Abstract
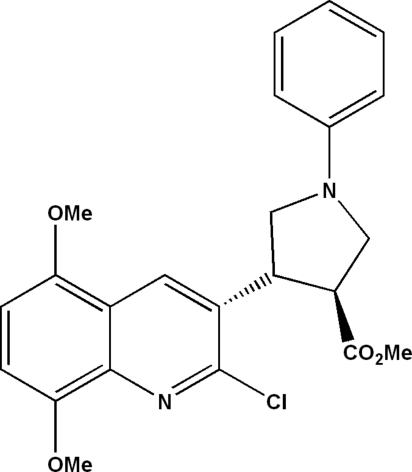
The molecule of the title compound, C23H23ClN2O4, contains a quinolyl unit linked to a functionalized pyrrolidine system with a 3,4-trans arrangement of the substituents. The unit cell contains two stereoisomers that have the absolute stereochemistry 3S,4R and 3R,4S. The pyrrolidine ring adopts a twist conformation with pseudo-rotation parameters P = 258.2 (3)° and τ(M) = 35.3 (1)°. The packing is stabilized by C—H⋯π interactions and offset π–π stacking (centroid-to-centroid distance = 3.849 Å, interplanar distance = 3.293 Å and slippage = 1.994 Å) between phenyl rings, leading to a two-dimensional network.
Related literature
For general background, see: Padwa et al. (1999 ▶); Sahu et al. (2002 ▶); Robert & Meunier (1998 ▶); Dow et al. (2006 ▶); Witherup et al. (1995 ▶); Kravchenko et al. (2005 ▶); Bouraiou et al. (2008 ▶); Rezig et al. (2000 ▶); Moussaoui et al. (2002 ▶); Menasra et al. (2005 ▶); Rao et al. (1981 ▶). For related structures, see: Belfaitah et al. (2006 ▶); Bouraiou et al. (2007a
▶,b
▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C23H23ClN2O4
M r = 426.88
Monoclinic,

a = 9.579 (1) Å
b = 17.518 (1) Å
c = 12.944 (2) Å
β = 109.01 (2)°
V = 2053.6 (5) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.22 mm−1
T = 296 (2) K
0.15 × 0.06 × 0.05 mm
Data collection
Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: none
9271 measured reflections
4717 independent reflections
3062 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.026
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.055
wR(F 2) = 0.178
S = 1.03
4717 reflections
274 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.38 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.33 e Å−3
Data collection: COLLECT (Nonius, 1998 ▶); cell refinement: SCALEPACK (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶); data reduction: DENZO (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶) and SCALEPACK; program(s) used to solve structure: SIR2002 (Burla et al., 2003 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEPIII (Burnett & Johnson, 1996 ▶), ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and CAMERON (Pearce et al., 2000 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: PLATON (Spek, 2003 ▶) and WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808031838/dn2384sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808031838/dn2384Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg1 is the centroid of the C17–C22 ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C12—H12B⋯Cg1i | 0.96 | 2.67 | 3.601 (3) | 164 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Professor Lahcéne Ouahab (Organométalliques et Materiaux Moléculaire, Université de Rennes I, France) for data collection facilities and Professor Abdelmadjid Debache (PHYSYNOR, Université Mentouri, Constantine, Algeria) for his assistance. Thanks are due to MESRS (Ministére de l’Enseignement Supérieur et de la Recherche Scientifique) for financial support.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Quinolines derivatives have attracted considerable interest for many years due to their presence in the skeleton of a large number of bioactive compounds and natural products (Padwa et al., 1999; Sahu et al. 2002). For example, quinoline alkaloids, such as quinine, chloroquin, mefloquine and amodiaquine, are used as efficient drugs for the treatment of malaria (Robert & Meunier, 1998; Dow et al., 2006). On the other hand, pyrrolidine containing compounds are also of significant importance because of their biological activities and widespread employment in catalysis (Witherup et al., 1995; Kravchenko et al., 2005). As a part of our program related to the preparation and biological evaluation of quinolyl derivatives (Belfaitah et al., 2006; Bouraiou et al., 2008, 2007a,b; Rezig et al., 2000; Moussaoui et al., 2002), we have previously reported the preparation of some 3-pyrrolylquinoline derivatives via an 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition/oxydation key sequence from quinolinyl α,β-unsaturated esters as starting materials (Menasra et al., 2005). In a continuation of our efforts in this area, we report here the crystal structure of new N-phenylpyrrolidine derivative bearing a quinoline ring at C-3 and ester group at C-4 via an 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reaction.
