Abstract
The asymmetric unit of the title compound, C5H7N2 +·C7H4NO4 −·C7H5NO4, consists of an aminopyridinium cation, a 4-nitrobenzoate anion and a neutral 4-nitrobenzoic acid molecule. The pyridine ring forms dihedral angles of 64.70 (5)° and 70.37 (5)°, respectively, with the benzene rings of 4-nitrobenzoic acid and 4-nitrobenzoate. In the crystal structure, the cations, anions and the neutral 4-nitrobenzoic acid molecules are linked by O—H⋯O and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming a two-dimensional network parallel to (001). Adjacent networks are cross-linked via C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and π–π stacking interactions [centroid–centroid distances 3.6339 (6) and 3.6566 (6) Å].
Related literature
For the biological activity of 4-aminopyridine, see: Judge et al. (2006 ▶); Schwid et al. (1997 ▶); Strupp et al. (2004 ▶). For related structures, see: Chao & Schempp (1977 ▶); Anderson et al. (2005 ▶); Andrau & White, (2003 ▶); Bhattacharya et al. (1994 ▶); Karle et al. (2003 ▶).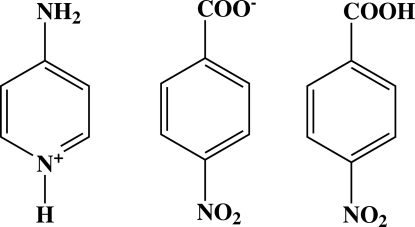
Experimental
Crystal data
C5H7N2 +·C7H4NO4 −·C7H5NO4
M r = 428.36
Triclinic,

a = 6.4561 (1) Å
b = 6.8598 (1) Å
c = 20.9055 (3) Å
α = 85.826 (1)°
β = 87.975 (1)°
γ = 86.188 (1)°
V = 920.92 (2) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.12 mm−1
T = 100.0 (1) K
0.40 × 0.36 × 0.29 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.952, T max = 0.965
24945 measured reflections
6647 independent reflections
5169 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.031
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.044
wR(F 2) = 0.132
S = 1.05
6647 reflections
284 parameters
1 restraint
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.43 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.39 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: APEX2; data reduction: SAINT (Bruker, 2005 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: SHELXTL; software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL and PLATON (Spek, 2003 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808027761/ci2664sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808027761/ci2664Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O3A—H1O3⋯O3Bi | 0.82 | 1.63 | 2.4457 (11) | 170 |
| N3—H3A⋯O3Bii | 0.86 | 2.14 | 2.9977 (12) | 172 |
| N3—H3B⋯O4Bi | 0.86 | 2.07 | 2.8758 (12) | 155 |
| N2—H1N2⋯O4Aiii | 0.85 (1) | 1.99 (1) | 2.7726 (12) | 153 (1) |
| C2B—H2BA⋯O1Biv | 0.93 | 2.52 | 3.2187 (13) | 133 |
| C8—H8A⋯O3Av | 0.93 | 2.56 | 3.4565 (13) | 161 |
| C12—H12A⋯O1Avi | 0.93 | 2.55 | 3.4427 (13) | 162 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii) 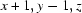 ; (iv)
; (iv)  ; (v)
; (v)  ; (vi)
; (vi)  .
.
Acknowledgments
HKF and SRJ thank the Malaysian Government and Universiti Sains Malaysia for Science Fund grant No. 305/PFIZIK/613312. SRJ thanks Universiti Sains Malaysia for a post-doctoral research fellowship. CKQ thanks Universiti Sains Malaysia for a student assistanceship.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
4-Aminopyridine (Fampridine) is used clinically in Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome and multiple sclerosis because by blocking potassium channels, it prolongs the action potentials thereby increasing transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction (Judge et al., 2006; Schwid et al., 1997; Strupp et al., 2004). The crystal structure of 4-aminopyridine has been reported (Chao & Schempp, 1977; Anderson et al., 2005). As an extension of our systematic study of hydrogen bonding patterns of 4-aminopyridine with aromatic carboxylic acids, we report here the crystal structure of the title compound.
