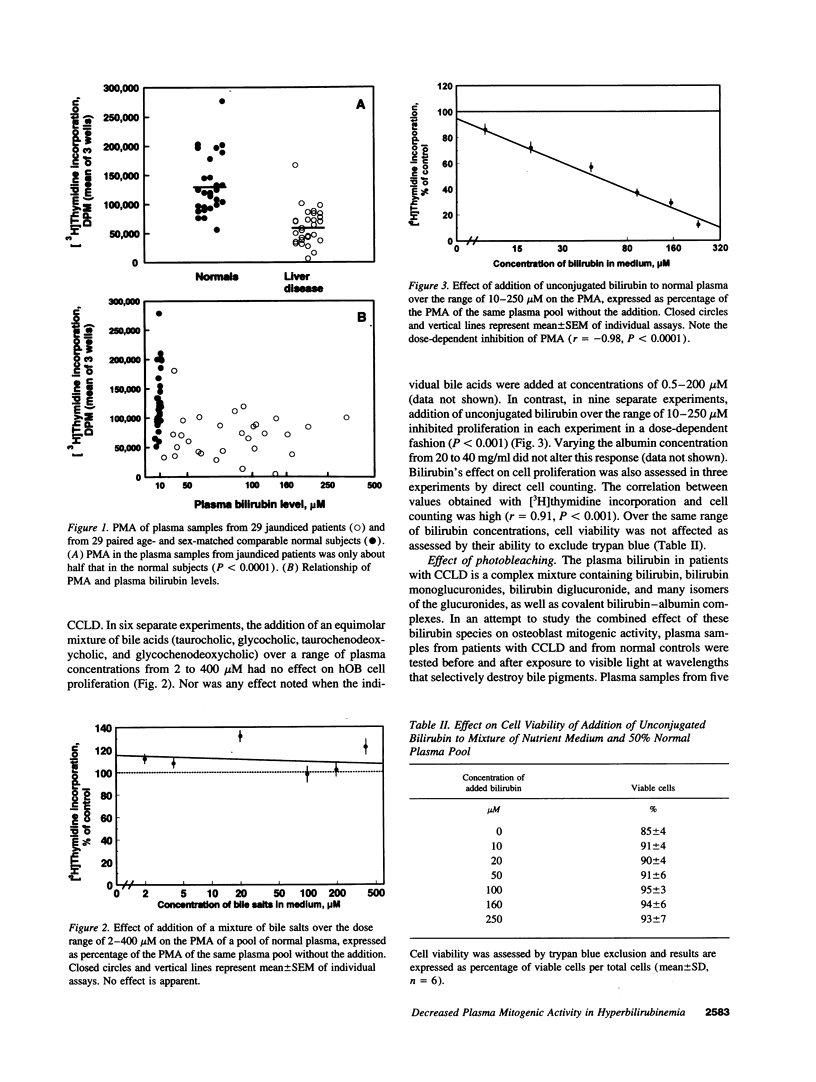
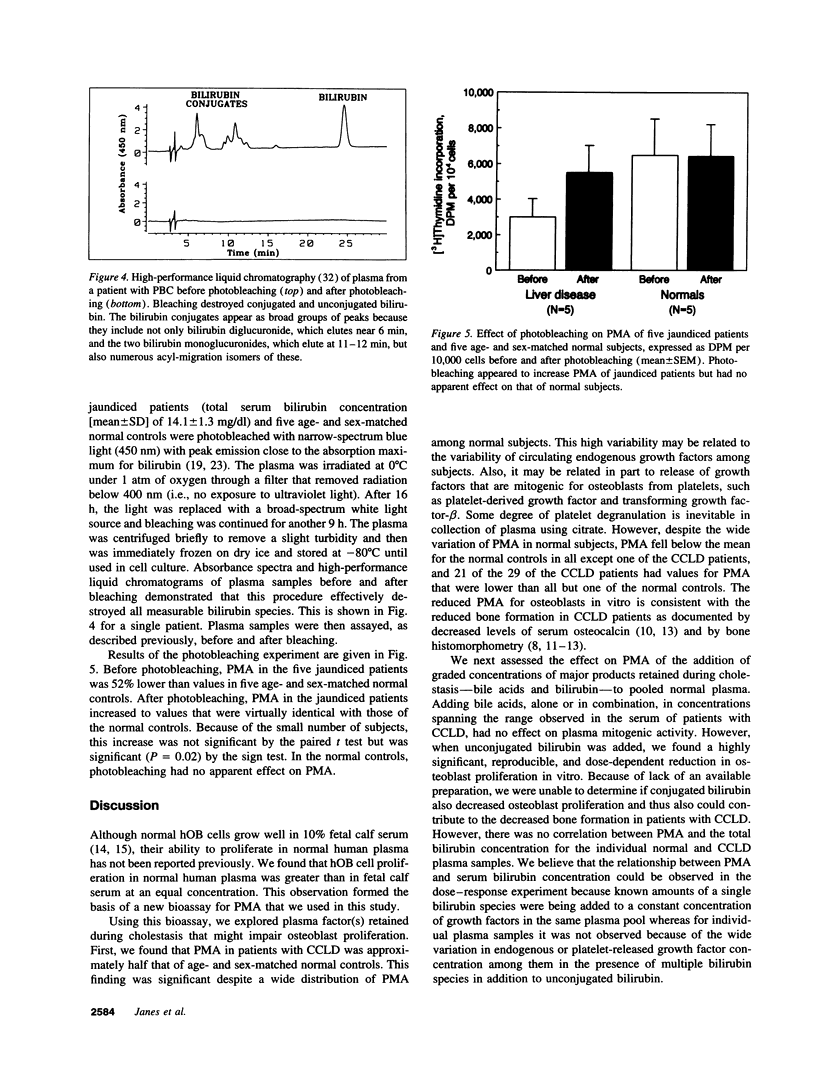
Because the osteoporosis occurring in chronic cholestatic liver disease (CCLD) is associated with decreased bone formation and is reversible by liver transplantation, substances retained in plasma during cholestasis may impair osteoblast function. This hypothesis was tested using a new bioassay that measures plasma mitogenic activity (PMA) for normal human osteoblast-like (hOB) cells. In 29 jaundiced patients, mean PMA was 56.4% (P < 0.001) of that in 29 age- and sex-matched normal subjects, and the decrease in PMA was similar in the 14 with CCLD and the 15 with other causes of jaundice. Bile acids and bilirubin are the two major groups of products retained during cholestasis. The common conjugated bile acids and bilirubin were added to normal human plasma in concentrations simulating those found in patients with CCLD. Various bile salts had no effect on PMA whereas unconjugated bilirubin decreased PMA in a dose-dependent fashion (r = -0.98, P < 0.0001) without affecting cell viability. Relatively selective removal of bilirubin from the plasma by photobleaching normalized the decreased PMA in five jaundiced patients but produced no apparent change in five normal subjects. These data support the hypothesis that hyperbilirubinemia or possibly other photolabile substances impair osteoblast proliferative capacity and thus may play a major role in the pathogenesis of the osteoporosis associated with CCLD.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AHRENS E. H., Jr, PAYNE M. A., KUNKEL H. G., EISENMENGER W. J., BLONDHEIM S. H. Primary biliary cirrhosis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1950 Dec;29(4):299–364. doi: 10.1097/00005792-195012000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ATKINSON M., NORDIN B. E., SHERLOCK S. Malabsorption and bone disease in prolonged obstructive jaundice. Q J Med. 1956 Jul;25(99):299–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz E. W., Jr, Getz M. J., Wells D. J., Moses H. L. Nuclear RNA polymerase activities and poly(A)-containing mRNA accumulation in cultured AKR mouse embryo cells stimulated to proliferate. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Aug;108(1):157–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowger M. L., Igo R. P., Labbe R. F. The mechanism of bilirubin toxicity studied with purified respiratory enzyme and tissue culture systems. Biochemistry. 1965 Dec;4(12):2763–2770. doi: 10.1021/bi00888a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond T. H., Stiel D., Lunzer M., McDowall D., Eckstein R. P., Posen S. Hepatic osteodystrophy. Static and dynamic bone histomorphometry and serum bone Gla-protein in 80 patients with chronic liver disease. Gastroenterology. 