Abstract
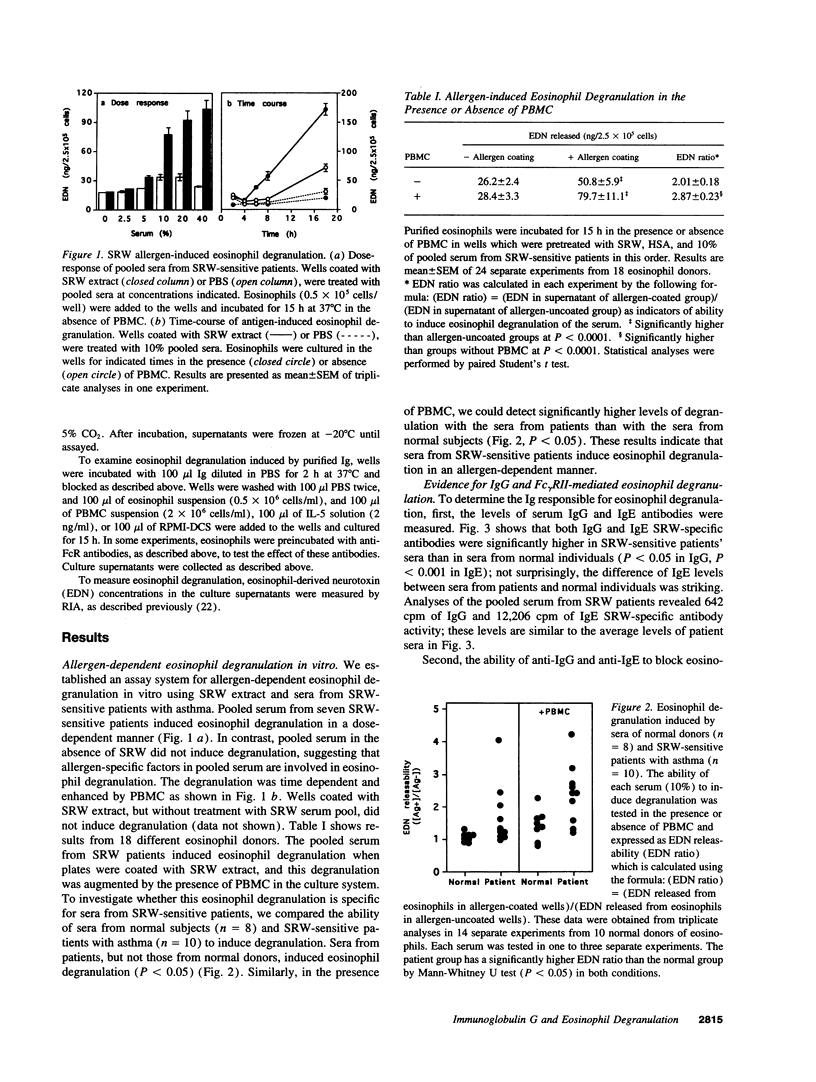
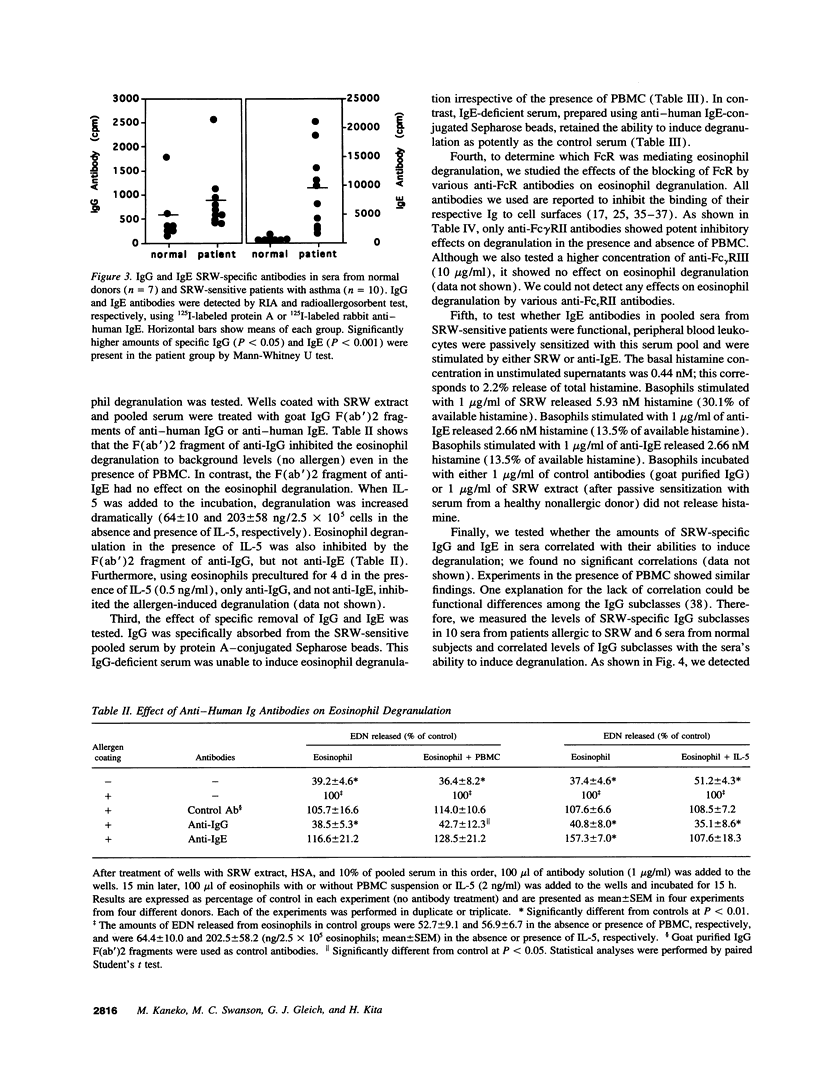
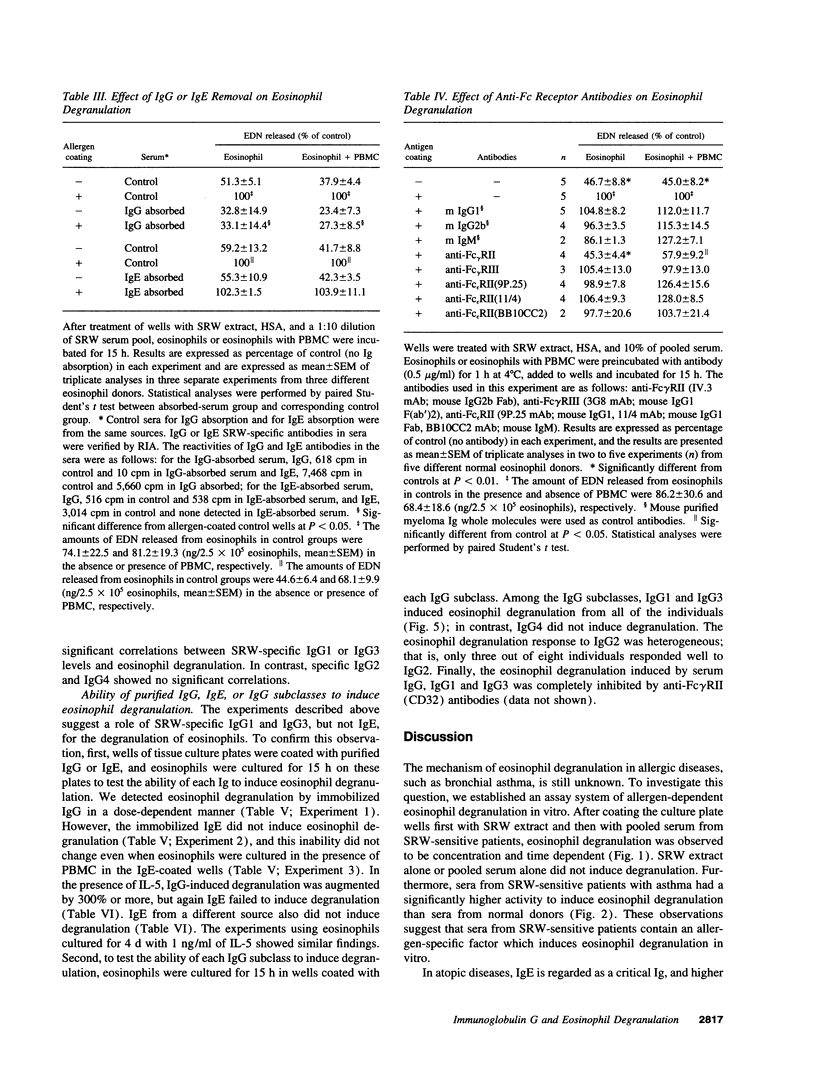
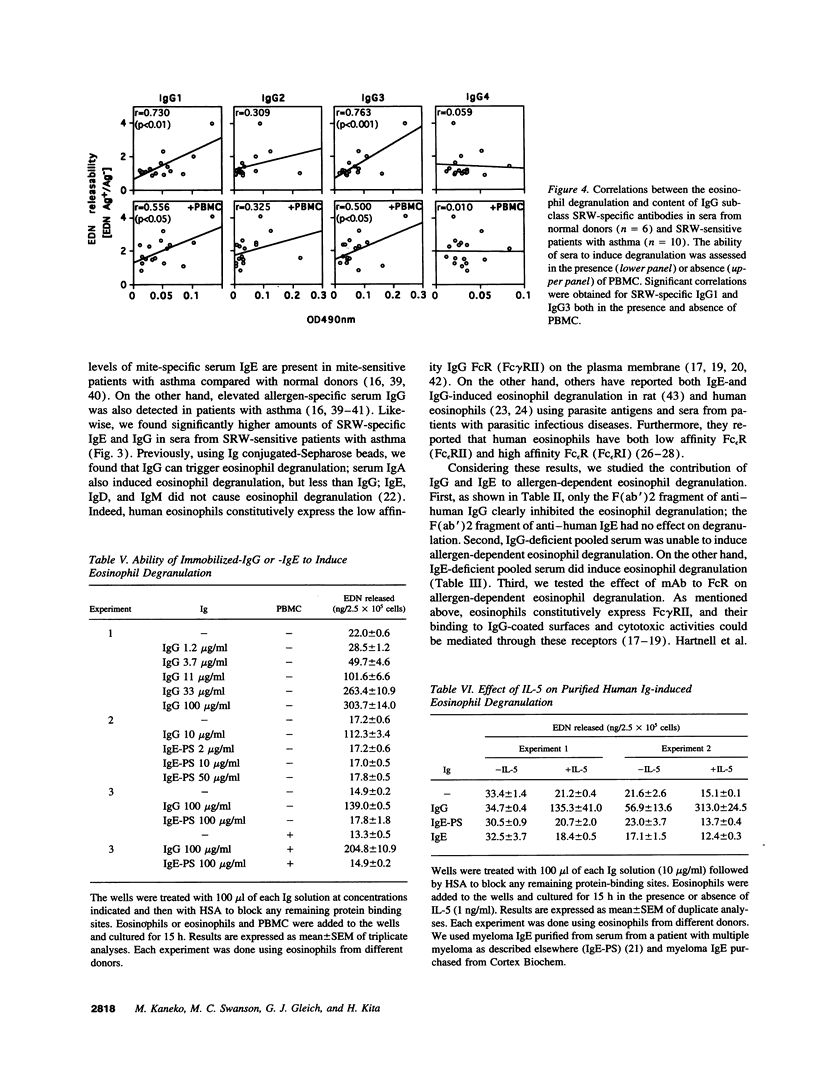
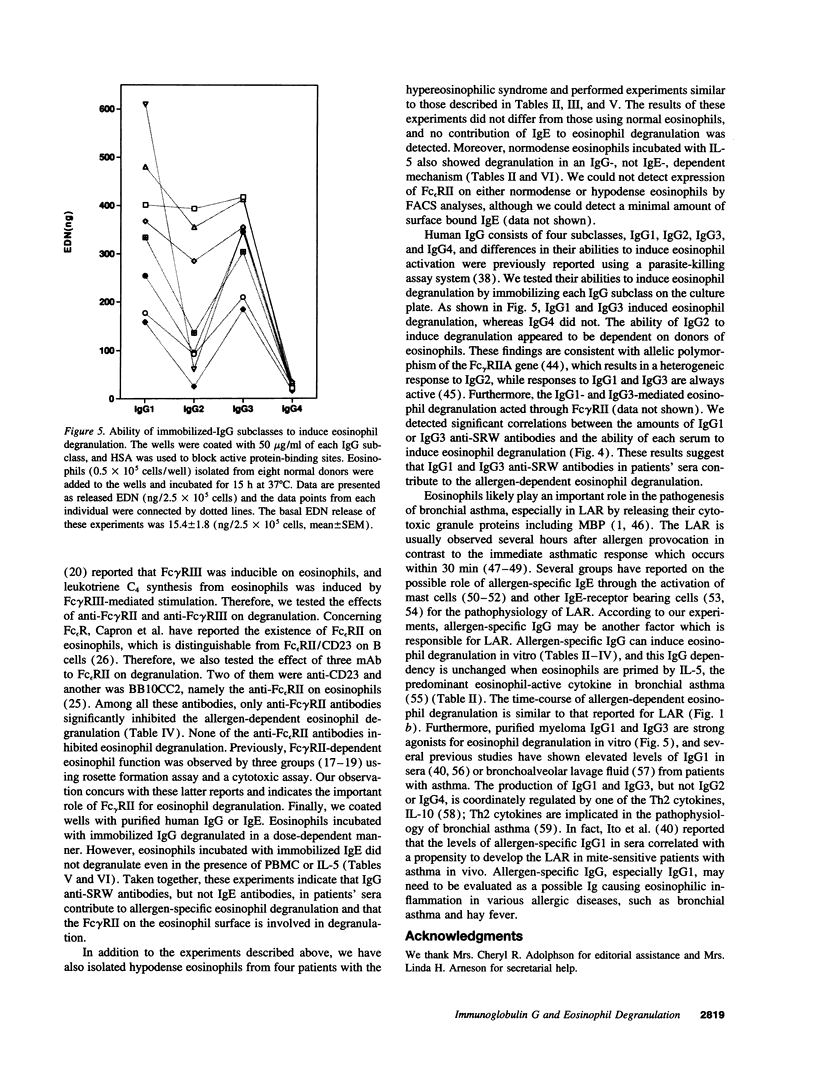
Evidence suggests that eosinophils contribute to inflammation in bronchial asthma by releasing chemical mediators and cytotoxic granule proteins. To investigate the mechanism of eosinophil degranulation in asthma, we established an in vitro model of allergen-induced degranulation. We treated tissue culture plates with short ragweed pollen (SRW) extract and sera from either normal donors or SRW-sensitive patients with asthma. Eosinophils were incubated in the wells and degranulation was assessed by measurement of eosinophil-derived neurotoxin in supernatants. We detected degranulation only when sera from SRW-sensitive patients were reacted with SRW. Anti-IgG and anti-Fc gamma RII mAb, but not anti-IgE or anti-Fc epsilon RII mAb, abolished the degranulation. IgG-depleted serum did not induce degranulation; IgE-depleted serum triggered as much degranulation as untreated serum. Furthermore, serum levels of SRW-specific IgG1 or IgG3 correlated with the amounts of released eosinophil-derived neurotoxin. When eosinophils were cultured in wells coated with purified IgG or IgE, eosinophil degranulation was observed only with IgG. Finally, human IgG1 and IgG3, and less consistently IgG2, but not IgG4, induced degranulation. Thus, sera from patients with SRW-sensitive asthma induce eosinophil degranulation in vitro through antigen-specific IgG1 and IgG3 antibodies. These antibodies may be responsible for degranulation of eosinophils in inflammatory reactions, such as bronchial asthma.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abu-Ghazaleh R. I., Fujisawa T., Mestecky J., Kyle R. A., Gleich G. J. IgA-induced eosinophil degranulation. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 1;142(7):2393–2400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayars G. H., Altman L. C., Gleich G. J., Loegering D. A., Baker C. B. Eosinophil- and eosinophil granule-mediated pneumocyte injury. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1985 Oct;76(4):595–604. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(85)90781-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. J. New concepts in the pathogenesis of bronchial hyperresponsiveness and asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1989 Jun;83(6):1013–1026. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(89)90441-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnefoy J. Y., Aubry J. P., Peronne C., Wijdenes J., Banchereau J. Production and characterization of a monoclonal antibody specific for the human lymphocyte low affinity receptor for IgE: CD 23 is a low affinity receptor for IgE. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):2970–2978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booij-Noord H., Orie N. G., De Vries K. Immediate and late bronchial obstructive reactions to inhalation of house dust and protective effects of disodium cromoglycate and prednisolone. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1971 Dec;48(6):344–354. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(71)90080-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brière F., Servet-Delprat C., Bridon J. M., Saint-Remy J. M., Banchereau J. Human interleukin 10 induces naive surface immunoglobulin D+ (sIgD+) B cells to secrete IgG1 and IgG3. J Exp Med. 1994 Feb 1;179(2):757–762. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.2.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant D. H., Burns M. W., Lazarus L. Identification of IgG antibody as a carrier of reaginic activity in asthmatic patients. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1975 Dec;56(6):417–428. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(75)90060-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron M., Jouault T., Prin L., Joseph M., Ameisen J. C., Butterworth A. E., Papin J. P., Kusnierz J. P., Capron A. Functional study of a monoclonal antibody to IgE Fc receptor (Fc epsilon R2) of eosinophils, platelets, and macrophages. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):72–89. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durham S. R., Lee T. H., Cromwell O., Shaw R. J., Merrett T. G., Merrett J., Cooper P., Kay A. B. Immunologic studies in allergen-induced late-phase asthmatic reactions. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1984 Jul;74(1):49–60. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(84)90086-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durham S. R., Loegering D. A., Dunnette S., Gleich G. J., Kay A. B. Blood eosinophils and eosinophil-derived proteins in allergic asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1989 Dec;84(6 Pt 1):931–936. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(89)90391-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filley W. V., Holley K. E., Kephart G. M., Gleich G. J. Identification by immunofluorescence of eosinophil granule major basic protein in lung tissues of patients with bronchial asthma. Lancet. 1982 Jul 3;2(8288):11–16. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91152-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frigas E., Loegering D. A., Solley G. O., Farrow G. M., Gleich G. J. Elevated levels of the eosinophil granule major basic protein in the sputum of patients with bronchial asthma. Mayo Clin Proc. 1981 Jun;56(6):345–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleich G. J., Adolphson C. R. The eosinophilic leukocyte: structure and function. Adv Immunol. 1986;39:177–253. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60351-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleich G. J., Frigas E., Loegering D. A., Wassom D. L., Steinmuller D. Cytotoxic properties of the eosinophil major basic protein. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2925–2927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. R., Burd P. R., Galli S. J. Mast cells as a source of multifunctional cytokines. Immunol Today. 1990 Dec;11(12):458–464. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90176-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. R., Galli S. J. Release of both preformed and newly synthesized tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha)/cachectin by mouse mast cells stimulated via the Fc epsilon RI. A mechanism for the sustained action of mast cell-derived TNF-alpha during IgE-dependent biological responses. J Exp Med. 1991 Jul 1;174(1):103–107. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gounni A. S., Lamkhioued B., Ochiai K., Tanaka Y., Delaporte E., Capron A., Kinet J. P., Capron M. High-affinity IgE receptor on eosinophils is involved in defence against parasites. Nature. 1994 Jan 13;367(6459):183–186. doi: 10.1038/367183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grangette C., Gruart V., Ouaissi M. A., Rizvi F., Delespesse G., Capron A., Capron M. IgE receptor on human eosinophils (FcERII). Comparison with B cell CD23 and association with an adhesion molecule. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 1;143(11):3580–3588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziano R. F., Looney R. J., Shen L., Fanger M. W. Fc gamma R-mediated killing by eosinophils. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):230–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansel T. T., De Vries I. J., Iff T., Rihs S., Wandzilak M., Betz S., Blaser K., Walker C. An improved immunomagnetic procedure for the isolation of highly purified human blood eosinophils. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Dec 15;145(1-2):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90315-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartnell A., Kay A. B., Wardlaw A. J. IFN-gamma induces expression of Fc gamma RIII (CD16) on human eosinophils. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 1;148(5):1471–1478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastie A. T., Loegering D. A., Gleich G. J., Kueppers F. The effect of purified human eosinophil major basic protein on mammalian ciliary activity. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Apr;135(4):848–853. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.4.848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ide M., Weiler D., Kita H., Gleich G. J. Ammonium chloride exposure inhibits cytokine-mediated eosinophil survival. J Immunol Methods. 1994 Feb 10;168(2):187–196. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(94)90054-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Kudo K., Okudaira H., Yoshinoya S., Morita Y., Nakagawa T., Akiyama K., Urata C., Hayakawa T., Ohta K. IgG1 antibodies to house dust mite (Dermatophagoides farinae) and late asthmatic response. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1986;81(1):69–74. doi: 10.1159/000234110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz H. R., Raizman M. B., Gartner C. S., Scott H. C., Benson A. C., Austen K. F. Secretory granule mediator release and generation of oxidative metabolites of arachidonic acid via Fc-IgG receptor bridging in mouse mast cells. J Immunol. 1992 Feb 1;148(3):868–871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalife J., Capron M., Cesbron J. Y., Tai P. C., Taelman H., Prin L., Capron A. Role of specific IgE antibodies in peroxidase (EPO) release from human eosinophils. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 1;137(5):1659–1664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalife J., Capron M., Grzych J. M., Bazin H., Capron A. Extracellular release of rat eosinophil peroxidase (EPO) I. Role of anaphylactic immunoglobulins. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1968–1974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalife J., Dunne D. W., Richardson B. A., Mazza G., Thorne K. J., Capron A., Butterworth A. E. Functional role of human IgG subclasses in eosinophil-mediated killing of schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4422–4427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitani S., Ito K., Miyamoto T. IgG, IgA, and IgM antibodies to mite in sera and sputa from asthmatic patients. Ann Allergy. 1985 Oct;55(4):612–620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenderman L., Hermans S. W., Capel P. J., van de Winkel J. G. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor induces sequential activation and deactivation of binding via a low-affinity IgG Fc receptor, hFc gamma RII, on human eosinophils. Blood. 1993 May 1;81(9):2413–2419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. T. S-type mammalian lectins in allergic inflammation. Immunol Today. 1993 Oct;14(10):486–490. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90263-K. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Looney R. J., Ryan D. H., Takahashi K., Fleit H. B., Cohen H. J., Abraham G. N., Anderson C. L. Identification of a second class of IgG Fc receptors on human neutrophils. A 40 kilodalton molecule also found on eosinophils. J Exp Med. 1986 Apr 1;163(4):826–836. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.4.826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro R. C., Hostoffer R. W., Cooper M. D., Bonner J. R., Gartland G. L., Kubagawa H. Definition of immunoglobulin A receptors on eosinophils and their enhanced expression in allergic individuals. J Clin Invest. 1993 Oct;92(4):1681–1685. doi: 10.1172/JCI116754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motojima S., Frigas E., Loegering D. A., Gleich G. J. Toxicity of eosinophil cationic proteins for guinea pig tracheal epithelium in vitro. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Mar;139(3):801–805. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.3.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oettgen H. C., Martin T. R., Wynshaw-Boris A., Deng C., Drazen J. M., Leder P. Active anaphylaxis in IgE-deficient mice. Nature. 1994 Aug 4;370(6488):367–370. doi: 10.1038/370367a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi T., Kita H., Weiler D., Sur S., Sedgwick J. B., Calhoun W. J., Busse W. W., Abrams J. S., Gleich G. J. IL-5 is the predominant eosinophil-active cytokine in the antigen-induced pulmonary late-phase reaction. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Apr;147(4):901–907. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/147.4.901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Out T. A., van de Graaf E. A., van den Berg N. J., Jansen H. M. IgG subclasses in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from patients with asthma. Scand J Immunol. 1991 Jun;33(6):719–727. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1991.tb02546.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Outschoorn I. M., Natta C. L. IgG subclass alterations in adult asthma. Microbiol Immunol. 1992;36(9):977–982. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1992.tb02101.