The asymmetric unit of the title compound contains one 4-aminopyridinium cation, one 4-nitrobenzoate anion and one 4-nitrobenzoic acid molecule. A proton transfer from the carboxyl group of 4-nitrobenzoic acid to atom N2 of 4-aminopyridine resulted in the formation of ions. This lead to the widening of C8—N2—C12 angle of the pyridine ring to 120.86 (9)°, compared to 115.25 (13)° in the unprotonated 4-aminopyridine (Anderson et al., 2005). This type of protonation is observed in various 4-aminopyridine acid complexes (Bhattacharya et al., 1994; Karle et al., 2003). The bond lengths and angles of the 4-aminopyridne are comparable to the values reported earlier for 4-aminopyridine (Chao & Schempp, 1977; Anderson et al., 2005). The bond lengths and angles of the 4-nitrobenzoic acid is found to be normal(Andrau & White, 2003).
The dihedral angle between the benzene rings of 4-nitrobenzoic acid (C1A-C6A) and 4-nitrobenzoate (C1B-C6B) units is 6.62 (5)°. The pyridine (N2/C8—C12) ring forms dihedral angles of 64.70 (5)° and 70.37 (5)°, respectively, with the C1A-C6A and C1B-C6B rings.
In the crystal structure, the cations, anions and the neutral 4-nitrobenzoic acid molecules are linked to form a two-dimensional network (Fig. 2) parallel to the (0 0 1) by O—H···O and N—H···O hydrogen bonds (Table 1). The adjacent networks are cross-linked via C—H···O hydrogen bonds. The crystal packing is further consolidated by π–π stacking interactions between symmetry-related C1A-C6A (centroid Cg1) and C1B-C6B (centroid Cg2) rings, with Cg1···Cg1i and Cg2···Cg2vii distances of 3.6566 (6) Å and 3.6339 (6) Å, respectively [symmetry codes: (i) 1-x, 2-y, 1-z; (vii) 2-x, 2-y, 2-z].
Experimental
4-Aminopyridine and 4-nitrobenzoic acid were mixed in equimolar ratio in methanol and warmed in a water bath for 2 h. Colourless single crystals were obtained after a week on slow evaporation.
Refinement
Atom H1N2 was located from a difference map and was refined with the N-H distance restrained to 0.85 (1) Å. The remaining H atoms were positioned geometrically with C-H = 0.93 Å, N-H = 0.86 Å and O-H = 0.82Å, and refined using a riding model, with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C,N) and 1.5Ueq(O).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The asymmetric unit of the title compound, showing 50% probability displacement ellipsoids and the atom-numbering scheme.
Fig. 2.
The crystal packing of the title compound, viewed along the a axis. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C5H7N2+·C7H4NO4−·C7H5NO4 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 428.36 | F(000) = 444 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.545 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 6.4561 (1) Å | Cell parameters from 6200 reflections |
