Abstract
The title compound, C12H11N3O2, was prepared by the reaction of isonicotinohydrazide and 5-methylfuran-2-carbaldehyde. The pyridine ring makes a dihedral angle of 46.90 (9)° with the mean plane of the furan ring. The crystal packing is stabilized by a bifurcated intermolecular N—H⋯(N,O) interaction.
Related literature
For general background, see: Cimerman et al. (1997 ▶). For bond-length data, see: Chiu et al. (1998 ▶).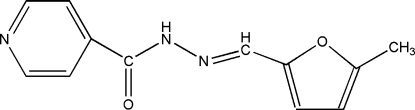
Experimental
Crystal data
C12H11N3O2
M r = 229.24
Tetragonal,

a = 17.313 (3) Å
c = 15.749 (5) Å
V = 4720.5 (18) Å3
Z = 16
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 293 (2) K
0.25 × 0.20 × 0.19 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: none
14901 measured reflections
2911 independent reflections
2151 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.028
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.041
wR(F 2) = 0.117
S = 1.04
2911 reflections
155 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.17 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.14 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 1997 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 1997 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808037276/at2662sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808037276/at2662Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2A⋯O1i | 0.86 | 2.18 | 2.9083 (19) | 143 |
| N2—H2A⋯N3i | 0.86 | 2.58 | 3.3255 (19) | 146 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Schiff bases have received considerable attention in the literature. They are attractive from several points of view, such as the possibility of analytical application (Cimerman et al., 1997). As part of our search for new schiff base compounds we synthesized the title compound (I), and describe its structure here.
In the title compound (I) (Fig. 1), the C12—N3 bond length of 1.2812 (17)Å is comparable with C—N double bond [1.284 (2) Å] reported (Chiu et al., 1998). The pyridine ring (N1/C1–C5) makes a dihedral angle of 46.90 (9)°, with the plane of the furan ring (O2/C6–C9).
The crsytal packing is stabilized by intermolecular N—H···O, N—H···N hydrogen bonds (Table 1, Fig. 2).
Experimental
A mixture of the isonicotinohydrazide (0.1 mol), and 5-methylfuran-2-carbaldehyde (0.1 mol) was stirred in refluxing ethanol (20 mL) for 4 h to afford the title compound (0.082 mol, yield 82%). Single crystals suitable for X-ray measurements were obtained by recrystallization from ethanol at room temperature.
Refinement
All H atoms were fixed geometrically and allowed to ride on their attached atoms, with C—H distances in the range 0.93-0.97 Å and N—H = 0.86 Å, and with Uiso=1.2–1.5Ueq(N,C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I) showing 30% probability displacement ellipsoids and the atom-numbering scheme.
Crystal data
| C12H11N3O2 | Z = 16 |
| Mr = 229.24 | F000 = 1920 |
| Tetragonal, I41/a | Dx = 1.290 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -I 4ad | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 17.313 (3) Å | Cell parameters from 4665 reflections |
| b = 17.313 (3) Å | θ = 2.9–27.2º |
| c = 15.749 (5) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| α = 90º | T = 273 (2) K |
| β = 90º | Block, yellow |
| γ = 90º | 0.25 × 0.20 × 0.19 mm |
