Abstract
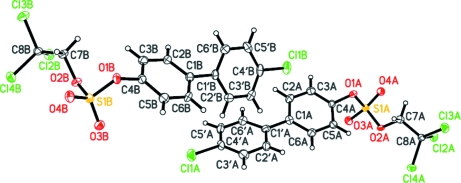
The title compound, C14H10Cl4O4S, is an intermediate in the synthesis of the PCB sulfate monoester of 4′-chloro-biphenyl-4-ol. Both the sulfate monoester and 4′-chloro-biphenyl-4-ol are metabolites of PCB 3 (4-chlorobiphenyl). There are two molecules with different conformations in the asymmetric unit. The solid state dihedral angles between the benzene rings are 18.52 (10) and 41.84 (16)° in the two molecules, whereas the dihedral angles between the least-squares plane of the sulfated benzene ring and O—S (Ar—C—O—S) are 66.2 (3) and 89.3 (3)°. The crystal was an inversion twin with a refined component fraction of 0.44 (7).
Related literature
For similar structures of hydroxylated chlorobiphenyls and their derivatives, see: Rissanen et al. (1988a
▶,b
▶); Lehmler et al. (2001 ▶, 2002 ▶); Desiraju et al. (1979 ▶); Vyas et al. (2006 ▶). For a review of structures of sulfuric acid aryl mono esters, see: Brandao et al. (2005 ▶). For additional background, see: Letcher et al. (2000 ▶); Liu et al. (2004 ▶, 2006 ▶); Sacco & James (2005 ▶); Shaikh et al. (2008 ▶); Tampal et al. (2002 ▶); Hansen (1999 ▶); Robertson & Hansen (2001 ▶).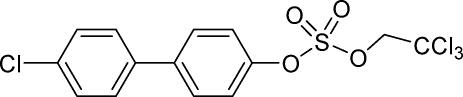
Experimental
Crystal data
C14H10Cl4O4S
M r = 416.08
Orthorhombic,
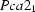
a = 9.6305 (19) Å
b = 30.273 (6) Å
c = 11.330 (2) Å
V = 3303.3 (11) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.86 mm−1
T = 90.0 (2) K
0.40 × 0.34 × 0.18 mm
Data collection
Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SCALEPACK; Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶) T min = 0.679, T max = 0.861
25566 measured reflections
6476 independent reflections
4862 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.063
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.044
wR(F 2) = 0.109
S = 1.05
6476 reflections
415 parameters
1 restraint
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.51 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.56 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), 2481 Friedel Pairs
Flack parameter: 0.44 (7)
Data collection: COLLECT (Nonius, 1998 ▶); cell refinement: SCALEPACK (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶); data reduction: DENZO-SMN (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: XP in SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97 and local procedures.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808038865/dn2403sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808038865/dn2403Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grants ES05605, ES012475 and ES013661 from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, NIH.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are a major class of man-made, persistent organic pollutants and represent an environmental and health concern due to their toxicity and resistance to biodegradation (Robertson & Hansen, 2001; Hansen, 1999). PCB congeners with a lower degree of chlorination are especially prone to undergo oxidative metabolism to hydroxylated (OH)-PCBs (Letcher et al., 2000). OH-PCBs can be further transformed to glucuronides (Tampal et al., 2002) or sulfates (Liu et al., 2006, Sacco & James, 2005). These PCB metabolites are more hydrophilic than PCBs and OH-PCBs and are expected to be more easily excreted. Despite the potential importance of sulfated PCB metabolites, PCB sulfate monoesters and analogous compounds have not been synthesized experimentally and their detailed molecular structure is unknown. Similarly, only few structures of hydroxylated chlorobiphenyl derivatives (Rissanen et al. 1988a, 1988b; Lehmler et al., 2001, 2002; Desiraju et al., 1979; Vyas et al., 2006) and sulfuric acid aryl mono esters (Brandao et al., 2005) have been reported.
Herein we report the crystal structure of the title compound, a trichloro-ethyl PCB sulfate diester intermediate of a putative sulfate metabolite of PCB3 (4-chlorobiphenyl). The asymmetric unit of the crystal structure contains two molecules with different conformations (Fig. 1), an observation that highlights the flexibility of PCB derivatives that lack multiple ortho chlorine substituents. The dihedral angles between the two benzene rings in the biphenyl moiety are 18.52 (10)° and 41.84 (16)° for molecules A and B, respectively. Similar to molecule B, other PCB derivatives with no ortho chlorine substituent adopt dihedral angles of 39.42° (4,4'-dichhlorobiphenyl), 41.31 (07)° (3,3',5'-trichloro-4-methoxy-biphenyl) and 43.94 (06)° (3,3',4,4'-tetrachlorobiphenyl) in the solid state (Shaikh et al., 2008). The calculated dihedral angle of the title compound is 41.2° (Shaikh et al., 2008), which is comparable to that of molecule B, but significantly larger than that of molecule A. The dihedral angle formed by the least-squares plane of the sulfated benzene ring and O1—S1 (Ar—C4—O1—S1) was 66.2 (3)° and 89.3 (3)° for molecules A and B, respectively. These dihedral angles are larger than the calculated Ar—C4—O1—S1 dihedral angle of approximately 54° (calculated with AM1 as implemented by ArgusLab, Version 4.0.1). Overall, these deviations from the energetically most favorable conformation of the title compound are due to crystal packing effects, which allow the molecule to adopt an energetically unfavorable conformation to maximize intermolecular interactions, and thus the lattice energy in the crystal.