| b = 6.8598 (1) Å | θ = 2.2–29.2° |
| c = 20.9055 (3) Å | µ = 0.12 mm−1 |
| α = 85.826 (1)° | T = 100 K |
| β = 87.975 (1)° | Block, colourless |
| γ = 86.188 (1)° | 0.40 × 0.36 × 0.29 mm |
| V = 920.92 (2) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer | 6647 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 5169 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.031 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 32.5°, θmin = 1.0° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005) | h = −9→9 |
| Tmin = 0.952, Tmax = 0.965 | k = −10→10 |
| 24945 measured reflections | l = −31→31 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.044 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.132 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.05 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0736P)2 + 0.1221P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 6647 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 284 parameters | Δρmax = 0.43 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Δρmin = −0.39 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. The data was collected with the Oxford Cyrosystem Cobra low-temperature attachment. |
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1A | 0.61416 (13) | 0.64153 (13) | 0.61139 (4) | 0.02534 (18) | |
| O1B | 1.43798 (12) | 0.64460 (14) | 1.07244 (4) | 0.02613 (19) | |
| O2A | 0.89023 (12) | 0.63198 (13) | 0.54960 (4) | 0.02492 (18) | |
| O2B | 1.15700 (13) | 0.66730 (15) | 1.13139 (4) | 0.02794 (19) | |
| O3A | 0.31404 (11) | 0.97209 (12) | 0.29069 (4) | 0.02024 (16) | |
| H1O3 | 0.2342 | 1.0163 | 0.2628 | 0.030* | |
| O3B | 0.89111 (11) | 0.90736 (11) | 0.80183 (4) | 0.01831 (15) | |
| O4A | 0.02402 (11) | 0.98398 (11) | 0.35318 (4) | 0.01950 (16) | |
| O4B | 0.59084 (12) | 0.90329 (13) | 0.85892 (4) | 0.02425 (18) | |
| N1A | 0.70215 (13) | 0.66162 (13) | 0.55851 (4) | 0.01667 (17) | |
| N1B | 1.24848 (13) | 0.67136 (13) | 1.07904 (4) | 0.01646 (17) | |
| N2 | 0.80980 (14) | 0.30341 (13) | 0.29153 (4) | 0.01904 (18) | |
| N3 | 0.73597 (13) | 0.85350 (13) | 0.20200 (5) | 0.02020 (18) | |
| H3A | 0.8354 | 0.9309 | 0.2022 | 0.024* | |
| H3B | 0.6223 | 0.8922 | 0.1834 | 0.024* | |
| C1A | 0.24956 (15) | 0.84572 (14) | 0.46101 (5) | 0.01507 (18) | |
| H1AA | 0.1084 | 0.8790 | 0.4667 | 0.018* | |
| C1B | 1.11431 (15) | 0.75402 (14) | 0.90711 (5) | 0.01505 (18) | |
| H1BA | 1.1788 | 0.7482 | 0.8667 | 0.018* | |
| C2A | 0.36551 (15) | 0.77640 (14) | 0.51351 (5) | 0.01593 (18) | |
