Abstract
The asymmetric unit of the title crystal structure, [Cd3(NCS)6(C7H6N4)2]n, contains two independent CdII ions, one of which is located on a crystallographic inversion center. Each independent CdII ion is in a slightly distorted octahedral coordination environment, but the disortion from ideally octahedral is greater in the environment of the CdII ion on a general position. Both thiocyanate ligands act as bridges connecting independent CdII ions, and the 2-(pyrazol-1-yl)pyrazine ligands chelate one CdII ion in a bidentate mode while the remaining N atom of the pyrazine ring coordinates to a symmetry-related CdII ion, forming a two-dimensional structure parallel to (211).
Related literature
For background information, see: Shi, Sun, Liu et al. (2006 ▶); Shi, Sun, Zhang et al. (2006 ▶). 
Experimental
Crystal data
[Cd3(NCS)6(C7H6N4)2]
M r = 978.00
Triclinic,

a = 7.0309 (9) Å
b = 8.6178 (12) Å
c = 13.7373 (18) Å
α = 87.889 (2)°
β = 85.173 (2)°
γ = 68.060 (2)°
V = 769.32 (18) Å3
Z = 1
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 2.50 mm−1
T = 298 (2) K
0.38 × 0.16 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.450, T max = 0.788
4043 measured reflections
2805 independent reflections
2625 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.013
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.022
wR(F 2) = 0.056
S = 1.06
2805 reflections
196 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.61 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.51 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 1997 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 1997 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: SHELXTL; software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808032285/lh2704sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808032285/lh2704Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Selected bond lengths (Å).
| Cd1—N2 | 2.286 (3) |
| Cd1—N7i | 2.426 (2) |
| Cd1—S2 | 2.6832 (8) |
| Cd2—N1ii | 2.244 (2) |
| Cd2—N3 | 2.303 (3) |
| Cd2—N5 | 2.385 (2) |
| Cd2—N4 | 2.436 (2) |
| Cd2—S1 | 2.6603 (9) |
| Cd2—S3 | 2.7427 (8) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 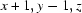 ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
For a considerable time, interest has focused on polymeric coordination compounds because such new coordination polymers may afford new materials with useful properties, such as catalytic activity, micro-porosity, electrical conductivity, non-linear optical activity and magnetic coupling behavior. The thiocyanide anion is a very common bridging ligand and many muti-nuclear complexes containing this ligand have been reported. Some of these complexes exhibit interesting magnetic coupling properties (Shi, Sun, Liu et al., 2006; Shi, Sun, Zhang et al., 2006)). The 2-(pyrazole-1-yl)-pyrazine molecule can act as a bridge ligand due to its structural character and up till now no crystal structures of complexes with this ligand have been reported. Under the motivation of preparing new coordination polymers containing mixed bridging ligands, we have synthesized the title coordination polymer and herein we report its crystal structure (I).
Fig. 1 shows the coordination around each independent CdII ion. Atom Cd1 is located on a crystallographic inversion center. In the crystal structure thiocyanade anions act as bridging ligands and connect symmetry related CdII ions [with Cd···Cd = 5.8122 (6)Å for Cd1···Cd2 and 5.7411 (7) Å for Cd2···Cd2ii; symmetry code: (ii) -x+1, -y+1, -z+1] forming an eight-membered ring which acts as a repeat unit of the structure in one-dimension [Fig. 2]. The 2-(pyrazole-1-yl)-pyrazine ligand functions as a tridentate bridging ligand and coordinates to symmetry related CdII ions [with a Cd···Cd separation of 7.6144 (7)Å] connecting the structure further into two-dimensions. Figure 2 also shows that in the two-dimensional structure there are two different types of rings formed by the 2-(pyrazole-1-yl)-pyrazine bridging ligand. An 18-membered ring consists of four CdII ions, two thiocyanato ligands and two 2-(pyrazole-1-yl)-pyrazine bridging ligands while a 26-membered ring consists of two 2-(pyrazole-1-yl)-pyrazine bridging ligands, four thiocyanade ligands and six CdII ions. The 18-membered rings and the 26-membered rings are arranged alternately in the two-dimensional structure.
Experimental
7 ml 3-(pyrazole-2-yloxy)-pyridine (0.0365 g, 0.250 mmol) methanol solution, 7 ml C d(ClO4)26H2O (0.1048 g, 0.250 mmol) H2O solution and 4 ml NaSCN (0.0405 g, 0.500 mmol) H2O solution were mixed together and stirred for a few minutes. Colorless single crystals were obtained after allowing the filtrate to stand at room temperature for four months.
