Abstract
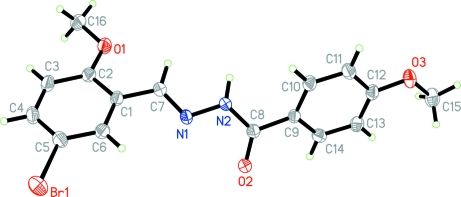
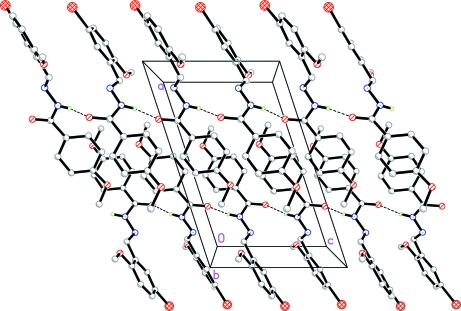
In the title compound, C16H15BrN2O3, the benzohydrazide group is not planar and the molecule exists in a trans configuration with respect to the methylidene unit. The dihedral angle between the two substituted benzene rings is 75.6 (2)°. In the crystal structure, molecules are linked by intermolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds involving carbonyl and amine functionalities, to form chains parallel to the c cell axis.
Related literature
For the biological activities of hydrazones, see: Zhong et al. (2007 ▶); Raj et al. (2007 ▶); Jimenez-Pulido et al. (2008 ▶). For related structures, see: Yehye et al. (2008 ▶); Fun, Patil, Jebas et al. (2008 ▶); Fun, Patil, Rao et al. (2008 ▶); Yang et al. (2008 ▶); Ejsmont et al. (2008 ▶).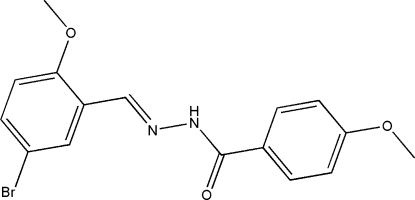
Experimental
Crystal data
C16H15BrN2O3
M r = 363.21
Monoclinic,
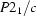
a = 12.438 (4) Å
b = 16.684 (6) Å
c = 7.863 (3) Å
β = 108.218 (6)°
V = 1549.8 (9) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 2.67 mm−1
T = 298 (2) K
0.20 × 0.20 × 0.18 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 1998 ▶) T min = 0.593, T max = 0.620
8697 measured reflections
3245 independent reflections
2068 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.034
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.038
wR(F 2) = 0.093
S = 1.01
3245 reflections
205 parameters
1 restraint
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.50 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.47 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 1998 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 1998 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808035472/bh2202sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808035472/bh2202Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2⋯O2i | 0.890 (10) | 1.966 (12) | 2.835 (3) | 165 (2) |
Symmetry code: (i) 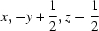 .
.
Acknowledgments
Financial support of this work was provided by the Research Foundation of Liaoning Province (project No. 2008470).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Hydrazones derived from the condensation of aldehydes with hydrazides have been demonstrated to possess excellent biological activities (Zhong et al., 2007; Raj et al., 2007; Jimenez-Pulido et al., 2008). Due to the easy synthesis of such compounds, a great deal of hydrazones have been synthesized and structurally characterized (Yehye et al., 2008; Fun, Patil, Jebas et al., 2008; Fun, Patil, Rao et al., 2008;Yang et al., 2008; Ejsmont et al., 2008). We report herein the crystal structure of the title new compound, (I).
In the structure of the title compound (Fig. 1) the molecule exists in a trans configuration with respect to the methylidene unit. The dihedral angle between the two substituted benzene rings is 75.6 (2)°. In both the 5-bromo-2-methoxyphenyl unit and the 4-methoxyphenyl unit, the methoxy groups are nearly coplanar with the corresponding mean planes of the C1···C6 and C9···C14 rings, respectively. Atoms C16 and C15 deviate from their corresponding benzene rings by 0.058 (2) and 0.059 (2) Å respectively. The torsion angle of C7—N1—N2—C8 is 19.4 (3)°. The bond lengths and angles are found in expected ranges.
In the crystal structure, molecules are linked by intermolecular N—H···O hydrogen bonds involving carbonyl and amine groups (Table 1), to form chains parallel to the c axis (Fig. 2).
Experimental
The compound was prepared by refluxing 5-bromo-2-methoxybenzaldehyde (1.0 mmol) with 4-methoxybenzohydrazide (1.0 mmol) in methanol (100 ml). Excess methanol was removed from the mixture by distillation. The colorless solid product was filtered, and washed three times with methanol. Colorless block crystals of the title compound were obtained from a methanol solution by slow evaporation in air.