| H2AA | 0.3048 | 0.7633 | 0.5545 | 0.019* | |
| C2B | 1.22778 (15) | 0.70459 (14) | 0.96180 (5) | 0.01522 (18) | |
| H2BA | 1.3685 | 0.6664 | 0.9587 | 0.018* | |
| C3B | 1.12614 (14) | 0.71350 (14) | 1.02109 (5) | 0.01397 (17) | |
| C3A | 0.57532 (15) | 0.72731 (14) | 0.50276 (5) | 0.01424 (17) | |
| C4A | 0.67164 (15) | 0.74110 (15) | 0.44250 (5) | 0.01592 (18) | |
| H4AA | 0.8119 | 0.7038 | 0.4369 | 0.019* | |
| C4B | 0.91589 (15) | 0.76542 (14) | 1.02843 (5) | 0.01527 (18) | |
| H4BA | 0.8513 | 0.7667 | 1.0689 | 0.018* | |
| C5A | 0.55303 (15) | 0.81214 (15) | 0.39071 (5) | 0.01621 (18) | |
| H5AA | 0.6142 | 0.8239 | 0.3498 | 0.019* | |
| C5B | 0.80500 (15) | 0.81538 (14) | 0.97324 (5) | 0.01517 (18) | |
| H5BA | 0.6638 | 0.8512 | 0.9766 | 0.018* | |
| C6A | 0.34218 (14) | 0.86598 (14) | 0.39989 (5) | 0.01412 (17) | |
| C6B | 0.90370 (14) | 0.81237 (14) | 0.91270 (5) | 0.01388 (17) | |
| C7A | 0.21250 (15) | 0.94696 (14) | 0.34447 (5) | 0.01498 (18) | |
| C7B | 0.78049 (15) | 0.87820 (14) | 0.85437 (5) | 0.01578 (18) | |
| C8 | 0.62995 (16) | 0.35854 (16) | 0.26207 (5) | 0.0195 (2) | |
| H8A | 0.5260 | 0.2709 | 0.2623 | 0.023* | |
| C9 | 0.59889 (15) | 0.54066 (15) | 0.23204 (5) | 0.01760 (19) | |
| H9A | 0.4736 | 0.5775 | 0.2126 | 0.021* | |
| C10 | 0.75805 (15) | 0.67391 (15) | 0.23052 (5) | 0.01566 (18) | |
| C11 | 0.94501 (15) | 0.60896 (15) | 0.26128 (5) | 0.01670 (19) | |
| H11A | 1.0538 | 0.6914 | 0.2611 | 0.020* | |
| C12 | 0.96496 (16) | 0.42621 (16) | 0.29097 (5) | 0.0186 (2) | |
| H12A | 1.0877 | 0.3849 | 0.3113 | 0.022* | |
| H1N2 | 0.839 (2) | 0.1892 (15) | 0.3080 (7) | 0.029 (4)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1A | 0.0250 (4) | 0.0384 (5) | 0.0118 (4) | −0.0024 (3) | −0.0008 (3) | 0.0048 (3) |
| O1B | 0.0158 (3) | 0.0428 (5) | 0.0191 (4) | 0.0041 (3) | −0.0028 (3) | −0.0013 (3) |
| O2A | 0.0172 (3) | 0.0361 (5) | 0.0207 (4) | 0.0016 (3) | −0.0036 (3) | 0.0012 (3) |
| O2B | 0.0228 (4) | 0.0485 (5) | 0.0115 (4) | 0.0012 (3) | 0.0006 (3) | 0.0003 (3) |
| O3A | 0.0183 (3) | 0.0303 (4) | 0.0116 (3) | −0.0013 (3) | −0.0025 (3) | 0.0027 (3) |
| O3B | 0.0174 (3) | 0.0258 (4) | 0.0114 (3) | −0.0009 (3) | −0.0003 (3) | 0.0006 (3) |
| O4A | 0.0158 (3) | 0.0236 (4) | 0.0182 (4) | 0.0011 (3) | −0.0016 (3) | 0.0026 (3) |
| O4B | 0.0145 (3) | 0.0368 (5) | 0.0198 (4) | 0.0011 (3) | −0.0020 (3) | 0.0071 (3) |
| N1A | 0.0179 (4) | 0.0178 (4) | 0.0145 (4) | −0.0016 (3) | −0.0034 (3) | −0.0001 (3) |
| N1B | 0.0167 (4) | 0.0194 (4) | 0.0131 (4) | 0.0003 (3) | −0.0014 (3) | −0.0010 (3) |
| N2 | 0.0213 (4) | 0.0188 (4) | 0.0161 (4) | 0.0014 (3) | 0.0009 (3) | 0.0017 (3) |
