Abstract
In the title compound, C12H12O5, molecules are linked into antiparallel hydrogen-bonded sheets through inversion dimers generated via two O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. Using the R 2 2(8) motif as a building block, hydrogen-bonded chains of a C 2 2(8) superstructure are then generated.
Related literature
For 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-pentene-1,5-dioic acid as a synthon in organic chemistry, see: Kon & Nanji (1933 ▶); Linstead (1941 ▶). A number of heterocycles such as pyridine-2,6-diones can be obtained from it, see: Pednekar et al. (2004 ▶). For hydrogen-bond motifs, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶).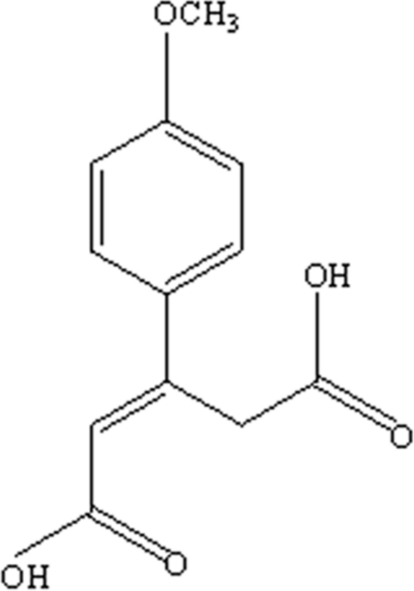
Experimental
Crystal data
C12H12O5
M r = 236.22
Monoclinic,

a = 5.011 (1) Å
b = 10.940 (2) Å
c = 20.438 (4) Å
β = 90.665 (3)°
V = 1120.3 (4) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.11 mm−1
T = 292 (2) K
0.52 × 0.32 × 0.25 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.902, T max = 0.973
8509 measured reflections
2190 independent reflections
2140 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.021
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.068
wR(F 2) = 0.150
S = 1.22
2190 reflections
157 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.32 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.29 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2004 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2004 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1999 ▶) and CAMERON (Watkin et al., 1993 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: PLATON (Spek, 2003 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808037495/bq2105sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808037495/bq2105Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H1⋯O2i | 0.82 | 1.82 | 2.636 (3) | 178 |
| O3—H3⋯O4ii | 0.82 | 1.85 | 2.672 (3) | 175 |
| C4—H4A⋯O2 | 0.97 | 2.19 | 2.834 (3) | 123 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Department of Science and Technology, India, for use of the CCD facility setup under the IRHPA–DST program at IISc.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
3-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-2-pentene-1,5-dioic acid (Kon & Nanji, 1933; Linstead, 1941) acts as a synthon in organic chemistry. It is a precursor for many heterocyclic ring structures due to its inherent ability to form cyclic anhydrides. A number of heterocycles like pyridine-2,6-diones can be obtained from this dicarboxylic acid (Pednekar et al., 2004). Introduction of double bond at the α,β-position of the glutaric acid, leads to the formation of a glutaconic acid. As a consequence of this, there is a noticeable change in its reactivity. The reactivity of methylene group at γ-position is primarily responsible for the electrophilic substitutions taking places at the γ-position of 3-(4-Methoxyphenyl) -2-pentene-1,5-dioic acid.
The title compound, (I) crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system in the centrosymmetric space group P21/c with Z = 4. Fig. 1 shows the asymmetric unit and the atom-numbering scheme. Selected bond lengths and torsion angles are given in Table 1.
In the asymmetric unit, compound (I) adopts the E conformation, with the =CH-COOH group in the plane of the methoxy phenyl ring (C6—C3—C2—C1 dihedral angle is 174.73°) while the –CH2—COOH group lies nearly perpendicular to the phenyl ring (C6—C3—C4—C5 dihedral angle is 89.25 °). Within the aryl rings, the C—C bonds are in the range of 1.374 (3) to 1.395 (3) Å, which is in accordance with those found in similar structures. The C—C single bonds (1.462 (3) to 1.511 (3) Å), C—C double bond (1.339 (3) Å) and C—O double bonds (1.219 (3) Å) are within the usual range.