Experimental
The title compound was synthesized from 4-chlorobiphenyl-4-ol by sulfation with 2,2,2-trichloroethyl sulfonyl chloride using 4-dimethylaminopyridine as catalyst (Liu et al. 2004). Crystals of the title compound suitable for crystal structure analysis were obtained from a methanolic solution by slowly evaporating the solvent.
Refinement
H atoms were found in difference Fourier maps and subsequently placed in idealized positions with constrained C—H distances of 0.99 Å (CH2) and 0.95 Å (CArH) with Uiso(H) values set to 1.2Ueq of the attached C atom.
The crystal was an inversion twin with a refined component fraction of 0.44 (7), i.e. essentially equal amounts of each component.
Figures
Fig. 1.
View of the title compound showing the atom-labelling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Crystal data
| C14H10Cl4O4S | F000 = 1680 |
| Mr = 416.08 | Dx = 1.673 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, Pca21 | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2c -2ac | Cell parameters from 4257 reflections |
| a = 9.6305 (19) Å | θ = 1.0–27.5º |
| b = 30.273 (6) Å | µ = 0.86 mm−1 |
| c = 11.330 (2) Å | T = 90.0 (2) K |
| V = 3303.3 (11) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 8 | 0.40 × 0.34 × 0.18 mm |
Data collection
| Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer | 6476 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 4862 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: graphite | Rint = 0.063 |
| Detector resolution: 18 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.5º |
| T = 90.0(2) K | θmin = 2.2º |
| ω scans at fixed χ = 55° | h = −12→12 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan(SCALEPACK; Otwinowski & Minor, 1997) | k = −39→38 |
| Tmin = 0.679, Tmax = 0.861 | l = −11→14 |
| 25566 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.044 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0569P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.109 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| S = 1.05 | Δρmax = 0.51 e Å−3 |
| 6476 reflections | Δρmin = −0.56 e Å−3 |
| 415 parameters | Extinction correction: none |
| 1 restraint | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 2481 Friedel Pairs |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Flack parameter: 0.44 (7) |
| Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1A | 0.37972 (11) | 0.52517 (4) | 0.22349 (11) | 0.0182 (3) | |
| O1A | 0.4951 (3) | 0.55663 (9) | 0.2732 (3) | 0.0189 (7) | |
| O2A | 0.3525 (3) | 0.49236 (9) | 0.3284 (3) | 0.0162 (7) | |
| O3A | 0.2535 (3) | 0.54799 (8) | 0.2091 (3) | 0.0228 (7) | |
| O4A | 0.4438 (3) | 0.50234 (10) | 0.1291 (3) | 0.0219 (7) | |
| Cl1A | 0.32327 (13) | 0.81401 (4) | 0.83893 (12) | 0.0332 (3) | |
| Cl2A | 0.34106 (12) | 0.39176 (4) | 0.28495 (11) | 0.0249 (3) | |
