Abstract
In the titile compound, C18H20Cl2N2O2, the piperazine ring adopts a chair conformation. The molecule has a non-crystallographic inversion centre in the middle of the piperazine ring at approximate position (3/4, 1/8, 3/8). There are intramolecular O—H⋯N hydrogen bonds forming S(6) ring motifs. Intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds generate antiparallel C(5) chain motifs propagating along the b axis, forming sheets parallel to the bc plane with a first-level graph-set S(6)C(5)R 6 6(26).
Related literature
For graph-set notations for hydrogen bonds, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶). For the synthesis of a ligand with two piperazine arms, see: Bharathi et al. (2006 ▶). For the use of piperazine derivatives as buffers, see: Good et al. (1966 ▶). For the monoclinic and orthorhombic polymorphs of a tetrachloro-2,2′-(piperazine-1,4-diyldimethylene)diphenol, see: Kubono & Yokoi (2007 ▶). For the structure of 1,4-bis(2-hydroxy-5-methylbenzyl)piperazine, see: Kuppayee et al. (1999 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C18H20Cl2N2O2
M r = 367.26
Orthorhombic,

a = 14.055 (4) Å
b = 21.214 (11) Å
c = 11.873 (3) Å
V = 3540 (2) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.38 mm−1
T = 298.1 K
0.18 × 0.13 × 0.13 mm
Data collection
Rigaku AFC-7R diffractometer
Absorption correction: none
5928 measured reflections
4066 independent reflections
2735 reflections with F 2 > 2σ(F 2)
R int = 0.039
3 standard reflections every 150 reflections intensity decay: 0.7%
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.039
wR(F 2) = 0.105
S = 1.00
2739 reflections
237 parameters
All H-atom parameters refined
Δρmax = 0.33 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.45 e Å−3
Data collection: WinAFC (Rigaku/MSC, 2006 ▶); cell refinement: WinAFC; data reduction: CrystalStructure (Rigaku/MSC, 2006 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SIR92 (Altomare et al., 1993 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: CRYSTALS (Betteridge et al., 2003 ▶); molecular graphics: PLATON (Spek, 2003 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: CrystalStructure.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808035769/si2120sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808035769/si2120Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H1⋯N1 | 0.85 | 1.88 | 2.649 (3) | 150 |
| O2—H20⋯N2 | 0.85 | 1.87 | 2.647 (3) | 151 |
| C7—H6⋯O2i | 0.95 | 2.59 | 3.230 (3) | 125 |
| C12—H15⋯O1ii | 0.95 | 2.56 | 3.300 (3) | 134 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 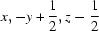 ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported financially in part by Grants-in-Aid (Nos. 19550040 and 20550075) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology, Japan.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Piprazine derivatives are widly utilized as buffers, e.g., 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid (HEPES) (Good et al., 1966), and can act as complexing reagents with metal ions (Bharathi et al., 2006).
The molecular structure of the title compound (Fig. 1) (I), consists of two chlorophenol arms and a piperazine ring, which adopt a chair conformation. The molecule has a pseudo-inversion centre in the middle of the piperazine ring at position (3/4, 1/8, 3/8). It is interesting to note that in the polymorh structures of dichlorophenol derivatives (Kubono & Yokoi, 2007) the molecules occupy crystallographic inversion centres (Z' = 1/2). The bond lengths and angles in (I) are normal and comparable with those in the monoclinic and orthorhombic polymorph structures (Kubono & Yokoi, 2007) and in the p-cresol derivative (Kuppayee et al., 1999). Intramolecular O—H···N hydrogen bonds in (I) have similar geometric parameters and higher level graph set notations as was observed in the polymorph structures. The torsion angles C1—C6—C7—N1 and N2—C12—C13—C18 are -34.8 (3) and 37.5 (3) °, respectively. The dihedral angles between the mean planes of two benzene rings are 4.68 (12) °.