The asymmetric unit of title compound contains a quinolyl unit linked to a functionalized pyrrolidine system with a 3,4-trans arrangement of the substituents (Fig. 1). The two rings of quinolyl moiety are fused in an axial fashion and form a dihedral angle of 0.67 (6)° and this quasi plane system forms dihedral angles of 83.76 (7)° with the phenyl ring.The pyrrolidine was obtained with conservation of the stereochemistry of starting alkene, giving only one diastereoisomer with no evidence of any other isomers in the 1H NMR spectra or thin-layer chromatography of the crude product. X-ray crystallography of (I) showed an asymmetric unit which contains only one stereoisomer and the analysis of the unit cell demonstrate that the second stereoisomer is generated via a symmetry element. The two stereoisomers have for each one, the absolute stereochemistry 3S,4R and 3R,4S of the new stereocenters created in the cycloaddition reactions.
The pyrrolidine ring adopts twist conformation on C13—C14 with pseudorotation parameters P = 258.2 (3)° and τ(M) = 35.3 (1)° (Rao et al., 1981), the C13 atom deviates by 0.213 (2)Å from the mean plane through the remaining atoms.
The packing is stabilized by C—H···π interaction involving the C17—C22 phenyl ring (Table 1). Offset π···π stacking between this phenyl ring and the symmetry (-x, -y, -z) related ring might also be considered with a centroid-to-centroid distance of 3.849 Å, an interplanar distance of 3.293Å and a slippage of 1.994Å (Spek, 2003). These weak interactions build up a two dimensional network (Fig. 2).
Experimental
The title compound I was synthesized by refluxing 1.0 mmol of (E)-methyl 3-(2-chloro-5,8-dimethoxyquinolin-3-yl) acrylate, 2.0 mmol of N-phenylglycine, and 5.0 mmol of CH2O in dry toluene (5.10-3M). The contents were then cooled and filtered off and the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to column chromatography (silica gel, eluent: CH2Cl2) to afford pure product. Crystals suitable for X-ray analysis were obtained by slow evaporation of a dichloromethane solution of (I).
Refinement
All H atoms were localized on Fourier maps but introduced in calculated positions and treated as riding on their parent C atom.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of the title compound with the atom-labeling scheme.Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms are represnted as small spheres of arbitrary radii.
Fig. 2.