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys J., Hutchcroft B. J. Bronchial provocation tests in etiologic diagnosis and analysis of asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1975 Dec;112(6):829–859. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1975.112.6.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruzansky J. J., Grammer L. C., Patterson R., Roberts M. Dissociation of IgE from receptors on human basophils. I. Enhanced passive sensitization for histamine release. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1949–1953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu W. Q., de Bruin D., Brownstein B. H., Pearse R., Ravetch J. V. Organization of the human and mouse low-affinity Fc gamma R genes: duplication and recombination. Science. 1990 May 11;248(4956):732–735. doi: 10.1126/science.2139735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzo M. C., Arruda L. K., Chapman M. D., Fernandez-Caldas E., Baggio D., Platts-Mills T. A., Naspitz C. K. IgG and IgE antibody responses to dust mite allergens among children with asthma in Brazil. Ann Allergy. 1993 Aug;71(2):152–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D. G., Kerigan A. T., Hargreave F. E., Chalmers R., Dolovich J. Late asthmatic responses induced by ragweed pollen allergen. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1974 Oct;54(4):244–254. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(74)90067-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D. S., Hamid Q., Ying S., Tsicopoulos A., Barkans J., Bentley A. M., Corrigan C., Durham S. R., Kay A. B. Predominant TH2-like bronchoalveolar T-lymphocyte population in atopic asthma. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jan 30;326(5):298–304. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199201303260504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld S. I., Looney R. J., Leddy J. P., Phipps D. C., Abraham G. N., Anderson C. L. Human platelet Fc receptor for immunoglobulin G. Identification as a 40,000-molecular-weight membrane protein shared by monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;76(6):2317–2322. doi: 10.1172/JCI112242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick J. B., Calhoun W. J., Gleich G. J., Kita H., Abrams J. S., Schwartz L. B., Volovitz B., Ben-Yaakov M., Busse W. W. Immediate and late airway response of allergic rhinitis patients to segmental antigen challenge. Characterization of eosinophil and mast cell mediators. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Dec;144(6):1274–1281. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/144.6.1274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L., Guyre P. M., Fanger M. W. Polymorphonuclear leukocyte function triggered through the high affinity Fc receptor for monomeric IgG. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 15;139(2):534–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soliman M. Y., Rosenstreich D. L. Natural immunity to dust mites in adults with chronic asthma. I. Mite-specific serum IgG and IgE. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Nov;134(5):962–968. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.5.962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens R. L., Austen K. F. Recent advances in the cellular and molecular biology of mast cells. Immunol Today. 1989 Nov;10(11):381–386. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90272-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomassini M., Tsicopoulos A., Tai P. C., Gruart V., Tonnel A. B., Prin L., Capron A., Capron M. Release of granule proteins by eosinophils from allergic and nonallergic patients with eosinophilia on immunoglobulin-dependent activation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1991 Sep;88(3 Pt 1):365–375. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(91)90099-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truong M. J., Gruart V., Liu F. T., Prin L., Capron A., Capron M. IgE-binding molecules (Mac-2/epsilon BP) expressed by human eosinophils. Implication in IgE-dependent eosinophil cytotoxicity. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Dec;23(12):3230–3235. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830231228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valerius T., Repp R., Kalden J. R., Platzer E. Effects of IFN on human eosinophils in comparison with other cytokines. A novel class of eosinophil activators with delayed onset of action. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 1;145(9):2950–2958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B., Rieger A., Kilgus O., Ochiai K., Maurer D., Födinger D., Kinet J. P., Stingl G. Epidermal Langerhans cells from normal human skin bind monomeric IgE via Fc epsilon RI. J Exp Med. 1992 May 1;175(5):1353–1365. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.5.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warmerdam P. A., van de Winkel J. G., Vlug A., Westerdaal N. A., Capel P. J. A single amino acid in the second Ig-like domain of the human Fc gamma receptor II is critical for human IgG2 binding. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 15;147(4):1338–1343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