| N3 | 0.0160 (4) | 0.0212 (4) | 0.0224 (5) | 0.0005 (3) | −0.0014 (3) | 0.0045 (3) |
| C1A | 0.0146 (4) | 0.0166 (4) | 0.0140 (4) | −0.0011 (3) | −0.0003 (3) | −0.0006 (3) |
| C1B | 0.0156 (4) | 0.0177 (4) | 0.0114 (4) | 0.0009 (3) | 0.0001 (3) | −0.0004 (3) |
| C2A | 0.0172 (4) | 0.0180 (4) | 0.0127 (4) | −0.0030 (3) | 0.0005 (3) | −0.0001 (3) |
| C2B | 0.0139 (4) | 0.0175 (4) | 0.0140 (4) | 0.0009 (3) | −0.0001 (3) | −0.0010 (3) |
| C3B | 0.0151 (4) | 0.0154 (4) | 0.0114 (4) | −0.0001 (3) | −0.0023 (3) | −0.0003 (3) |
| C3A | 0.0168 (4) | 0.0143 (4) | 0.0118 (4) | −0.0017 (3) | −0.0030 (3) | 0.0002 (3) |
| C4A | 0.0141 (4) | 0.0193 (4) | 0.0143 (4) | −0.0007 (3) | −0.0005 (3) | −0.0013 (3) |
| C4B | 0.0158 (4) | 0.0175 (4) | 0.0125 (4) | −0.0018 (3) | 0.0009 (3) | −0.0007 (3) |
| C5A | 0.0163 (4) | 0.0206 (4) | 0.0117 (4) | −0.0015 (3) | 0.0000 (3) | −0.0013 (3) |
| C5B | 0.0131 (4) | 0.0180 (4) | 0.0142 (4) | −0.0005 (3) | −0.0002 (3) | 0.0001 (3) |
| C6A | 0.0154 (4) | 0.0147 (4) | 0.0125 (4) | −0.0018 (3) | −0.0021 (3) | −0.0006 (3) |
| C6B | 0.0143 (4) | 0.0151 (4) | 0.0122 (4) | −0.0013 (3) | −0.0014 (3) | 0.0005 (3) |
| C7A | 0.0173 (4) | 0.0153 (4) | 0.0125 (4) | −0.0026 (3) | −0.0018 (3) | 0.0002 (3) |
| C7B | 0.0157 (4) | 0.0167 (4) | 0.0149 (4) | −0.0007 (3) | −0.0022 (3) | −0.0001 (3) |
| C8 | 0.0175 (4) | 0.0233 (5) | 0.0178 (5) | −0.0023 (4) | 0.0008 (4) | −0.0016 (4) |
| C9 | 0.0138 (4) | 0.0231 (5) | 0.0156 (5) | −0.0006 (3) | −0.0012 (3) | −0.0001 (4) |
| C10 | 0.0144 (4) | 0.0199 (4) | 0.0123 (4) | 0.0012 (3) | 0.0005 (3) | −0.0009 (3) |
| C11 | 0.0151 (4) | 0.0203 (4) | 0.0148 (4) | −0.0004 (3) | −0.0020 (3) | −0.0015 (4) |
| C12 | 0.0178 (4) | 0.0232 (5) | 0.0143 (5) | 0.0029 (3) | −0.0023 (3) | −0.0010 (4) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1A—N1A | 1.2278 (12) | C2A—H2AA | 0.93 |
| O1B—N1B | 1.2294 (11) | C2B—C3B | 1.3851 (14) |
| O2A—N1A | 1.2276 (11) | C2B—H2BA | 0.93 |
| O2B—N1B | 1.2244 (12) | C3B—C4B | 1.3863 (13) |
| O3A—C7A | 1.2877 (12) | C3A—C4A | 1.3848 (14) |
| O3A—H1O3 | 0.8200 | C4A—C5A | 1.3888 (14) |
| O3B—C7B | 1.2993 (12) | C4A—H4AA | 0.93 |
| O4A—C7A | 1.2362 (12) | C4B—C5B | 1.3890 (14) |
| O4B—C7B | 1.2263 (12) | C4B—H4BA | 0.93 |
| N1A—C3A | 1.4743 (12) | C5A—C6A | 1.3969 (13) |
| N1B—C3B | 1.4702 (13) | C5A—H5AA | 0.93 |
| N2—C12 | 1.3502 (14) | C5B—C6B | 1.3977 (14) |
| N2—C8 | 1.3523 (14) | C5B—H5BA | 0.93 |
| N2—H1N2 | 0.844 (9) | C6A—C7A | 1.5049 (13) |
| N3—C10 | 1.3301 (13) | C6B—C7B | 1.5047 (13) |
| N3—H3A | 0.86 | C8—C9 | 1.3626 (15) |
| N3—H3B | 0.86 | C8—H8A | 0.93 |
| C1A—C2A | 1.3877 (14) | C9—C10 | 1.4180 (14) |
| C1A—C6A | 1.3930 (14) | C9—H9A | 0.93 |
