Abstract
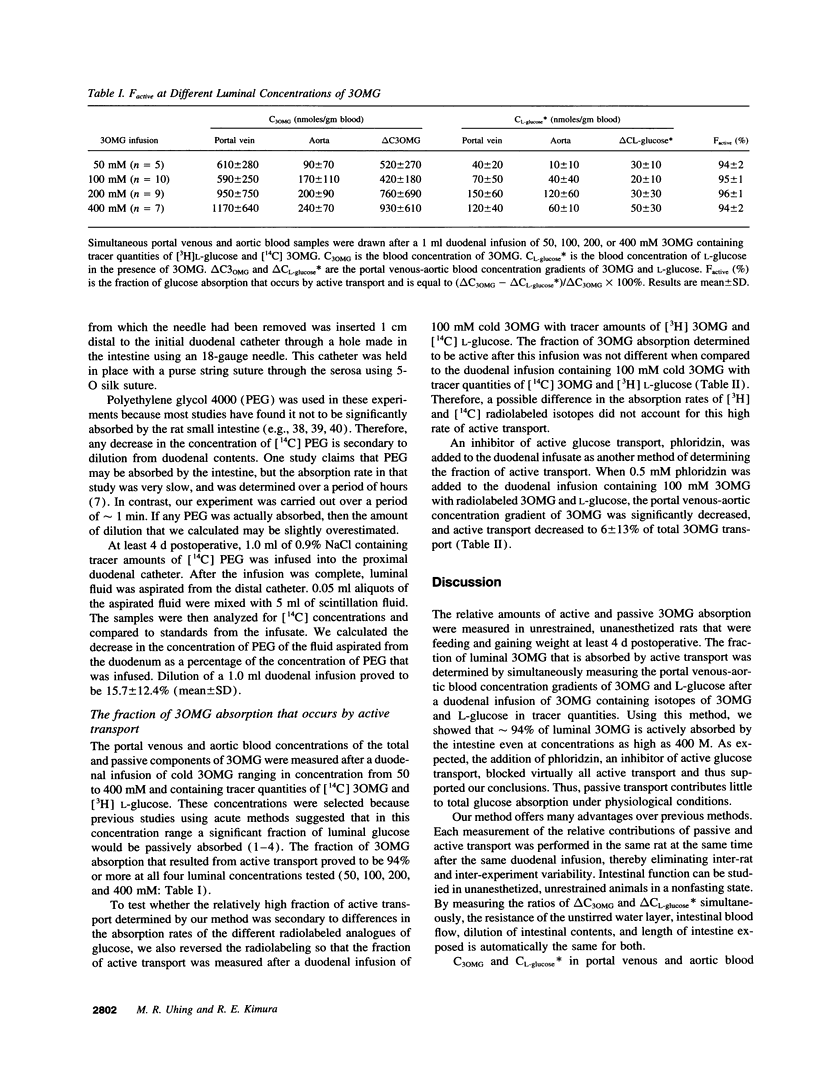
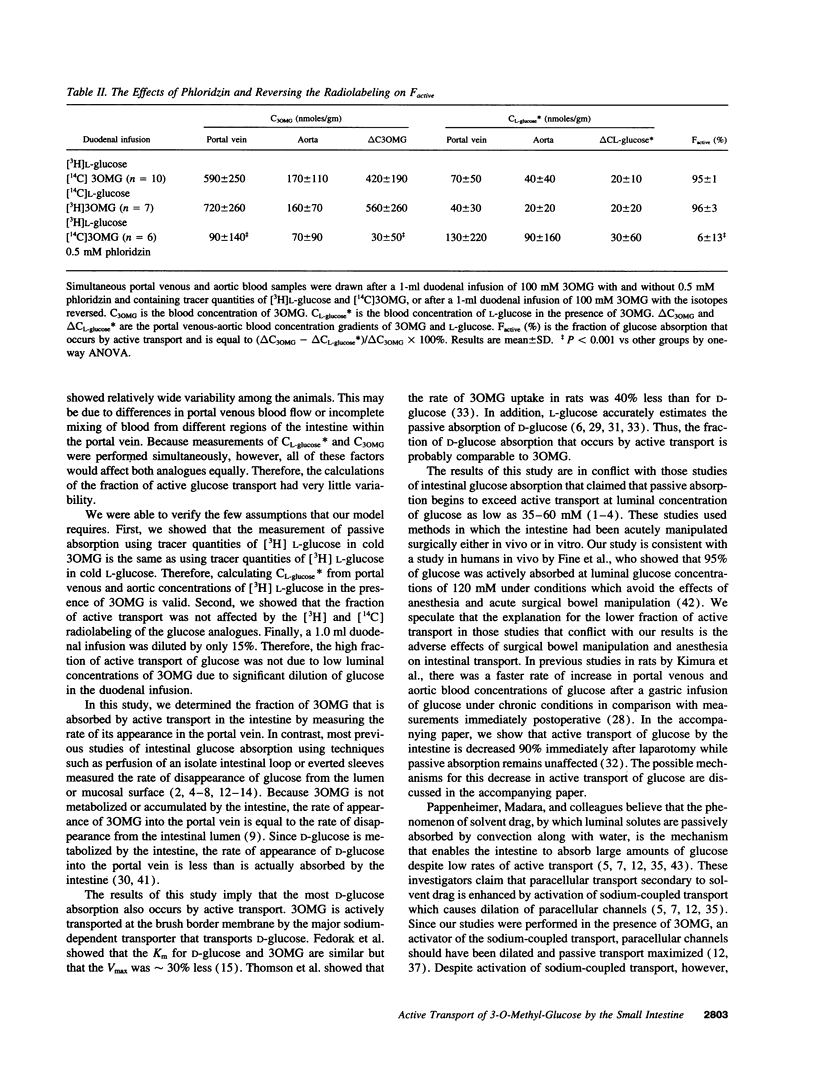
A method is described for determining the fraction of intestinal 3-O-methyl-glucose (3OMG) absorption that occurs by active transport in chronically catheterized rats without the influence of anesthesia or surgical bowel manipulation. That fraction was determined by simultaneously measuring portal venous-aortic blood concentration gradients (delta C) of 3-O-methyl-glucose (3OMG) and L-glucose, metabolically inert analogues of D-glucose. 3OMG is actively and passively absorbed by the same mechanisms as D-glucose, L-glucose is only passively absorbed. The fraction of 3OMG that is actively transported was calculated from the difference between 3OMG and L-glucose absorption, divided by total 3OMG absorption. We found that more than 94% of 3-O-methyl-glucose is absorbed by active transport when luminal concentrations range from 50 to 400 mM. We conclude that in unrestrained, unanesthetized chronically catheterized rats, most 3OMG is actively absorbed by the intestine even at high luminal concentrations.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson B. W., Levine A. S., Levitt D. G., Kneip J. M., Levitt M. D. Physiological measurement of luminal stirring in perfused rat jejunum. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jun;254(6 Pt 1):G843–G848. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.254.6.G843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atisook K., Carlson S., Madara J. L. Effects of phlorizin and sodium on glucose-elicited alterations of cell junctions in intestinal epithelia. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jan;258(1 Pt 1):C77–C85. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.1.C77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd C. A., Parsons D. S. Effects of vascular perfusion on the accumulation, distribution and transfer of 3-O-methyl-D-glucose within and across the small intestine. J Physiol. 1978 Jan;274:17–36. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buddington R. K., Diamond J. Ontogenetic development of nutrient transporters in cat intestine. Am J Physiol. 1992 Nov;263(5 Pt 1):G605–G616. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.263.5.G605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CSAKY T. Z., THALE M. Effect of ionic environment on intestinal sugar transport. J Physiol. 1960 Apr;151:59–65. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheeseman C. I., Harley B. Adaptation of glucose transport across rat enterocyte basolateral membrane in response to altered dietary carbohydrate intake. J Physiol. 1991 Jun;437:563–575. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debnam E. S., Karasov W. H., Thompson C. S. Nutrient uptake by rat enterocytes during diabetes mellitus; evidence for an increased sodium electrochemical gradient. J Physiol. 1988 Mar;397:503–512. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debnam E. S., Levin R. J. An experimental method of identifying and quantifying the active transfer electrogenic component from the diffusive component during sugar absorption measured in vivo. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;246(1):181–196. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedorak R. N., Chang E. B., Madara J. L., Field M. Intestinal adaptation to diabetes. Altered Na-dependent nutrient absorption in streptozocin-treated chronically diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jun;79(6):1571–1578. doi: 10.1172/JCI112991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedorak R. N., Thomson A. B., Porter V. M. Adaptation of intestinal glucose transport in rats with diabetes mellitus occurs independent of hyperphagia. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;69(8):1143–1148. doi: 10.1139/y91-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine K. D., Santa Ana C. A., Porter J. L., Fordtran J. S. Effect of D-glucose on intestinal permeability and its passive absorption in human small intestine in vivo. Gastroenterology. 1993 Oct;105(4):1117–1125. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90957-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French A. B., Brown I. F., Good C. J., McLeod G. M. Comparison of phenol red and polyethyleneglycol as nonabsorbable markers for the study of intestinal absorption in humans. Am J Dig Dis. 1968 Jun;13(6):558–564. doi: 10.1007/BF02233070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumbleton M., Nicholls P. J., Taylor G. Differential effects of anesthetic regimens on gentamicin pharmacokinetics in the rat: a comparison with chronically catheterized conscious animals. Pharm Res. 1990 Jan;7(1):41–45. doi: 10.1023/a:1015879324354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumbleton M., Nicholls P. J., Taylor G. Differential influence of laboratory anaesthetic regimens upon renal and hepatosplanchnic haemodynamics in the rat. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1990 Oct;42(10):693–697. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1990.tb06561.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakim A. A., Lifson N. Effects of pressure on water and solute transport by dog intestinal mucosa in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1969 Feb;216(2):276–284. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.2.276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander D., Koyama S., Dadufalza V., Tran D. Q., Krugliak P., Ma T., Ling K. Y. Polyethylene glycol 900 permeability of rat intestinal and colonic segments in vivo and brush border membrane vesicles in vitro. J Lab Clin Med. 1989 Apr;113(4):505–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karasov W. H., Debnam E. S. Rapid adaptation of intestinal glucose transport: a brush-border or basolateral phenomenon? Am J Physiol. 1987 Jul;253(1 Pt 1):G54–G61. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1987.253.1.G54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karbach U., Wanitschke R. Influence of serosal hydrostatic pressure on net water and electrolyte transport across the isolated rat colonic mucosa exposed to different secretagogues. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 Oct;327(4):336–341. doi: 10.1007/BF00506246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura R. E., LaPine T. R., Gooch W. M., 3rd Portal venous and aortic glucose and lactate changes in a chronically catheterized rat. Pediatr Res. 1988 Feb;23(2):235–240. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198802000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura R. E., Thulin G., Warshaw J. B. The effect of ketone bodies and fatty acid on intestinal glucose metabolism during development. Pediatr Res. 1984 Jul;18(7):575–578. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198407000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Pappenheimer J. R. Structural basis for physiological regulation of paracellular pathways in intestinal epithelia. J Membr Biol. 1987;100(2):149–164. doi: 10.1007/BF02209147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRoberts J. A., Aranda R., Riley N., Kang H. Insulin regulates the paracellular permeability of cultured intestinal epithelial cell monolayers. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1127–1134. doi: 10.1172/JCI114544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meddings J. B., DeSouza D., Goel M., Thiesen S. Glucose transport and microvillus membrane physical properties along the crypt-villus axis of the rabbit. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1099–1107. doi: 10.1172/JCI114541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meddings J. B., Westergaard H. Intestinal glucose transport using perfused rat jejunum in vivo: model analysis and derivation of corrected kinetic constants. Clin Sci (Lond) 1989 Apr;76(4):403–413. doi: 10.1042/cs0760403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. L., Schedl H. P. Total recovery studies of nonabsorbable indicators in the rat small intestine. Gastroenterology. 1970 Jan;58(1):40–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moe A. J., Jackson M. J. Isolation and characterization of brush border membrane vesicles from pig small intestine. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1987;88(3):511–517. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(87)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mokuda O., Sakamoto Y., Ikeda T., Mashiba H. Direct inhibitory effect of high glucose in mesenteric artery on glucose absorption from isolated perfused rat intestine. Ann Nutr Metab. 1989;33(6):330–332. doi: 10.1159/000177554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami E., Saito M., Suda M. Contribution of diffusive pathway in intestinal absorption of glucose in rat under normal feeding condition. Experientia. 1977 Nov 15;33(11):1469–1470. doi: 10.1007/BF01918813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer J. R. On the coupling of membrane digestion with intestinal absorption of sugars and amino acids. Am J Physiol. 1993 Sep;265(3 Pt 1):G409–G417. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1993.265.3.G409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer J. R. Physiological regulation of transepithelial impedance in the intestinal mucosa of rats and hamsters. J Membr Biol. 1987;100(2):137–148. doi: 10.1007/BF02209146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer J. R., Reiss K. Z. Contribution of solvent drag through intercellular junctions to absorption of nutrients by the small intestine of the rat. J Membr Biol. 1987;100(2):123–136. doi: 10.1007/BF02209145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porteous J. W., Hutchison J. D., Undrill V. The luminally- and vascularly-perfused small intestine as an experimental system for the study of translocation and metabolism. Proc Nutr Soc. 1984 Jun;43(2):141–160. doi: 10.1079/pns19840038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich-Denson C., Kimura R. E. Evidence in vivo that most of the intraluminally absorbed glucose is absorbed intact into the portal vein and not metabolized to lactate. Biochem J. 1988 Sep 15;254(3):931–934. doi: 10.1042/bj2540931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schedl H. P. Use of polyethylene glycol and phenol red as unabsorbed indicators for intestinal absorption studies in man. Gut. 1966 Apr;7(2):159–163. doi: 10.1136/gut.7.2.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjövall H., Hagman I., Abrahamsson H. Relationship between interdigestive duodenal motility and fluid transport in humans. Am J Physiol. 1990 Sep;259(3 Pt 1):G348–G354. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.259.3.G348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens B. R., Kaunitz J. D., Wright E. M. Intestinal transport of amino acids and sugars: advances using membrane vesicles. Annu Rev Physiol. 1984;46:417–433. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.46.030184.002221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. B., Hotke C. A., Weinstein W. M. Comparison of kinetic constants of hexose uptake in four animal species and man. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1982;72(1):225–236. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(82)90037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhing M. R., Kimura R. E. The effect of surgical bowel manipulation and anesthesia on intestinal glucose absorption in rats. J Clin Invest. 1995 Jun;95(6):2790–2798. doi: 10.1172/JCI117983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON T. H., LANDAU B. R. Specificity of sugar transport by the intestine of the hamster. Am J Physiol. 1960 Jan;198:99–102. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.198.1.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westergaard H., Holtermüller K. H., Dietschy J. M. Measurement of resistance of barriers to solute transport in vivo in rat jejunum. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jun;250(6 Pt 1):G727–G735. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.250.6.G727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westergaard H. Insulin modulates rat intestinal glucose transport: effect of hypoinsulinemia and hyperinsulinemia. Am J Physiol. 1989 May;256(5 Pt 1):G911–G918. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.256.5.G911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