| Cl3A | 0.55811 (11) | 0.39177 (4) | 0.46162 (11) | 0.0250 (3) | |
| Cl4A | 0.28608 (11) | 0.42787 (4) | 0.51617 (10) | 0.0251 (3) | |
| C1A | 0.4100 (4) | 0.66199 (14) | 0.5036 (4) | 0.0185 (10) | |
| C2A | 0.4593 (5) | 0.66887 (14) | 0.3888 (4) | 0.0253 (10) | |
| H2A | 0.4777 | 0.6981 | 0.3627 | 0.030* | |
| C3A | 0.4817 (4) | 0.63383 (14) | 0.3129 (4) | 0.0255 (11) | |
| H3A | 0.5129 | 0.6390 | 0.2346 | 0.031* | |
| C4A | 0.4583 (4) | 0.59162 (14) | 0.3517 (4) | 0.0169 (10) | |
| C5A | 0.4137 (4) | 0.58287 (15) | 0.4644 (4) | 0.0192 (10) | |
| H5A | 0.4002 | 0.5534 | 0.4905 | 0.023* | |
| C6A | 0.3889 (4) | 0.61848 (14) | 0.5396 (4) | 0.0203 (11) | |
| H6A | 0.3567 | 0.6129 | 0.6174 | 0.024* | |
| C7A | 0.4706 (4) | 0.46577 (13) | 0.3666 (4) | 0.0171 (10) | |
| H7A1 | 0.5192 | 0.4804 | 0.4329 | 0.021* | |
| H7A2 | 0.5371 | 0.4619 | 0.3008 | 0.021* | |
| C8A | 0.4136 (4) | 0.42113 (14) | 0.4058 (4) | 0.0174 (10) | |
| C1'A | 0.3849 (4) | 0.69949 (14) | 0.5865 (4) | 0.0202 (10) | |
| C2'A | 0.3782 (4) | 0.69245 (14) | 0.7090 (4) | 0.0229 (10) | |
| H2'A | 0.3882 | 0.6634 | 0.7393 | 0.028* | |
| C3'A | 0.3573 (5) | 0.72738 (14) | 0.7862 (4) | 0.0278 (11) | |
| H3'A | 0.3519 | 0.7224 | 0.8689 | 0.033* | |
| C4'A | 0.3444 (5) | 0.76930 (14) | 0.7414 (4) | 0.0215 (11) | |
| C5'A | 0.3477 (4) | 0.77735 (13) | 0.6205 (4) | 0.0265 (11) | |
| H5'A | 0.3351 | 0.8064 | 0.5905 | 0.032* | |
| C6'A | 0.3696 (5) | 0.74235 (14) | 0.5456 (4) | 0.0259 (11) | |
| H6'A | 0.3744 | 0.7477 | 0.4631 | 0.031* | |
| S1B | 0.36151 (11) | 0.02678 (3) | 0.20279 (10) | 0.0170 (2) | |
| O1B | 0.4725 (3) | 0.06109 (9) | 0.1597 (3) | 0.0197 (7) | |
| O2B | 0.3431 (3) | −0.00442 (9) | 0.0931 (3) | 0.0180 (7) | |
| O3B | 0.2310 (3) | 0.04755 (8) | 0.2178 (3) | 0.0214 (7) | |
| O4B | 0.4277 (3) | 0.00352 (10) | 0.2956 (3) | 0.0210 (7) | |
| Cl1B | 0.29897 (13) | 0.31088 (4) | −0.42521 (12) | 0.0308 (3) | |
| Cl2B | 0.30154 (11) | −0.06864 (4) | −0.10670 (11) | 0.0226 (3) | |
| Cl3B | 0.55924 (11) | −0.10661 (4) | −0.02190 (12) | 0.0258 (3) | |
| Cl4B | 0.31521 (12) | −0.10380 (4) | 0.12863 (11) | 0.0249 (3) | |
| C1B | 0.3812 (5) | 0.16175 (14) | −0.0805 (4) | 0.0198 (10) | |
| C2B | 0.4206 (4) | 0.12024 (14) | −0.1204 (4) | 0.0201 (10) | |
| H2B | 0.4293 | 0.1149 | −0.2027 | 0.024* | |
| C3B | 0.4471 (4) | 0.08652 (15) | −0.0409 (5) | 0.0223 (11) | |
| H3B | 0.4745 | 0.0581 | −0.0680 | 0.027* | |
| C4B | 0.4335 (4) | 0.09461 (14) | 0.0765 (5) | 0.0183 (10) | |
| C5B | 0.3896 (4) | 0.13457 (13) | 0.1210 (4) | 0.0225 (10) | |
| H5B | 0.3788 | 0.1390 | 0.2035 | 0.027* | |
| C6B | 0.3617 (5) | 0.16827 (13) | 0.0406 (4) | 0.0218 (10) | |
| H6B | 0.3291 | 0.1960 | 0.0684 | 0.026* | |
| C7B | 0.4627 (4) | −0.03186 (14) | 0.0616 (4) | 0.0182 (10) | |
| H7B1 | 0.5231 | −0.0362 | 0.1313 | 0.022* | |
| H7B2 | 0.5177 | −0.0173 | −0.0011 | 0.022* | |