Refinement
H2 was located in a difference map and refined isotropically, with N2—H2 distance restrained to 0.90 (1) Å. Other H atoms were placed in calculated positions (C—H = 0.93–0.96 Å) and refined as riding atoms with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) and 1.5Ueq(methyl C). A rotating group model was used for the methyl groups.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I), showing 30% probability displacement ellipsoids for the non-hydrogen atoms.
Fig. 2.
The packing diagram of (I), viewed along the b axis. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C16H15BrN2O3 | F000 = 736 |
| Mr = 363.21 | Dx = 1.557 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 2110 reflections |
| a = 12.438 (4) Å | θ = 2.4–24.5º |
| b = 16.684 (6) Å | µ = 2.67 mm−1 |
| c = 7.863 (3) Å | T = 298 (2) K |
| β = 108.218 (6)º | Block, colorless |
| V = 1549.8 (9) Å3 | 0.20 × 0.20 × 0.18 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer | 3245 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2068 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: graphite | Rint = 0.034 |
| T = 298(2) K | θmax = 26.7º |
| ω scans | θmin = 1.7º |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan(SADABS; Bruker, 1998) | h = −14→15 |
| Tmin = 0.593, Tmax = 0.620 | k = −20→21 |
| 8697 measured reflections | l = −9→9 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.038 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.093 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0407P)2 + 0.1883P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.01 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 3245 reflections | Δρmax = 0.50 e Å−3 |
| 205 parameters | Δρmin = −0.47 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Extinction correction: none |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br1 | −0.31436 (3) | 0.22534 (2) | 0.94364 (5) | 0.07161 (17) | |
| N1 | 0.10628 (17) | 0.23762 (13) | 0.8539 (3) | 0.0380 (5) | |
| N2 | 0.19688 (18) | 0.26531 (13) | 0.8053 (3) | 0.0384 (5) | |
| O1 | 0.01300 (15) | 0.01461 (11) | 0.7292 (3) | 0.0509 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.26258 (15) | 0.33509 (11) | 1.0641 (2) | 0.0455 (5) | |
| O3 | 0.61120 (16) | 0.44804 (12) | 0.6741 (3) | 0.0603 (6) | |
| C1 | −0.0401 (2) | 0.14085 (16) | 0.8049 (3) | 0.0383 (6) | |
| C2 | −0.0634 (2) | 0.05851 (16) | 0.7802 (3) | 0.0414 (7) | |
| C3 | −0.1589 (2) | 0.02734 (18) | 0.8110 (4) | 0.0490 (7) | |
| H3 | −0.1738 | −0.0273 | 0.7967 | 0.059* | |
| C4 | −0.2318 (2) | 0.07627 (19) | 0.8625 (4) | 0.0498 (8) | |
| H4 | −0.2957 | 0.0548 | 0.8828 | 0.060* | |
| C5 | −0.2101 (2) | 0.15743 (18) | 0.8841 (4) | 0.0460 (7) | |
| C6 | −0.1148 (2) | 0.18901 (17) | 0.8578 (3) | 0.0429 (7) | |
| H6 | −0.1000 | 0.2435 | 0.8757 | 0.051* | |
| C7 | 0.0603 (2) | 0.17374 (16) | 0.7739 (3) | 0.0389 (6) | |
| H7 | 0.0915 | 0.1481 | 0.6953 | 0.047* | |
| C8 | 0.2703 (2) | 0.31655 (15) | 0.9165 (4) | 0.0369 (6) | |
| C9 | 0.3602 (2) | 0.34885 (15) | 0.8498 (3) | 0.0354 (6) | |
| C10 | 0.3494 (2) | 0.35720 (16) | 0.6705 (4) | 0.0425 (7) | |
| H10 | 0.2833 | 0.3400 | 0.5852 | 0.051* | |
| C11 | 0.4338 (2) | 0.39027 (18) | 0.6149 (4) | 0.0493 (7) | |
| H11 | 0.4246 | 0.3954 | 0.4934 | 0.059* | |
| C12 | 0.5326 (2) | 0.41596 (16) | 0.7408 (4) | 0.0432 (7) | |
| C13 | 0.5452 (2) | 0.40845 (18) | 0.9203 (4) | 0.0482 (7) | |
| H13 | 0.6115 | 0.4256 | 1.0054 | 0.058* | |
| C14 | 0.4593 (2) | 0.37549 (17) | 0.9738 (4) | 0.0462 (7) | |
| H14 | 0.4681 | 0.3711 | 1.0953 | 0.055* | |
| C15 | 0.7161 (3) | 0.4720 (2) | 0.7978 (5) | 0.0739 (11) | |
| H15A | 0.7031 | 0.5129 | 0.8749 | 0.111* | |
| H15B | 0.7644 | 0.4926 | 0.7338 | 0.111* | |