Partial packing view showing the C—H···π and π-π interactions drawn as dashed lines. H atoms not involved in H bonding interactions have been omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| C23H23ClN2O4 | F(000) = 896 |
| Mr = 426.88 | Dx = 1.381 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 4717 reflections |
| a = 9.579 (1) Å | θ = 2.0–27.5° |
| b = 17.518 (1) Å | µ = 0.22 mm−1 |
| c = 12.944 (2) Å | T = 296 K |
| β = 109.01 (2)° | Needle, white |
| V = 2053.6 (5) Å3 | 0.15 × 0.06 × 0.05 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer | 3062 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.026 |
| graphite | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 2.0° |
| φ scans, and ω scans with κ offsets | h = −12→12 |
| 9271 measured reflections | k = −22→22 |
| 4717 independent reflections | l = −16→16 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.055 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.178 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.03 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.102P)2 + 0.336P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4717 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 274 parameters | Δρmax = 0.38 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.33 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C2 | 0.4396 (2) | 0.31838 (12) | −0.07671 (19) | 0.0457 (5) | |
| C3 | 0.3691 (3) | 0.26052 (12) | −0.03567 (19) | 0.0482 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.3895 (3) | 0.18796 (12) | −0.0673 (2) | 0.0494 (5) | |
| H4 | 0.3446 | 0.1473 | −0.0443 | 0.059* | |
| C5 | 0.4777 (2) | 0.17338 (11) | −0.13446 (18) | 0.0417 (5) | |
| C6 | 0.5028 (3) | 0.09863 (12) | −0.16864 (19) | 0.0463 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.5869 (3) | 0.08969 (13) | −0.2347 (2) | 0.0514 (5) | |
| H7 | 0.6021 | 0.0411 | −0.2580 | 0.062* | |
| C8 | 0.6515 (3) | 0.15355 (14) | −0.2683 (2) | 0.0526 (6) | |
| H8 | 0.7089 | 0.1461 | −0.3131 | 0.063* | |
| C9 | 0.6317 (2) | 0.22567 (13) | −0.23653 (18) | 0.0465 (5) | |
| C10 | 0.5433 (2) | 0.23684 (12) | −0.16778 (17) | 0.0417 (5) | |
| C11 | 0.4590 (4) | −0.03500 (14) | −0.1605 (3) | 0.0733 (8) | |
| H11A | 0.4239 | −0.0394 | −0.2387 | 0.110* | |
| H11B | 0.4054 | −0.0697 | −0.1300 | 0.110* | |
| H11C | 0.5623 | −0.0473 | −0.1334 | 0.110* | |
| C12 | 0.7822 (3) | 0.28219 (17) | −0.3307 (3) | 0.0708 (8) | |
| H12A | 0.8597 | 0.2464 | −0.2973 | 0.106* | |
| H12B | 0.8247 | 0.3308 | −0.3377 | 0.106* | |
| H12C | 0.7244 | 0.2640 | −0.4017 | 0.106* | |
| C13 | 0.2718 (3) | 0.27974 (13) | 0.0337 (2) | 0.0520 (6) | |
| H13 | 0.3102 | 0.3251 | 0.0781 | 0.062* | |
| C14 | 0.1144 (3) | 0.29516 (14) | −0.0433 (2) | 0.0559 (6) | |
| H14 | 0.1170 | 0.3162 | −0.1129 | 0.067* | |
| C15 | 0.0444 (3) | 0.21579 (13) | −0.0605 (2) | 0.0548 (6) | |
| H15A | −0.0596 | 0.2188 | −0.0682 | 0.066* | |
| H15B | 0.0544 | 0.1921 | −0.1255 | 0.066* | |