In the crystal structure of (I), there are two intermolecular C—H···O hydrogen bonds (Table 1). Atom C7 in the molecule at (x, y, z) acts as hydrogen bond donor to atom O2 in the molecule at (x, 1/2 - y, z - 1/2), so forming a C(5) (Bernstein et al., 1995) chain running parallel to the [010] direction and generated by the c-glide plane at y = 1/4. In addition, atom C12 in the molecule at (x, y, z) acts as hydrogen bond donor to atom O1 atom in the molecule at (3/2 - x, -y, 1/2 + z), so forming a C(5) chain running parallel to the [010] direction and generated by the 21 screw axis along (3/4, 0, z). The molecules are linked by the combination of the two S(6) rings and the two antiparalle C(5) chains into a sheet parallel to b,c-plane with a first level graph set S(6)C(5)R66(26) (Fig. 2).
Experimental
A mixture of 4-chlorophenol (25.0 g, 194 mmol), piperazine (8.34 g, 97.2 mmol) and paraformaldehyde (5.82 g, 194 mmol) in methanol (80 ml) was refluxed for 6 h. The mixture was cooled to room temperature, then the solvent was evaporated under vacuum. The product was recrystallized from CHCl3—MeOH to give prismatic crystals of (I) [yeild 13.8 g (38.7%); m.p. 515.0–515.4 K]. Analysis calculated for C18H20Cl4N2O2: C 58.86, H 5.49, N 7.63%; found: C 58.50, H 5.44, N 7.55%. 1H-NMR(CDCl3, p.p.m., 400 MHz): 2.68 (brs, 8H, CH2), 3.69 (s, 4H, CH2), 6.75 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 2H, ArH), 6.96 (s, 2H, ArH), 7.13 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 2H, ArH), 10.6 (brs, 2H, OH).
Refinement
The H atoms of the hydroxyl groups were found from a difference Fourier map. The other H atoms were placed at idealized positions with C—H = 0.95 Å. All the H atoms were refined as a riding model with Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I) with the atom-labelling scheme and displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms are represented by circles of arbitrary size.
Fig. 2.
The molecular packing of (I), showing the formation of a sheet with a first level graph set S(6)C(5)R66(26). The hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines. The H atoms not involved in the hydrogen bonds have been omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| C18H20Cl2N2O2 | F000 = 1536.00 |
| Mr = 367.26 | Dx = 1.378 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, Pbca | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71069 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 18 reflections |
| a = 14.055 (4) Å | θ = 13.7–16.9º |
| b = 21.214 (11) Å | µ = 0.38 mm−1 |
| c = 11.873 (3) Å | T = 298.1 K |
| V = 3540 (2) Å3 | Prismatic, colorless |
| Z = 8 | 0.18 × 0.13 × 0.13 mm |
Data collection
| Rigaku AFC-7R diffractometer | θmax = 27.5º |
| ω scans | h = −10→18 |
| Absorption correction: none | k = 0→27 |
| 5928 measured reflections | l = −8→15 |
| 4066 independent reflections | 3 standard reflections |
| 2735 reflections with F2 > 2σ(F2) | every 150 reflections |
