Abstract
In the title compound, C20H17ClN4O2S, the dihedral angle between the two benzene rings is 65.9 (1)°; the corresponding angle between the 4-chlorophenyl and thiadiazole rings is 3.4 (8)°. The conformations of the N—H and C=O bonds are anti with respect to each other. The enone groups show a trans configuration. The structure displays intermolecular N—H⋯O, C—H⋯N, C—H⋯S and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonding.
Related literature
For 1,3,4-thiadiazole scaffold compounds and their biological activity, see: Tu et al. (2008 ▶). For the synthesis, see: Foroumadi et al. (1999 ▶); Levy & Palmer (1942 ▶); Song et al. (1992 ▶). For related structures, see: Fun et al. (2008 ▶); Gowda et al. (2008 ▶) Thiruvalluvar et al. (2008 ▶).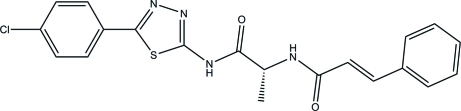
Experimental
Crystal data
C20H17ClN4O2S
M r = 412.89
Orthorhombic,

a = 6.6324 (15) Å
b = 8.575 (2) Å
c = 34.367 (8) Å
V = 1954.6 (8) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.33 mm−1
T = 296 (2) K
0.41 × 0.17 × 0.07 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: none
14721 measured reflections
4706 independent reflections
2807 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.046
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.043
wR(F 2) = 0.099
S = 1.02
4706 reflections
254 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.15 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.20 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), 1876 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: −0.12 (7)
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2004 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2004 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: APEX2; software used to prepare material for publication: APEX2 and publCIF (Westrip, 2008 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808030353/gw2052sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808030353/gw2052Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2A⋯O1i | 0.86 | 1.94 | 2.802 (3) | 175 |
| C7—H7A⋯N3ii | 0.93 | 2.54 | 3.446 (3) | 164 |
| C11—H11C⋯S1iii | 0.96 | 2.77 | 3.526 (3) | 136 |
| C20—H20A⋯O2iv | 0.93 | 2.48 | 3.380 (3) | 162 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  .
.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
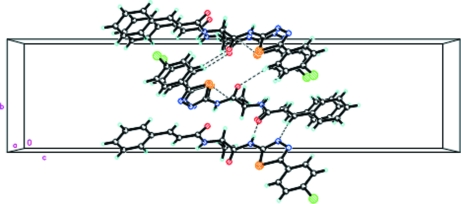
In our previous work, 1,3,4-thiadiazole scaffold compounds and their biological activity have been studied (Tu et al., 2008). In view of the importance of these organic materials, the title compound (Fig. 1) was synthesized (Foroumadi et al., 1999; Levy & Palmer 1942; Song et al., 1992) and its crystal structure is reported here. The structure of title compound, C20H17ClN4O2S, has orthorhombic (P212121) symmetry. The dihedral angles between the p-cholobenzene and thiadiazol rings is 3.4 (8) °, the corresponding values between the two benzene rings are measured to 65.9 (1)°. The conformations of the N—H and C=O bonds are anti with respect to each other. The enone groups are trans configurated. Bond lengths and angles are in normal ranges and comparable to those in related structures (Gowda et al., 2008; Fun et al., 2008; Thiruvalluvar et al., 2008). In the crystal structure, molecules are linked through intermolecular hydrogen bonds forming a three-dimensional network (Table 1, Figure 2).
Experimental
N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (5.7 mmol) was added to a cooled solution of N-cinnamoyl-D-alanine (5.6 mmol) and N-hydroxysuccinimide (5.6 mmol) in freshly distillation dioxane (30 ml). The reaction mixture was stirred overnight at room temperature. The insoluble material was filtered off and washed with cold dioxane. 2-Amino-5-(4-choloxyphenyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazole (5.5 mmol) was added to the filtrate and the reaction mixture was stirred for 48 hr at room temperature. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The residual was dissolved in EtOAc and the insoluble material was filtered off. The filtrate was washed successively with saturated Na2CO3 solution(20 ml, x 3), water(20 ml, x 1), 0.1 M HCl(20 ml, x 3) and water(20 ml, x 1). The organic layer evaporated in vacuo, the residual was recrystallized from methanol. Colorless block-shaped single crystals of the title compound suitable for X-ray diffraction analysis precipitated after several days.