| C8B | 0.4097 (4) | −0.07557 (14) | 0.0186 (4) | 0.0171 (10) | |
| C1'B | 0.3608 (4) | 0.19884 (14) | −0.1657 (4) | 0.0189 (10) | |
| C2'B | 0.2482 (5) | 0.22865 (12) | −0.1553 (4) | 0.0239 (10) | |
| H2'B | 0.1834 | 0.2250 | −0.0928 | 0.029* | |
| C3'B | 0.2307 (5) | 0.26276 (13) | −0.2336 (4) | 0.0236 (10) | |
| H3'B | 0.1553 | 0.2827 | −0.2245 | 0.028* | |
| C4'B | 0.3228 (5) | 0.26804 (14) | −0.3252 (4) | 0.0226 (11) | |
| C5'B | 0.4350 (5) | 0.23942 (14) | −0.3388 (4) | 0.0247 (11) | |
| H5'B | 0.4992 | 0.2435 | −0.4016 | 0.030* | |
| C6'B | 0.4515 (5) | 0.20517 (14) | −0.2599 (4) | 0.0243 (10) | |
| H6'B | 0.5270 | 0.1853 | −0.2700 | 0.029* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1A | 0.0188 (5) | 0.0180 (6) | 0.0177 (6) | −0.0007 (4) | 0.0011 (5) | 0.0019 (5) |
| O1A | 0.0170 (15) | 0.0174 (15) | 0.0223 (18) | −0.0042 (12) | 0.0023 (14) | 0.0009 (14) |
| O2A | 0.0143 (14) | 0.0185 (15) | 0.0160 (18) | −0.0006 (12) | 0.0034 (14) | 0.0059 (14) |
| O3A | 0.0188 (15) | 0.0225 (15) | 0.0270 (19) | 0.0033 (14) | −0.0026 (15) | 0.0035 (15) |
| O4A | 0.0294 (17) | 0.0197 (16) | 0.0167 (18) | 0.0004 (14) | 0.0044 (14) | −0.0007 (14) |
| Cl1A | 0.0430 (7) | 0.0242 (6) | 0.0323 (7) | −0.0018 (5) | −0.0001 (6) | −0.0100 (6) |
| Cl2A | 0.0281 (6) | 0.0220 (6) | 0.0245 (7) | −0.0004 (5) | −0.0071 (5) | −0.0060 (5) |
| Cl3A | 0.0226 (6) | 0.0234 (6) | 0.0289 (7) | 0.0048 (5) | −0.0031 (5) | 0.0023 (5) |
| Cl4A | 0.0253 (6) | 0.0273 (6) | 0.0227 (6) | 0.0025 (5) | 0.0079 (5) | 0.0047 (5) |
| C1A | 0.019 (2) | 0.020 (2) | 0.016 (2) | 0.0015 (18) | −0.003 (2) | 0.000 (2) |
| C2A | 0.031 (3) | 0.018 (2) | 0.027 (3) | −0.001 (2) | 0.002 (2) | 0.007 (2) |
| C3A | 0.029 (3) | 0.026 (2) | 0.022 (3) | 0.001 (2) | 0.006 (2) | 0.005 (2) |
| C4A | 0.015 (2) | 0.013 (2) | 0.023 (3) | 0.0012 (17) | −0.001 (2) | −0.0001 (19) |
| C5A | 0.022 (2) | 0.020 (2) | 0.016 (2) | 0.0024 (18) | 0.002 (2) | 0.002 (2) |
| C6A | 0.017 (2) | 0.019 (2) | 0.024 (3) | −0.0005 (19) | −0.002 (2) | 0.002 (2) |
| C7A | 0.017 (2) | 0.020 (2) | 0.014 (2) | 0.0019 (19) | −0.0016 (19) | 0.002 (2) |
| C8A | 0.014 (2) | 0.018 (2) | 0.020 (3) | 0.0034 (18) | 0.002 (2) | 0.003 (2) |
| C1'A | 0.019 (2) | 0.020 (2) | 0.021 (3) | −0.0009 (19) | 0.001 (2) | 0.005 (2) |
| C2'A | 0.030 (3) | 0.016 (2) | 0.023 (2) | 0.0041 (19) | 0.003 (2) | 0.001 (2) |
| C3'A | 0.030 (3) | 0.028 (3) | 0.026 (3) | 0.004 (2) | 0.001 (2) | 0.001 (2) |
| C4'A | 0.022 (2) | 0.019 (2) | 0.023 (3) | −0.0030 (18) | −0.004 (2) | −0.010 (2) |
| C5'A | 0.030 (3) | 0.015 (2) | 0.035 (3) | −0.0022 (19) | 0.000 (2) | 0.000 (2) |
| C6'A | 0.028 (3) | 0.020 (2) | 0.029 (3) | 0.001 (2) | 0.003 (2) | 0.001 (2) |
| S1B | 0.0177 (5) | 0.0161 (5) | 0.0173 (6) | −0.0012 (4) | −0.0013 (5) | 0.0001 (5) |
| O1B | 0.0210 (15) | 0.0143 (15) | 0.0237 (19) | −0.0025 (13) | −0.0017 (14) | 0.0024 (14) |