| Rint = 0.039 | intensity decay: 0.7% |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | All H-atom parameters refined |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.039 | w = 1/[0.0011Fo2 + σ(Fo2)]/(4Fo2) |
| wR(F2) = 0.105 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.00 | Δρmax = 0.33 e Å−3 |
| 2739 reflections | Δρmin = −0.45 e Å−3 |
| 237 parameters | Extinction correction: none |
Special details
| Geometry. The molecule adopts a non-crystallographic inversion centre in the middle of the piperazine ring at an approximate position (3/4, 1/8, 3/8). |
| Refinement. Refinement was performed using reflections with F2 > 2.0 σ(F2). The weighted R-factor (wR) and goodness of fit (S) are based on F2. R-factor (gt) are based on F. The threshold expression of F2 > 2.0 σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factor (gt). |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.43588 (6) | 0.27754 (4) | −0.07209 (8) | 0.0807 (3) | |
| Cl2 | 1.07341 (7) | −0.01127 (5) | 0.83011 (9) | 0.0914 (4) | |
| O1 | 0.75085 (15) | 0.11534 (9) | 0.07111 (17) | 0.0559 (7) | |
| O2 | 0.74244 (15) | 0.13266 (9) | 0.67705 (18) | 0.0643 (8) | |
| N1 | 0.73683 (16) | 0.16416 (11) | 0.2758 (2) | 0.0385 (7) | |
| N2 | 0.77032 (17) | 0.08768 (10) | 0.4717 (2) | 0.0385 (8) | |
| C1 | 0.6764 (2) | 0.15283 (15) | 0.0418 (2) | 0.0435 (10) | |
| C2 | 0.6298 (2) | 0.14079 (15) | −0.0579 (2) | 0.0506 (11) | |
| C3 | 0.5560 (2) | 0.17790 (18) | −0.0936 (2) | 0.0558 (12) | |
| C4 | 0.5283 (2) | 0.22809 (16) | −0.0274 (3) | 0.0526 (12) | |
| C5 | 0.5720 (2) | 0.24037 (15) | 0.0734 (2) | 0.0477 (11) | |
| C6 | 0.6466 (2) | 0.20327 (14) | 0.1097 (2) | 0.0398 (10) | |
| C7 | 0.6988 (2) | 0.21952 (13) | 0.2166 (2) | 0.0459 (10) | |
| C8 | 0.8043 (2) | 0.18345 (14) | 0.3642 (2) | 0.0483 (10) | |
| C9 | 0.8455 (2) | 0.12615 (13) | 0.4217 (2) | 0.0465 (10) | |
| C10 | 0.7022 (2) | 0.06864 (13) | 0.3845 (2) | 0.0451 (10) | |
| C11 | 0.6609 (2) | 0.12632 (13) | 0.3279 (2) | 0.0466 (10) | |
| C12 | 0.8101 (2) | 0.03329 (13) | 0.5321 (2) | 0.0476 (10) | |
| C13 | 0.8583 (2) | 0.05200 (14) | 0.6408 (2) | 0.0381 (10) | |
| C14 | 0.9375 (2) | 0.01930 (13) | 0.6786 (2) | 0.0451 (11) | |
| C15 | 0.9773 (2) | 0.03340 (15) | 0.7820 (3) | 0.0505 (11) | |
| C16 | 0.9415 (2) | 0.08039 (17) | 0.8475 (2) | 0.0544 (12) | |
| C17 | 0.8640 (2) | 0.11345 (15) | 0.8107 (3) | 0.0563 (12) | |
| C18 | 0.8214 (2) | 0.09977 (14) | 0.7088 (2) | 0.0432 (11) | |
| H1 | 0.7660 | 0.1247 | 0.1381 | 0.067* | |
| H2 | 0.6488 | 0.1057 | −0.1022 | 0.061* | |
| H3 | 0.5249 | 0.1702 | −0.1632 | 0.067* | |
| H4 | 0.5506 | 0.2748 | 0.1178 | 0.057* | |
| H5 | 0.6569 | 0.2415 | 0.2656 | 0.055* | |
| H6 | 0.7510 | 0.2460 | 0.1977 | 0.055* | |
| H7 | 0.8537 | 0.2074 | 0.3303 | 0.058* | |
| H8 | 0.7724 | 0.2085 | 0.4187 | 0.058* | |
| H9 | 0.8880 | 0.1390 | 0.4795 | 0.056* | |
| H10 | 0.8790 | 0.1019 | 0.3674 | 0.056* | |
| H11 | 0.7338 | 0.0442 | 0.3288 | 0.054* | |
| H12 | 0.6530 | 0.0443 | 0.4178 | 0.054* | |