Refinement
All H atoms were placed in calculated positions and refined as riding with (C—H = 0.93 Å) and Uiso = 1.2Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
Coordination around the two independent CdII ions in (I) with the atom-numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level [symmetry codes: (i) x-1, y+1, z (ii) -x+1, -y+1, -z+1 (iii) -x+1, -y, -z (iv) x+1, y-1, z (v) -x, -y+1, -z].
Fig. 2.
Part of the two-dimensional sheet structure of (I).
Crystal data
| [Cd3(NCS)6(C7H6N4)2] | Z = 1 |
| Mr = 978.00 | F(000) = 470 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 2.111 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 7.0309 (9) Å | Cell parameters from 3404 reflections |
| b = 8.6178 (12) Å | θ = 2.6–28.2° |
| c = 13.7373 (18) Å | µ = 2.50 mm−1 |
| α = 87.889 (2)° | T = 298 K |
| β = 85.173 (2)° | Bar, colorless |
| γ = 68.060 (2)° | 0.38 × 0.16 × 0.10 mm |
| V = 769.32 (18) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer | 2805 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2625 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.013 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 25.5°, θmin = 2.6° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −4→8 |
| Tmin = 0.450, Tmax = 0.788 | k = −10→10 |
| 4043 measured reflections | l = −15→16 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.022 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.056 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.06 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0271P)2 + 0.3586P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2805 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 196 parameters | Δρmax = 0.61 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.51 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.0009 (4) | 0.7101 (4) | 0.49099 (19) | 0.0358 (6) | |
| H1 | 0.0564 | 0.6478 | 0.5456 | 0.043* | |
| C2 | −0.1423 (5) | 0.8730 (4) | 0.4948 (2) | 0.0402 (7) | |
| H2 | −0.1990 | 0.9378 | 0.5502 | 0.048* | |
| C3 | −0.1821 (5) | 0.9178 (4) | 0.4006 (2) | 0.0383 (7) | |
| H3 | −0.2725 | 1.0200 | 0.3788 | 0.046* | |
| C4 | −0.0578 (4) | 0.7640 (3) | 0.24350 (18) | 0.0260 (5) | |
| C5 | 0.1109 (5) | 0.6225 (4) | 0.1068 (2) | 0.0381 (7) | |
| H5 | 0.2239 | 0.5397 | 0.0758 | 0.046* | |
| C6 | −0.0462 (5) | 0.7197 (4) | 0.0532 (2) | 0.0388 (7) | |
| H6 | −0.0368 | 0.7019 | −0.0137 | 0.047* | |
| C7 | 0.5004 (4) | 0.6931 (3) | 0.4694 (2) | 0.0312 (6) | |
| C8 | 0.2476 (4) | 0.1598 (3) | 0.21816 (19) | 0.0309 (6) | |
| C9 | 0.6045 (4) | 0.3004 (4) | 0.1046 (2) | 0.0369 (7) | |
| C13 | −0.2187 (4) | 0.8625 (3) | 0.18960 (19) | 0.0311 (6) | |
| H13 | −0.3319 | 0.9454 | 0.2206 | 0.037* | |
| Cd1 | 0.5000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.02922 (9) | |
| Cd2 | 0.35673 (3) | 0.47371 (2) | 0.314014 (13) | 0.02935 (8) | |