| O2B | 0.0156 (15) | 0.0191 (16) | 0.0192 (19) | 0.0025 (12) | −0.0009 (15) | −0.0058 (14) |
| O3B | 0.0179 (15) | 0.0198 (15) | 0.0265 (18) | 0.0001 (13) | −0.0005 (15) | −0.0040 (15) |
| O4B | 0.0246 (16) | 0.0219 (17) | 0.0166 (18) | 0.0001 (14) | −0.0045 (14) | 0.0031 (15) |
| Cl1B | 0.0450 (8) | 0.0191 (6) | 0.0285 (7) | −0.0008 (5) | −0.0068 (6) | 0.0054 (5) |
| Cl2B | 0.0221 (5) | 0.0255 (6) | 0.0203 (6) | −0.0011 (5) | −0.0054 (5) | −0.0012 (5) |
| Cl3B | 0.0193 (6) | 0.0255 (6) | 0.0326 (7) | 0.0056 (5) | −0.0011 (5) | −0.0071 (6) |
| Cl4B | 0.0291 (6) | 0.0221 (6) | 0.0235 (6) | −0.0017 (5) | 0.0031 (5) | 0.0044 (5) |
| C1B | 0.021 (2) | 0.014 (2) | 0.024 (3) | −0.0032 (18) | 0.002 (2) | −0.003 (2) |
| C2B | 0.022 (2) | 0.016 (2) | 0.022 (3) | −0.0002 (19) | 0.002 (2) | −0.003 (2) |
| C3B | 0.016 (2) | 0.020 (2) | 0.031 (3) | 0.0001 (18) | 0.002 (2) | −0.003 (2) |
| C4B | 0.015 (2) | 0.016 (2) | 0.024 (3) | 0.0002 (18) | −0.003 (2) | 0.004 (2) |
| C5B | 0.026 (2) | 0.022 (2) | 0.020 (2) | −0.0012 (19) | 0.001 (2) | −0.003 (2) |
| C6B | 0.026 (2) | 0.011 (2) | 0.028 (3) | 0.0037 (19) | 0.003 (2) | −0.0006 (19) |
| C7B | 0.015 (2) | 0.018 (2) | 0.022 (3) | 0.0026 (19) | −0.002 (2) | −0.004 (2) |
| C8B | 0.015 (2) | 0.018 (2) | 0.019 (2) | 0.0035 (18) | 0.001 (2) | 0.004 (2) |
| C1'B | 0.024 (2) | 0.014 (2) | 0.019 (3) | −0.0047 (18) | −0.002 (2) | −0.002 (2) |
| C2'B | 0.021 (2) | 0.022 (2) | 0.029 (3) | −0.0005 (19) | 0.005 (2) | −0.002 (2) |
| C3'B | 0.029 (3) | 0.015 (2) | 0.026 (3) | 0.0048 (19) | −0.003 (2) | −0.0025 (19) |
| C4'B | 0.030 (3) | 0.014 (2) | 0.024 (3) | −0.0054 (19) | −0.013 (2) | 0.000 (2) |
| C5'B | 0.029 (3) | 0.026 (2) | 0.019 (2) | −0.011 (2) | 0.001 (2) | 0.002 (2) |
| C6'B | 0.026 (2) | 0.020 (2) | 0.027 (3) | −0.001 (2) | 0.003 (2) | −0.005 (2) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| S1A—O3A | 1.408 (3) | S1B—O3B | 1.415 (3) |
| S1A—O4A | 1.415 (3) | S1B—O4B | 1.417 (3) |
| S1A—O1A | 1.568 (3) | S1B—O1B | 1.568 (3) |
| S1A—O2A | 1.571 (3) | S1B—O2B | 1.571 (3) |
| O1A—C4A | 1.427 (5) | O1B—C4B | 1.435 (5) |
| O2A—C7A | 1.459 (5) | O2B—C7B | 1.464 (5) |
| Cl1A—C4'A | 1.759 (5) | Cl1B—C4'B | 1.738 (5) |
| Cl2A—C8A | 1.776 (5) | Cl2B—C8B | 1.773 (5) |
| Cl3A—C8A | 1.768 (4) | Cl3B—C8B | 1.780 (4) |
| Cl4A—C8A | 1.765 (5) | Cl4B—C8B | 1.764 (5) |
| C1A—C6A | 1.394 (6) | C1B—C2B | 1.388 (6) |
| C1A—C2A | 1.400 (7) | C1B—C6B | 1.399 (6) |
| C1A—C1'A | 1.493 (6) | C1B—C1'B | 1.494 (6) |
| C2A—C3A | 1.383 (6) | C2B—C3B | 1.386 (6) |
| C2A—H2A | 0.9500 | C2B—H2B | 0.9500 |
| C3A—C4A | 1.370 (6) | C3B—C4B | 1.358 (7) |
| C3A—H3A | 0.9500 | C3B—H3B | 0.9500 |
| C4A—C5A | 1.373 (7) | C4B—C5B | 1.377 (6) |
| C5A—C6A | 1.395 (6) | C5B—C6B | 1.394 (6) |
| C5A—H5A | 0.9500 | C5B—H5B | 0.9500 |
| C6A—H6A | 0.9500 | C6B—H6B | 0.9500 |
