Abstract
The title compound, C9H9ClN2O5S, is of interest as a precursor to biologically active substituted quinolines and related compounds. The structure displays intermolecular C—H⋯O interactions. Each molecule is linked to two adjacent neighbours via weak centrosymmetric dimer-forming interactions, forming chains in the [101] direction.
Related literature
For synthesis and biological evaluation of sulfur-containing heterocyclic compounds, see: Zia-ur-Rehman et al. (2005 ▶, 2006 ▶, 2007 ▶, 2008 ▶); Wen et al. (2005 ▶); Zhang, Xu, Wen et al. (2006 ▶). For related molecules, see: (Wen et al., 2006 ▶; Zhang, Xu, Zou et al. (2006 ▶). For bond-length data, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶).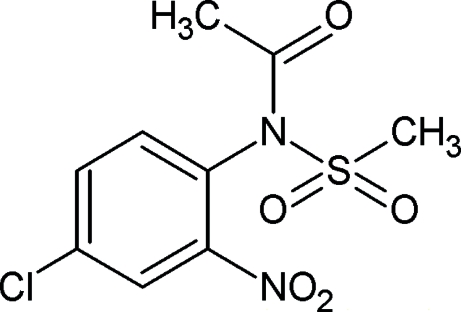
Experimental
Crystal data
C9H9ClN2O5S
M r = 292.70
Monoclinic,

a = 9.8071 (4) Å
b = 9.4310 (4) Å
c = 13.5679 (7) Å
β = 105.883 (2)°
V = 1207.00 (9) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.50 mm−1
T = 296 (2) K
0.25 × 0.15 × 0.09 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.913, T max = 0.956
13383 measured reflections
2988 independent reflections
2077 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.043
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.040
wR(F 2) = 0.104
S = 1.02
2981 reflections
163 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.43 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.31 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2003 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808032157/ez2142sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808032157/ez2142Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2—H2⋯O5i | 0.93 | 2.55 | 3.404 (3) | 153 |
| C9—H9B⋯O3ii | 0.96 | 2.58 | 3.521 (3) | 169 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the PCSIR Laboratories Complex, Lahore, Pakistan, for provision of the necessary chemicals, and the Higher Education Commission of Pakistan for the purchase of the diffractometer.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
N-(Substituted phenyl)acetamides are well known for their importance as intermediates in organic synthesis. They are used as precursors for the synthesis of many heterocyclic compounds, e.g. 2,5-piperazinedione (Wen et al., 2006), (quinolin-8-yloxy)acetamide (Zhang, Xu, Wen et al., 2006) and 2,2-(1,3,4-thiadiazolyl-2,5-dithio)diacetamide (Wen et al., 2005). In the present paper, the structure of N-(4-chloro-2-nitrophenyl)-N-(methylsulfonyl)acetamide (I) has been determined as part of a research program involving the synthesis and biological evaluation of sulfur containing heterocyclic compounds (Zia-ur-Rehman et al., 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008).
In the molecule of I (Fig. 1), the bond lengths and bond angles are similar to those in related molecules (Wen et al., 2006; Zhang, Xu, Zou et al., 2006) and are within normal ranges (Allen et al., 1987). The nitro group is slightly twisted out of the plane of the benzene ring, as indicated by O1—N1—C3—C2 and O2—N1—C3—C2 torsion angles of -16.7 (3) and 160.9 (2)°, respectively. Each molecule is linked to its neighbour via a centrosymmetric head-to-tail interaction between the methyl hydrogen H9B and the carbonyl oxygen [C9—H9B···O3]. Adjacent pairs of these molecules are then linked into chains via intermolecular [C2—H5···O5] interactions along the [101] direction (Table 1 and Fig. 2).
Experimental
A mixture of N-(4-chloro-2-nitrophenyl)methane sulfonamide (2.507 g; 10.0 mmoles) and acetic anhydride (10.0 ml) was heated to reflux for half an hour and then poured over crushed ice. Resultant solids were then washed with cold water and dried under reduced pressure. Yellow crystals were obtained by slow evaporation of an ethanolic solution over a period of two days.