| V = 4720.5 (18) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer | 2151 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.028 |
| Monochromator: graphite | θmax = 28.3º |
| T = 273(2) K | θmin = 1.8º |
| φ and ω scans | h = −16→23 |
| Absorption correction: none | k = −22→22 |
| 14901 measured reflections | l = −20→20 |
| 2911 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.041 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0456P)2 + 2.257P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.117 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.04 | Δρmax = 0.17 e Å−3 |
| 2911 reflections | Δρmin = −0.14 e Å−3 |
| 155 parameters | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.0031 (3) |
| Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O2 | 0.58347 (5) | 0.51303 (5) | 0.10958 (6) | 0.0482 (3) | |
| N3 | 0.72302 (6) | 0.49350 (7) | 0.03623 (7) | 0.0427 (3) | |
| C12 | 0.67464 (8) | 0.53721 (7) | −0.00223 (9) | 0.0423 (3) | |
| H12A | 0.6866 | 0.5578 | −0.0552 | 0.051* | |
| N2 | 0.79076 (6) | 0.47620 (7) | −0.00603 (7) | 0.0443 (3) | |
| H2A | 0.7980 | 0.4901 | −0.0578 | 0.053* | |
| C8 | 0.60143 (8) | 0.55421 (7) | 0.03726 (8) | 0.0417 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.83833 (7) | 0.42110 (8) | 0.11302 (7) | 0.0750 (4) | |
| C4 | 0.91448 (8) | 0.41092 (8) | −0.01179 (8) | 0.0442 (3) | |
| C11 | 0.84487 (8) | 0.43670 (9) | 0.03721 (8) | 0.0460 (3) | |
| C9 | 0.51105 (8) | 0.53616 (9) | 0.13450 (10) | 0.0513 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.54259 (8) | 0.60254 (8) | 0.01805 (10) | 0.0505 (4) | |
| H7A | 0.5402 | 0.6366 | −0.0276 | 0.061* | |
| C3 | 0.91374 (8) | 0.39635 (10) | −0.09860 (9) | 0.0531 (4) | |
| H3B | 0.8696 | 0.4056 | −0.1307 | 0.064* | |
| N1 | 1.04629 (8) | 0.35518 (10) | −0.09513 (9) | 0.0736 (5) | |
| C5 | 0.98256 (9) | 0.39741 (11) | 0.03194 (10) | 0.0640 (5) | |
| H5A | 0.9853 | 0.4061 | 0.0901 | 0.077* | |
| C2 | 0.98006 (9) | 0.36780 (11) | −0.13609 (10) | 0.0650 (5) | |
| H2B | 0.9784 | 0.3566 | −0.1938 | 0.078* | |
| C6 | 0.48512 (9) | 0.59116 (9) | 0.08124 (11) | 0.0561 (4) | |
| H6A | 0.4382 | 0.6170 | 0.0851 | 0.067* | |
| C1 | 1.04634 (10) | 0.37078 (13) | −0.01203 (12) | 0.0758 (6) | |
| H1B | 1.0920 | 0.3633 | 0.0180 | 0.091* | |
| C10 | 0.47813 (11) | 0.49172 (12) | 0.20700 (12) | 0.0760 (6) | |
| H10A | 0.4277 | 0.5113 | 0.2203 | 0.114* | |
| H10B | 0.5112 | 0.4971 | 0.2556 | 0.114* | |
| H10C | 0.4743 | 0.4382 | 0.1918 | 0.114* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O2 | 0.0471 (5) | 0.0516 (6) | 0.0459 (6) | 0.0050 (4) | 0.0087 (4) | 0.0080 (4) |
| N3 | 0.0440 (6) | 0.0466 (6) | 0.0374 (6) | 0.0030 (5) | 0.0080 (5) | 0.0042 (5) |
| C12 | 0.0482 (7) | 0.0410 (7) | 0.0377 (7) | −0.0013 (5) | 0.0043 (5) | 0.0035 (5) |
| N2 | 0.0455 (6) | 0.0564 (7) | 0.0309 (5) | 0.0060 (5) | 0.0089 (4) | 0.0086 (5) |
| C8 | 0.0469 (7) | 0.0390 (7) | 0.0393 (7) | −0.0019 (5) | 0.0027 (5) | 0.0022 (5) |
| O1 | 0.0740 (8) | 0.1156 (10) | 0.0355 (6) | 0.0391 (7) | 0.0150 (5) | 0.0225 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0432 (7) | 0.0547 (8) | 0.0346 (7) | 0.0036 (6) | 0.0027 (5) | 0.0012 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0493 (8) | 0.0564 (8) | 0.0324 (7) | 0.0078 (6) | 0.0065 (5) | 0.0053 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0462 (8) | 0.0537 (8) | 0.0540 (9) | 0.0000 (6) | 0.0107 (6) | −0.0028 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0529 (8) | 0.0440 (7) | 0.0545 (9) | 0.0040 (6) | 0.0006 (6) | 0.0051 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0429 (7) | 0.0785 (10) | 0.0379 (7) | 0.0050 (7) | −0.0012 (6) | −0.0047 (7) |