| H13 | 0.6301 | 0.1509 | 0.3839 | 0.056* | |
| H14 | 0.6161 | 0.1145 | 0.2718 | 0.056* | |
| H15 | 0.7599 | 0.0047 | 0.5485 | 0.057* | |
| H16 | 0.8557 | 0.0132 | 0.4853 | 0.057* | |
| H17 | 0.9651 | −0.0127 | 0.6331 | 0.054* | |
| H18 | 0.9701 | 0.0897 | 0.9181 | 0.065* | |
| H19 | 0.8387 | 0.1466 | 0.8555 | 0.068* | |
| H20 | 0.7346 | 0.1261 | 0.6069 | 0.077* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0581 (6) | 0.0946 (8) | 0.0893 (8) | 0.0015 (5) | −0.0153 (6) | 0.0291 (5) |
| Cl2 | 0.0782 (7) | 0.1153 (8) | 0.0806 (8) | 0.0288 (6) | −0.0241 (6) | −0.0050 (6) |
| O1 | 0.0720 (15) | 0.0498 (13) | 0.0459 (15) | 0.0121 (12) | −0.0003 (12) | −0.0089 (12) |
| O2 | 0.0803 (17) | 0.0591 (14) | 0.0534 (17) | 0.0224 (13) | −0.0010 (13) | −0.0097 (12) |
| N1 | 0.0419 (15) | 0.0361 (14) | 0.0377 (17) | −0.0053 (13) | −0.0039 (13) | 0.0012 (13) |
| N2 | 0.0441 (16) | 0.0304 (14) | 0.0410 (17) | −0.0081 (13) | −0.0031 (13) | 0.0035 (13) |
| C1 | 0.049 (2) | 0.041 (2) | 0.040 (2) | −0.0044 (18) | 0.0014 (18) | 0.0048 (18) |
| C2 | 0.064 (2) | 0.050 (2) | 0.037 (2) | −0.014 (2) | 0.005 (2) | 0.0001 (19) |
| C3 | 0.059 (2) | 0.067 (2) | 0.041 (2) | −0.025 (2) | −0.008 (2) | 0.007 (2) |
| C4 | 0.043 (2) | 0.058 (2) | 0.057 (2) | −0.0100 (19) | −0.004 (2) | 0.018 (2) |
| C5 | 0.045 (2) | 0.047 (2) | 0.051 (2) | −0.0007 (18) | 0.002 (2) | 0.0018 (18) |
| C6 | 0.049 (2) | 0.040 (2) | 0.031 (2) | −0.0032 (17) | 0.0062 (17) | −0.0026 (17) |
| C7 | 0.058 (2) | 0.0411 (19) | 0.039 (2) | 0.0042 (17) | 0.0026 (18) | −0.0027 (16) |
| C8 | 0.059 (2) | 0.044 (2) | 0.041 (2) | −0.0142 (18) | −0.0025 (18) | −0.0003 (17) |
| C9 | 0.050 (2) | 0.045 (2) | 0.045 (2) | −0.0105 (18) | −0.0053 (17) | −0.0001 (18) |
| C10 | 0.046 (2) | 0.039 (2) | 0.050 (2) | −0.0127 (16) | −0.0053 (18) | 0.0023 (16) |
| C11 | 0.045 (2) | 0.051 (2) | 0.044 (2) | −0.0080 (17) | −0.0043 (16) | −0.0036 (17) |
| C12 | 0.058 (2) | 0.0357 (19) | 0.049 (2) | −0.0029 (16) | 0.0037 (18) | −0.0009 (16) |
| C13 | 0.049 (2) | 0.0341 (19) | 0.031 (2) | −0.0020 (17) | 0.0026 (17) | 0.0038 (16) |
| C14 | 0.052 (2) | 0.040 (2) | 0.043 (2) | 0.0028 (18) | 0.011 (2) | −0.0008 (17) |
| C15 | 0.050 (2) | 0.054 (2) | 0.048 (2) | 0.0009 (18) | −0.002 (2) | 0.0006 (19) |
| C16 | 0.060 (2) | 0.064 (2) | 0.039 (2) | −0.007 (2) | −0.0029 (19) | 0.0019 (19) |
| C17 | 0.077 (2) | 0.053 (2) | 0.039 (2) | 0.000 (2) | 0.011 (2) | −0.010 (2) |
| C18 | 0.054 (2) | 0.0357 (19) | 0.040 (2) | 0.0063 (17) | 0.0106 (19) | 0.0029 (17) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cl1—C4 | 1.751 (3) | C15—C16 | 1.361 (4) |
| Cl2—C15 | 1.746 (3) | C16—C17 | 1.367 (5) |
| O1—C1 | 1.359 (3) | C17—C18 | 1.381 (4) |
| O2—C18 | 1.364 (3) | O1—H1 | 0.848 |
| N1—C7 | 1.469 (3) | O2—H20 | 0.852 |
| N1—C8 | 1.472 (3) | C2—H2 | 0.950 |
| N1—C11 | 1.472 (3) | C3—H3 | 0.950 |
| N2—C9 | 1.461 (3) | C5—H4 | 0.950 |
| N2—C10 | 1.467 (3) | C7—H5 | 0.950 |
| N2—C12 | 1.469 (3) | C7—H6 | 0.950 |
| C1—C2 | 1.377 (4) | C8—H7 | 0.950 |