Refinement
H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model using SHELXL97 default values (Uĩso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(C) for CH and CH2 groups and Uĩso(H) = 1.5 Ueq(C) for CH3). Refinement with all data (Friedel opposites not merged) led to an unsuitably large error of the Flack parameter. The final refinement was therefore performed with a data set with merged Friedel pairs, hence the calculated Flack parameter is meaningless. The absolute configuration is nevertheless undoubtly as described since enantiomerically pure starting compounds were used and the reaction conditions are not condidered to lead to racemization or inversion.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of the title compound. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
The crystal packing of title compound, viewed along the a axis with hydrogen bonds drawn as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C20H17ClN4O2S | Dx = 1.403 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 412.89 | Melting point: 480 K |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 3308 reflections |
| a = 6.6324 (15) Å | θ = 2.4–21.0° |
| b = 8.575 (2) Å | µ = 0.33 mm−1 |
| c = 34.367 (8) Å | T = 296 K |
| V = 1954.6 (8) Å3 | Bolck, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.41 × 0.18 × 0.07 mm |
| F(000) = 856 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer | 2807 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.046 |
| graphite | θmax = 28.4°, θmin = 2.4° |
| φ and ω scans | h = −8→8 |
| 14721 measured reflections | k = −11→11 |
| 4706 independent reflections | l = −45→44 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.043 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.099 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0226P)2 + 0.0747P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.02 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 4706 reflections | Δρmax = 0.15 e Å−3 |
| 254 parameters | Δρmin = −0.20 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 1876 Friedel pairs |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Flack parameter: −0.12 (7) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.6789 (5) | 0.2710 (4) | 0.19355 (8) | 0.0782 (9) | |
| H1B | 0.6067 | 0.2030 | 0.1777 | 0.094* | |
| C2 | 0.6159 (6) | 0.2979 (4) | 0.23129 (10) | 0.0996 (13) | |
| H2B | 0.5024 | 0.2468 | 0.2408 | 0.120* | |
| C3 | 0.7184 (6) | 0.3981 (5) | 0.25465 (9) | 0.0977 (12) | |
| H3B | 0.6745 | 0.4158 | 0.2800 | 0.117* | |
| C4 | 0.8862 (6) | 0.4732 (4) | 0.24098 (8) | 0.0937 (12) | |
| H4B | 0.9551 | 0.5434 | 0.2568 | 0.112* | |
| C5 | 0.9526 (5) | 0.4443 (4) | 0.20360 (8) | 0.0756 (9) | |
| H5A | 1.0692 | 0.4927 | 0.1947 | 0.091* | |
| C6 | 0.8481 (5) | 0.3443 (3) | 0.17924 (7) | 0.0613 (8) | |
| C7 | 0.9087 (5) | 0.3172 (3) | 0.13882 (7) | 0.0612 (8) | |