The molecular assembly is stabilized by extensive intermolecular O—H···O hydrogen bonding, besides intramolecular C—H···O stabilizing weak interactions (Fig. 2). O1 at (x,y,z) acts as a hydrogen-bond donor to O2 at (3 - x,2 - y,-z) to form an inversion dimer centered at (1/2,0,0) and characterized by the usual R22(8) motif (Bernstein et al., 1995). The inversion dimer acts as a building block and leads to propagation of hydrogen bonded chains to generate a C22(8) superstructure. Similarly, O3 (x,y,z) acts as a hydrogen-bond donor to O4 at (2 - x,1 - y,-z) to form an inversion dimer centered at (1,1/2,0), also characterized by the R22(8) motif. Furthermore, the combination of two inversion dimers nearly perpendicular to one another leads to the formation of an intermolecular hydrogen-bonded staircase with neighboring inversion dimers generated via O1—H1···O2 strong hydrogen bonds being connected by O3—H3···O4 interactions. The overall supramolecular packing shows a layered arrangement, with alternate layers mutually parallel.
Experimental
To synthesize compound (I), citric acid [0.13 mol] was warmed in conc. H2SO4 (98%) with constant stirring till foam disappeared to obtain acetone dicarboxylic acid. By immersing the reaction flask in an ice bath; temperature was dropped down to 0°C. Anisole [0.113 mol] was then added slowly with vigorous stirring, over a period of one hour. During the addition, temperature was maintained at 0°C. Stirring was continued for a period of 6 hrs, while maintaining the temperature between 0°C to 5°C. The reaction mixture was then poured over crushed ice with stirring. The solid obtained was then filtered and washed with water and colorless single crystals grown from hot water (yield 12%, m.p. 445–447 K). 1H NMR (DMSO):δ 12.284 (s, 2H), 7.489 (d, 2H), 6.951 (d, 2H), 6.173 (s, 1H), 4.103 (s, 2H), 3.768 (s, 3H).
Refinement
All the H atoms were located and refined isotropically resulting in C—H bond lengths of 0.93 (3)–0.97 (3) Å.
Figures
Fig. 1.
View of the molecular structure of (I) with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms are shown as small spheres of arbitrary radius.
Fig. 2.
Packing diagram of (I) viewed down the c axis. The dotted lines indicate intermolecular O—H···O interactions.
Crystal data
| C12H12O5 | F000 = 496 |
| Mr = 236.22 | Dx = 1.401 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 2190 reflections |
| a = 5.011 (1) Å | θ = 2.0–26.0º |
| b = 10.940 (2) Å | µ = 0.11 mm−1 |
| c = 20.438 (4) Å | T = 292 (2) K |
| β = 90.665 (3)º | Cylindrical, colourless |
| V = 1120.3 (4) Å3 | 0.52 × 0.32 × 0.25 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer | 2190 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2140 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: graphite | Rint = 0.021 |
| T = 292(2) K | θmax = 26.0º |
| φ and ω scans | θmin = 2.0º |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan(SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −6→6 |
| Tmin = 0.903, Tmax = 0.973 | k = −13→13 |
| 8509 measured reflections | l = −23→25 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.068 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.151 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0537P)2 + 0.2183P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.22 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2190 reflections | Δρmax = 0.32 e Å−3 |