1989 Jan;96(1):213–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dibble J. B., Sheridan P., Losowsky M. S. A survey of vitamin D deficiency in gastrointestinal and liver disorders. Q J Med. 1984 Winter;53(209):119–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERNSTER L., ZETTERSTROM R. Bilirubin, an uncoupler of oxidative phosphorylation in isolated mitochondria. Nature. 1956 Dec 15;178(4546):1335–1337. doi: 10.1038/1781335a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastell R., Dickson E. R., Hodgson S. F., Wiesner R. H., Porayko M. K., Wahner H. W., Cedel S. L., Riggs B. L., Krom R. A. Rates of vertebral bone loss before and after liver transplantation in women with primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1991 Aug;14(2):296–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksen E. F., Colvard D. S., Berg N. J., Graham M. L., Mann K. G., Spelsberg T. C., Riggs B. L. Evidence of estrogen receptors in normal human osteoblast-like cells. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):84–86. doi: 10.1126/science.3388021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guañabens N., Parés A., Mariñoso L., Brancós M. A., Piera C., Serrano S., Rivera F., Rodés J. Factors influencing the development of metabolic bone disease in primary biliary cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1990 Oct;85(10):1356–1362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay J. E., Lindor K. D., Wiesner R. H., Dickson E. R., Krom R. A., LaRusso N. F. The metabolic bone disease of primary sclerosing cholangitis. Hepatology. 1991 Aug;14(2):257–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson S. F., Dickson E. R., Wahner H. W., Johnson K. A., Mann K. G., Riggs B. L. Bone loss and reduced osteoblast function in primary biliary cirrhosis. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Dec;103(6 ):855–860. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-6-855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long R. G., Skinner R. K., Wills M. R., Sherlock S. Serum-25-hydroxy-vitamin-D in untreated parenchymal and cholestatic liver disease. Lancet. 1976 Sep 25;2(7987):650–652. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92463-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markus B. H., Dickson E. R., Grambsch P. M., Fleming T. R., Mazzaferro V., Klintmalm G. B., Wiesner R. H., Van Thiel D. H., Starzl T. E. Efficiency of liver transplantation in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jun 29;320(26):1709–1713. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198906293202602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matloff D. S., Kaplan M. M., Neer R. M., Goldberg M. J., Bitman W., Wolfe H. J. Osteoporosis in primary biliary cirrhosis: effects of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 treatment. Gastroenterology. 1982 Jul;83(1 Pt 1):97–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonagh A. F., Lightner D. A. Hepatic uptake, transport and metabolism of alkylated bilirubins in Gunn rats and Sprague-Dawley rats. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 1994 Nov;40(7):965–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonagh A. F. The role of singlet oxygen in bilirubin photo-oxidation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Sep 17;44(6):1306–1311. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80228-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notter M. F., Kendig J. W. Differential sensitivity of neural cells to bilirubin toxicity. Exp Neurol. 1986 Dec;94(3):670–682. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(86)90246-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porayko M. K., Wiesner R. H., Hay J. E., Krom R. A., Dickson E. R., Beaver S., Schwerman L. Bone disease in liver transplant recipients: incidence, timing, and risk factors. Transplant Proc. 1991 Feb;23(1 Pt 2):1462–1465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raedsch R., Lauterburg B. H., Hofmann A. F. Altered bile acid metabolism in primary biliary cirrhosis. Dig Dis Sci. 1981 May;26(5):394–401. doi: 10.1007/BF01313580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen L. F., Wennberg R. P. Pharmacologic modification of bilirubin toxicity in tissue culture cells. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1972 May;3(3):567–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robey P. G., Termine J. D. Human bone cells in vitro. Calcif Tissue Int. 1985 Sep;37(5):453–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellon A. J., Davies A., Compston J., Williams R. Osteoporosis in chronic cholestatic liver disease. Q J Med. 1985 Nov;57(223):783–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellon A. J., Webb A., Compston J., Williams R. Low bone turnover state in primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1987 Jan-Feb;7(1):137–142. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiehl A. Disturbances of bile acid metabolism in cholestasis. Clin Gastroenterol. 1977 Jan;6(1):45–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thaler M. M. Bilirubin toxicity in hepatoma cells. Nat New Biol. 1971 Apr 14;230(15):218–219. doi: 10.1038/newbio230218a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilopoulou-Sellin R., Oyedeji C. O., Samaan N. A. Bilirubin inhibits cartilage metabolism and growth in vitro. Metabolism. 1989 Aug;38(8):759–762. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(89)90062-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilopoulou-Sellin R., Rey-Bear N., Oyedeji C. O. Bilirubin as an inhibitor of cartilage metabolism: effect on avian chondrocyte proliferation in cell culture. J Bone Miner Res. 1990 Jul;5(7):769–774. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650050714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Berge Henegouwen G. P., Brandt K. H., Eyssen H., Parmentier G. Sulphated and unsulphated bile acids in serum, bile, and urine of patients with cholestasis. Gut. 1976 Nov;17(11):861–869. doi: 10.1136/gut.17.11.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