| N1 | 0.5156 (4) | 0.6693 (3) | 0.55123 (18) | 0.0419 (6) | |
| N2 | 0.5526 (4) | 0.2304 (3) | 0.04926 (19) | 0.0445 (6) | |
| N3 | 0.2614 (4) | 0.2620 (3) | 0.26533 (18) | 0.0438 (6) | |
| N4 | 0.1055 (3) | 0.6441 (3) | 0.20341 (16) | 0.0298 (5) | |
| N5 | 0.0489 (3) | 0.6539 (3) | 0.40006 (16) | 0.0311 (5) | |
| N6 | −0.0646 (3) | 0.7848 (3) | 0.34443 (15) | 0.0292 (5) | |
| N7 | −0.2124 (3) | 0.8392 (3) | 0.09389 (16) | 0.0325 (5) | |
| S1 | 0.67535 (14) | 0.40534 (14) | 0.18169 (7) | 0.0617 (3) | |
| S2 | 0.22912 (12) | 0.01127 (9) | 0.15191 (5) | 0.03591 (17) | |
| S3 | 0.47355 (13) | 0.73397 (10) | 0.35252 (5) | 0.04143 (19) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0406 (16) | 0.0454 (16) | 0.0255 (14) | −0.0200 (14) | −0.0055 (12) | 0.0002 (12) |
| C2 | 0.0428 (17) | 0.0477 (17) | 0.0322 (15) | −0.0193 (14) | 0.0024 (13) | −0.0120 (13) |
| C3 | 0.0397 (16) | 0.0325 (15) | 0.0388 (16) | −0.0084 (13) | −0.0025 (13) | −0.0082 (12) |
| C4 | 0.0233 (13) | 0.0304 (13) | 0.0244 (13) | −0.0100 (11) | −0.0017 (10) | 0.0002 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0332 (15) | 0.0398 (16) | 0.0282 (14) | 0.0017 (13) | −0.0024 (12) | −0.0046 (12) |
| C6 | 0.0380 (16) | 0.0445 (16) | 0.0243 (14) | −0.0040 (13) | −0.0039 (12) | −0.0001 (12) |
| C7 | 0.0316 (14) | 0.0281 (13) | 0.0344 (16) | −0.0105 (11) | −0.0082 (12) | −0.0009 (11) |
| C8 | 0.0312 (15) | 0.0360 (15) | 0.0247 (13) | −0.0121 (12) | −0.0023 (11) | 0.0042 (12) |
| C9 | 0.0312 (15) | 0.0371 (15) | 0.0368 (16) | −0.0075 (13) | 0.0061 (12) | −0.0059 (13) |
| C13 | 0.0250 (13) | 0.0337 (14) | 0.0285 (14) | −0.0036 (11) | −0.0035 (11) | 0.0007 (11) |
| Cd1 | 0.02909 (16) | 0.03095 (15) | 0.02367 (15) | −0.00539 (12) | −0.00732 (11) | −0.00178 (11) |
| Cd2 | 0.02855 (12) | 0.03169 (12) | 0.02402 (12) | −0.00559 (9) | −0.00708 (8) | −0.00237 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0545 (16) | 0.0386 (14) | 0.0348 (14) | −0.0171 (12) | −0.0183 (12) | 0.0057 (11) |
| N2 | 0.0539 (17) | 0.0435 (15) | 0.0377 (14) | −0.0203 (13) | 0.0023 (12) | −0.0115 (12) |
| N3 | 0.0551 (17) | 0.0472 (15) | 0.0326 (13) | −0.0228 (13) | −0.0010 (12) | −0.0081 (12) |
| N4 | 0.0251 (11) | 0.0327 (12) | 0.0280 (12) | −0.0062 (10) | −0.0057 (9) | 0.0008 (9) |
| N5 | 0.0288 (12) | 0.0353 (12) | 0.0266 (11) | −0.0088 (10) | −0.0045 (9) | 0.0028 (9) |
| N6 | 0.0260 (11) | 0.0327 (12) | 0.0263 (11) | −0.0072 (9) | −0.0057 (9) | −0.0008 (9) |
| N7 | 0.0271 (12) | 0.0367 (12) | 0.0283 (12) | −0.0053 (10) | −0.0056 (10) | 0.0032 (10) |
| S1 | 0.0419 (5) | 0.0957 (7) | 0.0566 (5) | −0.0359 (5) | 0.0139 (4) | −0.0407 (5) |
| S2 | 0.0423 (4) | 0.0402 (4) | 0.0301 (4) | −0.0209 (3) | −0.0007 (3) | −0.0051 (3) |
| S3 | 0.0571 (5) | 0.0523 (5) | 0.0274 (4) | −0.0342 (4) | −0.0067 (3) | 0.0023 (3) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—N5 | 1.327 (3) | C9—N2 | 1.148 (4) |