| 157 parameters | Δρmin = −0.29 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction correction: none |
Special details
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | −0.2159 (4) | 0.55290 (16) | 0.45189 (9) | 0.0564 (6) | |
| O2 | −0.4196 (4) | 0.37432 (18) | 0.46474 (10) | 0.0687 (7) | |
| O3 | −0.2679 (5) | 0.0034 (2) | 0.44062 (11) | 0.0841 (9) | |
| O4 | 0.0612 (4) | 0.13111 (19) | 0.46215 (11) | 0.0771 (8) | |
| O5 | 0.6191 (4) | 0.16520 (18) | 0.15123 (9) | 0.0627 (7) | |
| C1 | −0.2519 (5) | 0.4369 (2) | 0.43791 (11) | 0.0464 (7) | |
| C2 | −0.0718 (5) | 0.3943 (2) | 0.38696 (11) | 0.0440 (7) | |
| C3 | −0.0755 (4) | 0.2846 (2) | 0.35786 (11) | 0.0405 (7) | |
| C4 | −0.2604 (4) | 0.1838 (2) | 0.37974 (12) | 0.0445 (7) | |
| C5 | −0.1392 (5) | 0.1029 (2) | 0.43137 (11) | 0.0434 (7) | |
| C6 | 0.1041 (4) | 0.2562 (2) | 0.30272 (11) | 0.0402 (7) | |
| C7 | 0.1417 (5) | 0.1368 (2) | 0.28065 (12) | 0.0490 (8) | |
| C8 | 0.3102 (5) | 0.1101 (2) | 0.23008 (13) | 0.0533 (8) | |
| C9 | 0.4516 (5) | 0.2015 (2) | 0.19929 (12) | 0.0479 (8) | |
| C10 | 0.4146 (5) | 0.3214 (2) | 0.21898 (13) | 0.0517 (8) | |
| C11 | 0.2436 (5) | 0.3467 (2) | 0.26956 (12) | 0.0488 (8) | |
| C12 | 0.7575 (7) | 0.2569 (3) | 0.11593 (16) | 0.0731 (11) | |
| H1 | −0.33195 | 0.57564 | 0.47710 | 0.0845* | |
| H2 | 0.05853 | 0.44896 | 0.37338 | 0.0528* | |
| H3 | −0.19480 | −0.03596 | 0.46989 | 0.1262* | |
| H4A | −0.42219 | 0.22012 | 0.39662 | 0.0534* | |
| H4B | −0.30956 | 0.13424 | 0.34214 | 0.0534* | |
| H7 | 0.04987 | 0.07345 | 0.30076 | 0.0587* | |
| H8 | 0.32931 | 0.02950 | 0.21641 | 0.0639* | |
| H10 | 0.50463 | 0.38443 | 0.19819 | 0.0621* | |
| H11 | 0.22033 | 0.42766 | 0.28206 | 0.0586* | |
| H12A | 0.63099 | 0.31041 | 0.09496 | 0.1099* | |
| H12B | 0.86702 | 0.21914 | 0.08343 | 0.1099* | |
| H12C | 0.86800 | 0.30320 | 0.14555 | 0.1099* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0599 (11) | 0.0484 (10) | 0.0612 (11) | −0.0047 (8) | 0.0206 (9) | 0.0003 (8) |
| O2 | 0.0753 (13) | 0.0570 (11) | 0.0744 (13) | −0.0160 (10) | 0.0334 (11) | −0.0041 (9) |
| O3 | 0.0967 (16) | 0.0679 (13) | 0.0869 (16) | −0.0389 (12) | −0.0369 (13) | 0.0386 (11) |
| O4 | 0.0760 (14) | 0.0718 (13) | 0.0828 (14) | −0.0282 (11) | −0.0339 (12) | 0.0371 (11) |
| O5 | 0.0659 (12) | 0.0635 (12) | 0.0590 (11) | 0.0089 (9) | 0.0095 (9) | −0.0162 (9) |
| C1 | 0.0473 (13) | 0.0478 (13) | 0.0440 (12) | −0.0040 (10) | 0.0020 (10) | 0.0071 (10) |
| C2 | 0.0465 (13) | 0.0430 (12) | 0.0427 (12) | −0.0048 (10) | 0.0041 (10) | 0.0076 (10) |
| C3 | 0.0376 (11) | 0.0424 (12) | 0.0412 (12) | −0.0005 (9) | −0.0060 (9) | 0.0119 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0398 (12) | 0.0434 (12) | 0.0503 (13) | −0.0038 (10) | −0.0024 (10) | 0.0054 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0468 (13) | 0.0424 (12) | 0.0410 (12) | −0.0089 (10) | 0.0003 (10) | 0.0056 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0401 (11) | 0.0387 (11) | 0.0417 (12) | 0.0023 (9) | −0.0058 (9) | 0.0043 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0551 (14) | 0.0399 (12) | 0.0517 (14) | −0.0056 (10) | −0.0068 (11) | 0.0004 (10) |
| C8 | 0.0620 (15) | 0.0406 (13) | 0.0569 (15) | 0.0041 (11) | −0.0096 (12) | −0.0104 (11) |
| C9 | 0.0455 (13) | 0.0532 (14) | 0.0448 (13) | 0.0077 (11) | −0.0041 (10) | −0.0082 (11) |
| C10 | 0.0545 (14) | 0.0431 (13) | 0.0578 (15) | 0.0008 (11) | 0.0128 (12) | 0.0006 (11) |