| H7A | 0.8246 | 0.2533 | 0.1242 | 0.073* | |
| C8 | 1.0669 (4) | 0.3722 (3) | 0.12100 (7) | 0.0584 (7) | |
| H8A | 1.1579 | 0.4314 | 0.1353 | 0.070* | |
| C9 | 1.1094 (4) | 0.3464 (3) | 0.07984 (7) | 0.0523 (7) | |
| C10 | 1.3357 (4) | 0.4044 (3) | 0.02573 (6) | 0.0483 (6) | |
| H10A | 1.3421 | 0.2934 | 0.0190 | 0.058* | |
| C11 | 1.5445 (4) | 0.4755 (3) | 0.02035 (8) | 0.0626 (8) | |
| H11A | 1.6384 | 0.4245 | 0.0374 | 0.094* | |
| H11B | 1.5397 | 0.5847 | 0.0264 | 0.094* | |
| H11C | 1.5870 | 0.4619 | −0.0061 | 0.094* | |
| C12 | 1.1836 (4) | 0.4831 (3) | −0.00072 (7) | 0.0494 (6) | |
| C13 | 1.0385 (4) | 0.4721 (3) | −0.06496 (7) | 0.0471 (6) | |
| C14 | 0.7573 (4) | 0.5583 (3) | −0.10172 (6) | 0.0494 (6) | |
| C15 | 0.5693 (4) | 0.6256 (3) | −0.11652 (7) | 0.0490 (6) | |
| C16 | 0.4931 (5) | 0.5842 (3) | −0.15249 (7) | 0.0639 (7) | |
| H16A | 0.5625 | 0.5115 | −0.1675 | 0.077* | |
| C17 | 0.3163 (5) | 0.6479 (3) | −0.16687 (8) | 0.0669 (8) | |
| H17A | 0.2679 | 0.6198 | −0.1913 | 0.080* | |
| C18 | 0.2142 (4) | 0.7538 (3) | −0.14421 (8) | 0.0589 (7) | |
| C19 | 0.2848 (5) | 0.7959 (3) | −0.10843 (8) | 0.0637 (8) | |
| H19A | 0.2137 | 0.8676 | −0.0935 | 0.076* | |
| C20 | 0.4600 (4) | 0.7328 (3) | −0.09455 (8) | 0.0591 (7) | |
| H20A | 0.5068 | 0.7619 | −0.0701 | 0.071* | |
| Cl1 | −0.00738 (13) | 0.83679 (9) | −0.16181 (2) | 0.0835 (3) | |
| N1 | 1.2732 (3) | 0.4188 (2) | 0.06588 (5) | 0.0537 (5) | |
| H1A | 1.3436 | 0.4758 | 0.0813 | 0.064* | |
| N2 | 1.1824 (3) | 0.4305 (2) | −0.03825 (5) | 0.0525 (5) | |
| H2A | 1.2768 | 0.3681 | −0.0455 | 0.063* | |
| N3 | 1.0265 (4) | 0.4021 (3) | −0.09856 (6) | 0.0590 (6) | |
| N4 | 0.8619 (4) | 0.4535 (2) | −0.12001 (6) | 0.0585 (6) | |
| O1 | 1.0027 (3) | 0.2679 (2) | 0.05768 (5) | 0.0672 (5) | |
| O2 | 1.0712 (3) | 0.5869 (2) | 0.00979 (5) | 0.0638 (5) | |
| S1 | 0.85258 (10) | 0.60793 (7) | −0.056449 (17) | 0.05201 (18) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.081 (3) | 0.090 (2) | 0.0635 (18) | −0.017 (2) | 0.0140 (18) | −0.0047 (16) |
| C2 | 0.112 (4) | 0.116 (3) | 0.070 (2) | −0.030 (3) | 0.029 (2) | −0.004 (2) |
| C3 | 0.110 (3) | 0.124 (3) | 0.0594 (19) | −0.021 (3) | 0.021 (2) | −0.006 (2) |
| C4 | 0.113 (3) | 0.114 (3) | 0.0541 (18) | −0.028 (3) | 0.0073 (19) | −0.0090 (18) |
| C5 | 0.080 (2) | 0.093 (2) | 0.0539 (17) | −0.0173 (19) | 0.0071 (16) | −0.0014 (15) |
| C6 | 0.068 (2) | 0.0673 (18) | 0.0484 (14) | −0.0030 (16) | 0.0023 (14) | 0.0034 (12) |
| C7 | 0.075 (2) | 0.0623 (16) | 0.0465 (15) | −0.0090 (16) | −0.0007 (15) | 0.0002 (13) |
| C8 | 0.0591 (19) | 0.0670 (17) | 0.0490 (15) | −0.0077 (15) | 0.0026 (13) | −0.0025 (13) |
| C9 | 0.0530 (19) | 0.0535 (15) | 0.0503 (14) | −0.0074 (13) | −0.0006 (13) | 0.0012 (12) |
| C10 | 0.0448 (15) | 0.0539 (14) | 0.0464 (13) | −0.0036 (14) | 0.0008 (12) | −0.0019 (11) |