| C1A—H1AA | 0.93 | C10—C11 | 1.4180 (13) |
| C1B—C2B | 1.3888 (13) | C11—C12 | 1.3580 (15) |
| C1B—C6B | 1.3949 (13) | C11—H11A | 0.93 |
| C1B—H1BA | 0.93 | C12—H12A | 0.93 |
| C2A—C3A | 1.3884 (13) | ||
| C7A—O3A—H1O3 | 109.5 | C3B—C4B—H4BA | 121.2 |
| O2A—N1A—O1A | 123.62 (9) | C5B—C4B—H4BA | 121.2 |
| O2A—N1A—C3A | 118.18 (9) | C4A—C5A—C6A | 120.21 (9) |
| O1A—N1A—C3A | 118.20 (8) | C4A—C5A—H5AA | 119.9 |
| O2B—N1B—O1B | 123.36 (9) | C6A—C5A—H5AA | 119.9 |
| O2B—N1B—C3B | 118.43 (8) | C4B—C5B—C6B | 120.61 (9) |
| O1B—N1B—C3B | 118.20 (9) | C4B—C5B—H5BA | 119.7 |
| C12—N2—C8 | 120.86 (9) | C6B—C5B—H5BA | 119.7 |
| C12—N2—H1N2 | 115.2 (11) | C1A—C6A—C5A | 119.99 (9) |
| C8—N2—H1N2 | 123.7 (11) | C1A—C6A—C7A | 119.15 (8) |
| C10—N3—H3A | 120.0 | C5A—C6A—C7A | 120.86 (9) |
| C10—N3—H3B | 120.0 | C1B—C6B—C5B | 120.08 (9) |
| H3A—N3—H3B | 120.0 | C1B—C6B—C7B | 121.02 (9) |
| C2A—C1A—C6A | 120.74 (9) | C5B—C6B—C7B | 118.88 (8) |
| C2A—C1A—H1AA | 119.6 | O4A—C7A—O3A | 125.63 (9) |
| C6A—C1A—H1AA | 119.6 | O4A—C7A—C6A | 119.65 (9) |
| C2B—C1B—C6B | 120.04 (9) | O3A—C7A—C6A | 114.72 (8) |
| C2B—C1B—H1BA | 120.0 | O4B—C7B—O3B | 125.05 (9) |
| C6B—C1B—H1BA | 120.0 | O4B—C7B—C6B | 120.18 (9) |
| C1A—C2A—C3A | 117.70 (9) | O3B—C7B—C6B | 114.75 (8) |
| C1A—C2A—H2AA | 121.2 | N2—C8—C9 | 120.94 (10) |
| C3A—C2A—H2AA | 121.2 | N2—C8—H8A | 119.5 |
| C3B—C2B—C1B | 118.35 (9) | C9—C8—H8A | 119.5 |
| C3B—C2B—H2BA | 120.8 | C8—C9—C10 | 119.85 (9) |
| C1B—C2B—H2BA | 120.8 | C8—C9—H9A | 120.1 |
| C2B—C3B—C4B | 123.20 (9) | C10—C9—H9A | 120.1 |
| C2B—C3B—N1B | 118.36 (8) | N3—C10—C11 | 120.35 (9) |
| C4B—C3B—N1B | 118.42 (9) | N3—C10—C9 | 122.38 (9) |
| C4A—C3A—C2A | 123.18 (9) | C11—C10—C9 | 117.27 (9) |
| C4A—C3A—N1A | 118.57 (8) | C12—C11—C10 | 119.88 (9) |
| C2A—C3A—N1A | 118.23 (9) | C12—C11—H11A | 120.1 |
| C3A—C4A—C5A | 118.16 (9) | C10—C11—H11A | 120.1 |
| C3A—C4A—H4AA | 120.9 | N2—C12—C11 | 121.19 (9) |
| C5A—C4A—H4AA | 120.9 | N2—C12—H12A | 119.4 |
| C3B—C4B—C5B | 117.67 (9) | C11—C12—H12A | 119.4 |
| C6A—C1A—C2A—C3A | −0.39 (14) | C4A—C5A—C6A—C1A | −0.97 (14) |
| C6B—C1B—C2B—C3B | 0.50 (14) | C4A—C5A—C6A—C7A | 178.78 (9) |
| C1B—C2B—C3B—C4B | 1.38 (15) | C2B—C1B—C6B—C5B | −1.98 (14) |
| C1B—C2B—C3B—N1B | −176.79 (9) | C2B—C1B—C6B—C7B | 176.30 (9) |
| O2B—N1B—C3B—C2B | −175.56 (9) | C4B—C5B—C6B—C1B | 1.65 (14) |
| O1B—N1B—C3B—C2B | 5.40 (14) | C4B—C5B—C6B—C7B | −176.66 (9) |
| O2B—N1B—C3B—C4B | 6.18 (14) | C1A—C6A—C7A—O4A | −4.01 (14) |
| O1B—N1B—C3B—C4B | −172.86 (9) | C5A—C6A—C7A—O4A | 176.24 (9) |
| C1A—C2A—C3A—C4A | −1.18 (15) | C1A—C6A—C7A—O3A | 175.76 (8) |
| C1A—C2A—C3A—N1A | 177.40 (8) | C5A—C6A—C7A—O3A | −3.99 (13) |