| C16 | 0.2513 (3) | 0.21506 (13) | 0.10654 (19) | 0.0487 (5) | |
| H16A | 0.3385 | 0.1830 | 0.1305 | 0.058* | |
| H16B | 0.2314 | 0.2351 | 0.1702 | 0.058* | |
| C17 | 0.0583 (2) | 0.11625 (12) | 0.08000 (18) | 0.0441 (5) | |
| C18 | −0.0791 (3) | 0.08503 (13) | 0.0195 (2) | 0.0500 (5) | |
| H18 | −0.1277 | 0.1023 | −0.0511 | 0.060* | |
| C19 | −0.1420 (3) | 0.02882 (15) | 0.0646 (2) | 0.0619 (7) | |
| H19 | −0.2333 | 0.0089 | 0.0237 | 0.074* | |
| C20 | −0.0738 (3) | 0.00156 (15) | 0.1677 (3) | 0.0694 (8) | |
| H20 | −0.1182 | −0.0361 | 0.1971 | 0.083* | |
| C21 | 0.0624 (3) | 0.03104 (15) | 0.2276 (2) | 0.0651 (7) | |
| H21 | 0.1104 | 0.0127 | 0.2976 | 0.078* | |
| C22 | 0.1281 (3) | 0.08755 (13) | 0.1845 (2) | 0.0519 (6) | |
| H22 | 0.2199 | 0.1066 | 0.2259 | 0.062* | |
| C23 | 0.0291 (3) | 0.34891 (17) | 0.0089 (3) | 0.0662 (7) | |
| C24 | −0.1671 (4) | 0.4343 (2) | −0.0293 (4) | 0.1079 (13) | |
| H24A | −0.2517 | 0.4048 | −0.0297 | 0.162* | |
| H24B | −0.1985 | 0.4769 | −0.0781 | 0.162* | |
| H24C | −0.1176 | 0.4527 | 0.0433 | 0.162* | |
| Cl1 | 0.41733 (7) | 0.41375 (3) | −0.04310 (5) | 0.0582 (2) | |
| N1 | 0.5228 (2) | 0.30920 (10) | −0.13716 (15) | 0.0447 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.1249 (2) | 0.17236 (11) | 0.03698 (15) | 0.0487 (5) | |
| O1 | 0.4375 (2) | 0.04110 (9) | −0.13011 (16) | 0.0635 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.6896 (2) | 0.29035 (10) | −0.26382 (16) | 0.0650 (5) | |
| O3 | 0.0479 (4) | 0.3523 (2) | 0.1042 (3) | 0.1496 (14) | |
| O4 | −0.0678 (3) | 0.38737 (15) | −0.0644 (2) | 0.0947 (8) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C2 | 0.0513 (12) | 0.0368 (10) | 0.0521 (12) | −0.0025 (9) | 0.0211 (10) | 0.0011 (9) |
| C3 | 0.0518 (13) | 0.0418 (11) | 0.0572 (14) | −0.0015 (9) | 0.0262 (11) | −0.0001 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0542 (13) | 0.0390 (10) | 0.0623 (14) | −0.0046 (9) | 0.0292 (11) | 0.0025 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0422 (11) | 0.0385 (10) | 0.0478 (12) | −0.0029 (8) | 0.0192 (9) | 0.0003 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0469 (12) | 0.0387 (11) | 0.0562 (13) | −0.0012 (9) | 0.0210 (10) | −0.0010 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0578 (14) | 0.0439 (11) | 0.0571 (14) | 0.0027 (10) | 0.0249 (11) | −0.0048 (10) |
| C8 | 0.0566 (14) | 0.0570 (13) | 0.0535 (13) | 0.0023 (11) | 0.0306 (11) | 0.0002 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0472 (12) | 0.0485 (12) | 0.0480 (12) | −0.0020 (9) | 0.0215 (10) | 0.0055 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0404 (11) | 0.0412 (11) | 0.0447 (12) | −0.0007 (8) | 0.0155 (9) | 0.0037 (8) |
| C11 | 0.088 (2) | 0.0378 (12) | 0.106 (2) | −0.0050 (13) | 0.0492 (18) | −0.0099 (13) |
| C12 | 0.0718 (18) | 0.0793 (18) | 0.0783 (19) | 0.0021 (14) | 0.0476 (16) | 0.0170 (15) |
| C13 | 0.0581 (14) | 0.0469 (12) | 0.0550 (14) | −0.0054 (10) | 0.0239 (11) | −0.0039 (10) |