| C1—C2 | 1.388 (4) | C9—S1 | 1.639 (3) |
| C1—H1 | 0.9300 | C13—N7 | 1.332 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.359 (4) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | Cd1—N2 | 2.286 (3) |
| C3—N6 | 1.357 (3) | Cd1—N2i | 2.286 (3) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | Cd1—N7ii | 2.426 (2) |
| C4—N4 | 1.319 (3) | Cd1—N7iii | 2.426 (2) |
| C4—C13 | 1.388 (4) | Cd1—S2i | 2.6832 (8) |
| C4—N6 | 1.399 (3) | Cd1—S2 | 2.6832 (8) |
| C5—N4 | 1.342 (3) | Cd2—N1iv | 2.244 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.365 (4) | Cd2—N3 | 2.303 (3) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | Cd2—N5 | 2.385 (2) |
| C6—N7 | 1.331 (4) | Cd2—N4 | 2.436 (2) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | Cd2—S1 | 2.6603 (9) |
| C7—N1 | 1.142 (3) | Cd2—S3 | 2.7427 (8) |
| C7—S3 | 1.643 (3) | N1—Cd2iv | 2.244 (2) |
| C8—N3 | 1.150 (4) | N5—N6 | 1.364 (3) |
| C8—S2 | 1.647 (3) | N7—Cd1v | 2.426 (2) |
| N5—C1—C2 | 111.8 (3) | N7ii—Cd1—S2 | 91.66 (6) |
| N5—C1—H1 | 124.1 | N7iii—Cd1—S2 | 88.34 (6) |
| C2—C1—H1 | 124.1 | S2i—Cd1—S2 | 180 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 105.6 (3) | N1iv—Cd2—N3 | 91.59 (9) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 127.2 | N1iv—Cd2—N5 | 93.71 (9) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 127.2 | N3—Cd2—N5 | 102.07 (9) |
| N6—C3—C2 | 106.9 (3) | N1iv—Cd2—N4 | 159.57 (9) |
| N6—C3—H3 | 126.6 | N3—Cd2—N4 | 83.77 (9) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 126.6 | N5—Cd2—N4 | 68.04 (7) |
| N4—C4—C13 | 122.2 (2) | N1iv—Cd2—S1 | 105.57 (8) |
| N4—C4—N6 | 116.7 (2) | N3—Cd2—S1 | 94.46 (7) |
| C13—C4—N6 | 121.1 (2) | N5—Cd2—S1 | 154.21 (6) |
| N4—C5—C6 | 121.4 (3) | N4—Cd2—S1 | 94.63 (6) |
| N4—C5—H5 | 119.3 | N1iv—Cd2—S3 | 93.51 (7) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.3 | N3—Cd2—S3 | 174.25 (7) |
| N7—C6—C5 | 121.9 (3) | N5—Cd2—S3 | 80.27 (6) |
| N7—C6—H6 | 119.0 | N4—Cd2—S3 | 92.33 (6) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.0 | S1—Cd2—S3 | 81.60 (3) |
| N1—C7—S3 | 178.1 (3) | C7—N1—Cd2iv | 156.4 (2) |
| N3—C8—S2 | 179.1 (3) | C9—N2—Cd1 | 151.9 (3) |
| N2—C9—S1 | 178.3 (3) | C8—N3—Cd2 | 160.7 (2) |
| N7—C13—C4 | 120.5 (2) | C4—N4—C5 | 116.7 (2) |
| N7—C13—H13 | 119.7 | C4—N4—Cd2 | 116.51 (17) |
| C4—C13—H13 | 119.7 | C5—N4—Cd2 | 126.65 (18) |
| N2—Cd1—N2i | 180 | C1—N5—N6 | 104.4 (2) |
| N2—Cd1—N7ii | 85.94 (9) | C1—N5—Cd2 | 134.13 (19) |
| N2i—Cd1—N7ii | 94.06 (9) | N6—N5—Cd2 | 112.89 (15) |
| N2—Cd1—N7iii | 94.06 (9) | C3—N6—N5 | 111.4 (2) |
| N2i—Cd1—N7iii | 85.94 (9) | C3—N6—C4 | 129.3 (2) |
| N7ii—Cd1—N7iii | 180 | N5—N6—C4 | 119.2 (2) |
| N2—Cd1—S2i | 86.38 (7) | C6—N7—C13 | 117.2 (2) |
| N2i—Cd1—S2i | 93.62 (7) | C6—N7—Cd1v | 121.71 (18) |
| N7ii—Cd1—S2i | 88.34 (6) | C13—N7—Cd1v | 120.98 (18) |
| N7iii—Cd1—S2i | 91.66 (6) | C9—S1—Cd2 | 98.65 (11) |