| H15C | 0.7517 | 0.4267 | 0.8684 | 0.111* | |
| C16 | −0.0095 (3) | −0.06880 (17) | 0.6972 (4) | 0.0563 (8) | |
| H16A | −0.0110 | −0.0943 | 0.8059 | 0.084* | |
| H16B | 0.0488 | −0.0925 | 0.6575 | 0.084* | |
| H16C | −0.0814 | −0.0757 | 0.6068 | 0.084* | |
| H2 | 0.212 (2) | 0.2407 (14) | 0.715 (3) | 0.044 (8)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br1 | 0.0574 (2) | 0.0821 (3) | 0.0863 (3) | 0.00286 (18) | 0.0383 (2) | −0.0118 (2) |
| N1 | 0.0331 (12) | 0.0430 (14) | 0.0405 (13) | −0.0059 (10) | 0.0154 (10) | −0.0001 (10) |
| N2 | 0.0398 (13) | 0.0409 (13) | 0.0403 (14) | −0.0086 (11) | 0.0208 (11) | −0.0065 (11) |
| O1 | 0.0498 (12) | 0.0413 (11) | 0.0670 (14) | −0.0080 (9) | 0.0260 (11) | −0.0072 (10) |
| O2 | 0.0488 (11) | 0.0473 (11) | 0.0470 (12) | −0.0117 (9) | 0.0244 (10) | −0.0083 (9) |
| O3 | 0.0472 (13) | 0.0689 (14) | 0.0728 (15) | −0.0201 (11) | 0.0300 (11) | −0.0025 (12) |
| C1 | 0.0363 (15) | 0.0414 (16) | 0.0361 (15) | −0.0074 (12) | 0.0098 (13) | −0.0008 (12) |
| C2 | 0.0401 (16) | 0.0453 (17) | 0.0371 (16) | −0.0058 (13) | 0.0098 (13) | −0.0017 (13) |
| C3 | 0.0483 (17) | 0.0462 (17) | 0.0525 (19) | −0.0146 (14) | 0.0158 (15) | −0.0021 (14) |
| C4 | 0.0411 (17) | 0.060 (2) | 0.0503 (18) | −0.0150 (15) | 0.0176 (15) | 0.0009 (15) |
| C5 | 0.0404 (16) | 0.058 (2) | 0.0410 (17) | −0.0019 (14) | 0.0145 (14) | 0.0009 (14) |
| C6 | 0.0437 (16) | 0.0433 (16) | 0.0412 (17) | −0.0049 (13) | 0.0125 (14) | −0.0019 (13) |
| C7 | 0.0372 (15) | 0.0417 (16) | 0.0404 (16) | −0.0035 (13) | 0.0158 (13) | −0.0020 (13) |
| C8 | 0.0368 (15) | 0.0318 (14) | 0.0436 (17) | 0.0025 (12) | 0.0147 (13) | 0.0013 (12) |
| C9 | 0.0328 (14) | 0.0328 (14) | 0.0422 (17) | −0.0033 (11) | 0.0142 (13) | −0.0010 (12) |
| C10 | 0.0350 (15) | 0.0479 (17) | 0.0422 (17) | −0.0075 (13) | 0.0086 (13) | −0.0016 (13) |
| C11 | 0.0504 (18) | 0.0560 (19) | 0.0450 (17) | −0.0098 (14) | 0.0201 (15) | 0.0023 (14) |
| C12 | 0.0365 (16) | 0.0385 (15) | 0.057 (2) | −0.0043 (12) | 0.0184 (15) | −0.0021 (13) |
| C13 | 0.0340 (16) | 0.0556 (19) | 0.054 (2) | −0.0106 (13) | 0.0128 (14) | −0.0093 (15) |
| C14 | 0.0453 (17) | 0.0554 (18) | 0.0400 (17) | −0.0063 (14) | 0.0165 (14) | −0.0055 (14) |
| C15 | 0.048 (2) | 0.087 (3) | 0.096 (3) | −0.0268 (18) | 0.036 (2) | −0.017 (2) |
| C16 | 0.062 (2) | 0.0428 (18) | 0.067 (2) | −0.0070 (15) | 0.0239 (17) | −0.0084 (15) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Br1—C5 | 1.888 (3) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C7 | 1.278 (3) | C7—H7 | 0.9300 |
| N1—N2 | 1.378 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.477 (3) |
| N2—C8 | 1.352 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.381 (4) |
| N2—H2 | 0.890 (10) | C9—C14 | 1.385 (4) |
| O1—C2 | 1.355 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.372 (4) |
| O1—C16 | 1.426 (3) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| O2—C8 | 1.233 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.383 (4) |
| O3—C12 | 1.355 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| O3—C15 | 1.419 (4) | C12—C13 | 1.377 (4) |
| C1—C6 | 1.386 (4) | C13—C14 | 1.379 (4) |
| C1—C2 | 1.405 (4) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C7 | 1.453 (3) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.386 (4) | C15—H15A | 0.9600 |
| C3—C4 | 1.371 (4) | C15—H15B | 0.9600 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C15—H15C | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.381 (4) | C16—H16A | 0.9600 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C16—H16B | 0.9600 |
| C5—C6 | 1.371 (4) | C16—H16C | 0.9600 |
| C7—N1—N2 | 115.0 (2) | C10—C9—C14 | 117.8 (2) |
| C8—N2—N1 | 118.5 (2) | C10—C9—C8 | 123.9 (2) |
| C8—N2—H2 | 122.6 (17) | C14—C9—C8 | 118.2 (2) |