| C11 | 0.0491 (19) | 0.0728 (18) | 0.0658 (17) | −0.0078 (15) | 0.0092 (14) | −0.0079 (14) |
| C12 | 0.0496 (18) | 0.0524 (15) | 0.0460 (14) | −0.0044 (13) | 0.0050 (12) | −0.0053 (11) |
| C13 | 0.0461 (16) | 0.0516 (13) | 0.0437 (13) | 0.0004 (12) | 0.0065 (12) | −0.0024 (11) |
| C14 | 0.0524 (18) | 0.0529 (15) | 0.0428 (13) | −0.0032 (13) | 0.0074 (12) | −0.0003 (11) |
| C15 | 0.0502 (17) | 0.0516 (14) | 0.0453 (14) | −0.0025 (13) | 0.0051 (12) | 0.0000 (12) |
| C16 | 0.067 (2) | 0.0747 (18) | 0.0499 (15) | 0.0125 (17) | 0.0012 (15) | −0.0069 (13) |
| C17 | 0.065 (2) | 0.081 (2) | 0.0540 (15) | 0.0083 (17) | −0.0075 (15) | −0.0055 (14) |
| C18 | 0.0460 (18) | 0.0622 (17) | 0.0686 (18) | 0.0037 (14) | −0.0010 (14) | 0.0109 (14) |
| C19 | 0.055 (2) | 0.0669 (18) | 0.0695 (18) | 0.0050 (15) | 0.0080 (15) | −0.0077 (14) |
| C20 | 0.056 (2) | 0.0666 (17) | 0.0545 (16) | 0.0020 (16) | 0.0009 (14) | −0.0103 (13) |
| Cl1 | 0.0582 (5) | 0.0923 (6) | 0.1001 (6) | 0.0079 (4) | −0.0089 (5) | 0.0129 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0521 (14) | 0.0672 (13) | 0.0417 (11) | −0.0115 (12) | −0.0006 (10) | −0.0046 (10) |
| N2 | 0.0508 (14) | 0.0629 (13) | 0.0439 (11) | 0.0086 (11) | 0.0030 (10) | −0.0048 (9) |
| N3 | 0.0611 (16) | 0.0685 (13) | 0.0472 (12) | 0.0108 (13) | 0.0006 (11) | −0.0074 (11) |
| N4 | 0.0591 (16) | 0.0676 (13) | 0.0488 (11) | 0.0069 (13) | 0.0014 (12) | −0.0090 (10) |
| O1 | 0.0605 (13) | 0.0815 (12) | 0.0595 (11) | −0.0230 (11) | 0.0052 (11) | −0.0127 (10) |
| O2 | 0.0666 (13) | 0.0715 (12) | 0.0534 (10) | 0.0174 (11) | −0.0024 (9) | −0.0166 (9) |
| S1 | 0.0507 (4) | 0.0584 (4) | 0.0469 (3) | 0.0047 (3) | 0.0040 (3) | −0.0059 (3) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—C6 | 1.377 (4) | C11—H11C | 0.9600 |
| C1—C2 | 1.382 (4) | C12—O2 | 1.216 (3) |
| C1—H1B | 0.9300 | C12—N2 | 1.367 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.359 (5) | C13—N3 | 1.304 (3) |
| C2—H2B | 0.9300 | C13—N2 | 1.372 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.369 (5) | C13—S1 | 1.721 (3) |
| C3—H3B | 0.9300 | C14—N4 | 1.298 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.380 (4) | C14—C15 | 1.465 (3) |
| C4—H4B | 0.9300 | C14—S1 | 1.732 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.384 (4) | C15—C16 | 1.382 (3) |
| C5—H5A | 0.9300 | C15—C20 | 1.393 (3) |
| C6—C7 | 1.465 (4) | C16—C17 | 1.385 (4) |
| C7—C8 | 1.303 (4) | C16—H16A | 0.9300 |
| C7—H7A | 0.9300 | C17—C18 | 1.375 (4) |
| C8—C9 | 1.459 (3) | C17—H17A | 0.9300 |
| C8—H8A | 0.9300 | C18—C19 | 1.364 (4) |
| C9—O1 | 1.239 (3) | C18—Cl1 | 1.741 (3) |
| C9—N1 | 1.340 (3) | C19—C20 | 1.368 (4) |
| C10—N1 | 1.446 (3) | C19—H19A | 0.9300 |
| C10—C12 | 1.517 (3) | C20—H20A | 0.9300 |
| C10—C11 | 1.524 (3) | N1—H1A | 0.8600 |
| C10—H10A | 0.9800 | N2—H2A | 0.8600 |
| C11—H11A | 0.9600 | N3—N4 | 1.389 (3) |
| C11—H11B | 0.9600 | ||