| C11 | 0.0542 (14) | 0.0350 (11) | 0.0575 (14) | 0.0025 (10) | 0.0104 (11) | 0.0005 (10) |
| C12 | 0.0732 (19) | 0.082 (2) | 0.0647 (18) | 0.0137 (16) | 0.0231 (15) | −0.0056 (16) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C1 | 1.313 (3) | C7—C8 | 1.374 (4) |
| O2—C1 | 1.219 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.381 (3) |
| O3—C5 | 1.280 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.385 (3) |
| O4—C5 | 1.219 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.378 (4) |
| O5—C9 | 1.359 (3) | C2—H2 | 0.9300 |
| O5—C12 | 1.421 (4) | C4—H4A | 0.9700 |
| O1—H1 | 0.8200 | C4—H4B | 0.9700 |
| O3—H3 | 0.8200 | C7—H7 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.462 (3) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.339 (3) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C6 | 1.483 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.511 (3) | C12—H12A | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.500 (3) | C12—H12B | 0.9600 |
| C6—C11 | 1.393 (3) | C12—H12C | 0.9600 |
| C6—C7 | 1.395 (3) | ||
| O1···O5i | 3.152 (3) | C10···H12A | 2.7700 |
| O1···C1ii | 3.234 (3) | C10···H12C | 2.7400 |
| O1···O1ii | 3.129 (3) | C10···H8vi | 2.9200 |
| O1···O2iii | 2.636 (3) | C11···H2 | 2.5800 |
| O2···O1iii | 2.636 (3) | C11···H8vi | 2.9400 |
| O2···C4 | 2.834 (3) | C12···H10 | 2.5400 |
| O2···C5 | 3.358 (3) | H1···O2iii | 1.8200 |
| O2···C1iii | 3.318 (3) | H1···C1iii | 2.7300 |
| O2···O2iii | 3.212 (3) | H1···H1iii | 2.5500 |
| O3···O4iv | 2.672 (3) | H2···C11 | 2.5800 |
| O4···C5iv | 3.380 (3) | H2···H11 | 2.0600 |
| O4···O3iv | 2.672 (3) | H2···O5vi | 2.9100 |
| O4···C2 | 3.328 (3) | H3···O4iv | 1.8500 |
| O5···O1v | 3.152 (3) | H3···C5iv | 2.7100 |
| O1···H12Bvi | 2.6300 | H3···H3iv | 2.4300 |
| O2···H4A | 2.1900 | H4A···O2 | 2.1900 |
| O2···H1iii | 1.8200 | H4A···C1 | 2.6500 |
| O3···H12Av | 2.8800 | H4A···C6ix | 3.0600 |
| O4···H3iv | 1.8500 | H4B···C7ix | 3.0100 |
| O5···H2vii | 2.9100 | H4B···C7 | 2.6000 |
| C1···O1ii | 3.234 (3) | H4B···C8ix | 2.9700 |
| C1···O2iii | 3.318 (3) | H4B···H7 | 2.1100 |
| C2···C8i | 3.558 (3) | H7···C4 | 2.5600 |
| C2···O4 | 3.328 (3) | H7···C5 | 2.8600 |
| C4···O2 | 2.834 (3) | H7···H4B | 2.1100 |
| C5···O2 | 3.358 (3) | H8···C2v | 2.8700 |
| C5···O4iv | 3.380 (3) | H8···C10vii | 2.9200 |
| C5···C7 | 3.422 (3) | H8···C11vii | 2.9400 |
| C7···C5 | 3.422 (3) | H8···H10vii | 2.4900 |
| C8···C10vii | 3.596 (3) | H8···H11vii | 2.5200 |
| C8···C2v | 3.558 (3) | H10···C12 | 2.5400 |
| C10···C8vi | 3.596 (3) | H10···H12A | 2.3500 |
| C1···H4A | 2.6500 | H10···H12C | 2.3000 |
| C1···H1iii | 2.7300 | H10···C8vi | 3.0100 |
| C2···H8i | 2.8700 | H10···H8vi | 2.4900 |
| C2···H11 | 2.6400 | H11···C2 | 2.6400 |
| C4···H7 | 2.5600 | H11···H2 | 2.0600 |
| C5···H3iv | 2.7100 | H11···C8vi | 3.1000 |
| C5···H7 | 2.8600 | H11···H8vi | 2.5200 |
| C6···H4Aviii | 3.0600 | H12A···C10 | 2.7700 |
| C7···H4B | 2.6000 | H12A···H10 | 2.3500 |
| C7···H4Bviii | 3.0100 | H12A···O3i | 2.8800 |
| C8···H10vii | 3.0100 | H12B···O1vii | 2.6300 |
| C8···H11vii | 3.1000 | H12C···C10 | 2.7400 |
| C8···H4Bviii | 2.9700 | H12C···H10 | 2.3000 |
| C9—O5—C12 | 118.0 (2) | C6—C11—C10 | 122.8 (2) |
| C1—O1—H1 | 109.00 | C1—C2—H2 | 117.00 |
| C5—O3—H3 | 109.00 | C3—C2—H2 | 117.00 |
| O1—C1—C2 | 112.3 (2) | C3—C4—H4A | 109.00 |
| O2—C1—C2 | 125.2 (2) | C3—C4—H4B | 109.00 |