| C7A—C8A | 1.524 (6) | C7B—C8B | 1.499 (6) |
| C7A—H7A1 | 0.9900 | C7B—H7B1 | 0.9900 |
| C7A—H7A2 | 0.9900 | C7B—H7B2 | 0.9900 |
| C1'A—C6'A | 1.386 (6) | C1'B—C6'B | 1.392 (6) |
| C1'A—C2'A | 1.406 (7) | C1'B—C2'B | 1.416 (6) |
| C2'A—C3'A | 1.387 (6) | C2'B—C3'B | 1.371 (6) |
| C2'A—H2'A | 0.9500 | C2'B—H2'B | 0.9500 |
| C3'A—C4'A | 1.372 (6) | C3'B—C4'B | 1.375 (7) |
| C3'A—H3'A | 0.9500 | C3'B—H3'B | 0.9500 |
| C4'A—C5'A | 1.392 (7) | C4'B—C5'B | 1.394 (6) |
| C5'A—C6'A | 1.374 (6) | C5'B—C6'B | 1.379 (6) |
| C5'A—H5'A | 0.9500 | C5'B—H5'B | 0.9500 |
| C6'A—H6'A | 0.9500 | C6'B—H6'B | 0.9500 |
| O3A—S1A—O4A | 121.9 (2) | O3B—S1B—O4B | 122.1 (2) |
| O3A—S1A—O1A | 110.81 (17) | O3B—S1B—O1B | 110.36 (16) |
| O4A—S1A—O1A | 105.03 (18) | O4B—S1B—O1B | 104.70 (17) |
| O3A—S1A—O2A | 104.68 (17) | O3B—S1B—O2B | 105.19 (17) |
| O4A—S1A—O2A | 109.64 (18) | O4B—S1B—O2B | 109.83 (18) |
| O1A—S1A—O2A | 103.31 (17) | O1B—S1B—O2B | 103.20 (17) |
| C4A—O1A—S1A | 119.9 (3) | C4B—O1B—S1B | 119.7 (3) |
| C7A—O2A—S1A | 116.3 (2) | C7B—O2B—S1B | 116.5 (3) |
| C6A—C1A—C2A | 117.5 (4) | C2B—C1B—C6B | 118.9 (4) |
| C6A—C1A—C1'A | 120.7 (4) | C2B—C1B—C1'B | 120.4 (4) |
| C2A—C1A—C1'A | 121.7 (4) | C6B—C1B—C1'B | 120.7 (4) |
| C3A—C2A—C1A | 121.1 (4) | C3B—C2B—C1B | 120.4 (5) |
| C3A—C2A—H2A | 119.4 | C3B—C2B—H2B | 119.8 |
| C1A—C2A—H2A | 119.4 | C1B—C2B—H2B | 119.8 |
| C4A—C3A—C2A | 119.3 (4) | C4B—C3B—C2B | 119.1 (5) |
| C4A—C3A—H3A | 120.3 | C4B—C3B—H3B | 120.5 |
| C2A—C3A—H3A | 120.3 | C2B—C3B—H3B | 120.5 |
| C3A—C4A—C5A | 122.0 (4) | C3B—C4B—C5B | 123.1 (5) |
| C3A—C4A—O1A | 116.8 (4) | C3B—C4B—O1B | 119.4 (4) |
| C5A—C4A—O1A | 120.9 (4) | C5B—C4B—O1B | 117.4 (4) |
| C4A—C5A—C6A | 118.2 (4) | C4B—C5B—C6B | 117.6 (4) |
| C4A—C5A—H5A | 120.9 | C4B—C5B—H5B | 121.2 |
| C6A—C5A—H5A | 120.9 | C6B—C5B—H5B | 121.2 |
| C1A—C6A—C5A | 121.8 (4) | C5B—C6B—C1B | 120.8 (4) |
| C1A—C6A—H6A | 119.1 | C5B—C6B—H6B | 119.6 |
| C5A—C6A—H6A | 119.1 | C1B—C6B—H6B | 119.6 |
| O2A—C7A—C8A | 107.1 (3) | O2B—C7B—C8B | 108.2 (3) |
| O2A—C7A—H7A1 | 110.3 | O2B—C7B—H7B1 | 110.1 |
| C8A—C7A—H7A1 | 110.3 | C8B—C7B—H7B1 | 110.1 |
| O2A—C7A—H7A2 | 110.3 | O2B—C7B—H7B2 | 110.1 |
| C8A—C7A—H7A2 | 110.3 | C8B—C7B—H7B2 | 110.1 |
| H7A1—C7A—H7A2 | 108.5 | H7B1—C7B—H7B2 | 108.4 |
| C7A—C8A—Cl4A | 110.8 (3) | C7B—C8B—Cl4B | 111.9 (3) |
| C7A—C8A—Cl3A | 105.5 (3) | C7B—C8B—Cl2B | 110.8 (3) |
| Cl4A—C8A—Cl3A | 110.6 (3) | Cl4B—C8B—Cl2B | 108.7 (2) |
| C7A—C8A—Cl2A | 111.2 (3) | C7B—C8B—Cl3B | 105.9 (3) |
| Cl4A—C8A—Cl2A | 109.3 (2) | Cl4B—C8B—Cl3B | 110.1 (2) |
| Cl3A—C8A—Cl2A | 109.5 (2) | Cl2B—C8B—Cl3B | 109.4 (3) |
| C6'A—C1'A—C2'A | 117.9 (4) | C6'B—C1'B—C2'B | 117.2 (4) |
| C6'A—C1'A—C1A | 121.3 (4) | C6'B—C1'B—C1B | 121.1 (4) |
| C2'A—C1'A—C1A | 120.9 (4) | C2'B—C1'B—C1B | 121.7 (4) |
| C3'A—C2'A—C1'A | 120.9 (4) | C3'B—C2'B—C1'B | 121.3 (4) |