| C14 | 0.0670 (15) | 0.0525 (13) | 0.0547 (14) | 0.0026 (11) | 0.0288 (12) | 0.0043 (11) |
| C15 | 0.0602 (14) | 0.0527 (13) | 0.0488 (13) | −0.0032 (11) | 0.0142 (11) | 0.0016 (10) |
| C16 | 0.0485 (12) | 0.0512 (12) | 0.0483 (12) | −0.0079 (10) | 0.0183 (10) | −0.0035 (9) |
| C17 | 0.0476 (12) | 0.0414 (10) | 0.0514 (12) | −0.0012 (9) | 0.0270 (10) | −0.0052 (9) |
| C18 | 0.0488 (13) | 0.0509 (12) | 0.0552 (13) | −0.0036 (10) | 0.0238 (11) | −0.0106 (10) |
| C19 | 0.0585 (15) | 0.0552 (13) | 0.0839 (19) | −0.0132 (12) | 0.0394 (14) | −0.0167 (13) |
| C20 | 0.081 (2) | 0.0564 (15) | 0.089 (2) | −0.0128 (14) | 0.0530 (18) | 0.0000 (14) |
| C21 | 0.0787 (18) | 0.0627 (15) | 0.0649 (16) | 0.0021 (14) | 0.0386 (14) | 0.0115 (12) |
| C22 | 0.0537 (13) | 0.0528 (13) | 0.0548 (14) | −0.0039 (10) | 0.0252 (11) | 0.0017 (10) |
| C23 | 0.0716 (17) | 0.0722 (17) | 0.0677 (18) | 0.0082 (14) | 0.0403 (15) | 0.0035 (14) |
| C24 | 0.075 (2) | 0.119 (3) | 0.134 (3) | 0.026 (2) | 0.040 (2) | −0.042 (3) |
| Cl1 | 0.0772 (4) | 0.0366 (3) | 0.0688 (4) | −0.0023 (3) | 0.0349 (3) | −0.0035 (2) |
| N1 | 0.0473 (10) | 0.0404 (9) | 0.0491 (10) | −0.0048 (8) | 0.0194 (8) | 0.0008 (7) |
| N2 | 0.0488 (10) | 0.0526 (11) | 0.0449 (10) | −0.0100 (8) | 0.0153 (8) | 0.0012 (8) |
| O1 | 0.0766 (12) | 0.0357 (8) | 0.0950 (14) | −0.0065 (8) | 0.0510 (11) | −0.0048 (8) |
| O2 | 0.0799 (12) | 0.0537 (10) | 0.0820 (13) | −0.0051 (9) | 0.0546 (11) | 0.0084 (8) |
| O3 | 0.196 (3) | 0.168 (3) | 0.098 (2) | 0.098 (3) | 0.065 (2) | 0.008 (2) |
| O4 | 0.0841 (15) | 0.1037 (17) | 0.0949 (17) | 0.0388 (13) | 0.0272 (13) | −0.0179 (13) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C2—N1 | 1.296 (3) | C13—H13 | 0.9800 |
| C2—C3 | 1.414 (3) | C14—C15 | 1.528 (3) |
| C2—Cl1 | 1.757 (2) | C14—C23 | 1.540 (4) |
| C3—C4 | 1.369 (3) | C14—H14 | 0.9800 |
| C3—C13 | 1.528 (3) | C15—N2 | 1.460 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.419 (3) | C15—H15A | 0.9700 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C15—H15B | 0.9700 |
| C5—C10 | 1.412 (3) | C16—N2 | 1.458 (3) |
| C5—C6 | 1.427 (3) | C16—H16A | 0.9700 |
| C6—C7 | 1.362 (3) | C16—H16B | 0.9700 |
| C6—O1 | 1.363 (3) | C17—N2 | 1.384 (3) |
| C7—C8 | 1.413 (3) | C17—C22 | 1.393 (3) |
| C7—H7 | 0.9300 | C17—C18 | 1.405 (3) |
| C8—C9 | 1.361 (3) | C18—C19 | 1.379 (3) |
| C8—H8 | 0.9300 | C18—H18 | 0.9300 |
| C9—O2 | 1.358 (3) | C19—C20 | 1.368 (4) |
| C9—C10 | 1.427 (3) | C19—H19 | 0.9300 |
| C10—N1 | 1.361 (3) | C20—C21 | 1.382 (4) |
| C11—O1 | 1.424 (3) | C20—H20 | 0.9300 |
| C11—H11A | 0.9600 | C21—C22 | 1.384 (3) |
| C11—H11B | 0.9600 | C21—H21 | 0.9300 |
| C11—H11C | 0.9600 | C22—H22 | 0.9300 |
| C12—O2 | 1.434 (3) | C23—O3 | 1.190 (4) |
| C12—H12A | 0.9600 | C23—O4 | 1.281 (4) |
| C12—H12B | 0.9600 | C24—O4 | 1.439 (3) |
| C12—H12C | 0.9600 | C24—H24A | 0.9600 |
| C13—C16 | 1.527 (3) | C24—H24B | 0.9600 |
| C13—C14 | 1.536 (4) | C24—H24C | 0.9600 |
| N1—C2—C3 | 126.9 (2) | C13—C14—H14 | 110.4 |