| C6—C1—C2 | 120.4 (3) | H11B—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—H1B | 119.8 | O2—C12—N2 | 121.2 (2) |
| C2—C1—H1B | 119.8 | O2—C12—C10 | 123.8 (2) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.6 (4) | N2—C12—C10 | 115.0 (2) |
| C3—C2—H2B | 119.7 | N3—C13—N2 | 121.0 (2) |
| C1—C2—H2B | 119.7 | N3—C13—S1 | 114.7 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.1 (3) | N2—C13—S1 | 124.11 (17) |
| C2—C3—H3B | 120.0 | N4—C14—C15 | 124.0 (2) |
| C4—C3—H3B | 120.0 | N4—C14—S1 | 114.2 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.6 (3) | C15—C14—S1 | 121.72 (18) |
| C3—C4—H4B | 120.2 | C16—C15—C20 | 117.6 (2) |
| C5—C4—H4B | 120.2 | C16—C15—C14 | 121.4 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.0 (3) | C20—C15—C14 | 121.0 (2) |
| C4—C5—H5A | 119.5 | C15—C16—C17 | 121.8 (3) |
| C6—C5—H5A | 119.5 | C15—C16—H16A | 119.1 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 118.3 (3) | C17—C16—H16A | 119.1 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 119.3 (3) | C18—C17—C16 | 118.4 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 122.3 (3) | C18—C17—H17A | 120.8 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 127.5 (3) | C16—C17—H17A | 120.8 |
| C8—C7—H7A | 116.2 | C19—C18—C17 | 121.1 (3) |
| C6—C7—H7A | 116.2 | C19—C18—Cl1 | 119.6 (2) |
| C7—C8—C9 | 123.8 (3) | C17—C18—Cl1 | 119.3 (2) |
| C7—C8—H8A | 118.1 | C18—C19—C20 | 120.1 (3) |
| C9—C8—H8A | 118.1 | C18—C19—H19A | 120.0 |
| O1—C9—N1 | 119.7 (2) | C20—C19—H19A | 120.0 |
| O1—C9—C8 | 124.6 (3) | C19—C20—C15 | 121.0 (3) |
| N1—C9—C8 | 115.7 (2) | C19—C20—H20A | 119.5 |
| N1—C10—C12 | 110.1 (2) | C15—C20—H20A | 119.5 |
| N1—C10—C11 | 110.0 (2) | C9—N1—C10 | 122.3 (2) |
| C12—C10—C11 | 110.7 (2) | C9—N1—H1A | 118.8 |
| N1—C10—H10A | 108.7 | C10—N1—H1A | 118.8 |
| C12—C10—H10A | 108.7 | C12—N2—C13 | 123.3 (2) |
| C11—C10—H10A | 108.7 | C12—N2—H2A | 118.3 |
| C10—C11—H11A | 109.5 | C13—N2—H2A | 118.3 |
| C10—C11—H11B | 109.5 | C13—N3—N4 | 111.8 (2) |
| H11A—C11—H11B | 109.5 | C14—N4—N3 | 112.5 (2) |
| C10—C11—H11C | 109.5 | C13—S1—C14 | 86.70 (12) |
| H11A—C11—H11C | 109.5 | ||
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.7 (6) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | 0.2 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.3 (6) | C16—C17—C18—Cl1 | 179.5 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −1.2 (6) | C17—C18—C19—C20 | 0.1 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 2.2 (5) | Cl1—C18—C19—C20 | −179.2 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.2 (5) | C18—C19—C20—C15 | 0.2 (4) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | −178.4 (3) | C16—C15—C20—C19 | −0.8 (4) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −1.7 (5) | C14—C15—C20—C19 | 179.8 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 176.8 (3) | O1—C9—N1—C10 | −2.3 (4) |