Refinement
H atoms bound to C were placed in geometric positions (C—H distance = 0.95 Å) using a riding model with Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The asymmetric unit of the title compound showing the atom labelling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
Perspective view of a portion of the crystal packing, viewed approximately down the b-axis, showing hydrogen bond interactions (dashed lines) along the [101] direction. H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonding have been omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| C9H9ClN2O5S | F(000) = 600 |
| Mr = 292.70 | Dx = 1.611 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Melting point: 401 K |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 9.8071 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 3121 reflections |
| b = 9.4310 (4) Å | θ = 2.7–27.2° |
| c = 13.5679 (7) Å | µ = 0.50 mm−1 |
| β = 105.883 (2)° | T = 296 K |
| V = 1207.00 (9) Å3 | Needle, light yellow |
| Z = 4 | 0.25 × 0.15 × 0.09 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer | 2988 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2077 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.043 |
| Detector resolution: 7.5 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 28.3°, θmin = 2.7° |
| φ and ω scans | h = −12→13 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | k = −12→12 |
| Tmin = 0.913, Tmax = 0.956 | l = −18→17 |
| 13383 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.040 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.104 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.02 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0426P)2 + 0.5587P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2981 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 163 parameters | Δρmax = 0.43 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.31 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.43935 (5) | 0.98058 (6) | 0.14520 (4) | 0.03097 (15) | |
| Cl1 | −0.20712 (6) | 0.67766 (7) | −0.00125 (6) | 0.0511 (2) | |
| N2 | 0.34896 (17) | 0.91810 (19) | 0.22582 (14) | 0.0276 (4) | |
| O5 | 0.34507 (18) | 0.96150 (18) | 0.04574 (13) | 0.0439 (4) | |
| C4 | 0.2107 (2) | 0.8605 (2) | 0.17969 (16) | 0.0269 (5) | |
| O3 | 0.52800 (17) | 0.97095 (19) | 0.36537 (13) | 0.0454 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.0872 (2) | 1.0934 (2) | 0.18329 (16) | 0.0361 (5) | |
| C3 | 0.0874 (2) | 0.9425 (2) | 0.15362 (17) | 0.0283 (5) | |
| O1 | −0.0130 (2) | 1.1651 (2) | 0.13957 (18) | 0.0695 (7) | |
| C1 | −0.0476 (2) | 0.7464 (3) | 0.07164 (19) | 0.0365 (5) | |
| O4 | 0.49004 (18) | 1.11878 (17) | 0.17659 (15) | 0.0477 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.1842 (2) | 1.1381 (2) | 0.25205 (18) | 0.0651 (6) | |
| C5 | 0.1996 (2) | 0.7188 (2) | 0.15196 (19) | 0.0359 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.2800 | 0.6618 | 0.1689 | 0.043* | |
| C6 | 0.0708 (2) | 0.6607 (3) | 0.09955 (19) | 0.0401 (6) | |
| H6 | 0.0639 | 0.5647 | 0.0833 | 0.048* | |
| C7 | 0.4104 (2) | 0.9221 (2) | 0.33238 (17) | 0.0315 (5) | |
| C2 | −0.0409 (2) | 0.8874 (2) | 0.09933 (18) | 0.0327 (5) | |
| H2 | −0.1215 | 0.9441 | 0.0816 | 0.039* | |
| C8 | 0.5815 (3) | 0.8637 (3) | 0.1615 (2) | 0.0501 (7) | |
| H8A | 0.5463 | 0.7690 | 0.1460 | 0.075* | |
| H8B | 0.6390 | 0.8679 | 0.2312 | 0.075* | |
| H8C | 0.6374 | 0.8899 | 0.1163 | 0.075* | |