| N1—C2—Cl1 | 114.55 (15) | C23—C14—H14 | 110.4 |
| C3—C2—Cl1 | 118.52 (17) | N2—C15—C14 | 105.40 (19) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 114.9 (2) | N2—C15—H15A | 110.7 |
| C4—C3—C13 | 123.70 (19) | C14—C15—H15A | 110.7 |
| C2—C3—C13 | 121.36 (19) | N2—C15—H15B | 110.7 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 121.5 (2) | C14—C15—H15B | 110.7 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.3 | H15A—C15—H15B | 108.8 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.3 | N2—C16—C13 | 104.32 (19) |
| C10—C5—C4 | 117.30 (19) | N2—C16—H16A | 110.9 |
| C10—C5—C6 | 119.41 (18) | C13—C16—H16A | 110.9 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 123.29 (18) | N2—C16—H16B | 110.9 |
| C7—C6—O1 | 125.5 (2) | C13—C16—H16B | 110.9 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 119.60 (19) | H16A—C16—H16B | 108.9 |
| O1—C6—C5 | 114.91 (18) | N2—C17—C22 | 120.6 (2) |
| C6—C7—C8 | 120.6 (2) | N2—C17—C18 | 121.5 (2) |
| C6—C7—H7 | 119.7 | C22—C17—C18 | 117.8 (2) |
| C8—C7—H7 | 119.7 | C19—C18—C17 | 120.1 (2) |
| C9—C8—C7 | 121.6 (2) | C19—C18—H18 | 120.0 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 119.2 | C17—C18—H18 | 120.0 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 119.2 | C20—C19—C18 | 121.8 (3) |
| O2—C9—C8 | 126.0 (2) | C20—C19—H19 | 119.1 |
| O2—C9—C10 | 115.04 (19) | C18—C19—H19 | 119.1 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 118.99 (19) | C19—C20—C21 | 118.7 (2) |
| N1—C10—C5 | 121.56 (18) | C19—C20—H20 | 120.6 |
| N1—C10—C9 | 118.70 (18) | C21—C20—H20 | 120.6 |
| C5—C10—C9 | 119.73 (19) | C20—C21—C22 | 120.8 (3) |
| O1—C11—H11A | 109.5 | C20—C21—H21 | 119.6 |
| O1—C11—H11B | 109.5 | C22—C21—H21 | 119.6 |
| H11A—C11—H11B | 109.5 | C21—C22—C17 | 120.8 (2) |
| O1—C11—H11C | 109.5 | C21—C22—H22 | 119.6 |
| H11A—C11—H11C | 109.5 | C17—C22—H22 | 119.6 |
| H11B—C11—H11C | 109.5 | O3—C23—O4 | 124.8 (3) |
| O2—C12—H12A | 109.5 | O3—C23—C14 | 124.3 (3) |
| O2—C12—H12B | 109.5 | O4—C23—C14 | 110.9 (2) |
| H12A—C12—H12B | 109.5 | O4—C24—H24A | 109.5 |
| O2—C12—H12C | 109.5 | O4—C24—H24B | 109.5 |
| H12A—C12—H12C | 109.5 | H24A—C24—H24B | 109.5 |
| H12B—C12—H12C | 109.5 | O4—C24—H24C | 109.5 |
| C16—C13—C3 | 115.15 (19) | H24A—C24—H24C | 109.5 |
| C16—C13—C14 | 103.61 (19) | H24B—C24—H24C | 109.5 |
| C3—C13—C14 | 108.3 (2) | C2—N1—C10 | 117.82 (18) |
| C16—C13—H13 | 109.8 | C17—N2—C16 | 120.98 (18) |
| C3—C13—H13 | 109.8 | C17—N2—C15 | 122.38 (19) |
| C14—C13—H13 | 109.8 | C16—N2—C15 | 111.38 (18) |
| C15—C14—C13 | 103.03 (19) | C6—O1—C11 | 117.75 (19) |
| C15—C14—C23 | 110.5 (2) | C9—O2—C12 | 117.3 (2) |
| C13—C14—C23 | 111.8 (2) | C23—O4—C24 | 117.5 (3) |
| C15—C14—H14 | 110.4 |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C12—H12B···Cg1i | 0.96 | 2.67 | 3.601 (3) | 164 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1, −y+1/2, z−1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: DN2384).