| N2—Cd1—S2 | 93.62 (7) | C8—S2—Cd1 | 101.07 (10) |
| N2i—Cd1—S2 | 86.38 (7) | C7—S3—Cd2 | 96.52 (10) |
| N5—C1—C2—C3 | −0.3 (4) | S1—Cd2—N5—C1 | −110.8 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—N6 | −0.3 (3) | S3—Cd2—N5—C1 | −64.9 (3) |
| N4—C5—C6—N7 | −0.5 (5) | N1iv—Cd2—N5—N6 | 169.76 (17) |
| N4—C4—C13—N7 | −0.5 (4) | N3—Cd2—N5—N6 | −97.82 (18) |
| N6—C4—C13—N7 | −178.6 (2) | N4—Cd2—N5—N6 | −19.70 (16) |
| N7ii—Cd1—N2—C9 | −30.1 (5) | S1—Cd2—N5—N6 | 30.9 (3) |
| N7iii—Cd1—N2—C9 | 149.9 (5) | S3—Cd2—N5—N6 | 76.83 (17) |
| S2i—Cd1—N2—C9 | −118.7 (5) | C2—C3—N6—N5 | 0.7 (3) |
| S2—Cd1—N2—C9 | 61.3 (5) | C2—C3—N6—C4 | 176.0 (3) |
| N1iv—Cd2—N3—C8 | −124.3 (8) | C1—N5—N6—C3 | −0.9 (3) |
| N5—Cd2—N3—C8 | 141.6 (8) | Cd2—N5—N6—C3 | −153.58 (19) |
| N4—Cd2—N3—C8 | 75.7 (8) | C1—N5—N6—C4 | −176.7 (2) |
| S1—Cd2—N3—C8 | −18.5 (8) | Cd2—N5—N6—C4 | 30.6 (3) |
| C13—C4—N4—C5 | 0.9 (4) | N4—C4—N6—C3 | 162.2 (3) |
| N6—C4—N4—C5 | 179.1 (3) | C13—C4—N6—C3 | −19.5 (4) |
| C13—C4—N4—Cd2 | −175.6 (2) | N4—C4—N6—N5 | −22.8 (3) |
| N6—C4—N4—Cd2 | 2.7 (3) | C13—C4—N6—N5 | 155.5 (2) |
| C6—C5—N4—C4 | −0.4 (4) | C5—C6—N7—C13 | 1.0 (5) |
| C6—C5—N4—Cd2 | 175.7 (2) | C5—C6—N7—Cd1v | −176.2 (2) |
| N1iv—Cd2—N4—C4 | 37.2 (3) | C4—C13—N7—C6 | −0.5 (4) |
| N3—Cd2—N4—C4 | 114.9 (2) | C4—C13—N7—Cd1v | 176.70 (19) |
| N5—Cd2—N4—C4 | 9.15 (18) | N1iv—Cd2—S1—C9 | 113.39 (13) |
| S1—Cd2—N4—C4 | −151.14 (18) | N3—Cd2—S1—C9 | 20.49 (14) |
| S3—Cd2—N4—C4 | −69.38 (19) | N5—Cd2—S1—C9 | −109.59 (17) |
| N1iv—Cd2—N4—C5 | −138.9 (3) | N4—Cd2—S1—C9 | −63.61 (13) |
| N3—Cd2—N4—C5 | −61.2 (3) | S3—Cd2—S1—C9 | −155.29 (12) |
| N5—Cd2—N4—C5 | −166.9 (3) | N2—Cd1—S2—C8 | −7.34 (12) |
| S1—Cd2—N4—C5 | 32.8 (2) | N2i—Cd1—S2—C8 | 172.66 (12) |
| S3—Cd2—N4—C5 | 114.6 (2) | N7ii—Cd1—S2—C8 | 78.70 (11) |
| C2—C1—N5—N6 | 0.7 (3) | N7iii—Cd1—S2—C8 | −101.30 (11) |
| C2—C1—N5—Cd2 | 144.6 (2) | N1iv—Cd2—S3—C7 | −19.29 (12) |
| N1iv—Cd2—N5—C1 | 28.0 (3) | N5—Cd2—S3—C7 | 73.89 (11) |
| N3—Cd2—N5—C1 | 120.4 (3) | N4—Cd2—S3—C7 | 141.13 (11) |
| N4—Cd2—N5—C1 | −161.5 (3) | S1—Cd2—S3—C7 | −124.53 (11) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y, −z; (ii) x+1, y−1, z; (iii) −x, −y+1, −z; (iv) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (v) x−1, y+1, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: LH2704).
References
- Bruker (1997). SMART and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.-M., Sun, Y.-M., Liu, Z., Liu, L.-D., Shi, W. & Cheng, P. (2006). Dalton Trans. pp. 376–380. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.-M., Sun, Y.-M., Zhang, X., Yi, L., Cheng, P. & Liu, L.-D. (2006). J. Phys. Chem. A, 110, 7677–7681. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808032285/lh2704sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808032285/lh2704Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