| C9 | 0.3259 (3) | 0.8606 (3) | 0.39765 (19) | 0.0415 (6) | |
| H9A | 0.2285 | 0.8887 | 0.3716 | 0.062* | |
| H9B | 0.3621 | 0.8944 | 0.4666 | 0.062* | |
| H9C | 0.3323 | 0.7591 | 0.3969 | 0.062* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0248 (3) | 0.0320 (3) | 0.0347 (3) | 0.0000 (2) | 0.0057 (2) | 0.0040 (2) |
| Cl1 | 0.0311 (3) | 0.0557 (4) | 0.0567 (4) | −0.0129 (3) | −0.0043 (3) | −0.0082 (3) |
| N2 | 0.0209 (8) | 0.0327 (9) | 0.0269 (10) | −0.0027 (7) | 0.0024 (7) | −0.0027 (8) |
| O5 | 0.0386 (9) | 0.0575 (11) | 0.0322 (10) | −0.0048 (8) | 0.0039 (8) | 0.0063 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0208 (9) | 0.0328 (11) | 0.0253 (11) | −0.0021 (8) | 0.0032 (8) | −0.0017 (9) |
| O3 | 0.0317 (9) | 0.0564 (11) | 0.0388 (10) | −0.0073 (8) | −0.0064 (8) | −0.0053 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0334 (10) | 0.0337 (10) | 0.0424 (12) | 0.0039 (8) | 0.0123 (9) | −0.0019 (9) |
| C3 | 0.0268 (10) | 0.0283 (11) | 0.0292 (12) | −0.0009 (8) | 0.0066 (9) | −0.0012 (9) |
| O1 | 0.0571 (13) | 0.0447 (11) | 0.0897 (17) | 0.0213 (10) | −0.0088 (12) | −0.0094 (11) |
| C1 | 0.0256 (11) | 0.0426 (13) | 0.0364 (14) | −0.0069 (10) | 0.0002 (10) | −0.0021 (10) |
| O4 | 0.0457 (10) | 0.0354 (9) | 0.0607 (13) | −0.0111 (8) | 0.0124 (9) | 0.0025 (8) |
| O2 | 0.0447 (11) | 0.0471 (11) | 0.0889 (17) | 0.0022 (9) | −0.0063 (11) | −0.0287 (11) |
| C5 | 0.0277 (11) | 0.0326 (11) | 0.0422 (15) | 0.0037 (9) | 0.0010 (10) | −0.0035 (10) |
| C6 | 0.0368 (13) | 0.0329 (12) | 0.0447 (15) | −0.0034 (10) | 0.0012 (11) | −0.0067 (11) |
| C7 | 0.0308 (11) | 0.0307 (11) | 0.0291 (13) | 0.0039 (9) | 0.0016 (10) | −0.0025 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0202 (10) | 0.0403 (12) | 0.0356 (13) | 0.0008 (9) | 0.0043 (9) | 0.0024 (10) |
| C8 | 0.0370 (14) | 0.0579 (17) | 0.0606 (19) | 0.0155 (12) | 0.0219 (13) | 0.0118 (14) |
| C9 | 0.0489 (14) | 0.0445 (14) | 0.0309 (14) | 0.0029 (11) | 0.0104 (12) | 0.0004 (11) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| S1—O4 | 1.4182 (17) | C1—C2 | 1.379 (3) |
| S1—O5 | 1.4232 (18) | C1—C6 | 1.380 (3) |
| S1—N2 | 1.6913 (19) | C5—C6 | 1.382 (3) |
| S1—C8 | 1.743 (2) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| Cl1—C1 | 1.732 (2) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| N2—C7 | 1.406 (3) | C7—C9 | 1.487 (3) |
| N2—C4 | 1.435 (2) | C2—H2 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.384 (3) | C8—H8A | 0.9600 |
| C4—C3 | 1.397 (3) | C8—H8B | 0.9600 |
| O3—C7 | 1.208 (3) | C8—H8C | 0.9600 |
| N1—O1 | 1.207 (2) | C9—H9A | 0.9600 |
| N1—O2 | 1.212 (3) | C9—H9B | 0.9600 |
| N1—C3 | 1.479 (3) | C9—H9C | 0.9600 |
| C3—C2 | 1.374 (3) | ||
| O4—S1—O5 | 118.97 (11) | C4—C5—H5 | 119.5 |
| O4—S1—N2 | 109.18 (10) | C1—C6—C5 | 119.4 (2) |
| O5—S1—N2 | 104.46 (9) | C1—C6—H6 | 120.3 |
| O4—S1—C8 | 109.91 (13) | C5—C6—H6 | 120.3 |
| O5—S1—C8 | 109.27 (13) | O3—C7—N2 | 119.2 (2) |
| N2—S1—C8 | 103.88 (11) | O3—C7—C9 | 124.0 (2) |
| C7—N2—C4 | 123.11 (18) | N2—C7—C9 | 116.74 (19) |
| C7—N2—S1 | 120.17 (14) | C3—C2—C1 | 118.6 (2) |
| C4—N2—S1 | 116.71 (14) | C3—C2—H2 | 120.7 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 117.84 (19) | C1—C2—H2 | 120.7 |