References
- Belfaitah, A., Ladraa, S., Bouraiou, A., Benali-Cherif, N., Debache, A. & Rhouati, S. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o1355–o1357.
- Bouraiou, A., Belfaitah, A., Bouacida, S., Benard-Rocherulle, P. & Carboni, B. (2007a). Acta Cryst. E63, o2133–o2135.
- Bouraiou, A., Belfaitah, A., Bouacida, S., Benard-Rocherulle, P. & Carboni, B. (2007b). Acta Cryst. E63, o1626–o1628.
- Bouraiou, A., Debache, A., Rhouati, S., Carboni, B. & Belfaitah, A. (2008). J. Heterocycl. Chem.45, 329–333.
- Burla, M. C., Camalli, M., Carrozzini, B., Cascarano, G. L., Giacovazzo, C., Polidori, G. & Spagna, R. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst.36, 1103.
- Burnett, M. N. & Johnson, C. K. (1996). ORTEPIII Report ORNL-6895. Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Tennessee, USA.
- Dow, G. S., et al. (2006). Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.50, 4132–4143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst.32, 837–838.
- Kravchenko, D. V., Kysil, V. M., Tkachenko, S. E., Maliarchouk, S., Okun, I. M. & Ivachtchenko, A. V. (2005). Eur. J. Med. Chem.40, 1377–1383. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Menasra, H., Kedjadja, A., Debache, A., Rhouati, S., Carboni, B. & Belfaitah, A. (2005). Synth. Commun.35, 2779–2788.
- Moussaoui, F., Belfaitah, A., Debache, A. & Rhouati, S. (2002). J. Soc. Alger. Chim.12, 71–78.
- Nonius (1998). COLLECT Nonius BV, Delft The Netherlands.
- Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. (1997). Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 276, Macromolecular Crystallography, Part A, edited by C. W. Carter Jr & R. M. Sweet, pp. 307–326. New York: Academic Press.
- Padwa, A., Brodney, M. A., Liu, B., Satake, K. & Wu, T. (1999). J. Org. Chem.64, 3595–3607. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Pearce, L., Prout, C. K. & Watkin, D. J. (2000). CAMERON Chemical Crystallography Laboratory, University of Oxford, England.
- Rao, S. T., Westhof, E. & Sundaralingam, M. (1981). Acta Cryst. A37, 421–425.
- Rezig, R., Chebah, M., Rhouati, S., Ducki, S. & Lawrence, N. (2000). J. Soc. Alger. Chim.10, 111–120.
- Robert, A. & Meunier, B. (1998). Chem. Soc. Rev.27, 273–274.
- Sahu, N. P., Pal, C., Mandal, N. B., Banerjee, S., Raha, M., Kundu, A. P., Basu, A., Ghosh, M., Roy, K. & Bandyopadhyay, S. (2002). Bioorg. Med. Chem.10, 1687–1693. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst.36, 7–13.
- Witherup, K., Ranson, R. W., Graham, A. C., Barnard, A. M., Salvatore, M. J., Limma, W. C., Anderson, P. S., Pitzenberger, S. M. & Varga, S. L. (1995). J. Am. Chem. Soc.117, 6682–6685.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808031838/dn2384sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808031838/dn2384Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