| O2A—N1A—C3A—C4A | 3.87 (13) | C1B—C6B—C7B—O4B | 170.01 (9) |
| O1A—N1A—C3A—C4A | −176.87 (9) | C5B—C6B—C7B—O4B | −11.69 (14) |
| O2A—N1A—C3A—C2A | −174.77 (9) | C1B—C6B—C7B—O3B | −11.13 (13) |
| O1A—N1A—C3A—C2A | 4.48 (13) | C5B—C6B—C7B—O3B | 167.17 (9) |
| C2A—C3A—C4A—C5A | 1.64 (15) | C12—N2—C8—C9 | −1.21 (16) |
| N1A—C3A—C4A—C5A | −176.93 (8) | N2—C8—C9—C10 | 1.08 (16) |
| C2B—C3B—C4B—C5B | −1.70 (15) | C8—C9—C10—N3 | −179.88 (10) |
| N1B—C3B—C4B—C5B | 176.47 (9) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −0.23 (15) |
| C3A—C4A—C5A—C6A | −0.53 (14) | N3—C10—C11—C12 | 179.16 (10) |
| C3B—C4B—C5B—C6B | 0.15 (14) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −0.50 (15) |
| C2A—C1A—C6A—C5A | 1.44 (14) | C8—N2—C12—C11 | 0.45 (16) |
| C2A—C1A—C6A—C7A | −178.30 (9) | C10—C11—C12—N2 | 0.41 (16) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O3A—H1O3···O3Bi | 0.82 | 1.63 | 2.4457 (11) | 170 |
| N3—H3A···O3Bii | 0.86 | 2.14 | 2.9977 (12) | 172 |
| N3—H3B···O4Bi | 0.86 | 2.07 | 2.8758 (12) | 155 |
| N2—H1N2···O4Aiii | 0.85 (1) | 1.99 (1) | 2.7726 (12) | 153 (1) |
| C2B—H2BA···O1Biv | 0.93 | 2.52 | 3.2187 (13) | 133 |
| C8—H8A···O3Av | 0.93 | 2.56 | 3.4565 (13) | 161 |
| C12—H12A···O1Avi | 0.93 | 2.55 | 3.4427 (13) | 162 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+2, −z+1; (ii) −x+2, −y+2, −z+1; (iii) x+1, y−1, z; (iv) −x+3, −y+1, −z+2; (v) x, y−1, z; (vi) −x+2, −y+1, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: CI2664).
References
- Anderson, F. P., Gallagher, J. F., Kenny, P. T. M. & Lough, A. J. (2005). Acta Cryst. E61, o1350–o1353.
- Andrau, L. & White, J. (2003). Acta Cryst. E59, o77–o79. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, S., Dastidar, P. & Guru Row, T. N. (1994). Chem. Mater.6, 531–537.
- Bruker (2005). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Chao, M. & Schempp, E. (1977). Acta Cryst. B33, 1557–1564.
- Judge, S. & Bever, C. (2006). Pharmacol. Ther.111, 224–259. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Karle, I., Gilardi, R. D., Chandrashekhar Rao, Ch., Muraleedharan, K. M. & Ranganathan, S. (2003). J. Chem. Crystallogr.33, 727–749.
- Schwid, S. B., Petrie, M. D., McDermott, M. P., Tierney, D. S., Mason, D. H. & Goodman, A. D. (1997). Neurology, 48, 817–821. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst.36, 7–13.
- Strupp, M., Kalla, R., Dichgans, M., Fraitinger, T., Glasauer, S. & Brandt, T. (2004). Neurology, 62, 1623–1625. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808027761/ci2664sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808027761/ci2664Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