| C3'A—C2'A—H2'A | 119.5 | C3'B—C2'B—H2'B | 119.4 |
| C1'A—C2'A—H2'A | 119.5 | C1'B—C2'B—H2'B | 119.4 |
| C4'A—C3'A—C2'A | 119.0 (4) | C2'B—C3'B—C4'B | 119.8 (4) |
| C4'A—C3'A—H3'A | 120.5 | C2'B—C3'B—H3'B | 120.1 |
| C2'A—C3'A—H3'A | 120.5 | C4'B—C3'B—H3'B | 120.1 |
| C3'A—C4'A—C5'A | 121.6 (4) | C3'B—C4'B—C5'B | 120.8 (4) |
| C3'A—C4'A—Cl1A | 119.3 (4) | C3'B—C4'B—Cl1B | 119.6 (4) |
| C5'A—C4'A—Cl1A | 119.1 (4) | C5'B—C4'B—Cl1B | 119.6 (4) |
| C6'A—C5'A—C4'A | 118.5 (4) | C6'B—C5'B—C4'B | 119.0 (4) |
| C6'A—C5'A—H5'A | 120.8 | C6'B—C5'B—H5'B | 120.5 |
| C4'A—C5'A—H5'A | 120.8 | C4'B—C5'B—H5'B | 120.5 |
| C5'A—C6'A—C1'A | 122.1 (5) | C5'B—C6'B—C1'B | 121.9 (4) |
| C5'A—C6'A—H6'A | 118.9 | C5'B—C6'B—H6'B | 119.0 |
| C1'A—C6'A—H6'A | 118.9 | C1'B—C6'B—H6'B | 119.0 |
| O3A—S1A—O1A—C4A | 32.4 (4) | O3B—S1B—O1B—C4B | −38.3 (4) |
| O4A—S1A—O1A—C4A | 165.9 (3) | O4B—S1B—O1B—C4B | −171.3 (3) |
| O2A—S1A—O1A—C4A | −79.2 (3) | O2B—S1B—O1B—C4B | 73.7 (3) |
| O3A—S1A—O2A—C7A | −176.8 (3) | O3B—S1B—O2B—C7B | −177.1 (3) |
| O4A—S1A—O2A—C7A | 50.8 (3) | O4B—S1B—O2B—C7B | −44.0 (4) |
| O1A—S1A—O2A—C7A | −60.8 (3) | O1B—S1B—O2B—C7B | 67.2 (3) |
| C6A—C1A—C2A—C3A | 2.1 (7) | C6B—C1B—C2B—C3B | −3.4 (7) |
| C1'A—C1A—C2A—C3A | −179.8 (4) | C1'B—C1B—C2B—C3B | 176.3 (4) |
| C1A—C2A—C3A—C4A | −1.6 (7) | C1B—C2B—C3B—C4B | 0.3 (6) |
| C2A—C3A—C4A—C5A | −0.3 (7) | C2B—C3B—C4B—C5B | 2.3 (7) |
| C2A—C3A—C4A—O1A | −174.5 (4) | C2B—C3B—C4B—O1B | −174.6 (4) |
| S1A—O1A—C4A—C3A | −116.3 (4) | S1B—O1B—C4B—C3B | −90.7 (4) |
| S1A—O1A—C4A—C5A | 69.5 (5) | S1B—O1B—C4B—C5B | 92.3 (4) |
| C3A—C4A—C5A—C6A | 1.6 (7) | C3B—C4B—C5B—C6B | −1.6 (7) |
| O1A—C4A—C5A—C6A | 175.5 (4) | O1B—C4B—C5B—C6B | 175.3 (4) |
| C2A—C1A—C6A—C5A | −0.8 (6) | C4B—C5B—C6B—C1B | −1.6 (7) |
| C1'A—C1A—C6A—C5A | −179.0 (4) | C2B—C1B—C6B—C5B | 4.0 (7) |
| C4A—C5A—C6A—C1A | −1.0 (7) | C1'B—C1B—C6B—C5B | −175.7 (4) |
| S1A—O2A—C7A—C8A | −146.0 (3) | S1B—O2B—C7B—C8B | 143.8 (3) |
| O2A—C7A—C8A—Cl4A | −55.9 (4) | O2B—C7B—C8B—Cl4B | −61.5 (4) |
| O2A—C7A—C8A—Cl3A | −175.6 (3) | O2B—C7B—C8B—Cl2B | 59.9 (4) |
| O2A—C7A—C8A—Cl2A | 65.8 (4) | O2B—C7B—C8B—Cl3B | 178.4 (3) |
| C6A—C1A—C1'A—C6'A | −162.8 (4) | C2B—C1B—C1'B—C6'B | −41.0 (6) |
| C2A—C1A—C1'A—C6'A | 19.1 (7) | C6B—C1B—C1'B—C6'B | 138.6 (5) |
| C6A—C1A—C1'A—C2'A | 18.2 (6) | C2B—C1B—C1'B—C2'B | 138.2 (5) |
| C2A—C1A—C1'A—C2'A | −159.9 (4) | C6B—C1B—C1'B—C2'B | −42.1 (6) |
| C6'A—C1'A—C2'A—C3'A | −0.1 (7) | C6'B—C1'B—C2'B—C3'B | −1.1 (7) |
| C1A—C1'A—C2'A—C3'A | 178.9 (4) | C1B—C1'B—C2'B—C3'B | 179.6 (4) |
| C1'A—C2'A—C3'A—C4'A | −0.7 (7) | C1'B—C2'B—C3'B—C4'B | 0.9 (7) |
| C2'A—C3'A—C4'A—C5'A | 2.0 (7) | C2'B—C3'B—C4'B—C5'B | −0.8 (7) |
| C2'A—C3'A—C4'A—Cl1A | −178.0 (3) | C2'B—C3'B—C4'B—Cl1B | 179.2 (3) |
| C3'A—C4'A—C5'A—C6'A | −2.5 (7) | C3'B—C4'B—C5'B—C6'B | 0.9 (7) |
| Cl1A—C4'A—C5'A—C6'A | 177.6 (3) | Cl1B—C4'B—C5'B—C6'B | −179.0 (3) |