| C1—C6—C7—C8 | −177.5 (3) | C8—C9—N1—C10 | 179.8 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 4.0 (5) | C12—C10—N1—C9 | 67.6 (3) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | −176.3 (2) | C11—C10—N1—C9 | −170.1 (2) |
| C7—C8—C9—O1 | −1.3 (4) | O2—C12—N2—C13 | −9.9 (4) |
| C7—C8—C9—N1 | 176.5 (3) | C10—C12—N2—C13 | 171.0 (2) |
| N1—C10—C12—O2 | 24.2 (3) | N3—C13—N2—C12 | −170.0 (2) |
| C11—C10—C12—O2 | −97.7 (3) | S1—C13—N2—C12 | 5.7 (3) |
| N1—C10—C12—N2 | −156.8 (2) | N2—C13—N3—N4 | 175.5 (2) |
| C11—C10—C12—N2 | 81.4 (3) | S1—C13—N3—N4 | −0.5 (3) |
| N4—C14—C15—C16 | −2.3 (4) | C15—C14—N4—N3 | −176.1 (2) |
| S1—C14—C15—C16 | −179.3 (2) | S1—C14—N4—N3 | 1.1 (3) |
| N4—C14—C15—C20 | 177.1 (2) | C13—N3—N4—C14 | −0.4 (3) |
| S1—C14—C15—C20 | 0.1 (3) | N3—C13—S1—C14 | 0.9 (2) |
| C20—C15—C16—C17 | 1.1 (4) | N2—C13—S1—C14 | −175.0 (2) |
| C14—C15—C16—C17 | −179.5 (2) | N4—C14—S1—C13 | −1.2 (2) |
| C15—C16—C17—C18 | −0.8 (4) | C15—C14—S1—C13 | 176.1 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2A···O1i | 0.86 | 1.94 | 2.802 (3) | 175. |
| C7—H7A···O1 | 0.93 | 2.58 | 2.888 (3) | 100. |
| C7—H7A···N3ii | 0.93 | 2.54 | 3.446 (3) | 164. |
| C11—H11C···S1iii | 0.96 | 2.77 | 3.526 (3) | 136. |
| C20—H20A···S1 | 0.93 | 2.69 | 3.105 (3) | 108. |
| C20—H20A···O2iv | 0.93 | 2.48 | 3.380 (3) | 162. |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1/2, −y+1/2, −z; (ii) x−1/2, −y+1/2, −z; (iii) x+1, y, z; (iv) x−1/2, −y+3/2, −z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: GW2052).
References
- Bruker (2004). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Foroumadi, A., Daneshtalab, M. & Shafiee, A. (1999). Arzneim. Forsch.49, 1035–1038. [PubMed]
- Fun, H.-K., Chantrapromma, S., Patil, P. S., Karthikeyan, M. S. & Dharmaprakash, S. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o956–o957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Gowda, B. T., Tokarčík, M., Kožíšek, J., Sowmya, B. P. & Fuess, H. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Levy, M. & Palmer, A. H. (1942). J. Biol. Chem.146, 493–495.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Song, K. S., Ishikawa, Y., Kobayashi, S., Sankawa, U. & Ebizuka, Y. (1992). Phytochemistry, 31, 823–826.
- Thiruvalluvar, A., Subramanyam, M., Butcher, R. J., Karabasanagouda, T. & Adhikari, A. V. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o1263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Tu, G. G., Li, S. H., Huang, H. M., Li, G., Xiong, F., Mai, X., Zhu, H. W., Kuang, B. H. & Xu, W. F. (2008). Bioorg. Med. Chem.16, 6663–6668. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2008). publCIF In preparation.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808030353/gw2052sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808030353/gw2052Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report