| O1—C1—O2 | 122.6 (2) | C5—C4—H4A | 109.00 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 126.6 (2) | C5—C4—H4B | 109.00 |
| C2—C3—C6 | 121.3 (2) | H4A—C4—H4B | 108.00 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 121.9 (2) | C6—C7—H7 | 119.00 |
| C4—C3—C6 | 116.84 (19) | C8—C7—H7 | 119.00 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 113.20 (18) | C7—C8—H8 | 120.00 |
| O3—C5—C4 | 113.9 (2) | C9—C8—H8 | 120.00 |
| O4—C5—C4 | 122.6 (2) | C9—C10—H10 | 120.00 |
| O3—C5—O4 | 123.6 (2) | C11—C10—H10 | 120.00 |
| C7—C6—C11 | 116.0 (2) | C6—C11—H11 | 119.00 |
| C3—C6—C7 | 121.8 (2) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.00 |
| C3—C6—C11 | 122.2 (2) | O5—C12—H12A | 109.00 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 121.9 (2) | O5—C12—H12B | 109.00 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 120.8 (2) | O5—C12—H12C | 109.00 |
| O5—C9—C10 | 124.9 (2) | H12A—C12—H12B | 109.00 |
| O5—C9—C8 | 116.2 (2) | H12A—C12—H12C | 109.00 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 118.8 (2) | H12B—C12—H12C | 109.00 |
| C9—C10—C11 | 119.6 (2) | ||
| C12—O5—C9—C8 | 176.7 (2) | C3—C4—C5—O3 | −166.2 (2) |
| C12—O5—C9—C10 | −3.4 (4) | C3—C4—C5—O4 | 14.9 (3) |
| O1—C1—C2—C3 | −173.4 (2) | C3—C6—C7—C8 | −179.3 (2) |
| O2—C1—C2—C3 | 5.9 (4) | C11—C6—C7—C8 | 1.2 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −5.7 (4) | C3—C6—C11—C10 | 178.9 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C6 | 174.8 (2) | C7—C6—C11—C10 | −1.6 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −90.4 (3) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | 0.5 (4) |
| C6—C3—C4—C5 | 89.2 (2) | C7—C8—C9—O5 | 178.0 (2) |
| C2—C3—C6—C7 | 166.9 (2) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | −1.9 (4) |
| C2—C3—C6—C11 | −13.6 (3) | O5—C9—C10—C11 | −178.4 (2) |
| C4—C3—C6—C7 | −12.7 (3) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 1.5 (4) |
| C4—C3—C6—C11 | 166.8 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C6 | 0.3 (4) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, y+1/2, −z+1/2; (ii) −x, −y+1, −z+1; (iii) −x−1, −y+1, −z+1; (iv) −x, −y, −z+1; (v) −x, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (vi) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+1/2; (vii) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (viii) x+1, y, z; (ix) x−1, y, z.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1···O2iii | 0.82 | 1.82 | 2.636 (3) | 178 |
| O3—H3···O4iv | 0.82 | 1.85 | 2.672 (3) | 175 |
| C4—H4A···O2 | 0.97 | 2.19 | 2.834 (3) | 123 |
Symmetry codes: (iii) −x−1, −y+1, −z+1; (iv) −x, −y, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BQ2105).
References
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl.34, 1555–1573.
- Bruker (2004). SMART and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst.32, 837–838.
- Kon, G. A. R. & Nanji, E. R. (1933). J. Chem. Soc. Trans.2, 2434–2439.
- Linstead, R. P. (1941). J. Chem. Soc. p. 457.
- Pednekar, S., Jain, A. & Menon, K. (2004). Indian J. Heterocycl. Chem.14, 1–6.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst.36, 7–13.
- Watkin, D. J., Pearce, L. & Prout, C. K. (1993). CAMERON Chemical Crystallography Laboratory, University of Oxford, England.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808037495/bq2105sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808037495/bq2105Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