| C5—C4—N2 | 118.61 (18) | S1—C8—H8A | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—N2 | 123.35 (18) | S1—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| O1—N1—O2 | 123.1 (2) | H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| O1—N1—C3 | 117.83 (19) | S1—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| O2—N1—C3 | 119.05 (19) | H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 121.92 (19) | H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—N1 | 116.14 (18) | C7—C9—H9A | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—N1 | 121.95 (18) | C7—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 121.1 (2) | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—Cl1 | 119.02 (18) | C7—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—Cl1 | 119.86 (18) | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 121.1 (2) | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.5 | ||
| O4—S1—N2—C7 | −50.92 (18) | O1—N1—C3—C4 | 163.6 (2) |
| O5—S1—N2—C7 | −179.19 (16) | O2—N1—C3—C4 | −18.8 (3) |
| C8—S1—N2—C7 | 66.30 (19) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.5 (4) |
| O4—S1—N2—C4 | 130.04 (16) | N2—C4—C5—C6 | −174.5 (2) |
| O5—S1—N2—C4 | 1.77 (17) | C2—C1—C6—C5 | −3.1 (4) |
| C8—S1—N2—C4 | −112.74 (18) | Cl1—C1—C6—C5 | 175.8 (2) |
| C7—N2—C4—C5 | −91.8 (3) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | 2.1 (4) |
| S1—N2—C4—C5 | 87.2 (2) | C4—N2—C7—O3 | 179.2 (2) |
| C7—N2—C4—C3 | 93.5 (3) | S1—N2—C7—O3 | 0.2 (3) |
| S1—N2—C4—C3 | −87.5 (2) | C4—N2—C7—C9 | 1.0 (3) |
| C5—C4—C3—C2 | −2.1 (3) | S1—N2—C7—C9 | −178.00 (16) |
| N2—C4—C3—C2 | 172.6 (2) | C4—C3—C2—C1 | 1.2 (4) |
| C5—C4—C3—N1 | 177.6 (2) | N1—C3—C2—C1 | −178.6 (2) |
| N2—C4—C3—N1 | −7.7 (3) | C6—C1—C2—C3 | 1.5 (4) |
| O1—N1—C3—C2 | −16.7 (3) | Cl1—C1—C2—C3 | −177.41 (18) |
| O2—N1—C3—C2 | 160.9 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C2—H2···O5i | 0.93 | 2.55 | 3.404 (3) | 153 |
| C9—H9B···O3ii | 0.96 | 2.58 | 3.521 (3) | 169 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+2, −z; (ii) −x+1, −y+2, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: EZ2142).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Bruker (2007). APEX2, SMART and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst.32, 837–838.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst.36, 7–13.
- Wen, Y.-H., Li, X.-M., Xu, L.-L., Tang, X.-F. & Zhang, S.-S. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o4427–o4428.
- Wen, Y.-H., Zhang, S.-S., Yu, B.-H., Li, X.-M. & Liu, Q. (2005). Acta Cryst. E61, o347–o348.
- Zhang, S.-S., Xu, L.-L., Wen, H.-L., Li, X.-M. & Wen, Y.-H. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o3071–o3072.
- Zhang, S.-S., Xu, L.-L., Zou, J., Bi, S. & Wen, Y.-H. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o4478–o4479.
- Zia-ur-Rehman, M., Choudary, J. A. & Ahmad, S. (2005). Bull. Korean Chem. Soc.26, 1771–1175.
- Zia-ur-Rehman, M., Choudary, J. A., Ahmad, S. & Siddiqui, H. L. (2006). Chem. Pharm. Bull.54, 1175–1178. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Zia-ur-Rehman, M., Choudary, J. A., Elsegood, M. R. J., Siddiqui, H. L. & Khan, K. M. (2008). Eur. J. Med. Chem. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2008.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Zia-ur-Rehman, M., Choudary, J. A., Elsegood, M. R. J., Siddiqui, H. L. & Weaver, G. W. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o4215–o4216.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808032157/ez2142sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808032157/ez2142Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