| C4'A—C5'A—C6'A—C1'A | 1.6 (7) | C4'B—C5'B—C6'B—C1'B | −1.2 (7) |
| C2'A—C1'A—C6'A—C5'A | −0.4 (7) | C2'B—C1'B—C6'B—C5'B | 1.3 (7) |
| C1A—C1'A—C6'A—C5'A | −179.4 (4) | C1B—C1'B—C6'B—C5'B | −179.5 (4) |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: DN2403).
References
- Brandao, T. A. S., Priebe, J. P., Damasceno, A. S., Bortoluzzia, A. J., Kirby, A. J. & Nome, F. (2005). J. Mol. Struct.734, 205–209.
- Desiraju, G. R., Paul, I. C. & Curtin, D. Y. (1979). Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst.52, 259–266.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Hansen, L. G. (1999). The Ortho Side of PCBs Boston: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
- Lehmler, H.-J., Robertson, L. W. & Parkin, S. (2001). Acta Cryst. E57, o590–o591.
- Lehmler, H.-J., Robertson, L. W., Parkin, S. & Brock, C. P. (2002). Acta Cryst. B58, 140–147. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Letcher, R. J., Klasson-Wehler, E. & Bergman, A. (2000). The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry, Vol. 3 Part K, New Types of Persistent Halogenated Compounds, edited by J. Paasivirta, pp. 315–359. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Verlag.
- Liu, Y., Apak, T. I., Lehmler, H.-J., Robertson, L. W. & Duffel, M. W. (2006). Chem. Res. Toxicol.19, 1420–1425. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y., Lien, I. F. F., Ruttgaizer, S., Dove, P. & Taylor, S. D. (2004). Org. Lett.6, 209–212. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Nonius (1998). COLLECT Nonius BV, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. (1997). Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 276, Macromolecular Crystallography, Part A, edited by C. W. Carter Jr & R. M. Sweet, pp. 307–326. New York: Academic Press.
- Rissanen, K., Valkonen, J. & Mannila, B. (1988a). Acta Cryst. C44, 682–684.
- Rissanen, K., Valkonen, J. & Mannila, B. (1988b). Acta Cryst. C44, 684–686.
- Robertson, L. W. & Hansen, L. G. (2001). Recent Advances in the Environmental Toxicology and Health Effects of PCBs Lexington, USA: University Press of Kentucky.
- Sacco, J. C. & James, M. O. (2005). Drug Metab. Dispos.33, 1341–1348. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, N. S., Parkin, S., Luthe, G. & Lehmler, H. J. (2008). Chemosphere, 70, 1694–1698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Tampal, N., Lehmler, H.-J., Espandiari, P., Malmberg, T. & Robertson, L. W. (2002). Chem. Res. Toxicol.15, 1259–1266. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Vyas, S. M., Parkin, S. & Lehmler, H.-J. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o2905–o2906.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808038865/dn2403sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808038865/dn2403Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report