| N1—N2—H2 | 117.5 (17) | C11—C10—C9 | 121.8 (3) |
| C2—O1—C16 | 117.6 (2) | C11—C10—H10 | 119.1 |
| C12—O3—C15 | 117.8 (2) | C9—C10—H10 | 119.1 |
| C6—C1—C2 | 118.7 (2) | C10—C11—C12 | 119.6 (3) |
| C6—C1—C7 | 121.5 (2) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.2 |
| C2—C1—C7 | 119.8 (2) | C12—C11—H11 | 120.2 |
| O1—C2—C3 | 124.6 (3) | O3—C12—C13 | 124.6 (2) |
| O1—C2—C1 | 115.9 (2) | O3—C12—C11 | 115.6 (3) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.5 (3) | C13—C12—C11 | 119.7 (3) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 120.7 (3) | C12—C13—C14 | 119.9 (3) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.7 | C12—C13—H13 | 120.0 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.7 | C14—C13—H13 | 120.0 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.9 (3) | C13—C14—C9 | 121.2 (3) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.0 | C13—C14—H14 | 119.4 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.0 | C9—C14—H14 | 119.4 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 120.2 (3) | O3—C15—H15A | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—Br1 | 120.0 (2) | O3—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—Br1 | 119.8 (2) | H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 121.0 (3) | O3—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.5 | H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 119.5 | H15B—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| N1—C7—C1 | 120.5 (2) | O1—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| N1—C7—H7 | 119.7 | O1—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C1—C7—H7 | 119.7 | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| O2—C8—N2 | 122.1 (2) | O1—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| O2—C8—C9 | 122.2 (2) | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| N2—C8—C9 | 115.7 (2) | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2···O2i | 0.890 (10) | 1.966 (12) | 2.835 (3) | 165 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y+1/2, z−1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BH2202).
References
- Bruker (1998). SMART, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Ejsmont, K., Zareef, M., Arfan, M., Bashir, S. A. & Zaleski, J. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o1128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Fun, H.-K., Patil, P. S., Jebas, S. R., Sujith, K. V. & Kalluraya, B. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o1594–o1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Fun, H.-K., Patil, P. S., Rao, J. N., Kalluraya, B. & Chantrapromma, S. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Pulido, S. B., Linares-Ordonez, F. M., Martinez-Martos, J. M., Moreno-Carretero, M. N., Quiros-Olozabal, M. & Ramirez-Exposito, M. J. (2008). J. Inorg. Biochem.102, 1677–1683. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Raj, K. K. V., Narayana, B., Ashalatha, B. V., Kumari, N. S. & Sarojini, B. K. (2007). Eur. J. Med. Chem.42, 425–429. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Yang, T., Cao, G.-B., Xiang, J.-M. & Zhang, L.-H. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o1186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Yehye, W. A., Rahman, N. A., Ariffin, A. & Ng, S. W. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o1824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X., Wei, H.-L., Liu, W.-S., Wang, D.-Q. & Wang, X. (2007). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett.17, 3774–3777. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808035472/bh2202sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808035472/bh2202Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report