| C1—C6 | 1.404 (4) | C8—H8 | 0.950 |
| C2—C3 | 1.369 (4) | C9—H9 | 0.950 |
| C3—C4 | 1.380 (5) | C9—H10 | 0.950 |
| C4—C5 | 1.371 (5) | C10—H11 | 0.950 |
| C5—C6 | 1.380 (4) | C10—H12 | 0.950 |
| C6—C7 | 1.507 (4) | C11—H13 | 0.950 |
| C8—C9 | 1.509 (4) | C11—H14 | 0.950 |
| C10—C11 | 1.512 (3) | C12—H15 | 0.950 |
| C12—C13 | 1.510 (4) | C12—H16 | 0.950 |
| C13—C14 | 1.386 (4) | C14—H17 | 0.950 |
| C13—C18 | 1.395 (4) | C16—H18 | 0.950 |
| C14—C15 | 1.383 (4) | C17—H19 | 0.950 |
| C7—N1—C8 | 110.6 (2) | C2—C3—H3 | 121.3 |
| C7—N1—C11 | 111.9 (2) | C4—C3—H3 | 119.9 |
| C8—N1—C11 | 108.6 (2) | C4—C5—H4 | 119.2 |
| C9—N2—C10 | 109.8 (2) | C6—C5—H4 | 120.4 |
| C9—N2—C12 | 111.2 (2) | N1—C7—H5 | 109.0 |
| C10—N2—C12 | 112.1 (2) | N1—C7—H6 | 107.8 |
| O1—C1—C2 | 118.5 (2) | C6—C7—H5 | 109.0 |
| O1—C1—C6 | 121.9 (2) | C6—C7—H6 | 108.1 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 119.5 (3) | H5—C7—H6 | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 121.3 (3) | N1—C8—H7 | 108.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 118.8 (3) | N1—C8—H8 | 109.8 |
| Cl1—C4—C3 | 120.0 (2) | C9—C8—H7 | 110.0 |
| Cl1—C4—C5 | 118.9 (2) | C9—C8—H8 | 108.9 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 121.1 (3) | H7—C8—H8 | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.3 (3) | N2—C9—H9 | 108.7 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 118.8 (2) | N2—C9—H10 | 109.4 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 120.9 (2) | C8—C9—H9 | 109.7 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 120.2 (2) | C8—C9—H10 | 108.7 |
| N1—C7—C6 | 113.4 (2) | H9—C9—H10 | 109.5 |
| N1—C8—C9 | 110.2 (2) | N2—C10—H11 | 109.6 |
| N2—C9—C8 | 110.9 (2) | N2—C10—H12 | 109.3 |
| N2—C10—C11 | 110.0 (2) | C11—C10—H11 | 108.2 |
| N1—C11—C10 | 110.5 (2) | C11—C10—H12 | 110.3 |
| N2—C12—C13 | 112.4 (2) | H11—C10—H12 | 109.5 |
| C12—C13—C14 | 120.3 (2) | N1—C11—H13 | 109.0 |
| C12—C13—C18 | 121.3 (2) | N1—C11—H14 | 109.3 |
| C14—C13—C18 | 118.3 (2) | C10—C11—H13 | 108.0 |
| C13—C14—C15 | 120.3 (2) | C10—C11—H14 | 110.6 |
| Cl2—C15—C14 | 119.1 (2) | H13—C11—H14 | 109.5 |
| Cl2—C15—C16 | 119.8 (2) | N2—C12—H15 | 108.6 |
| C14—C15—C16 | 121.0 (3) | N2—C12—H16 | 108.9 |
| C15—C16—C17 | 119.3 (3) | C13—C12—H15 | 109.0 |
| C16—C17—C18 | 121.1 (3) | C13—C12—H16 | 108.4 |
| O2—C18—C13 | 120.9 (2) | H15—C12—H16 | 109.5 |
| O2—C18—C17 | 119.1 (2) | C13—C14—H17 | 120.1 |
| C13—C18—C17 | 119.9 (3) | C15—C14—H17 | 119.6 |
| C1—O1—H1 | 107.2 | C15—C16—H18 | 119.9 |
| C18—O2—H20 | 107.0 | C17—C16—H18 | 120.8 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.1 | C16—C17—H19 | 119.9 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.5 | C18—C17—H19 | 118.9 |
| C7—N1—C8—C9 | −178.0 (2) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | 1.4 (5) |
| C8—N1—C7—C6 | 167.4 (2) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.2 (4) |
| C7—N1—C11—C10 | 178.1 (2) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | 175.9 (2) |
| C11—N1—C7—C6 | −71.4 (3) | C1—C6—C7—N1 | −34.8 (3) |