| N1 | 0.0497 (8) | 0.1162 (13) | 0.0550 (8) | 0.0166 (8) | 0.0024 (6) | −0.0196 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0577 (9) | 0.0961 (13) | 0.0381 (8) | 0.0182 (9) | −0.0062 (7) | −0.0109 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0546 (9) | 0.1006 (13) | 0.0399 (8) | 0.0090 (9) | 0.0034 (7) | −0.0151 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0468 (8) | 0.0544 (9) | 0.0672 (10) | 0.0085 (6) | 0.0047 (7) | −0.0014 (7) |
| C1 | 0.0483 (9) | 0.1212 (16) | 0.0579 (10) | 0.0220 (10) | −0.0099 (7) | −0.0188 (10) |
| C10 | 0.0718 (12) | 0.0839 (13) | 0.0722 (12) | 0.0022 (9) | 0.0292 (9) | 0.0134 (10) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O2—C9 | 1.3735 (16) | C7—C6 | 1.421 (2) |
| O2—C8 | 1.3793 (16) | C7—H7A | 0.9300 |
| N3—C12 | 1.2812 (17) | C3—C2 | 1.383 (2) |
| N3—N2 | 1.3813 (15) | C3—H3B | 0.9300 |
| C12—C8 | 1.4421 (18) | N1—C2 | 1.334 (2) |
| C12—H12A | 0.9300 | N1—C1 | 1.336 (2) |
| N2—C11 | 1.3450 (17) | C5—C1 | 1.383 (2) |
| N2—H2A | 0.8600 | C5—H5A | 0.9300 |
| C8—C7 | 1.3526 (19) | C2—H2B | 0.9300 |
| O1—C11 | 1.2293 (16) | C6—H6A | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.385 (2) | C1—H1B | 0.9300 |
| C4—C3 | 1.3904 (19) | C10—H10A | 0.9600 |
| C4—C11 | 1.4990 (18) | C10—H10B | 0.9600 |
| C9—C6 | 1.346 (2) | C10—H10C | 0.9600 |
| C9—C10 | 1.490 (2) | ||
| C9—O2—C8 | 106.92 (11) | C2—C3—C4 | 118.50 (14) |
| C12—N3—N2 | 117.08 (11) | C2—C3—H3B | 120.7 |
| N3—C12—C8 | 119.42 (12) | C4—C3—H3B | 120.7 |
| N3—C12—H12A | 120.3 | C2—N1—C1 | 116.18 (14) |
| C8—C12—H12A | 120.3 | C1—C5—C4 | 119.14 (14) |
| C11—N2—N3 | 117.23 (11) | C1—C5—H5A | 120.4 |
| C11—N2—H2A | 121.4 | C4—C5—H5A | 120.4 |
| N3—N2—H2A | 121.4 | N1—C2—C3 | 124.47 (14) |
| C7—C8—O2 | 109.55 (12) | N1—C2—H2B | 117.8 |
| C7—C8—C12 | 133.77 (13) | C3—C2—H2B | 117.8 |
| O2—C8—C12 | 116.66 (11) | C9—C6—C7 | 107.52 (13) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 117.78 (13) | C9—C6—H6A | 126.2 |
| C5—C4—C11 | 118.59 (12) | C7—C6—H6A | 126.2 |
| C3—C4—C11 | 123.56 (12) | N1—C1—C5 | 123.88 (15) |
| O1—C11—N2 | 122.64 (12) | N1—C1—H1B | 118.1 |
| O1—C11—C4 | 120.56 (13) | C5—C1—H1B | 118.1 |
| N2—C11—C4 | 116.79 (11) | C9—C10—H10A | 109.5 |
| C6—C9—O2 | 109.43 (13) | C9—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C6—C9—C10 | 135.66 (15) | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| O2—C9—C10 | 114.68 (14) | C9—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 106.55 (13) | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7A | 126.7 | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7A | 126.7 |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2A···O1i | 0.86 | 2.18 | 2.9083 (19) | 143 |
| N2—H2A···N3i | 0.86 | 2.58 | 3.3255 (19) | 146 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −y+5/4, x−1/4, z−1/4.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: AT2662).
References
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808037276/at2662sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808037276/at2662Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