| C8—N1—C11—C10 | −59.5 (2) | C5—C6—C7—N1 | 149.3 (2) |
| C11—N1—C8—C9 | 58.7 (2) | N1—C8—C9—N2 | −58.8 (3) |
| C9—N2—C10—C11 | −57.8 (2) | N2—C10—C11—N1 | 59.6 (2) |
| C10—N2—C9—C8 | 57.8 (2) | N2—C12—C13—C14 | −146.3 (2) |
| C9—N2—C12—C13 | 72.3 (3) | N2—C12—C13—C18 | 37.5 (3) |
| C12—N2—C9—C8 | −177.5 (2) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −175.2 (2) |
| C10—N2—C12—C13 | −164.3 (2) | C12—C13—C18—O2 | −2.4 (4) |
| C12—N2—C10—C11 | 178.0 (2) | C12—C13—C18—C17 | 176.4 (2) |
| O1—C1—C2—C3 | −178.2 (3) | C14—C13—C18—O2 | −178.6 (2) |
| O1—C1—C6—C5 | 178.4 (2) | C14—C13—C18—C17 | 0.1 (3) |
| O1—C1—C6—C7 | 2.4 (4) | C18—C13—C14—C15 | 1.1 (4) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −1.2 (4) | C13—C14—C15—Cl2 | 176.9 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | −177.2 (2) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −1.6 (4) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 1.4 (5) | Cl2—C15—C16—C17 | −177.5 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.3 (5) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | 1.0 (5) |
| C2—C3—C4—Cl1 | 178.6 (2) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | 0.2 (5) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −1.2 (5) | C16—C17—C18—O2 | 178.0 (3) |
| Cl1—C4—C5—C6 | −178.4 (2) | C16—C17—C18—C13 | −0.8 (5) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1···N1 | 0.85 | 1.88 | 2.649 (3) | 150 |
| O2—H20···N2 | 0.85 | 1.87 | 2.647 (3) | 151 |
| C7—H6···O2i | 0.95 | 2.59 | 3.230 (3) | 125 |
| C12—H15···O1ii | 0.95 | 2.57 | 3.300 (3) | 134 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y+1/2, z−1/2; (ii) −x+3/2, −y, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: SI2120).
References
- Altomare, A., Cascarano, G., Giacovazzo, C. & Guagliardi, A. (1993). J. Appl. Cryst.26, 343–350.
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl.34, 1555–1573.
- Betteridge, P. W., Carruthers, J. R., Cooper, R. I., Prout, K. & Watkin, D. J. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst.36, 1487.
- Bharathi, K. S., Rahiman, A. K., Rajesh, K., Sreedaran, S., Aravindan, P. G., Velmurugan, D. & Narayanan, V. (2006). Polyhedron, 25, 2859–2868.
- Good, N. E., Winget, G. D., Winter, W., Connolly, T. N., Izawa, S. & Singh, R. M. (1966). Biochemistry, 5, 467–477. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kubono, K. & Yokoi, K. (2007). Acta Cryst. C63, o535–o537. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kuppayee, M., Kumaran, D., Ponnuswamy, M. N., Kandaswamy, M., Violet, M. J., Chinnakali, K. & Fun, H.-K. (1999). Acta Cryst. C55, 2147–2149.
- Rigaku/MSC (2006). WinAFC and CrystalStructure Rigaku/MSC, The Woodlands, Texas, USA.
- Spek, A. L. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst.36, 7–13.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808035769/si2120sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808035769/si2120Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




